这里写目录标题
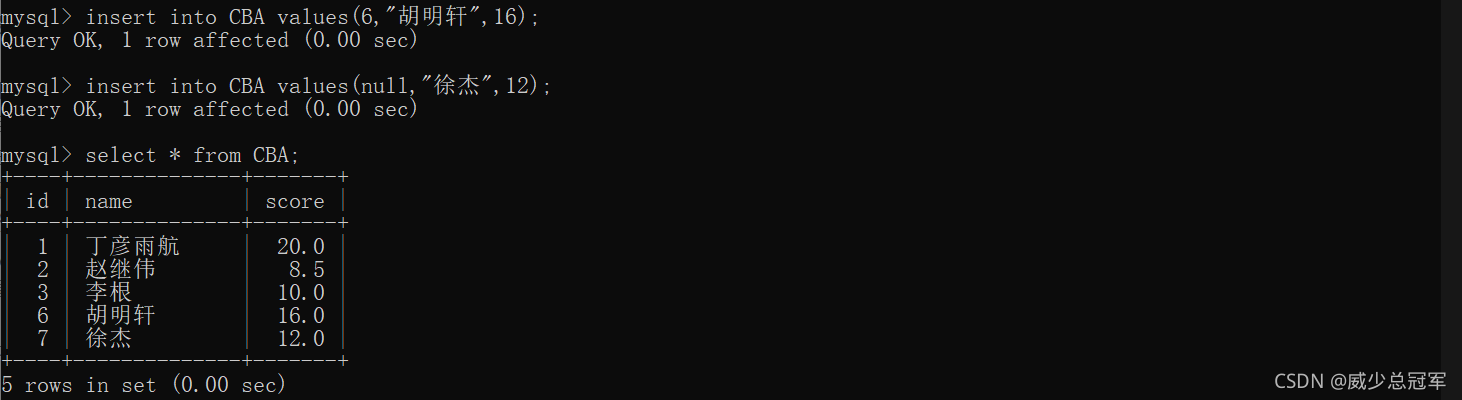
MySQL表的增删改查
数据库约束
not null
指定某列不能存null值
create table [表名](id int not null);
unique
保证某列的每一行的值是唯一的
create table [表名](id int unique);
default
当列没有被赋值时,指定默认值,不指定时为null
create table [表名](id int default 10);

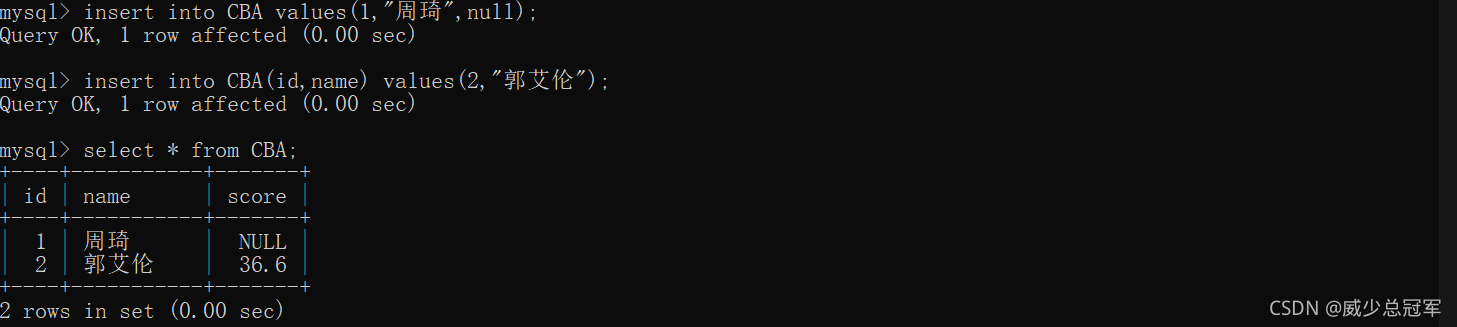
primary key
主键----not null 和 unique 的结合
一张表中只有一列是主键,主键相当于一行记录的确定身份的唯一标识,就是“身份证号码”
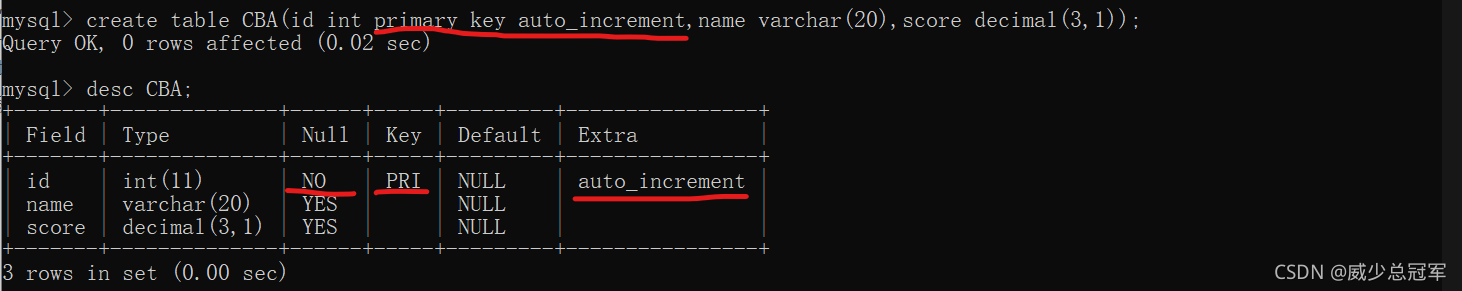
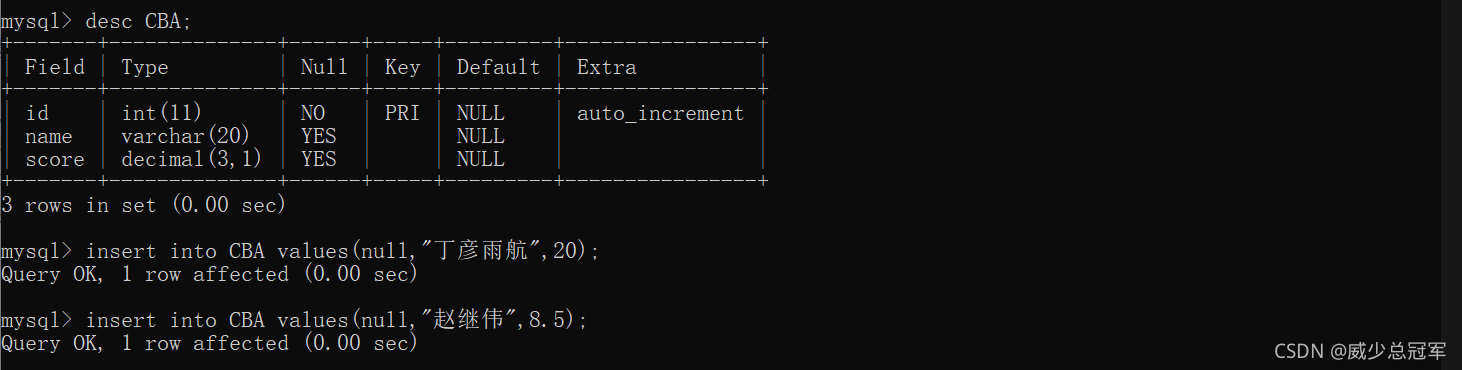

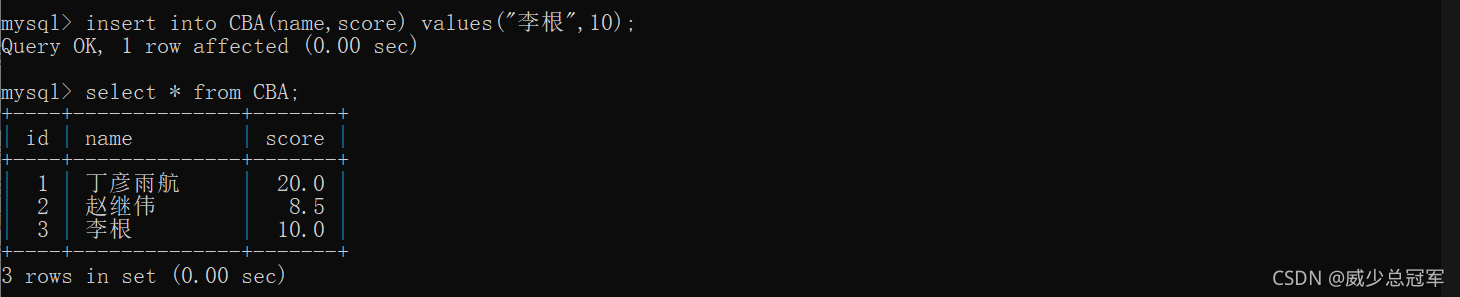
- 设计表的时候一般设计一个主键,主键可以是数字,也可以是字符串
- 数字类型的主键,可搭配使用自增----auto_increment(在primary key 后面搭配),叫做自增主键
- 如果当前列是自增主键,插入列的时候该列可为 null ,表示由MySQL自己生成主键的值;指定列插入时,如果没有自增主键的列,
MySQL自己生成主键的值
4.自增主键相当于在MySQL内部维护了一个“全局变量”,每次插入记录如果指定的是null。全局变量++;即使删除前面的数据,全局变量不受影响,继续++;
5.不同的MySQL之间不能共享这个变量

foreign key
外键 两张表之间的关联关系
常见于学生表和班级表,订单表和商品表
foreign key(列) references 主表(列)
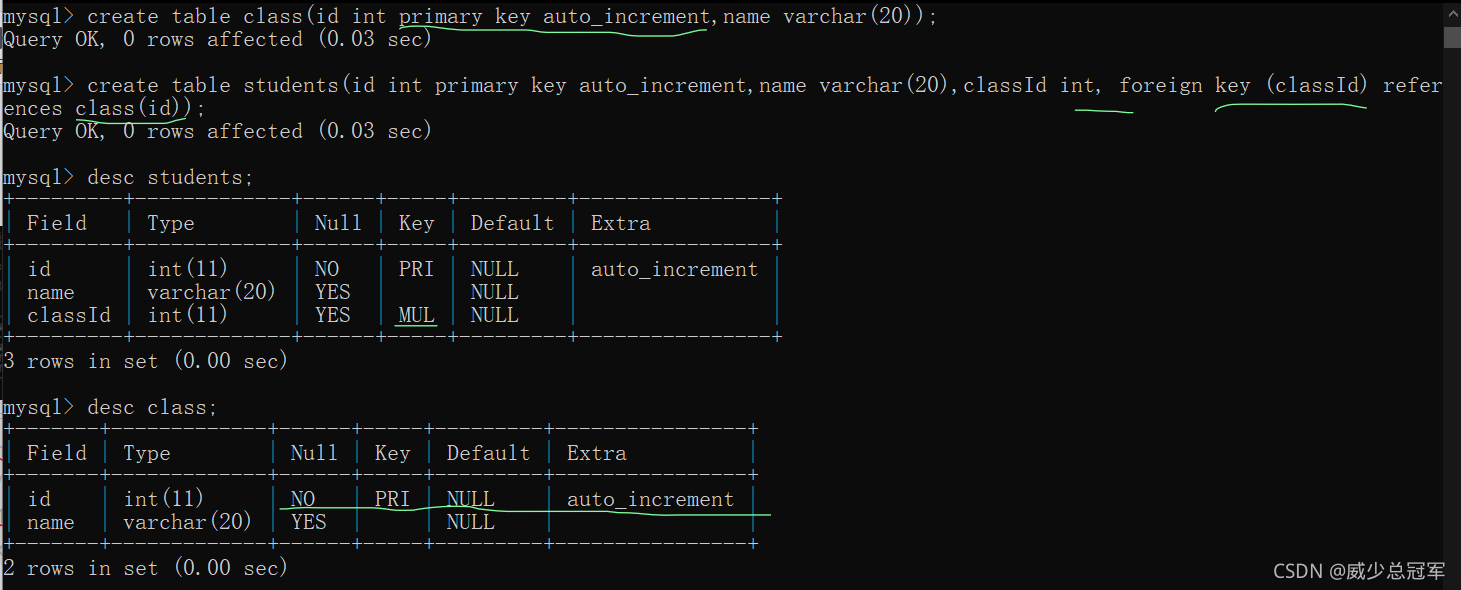
- references是依赖的意思,子表某列的数据必须在主表的指定列中存在
- 被依赖的数据必须是主表中的主键,不能随便删改
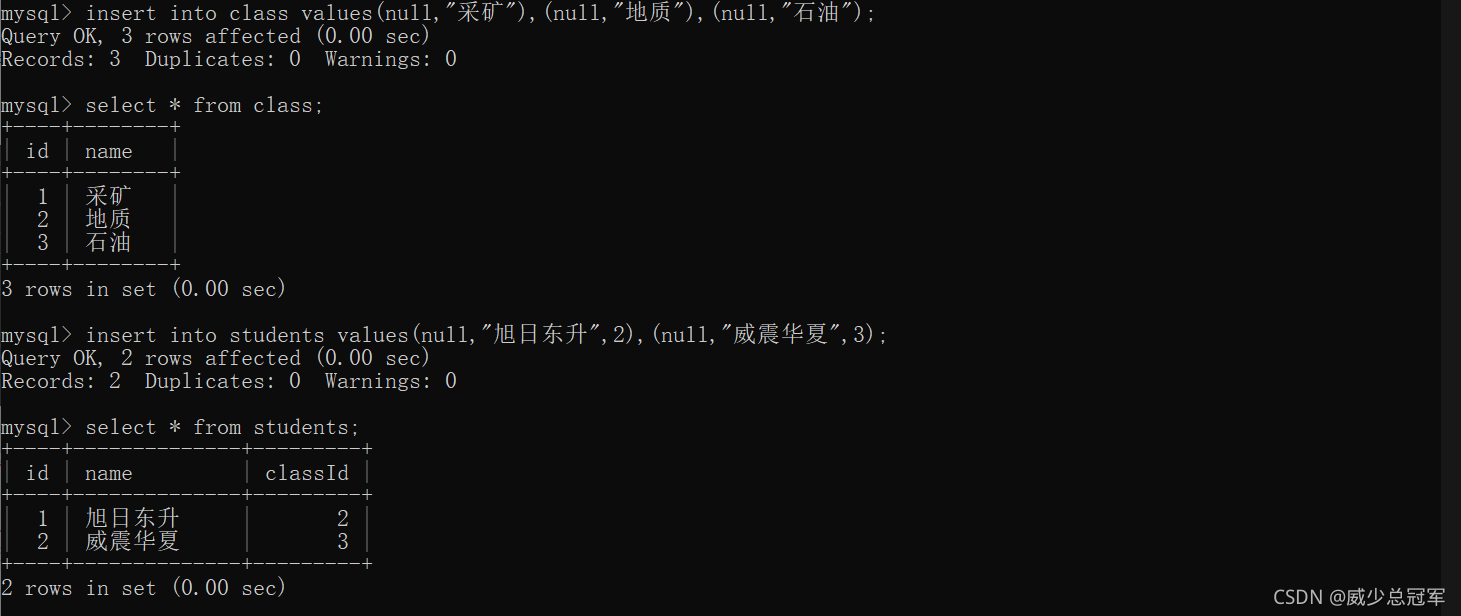

- 外键约束有利有弊
如要删除主表中主键的数据,恐会影响子表,可在子表中添加一列数据,采用“逻辑删除”,而非“物理删除”
数据过多也不怕,磁盘不值钱 - 主表中主键中受依赖的数据不能删,但是此时没有受依赖的数据可以删

新增
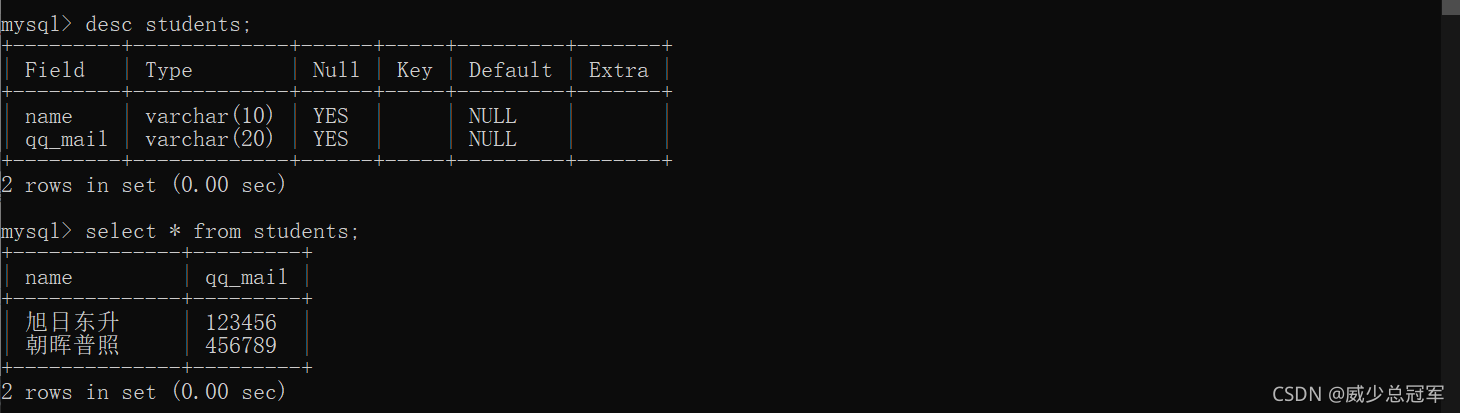
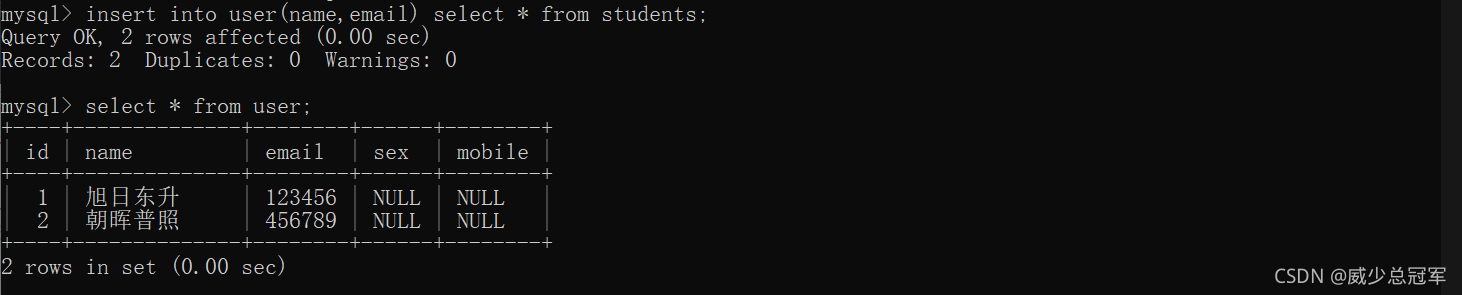
将查询结果插入到表中,可用于将一张表的数据插入到另一张表中
查询结果的列数和类型必须和插入数据的表相匹配
varchar(20) ---->varchar(100) , OK
varchar(100)---->varchar(20),可能OK,关键看查询记录中对应数据的大小
insert into [表名](列名,列名...) select
查询
聚合查询
| 聚合函数 | |
|---|---|
| count( ) | 返回查询到的数据的行数,null不会计入到结果 |
| sum( ) | 返回查询到数据的总和 |
| avg( ) | 返回查询到数据的平均值 |
| max( ) | 返回查询到数据的最大值 |
| min( ) | 返回查询到数据的最小值 |
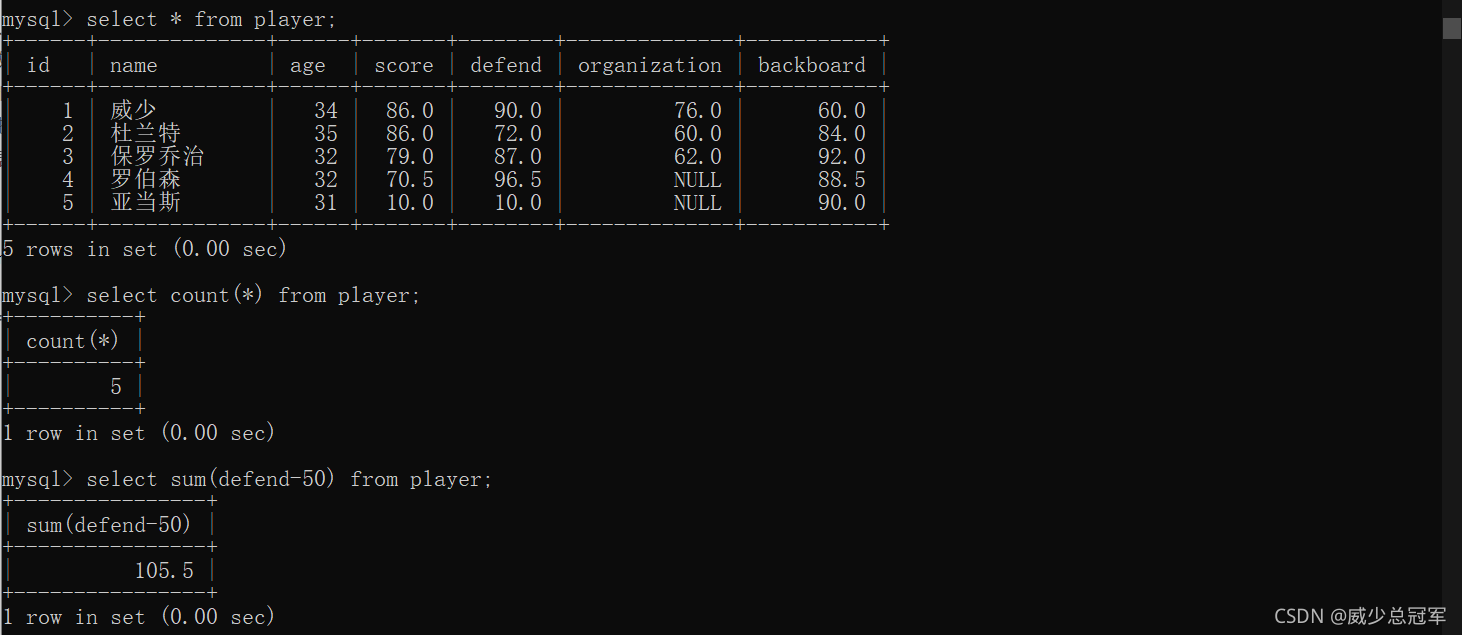
行和行之间的运算
select sum(math) from [表名]
相当于先执行select math from [表名]
再根据其查询的结果,进行计算,展现计算结果

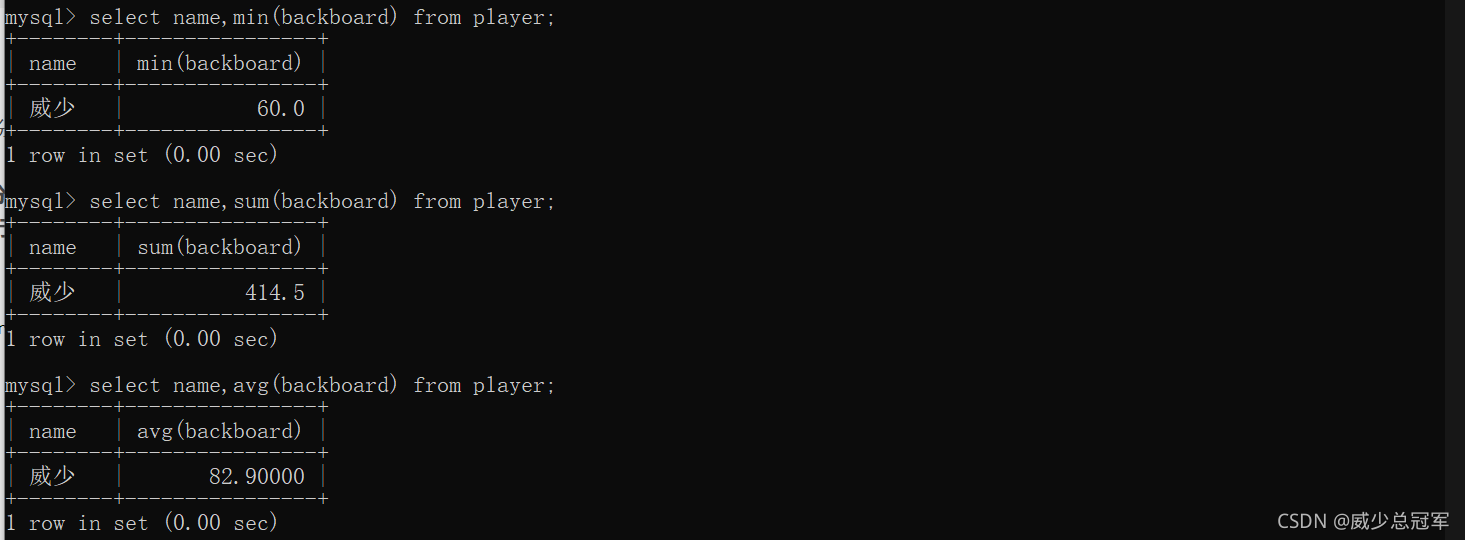
在backboard>90的记录中找到最小值
先执行 select backboard from player where backboard>90;
在进行计算,得出结果
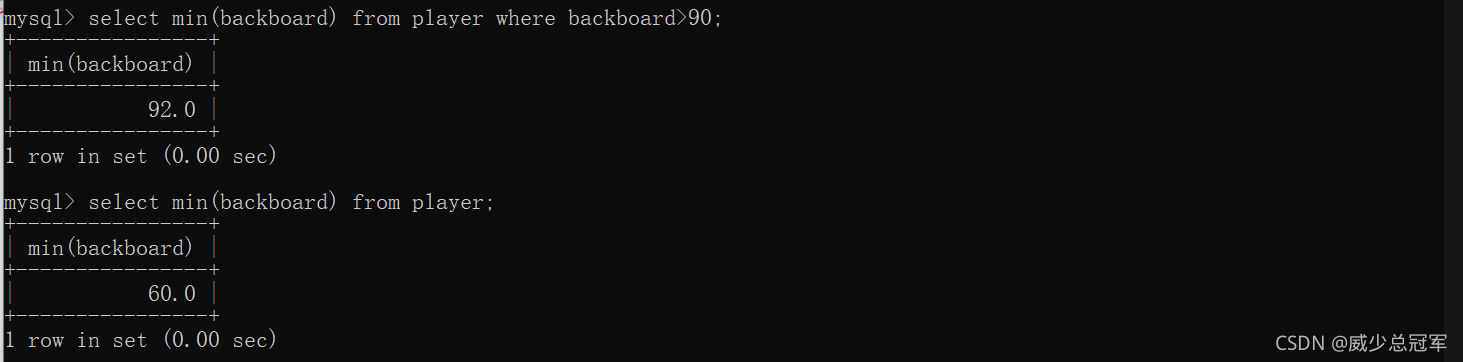
看其他列如何展现,展现第一行的对应值
group by
使用group by 进行分组查询
分组聚合:
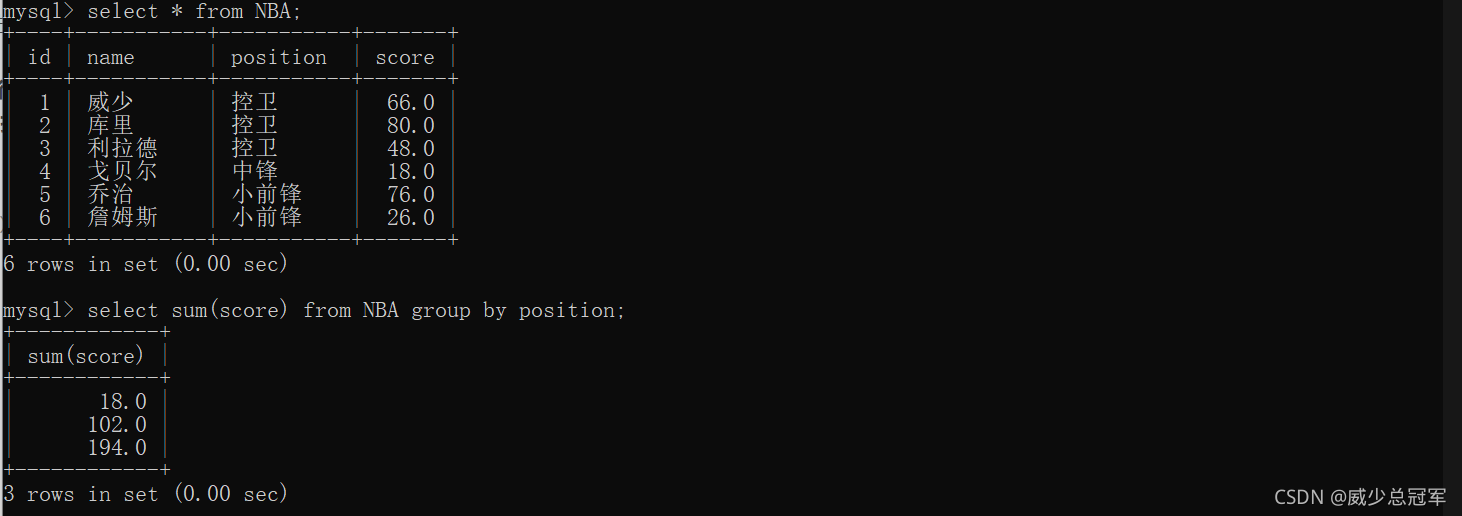
根据指定列进行分组,指定列中值相同的记录(行)分到一组中,在针对每一组分别执行聚合函数
select sum(列名) from [表名] group by [列名],[列名]...
将球员按照相同的position分组,计算各组的sum(score)
having
having针对聚合后的数据进行筛选
where根据需求,也可以和group by 搭配,是针对聚合前的数据进行筛选的
select sum() from [表名] where... group by...
select sum() from [表名] group by...having...
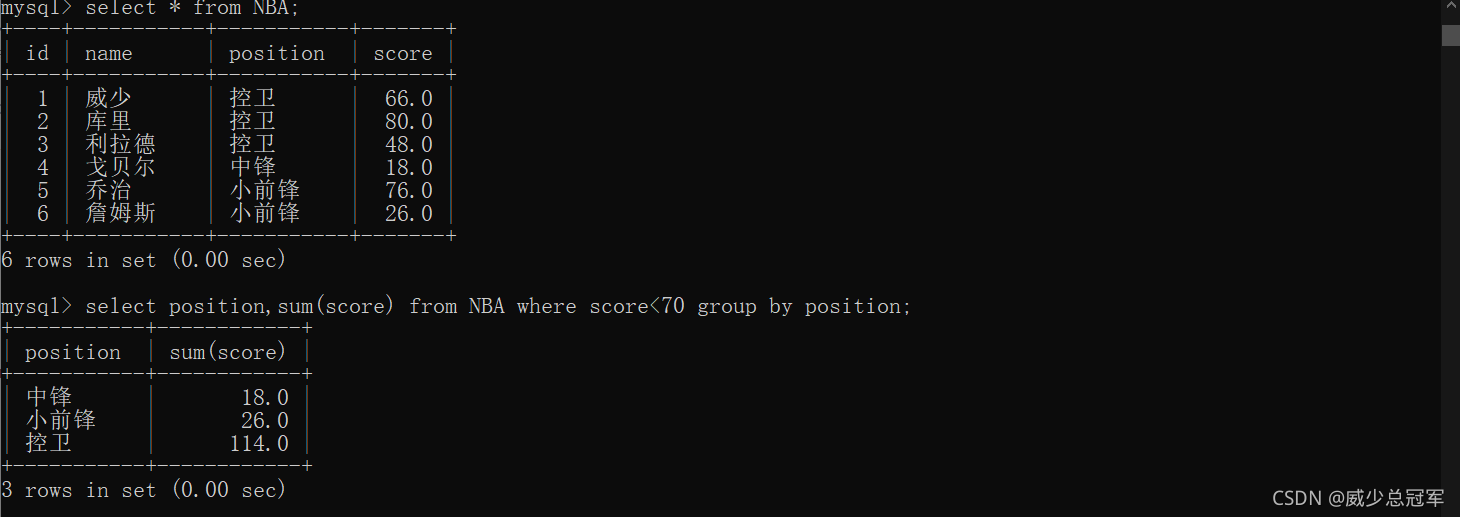
//不同位置分数<70的球员的数据总和
//先筛选出score<70的记录,再分组,再计算
select position,sum(score) from NBA where score<70 group by position
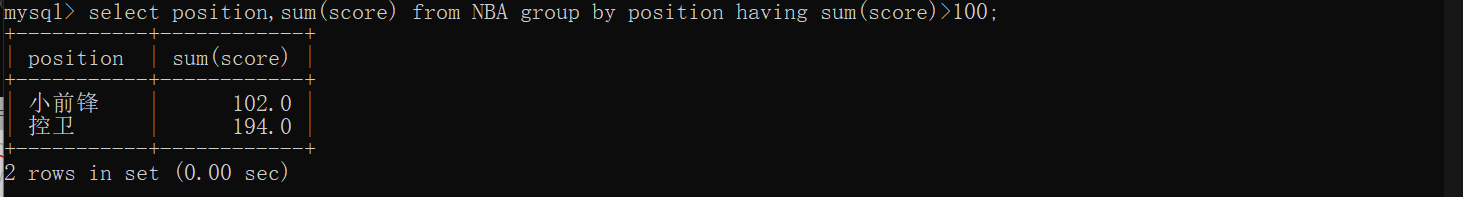
//显示分数总和>100的位置
//先分组,再计算,再筛选
select position,sum(score) from NBA group by position having sum(score)>100
联合查询(多表查询)
多张表联合查询,运用笛卡尔积
笛卡尔积
- 两张表中的每行数据,进行排列组合,笛卡尔积中有很多的“无效记录”
- 因为涉及到多张表,可能有相同的列名," . " 可以用来某表的某列,也可以访问某库的某表
- 外键和内键约束不会影响笛卡尔积
select from 表1,表2 where...
select from 表1 join 表2 on ...
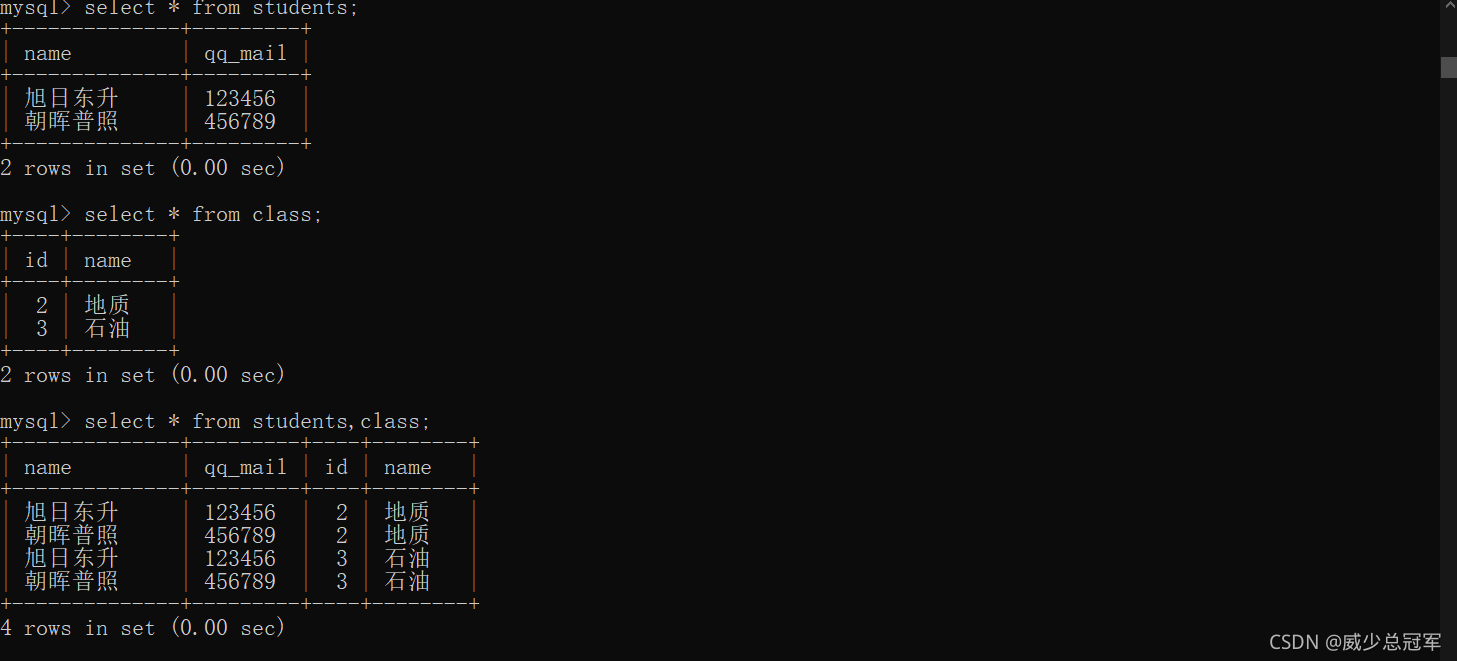




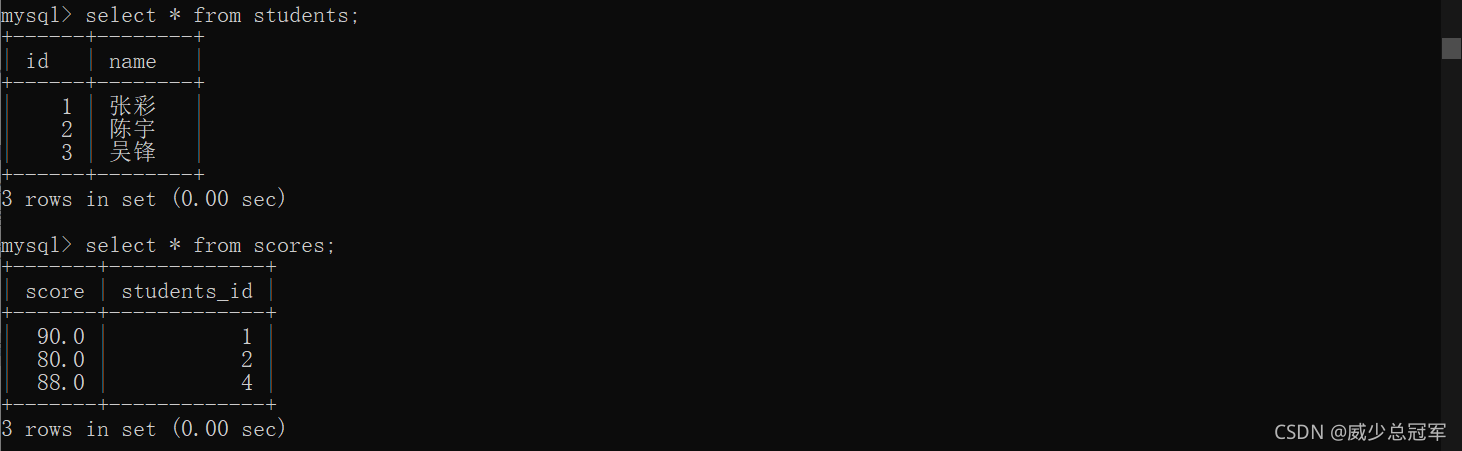
- 查询威少的成绩
//两张表进行笛卡尔积
select * from score,student;
//去掉无效数据,留下每个学生成绩与自己的信息的组合
select * from score,student where score.student_id = student.id;
//找到威少
select * from score,student where score.student_id = student.id and student.name = "威少";
select score.score,score.course_id from score,student where score.student_id = student.id and student.name = "威少";

更牛逼一点,查询每个科目的成绩
select score.score,student.name,course.name from score,student,course where score.student_id = student.id and student.name = "威少";
select score.score,course.name from score,student,course where score.student_id = student.id and student.name = "威少" and course.id = score.course_id;

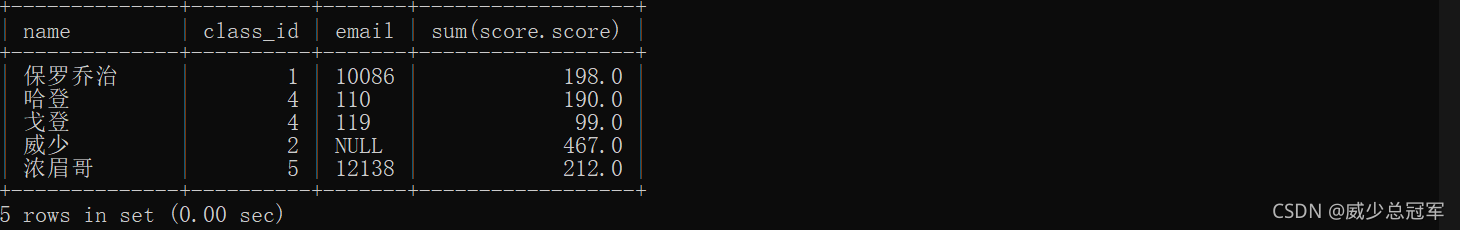
2.查询每个同学的总成绩及个人信息
select student.name,student.class_id,student.email,sum(score.score) from score,student where student.id = student_id group by student_id;
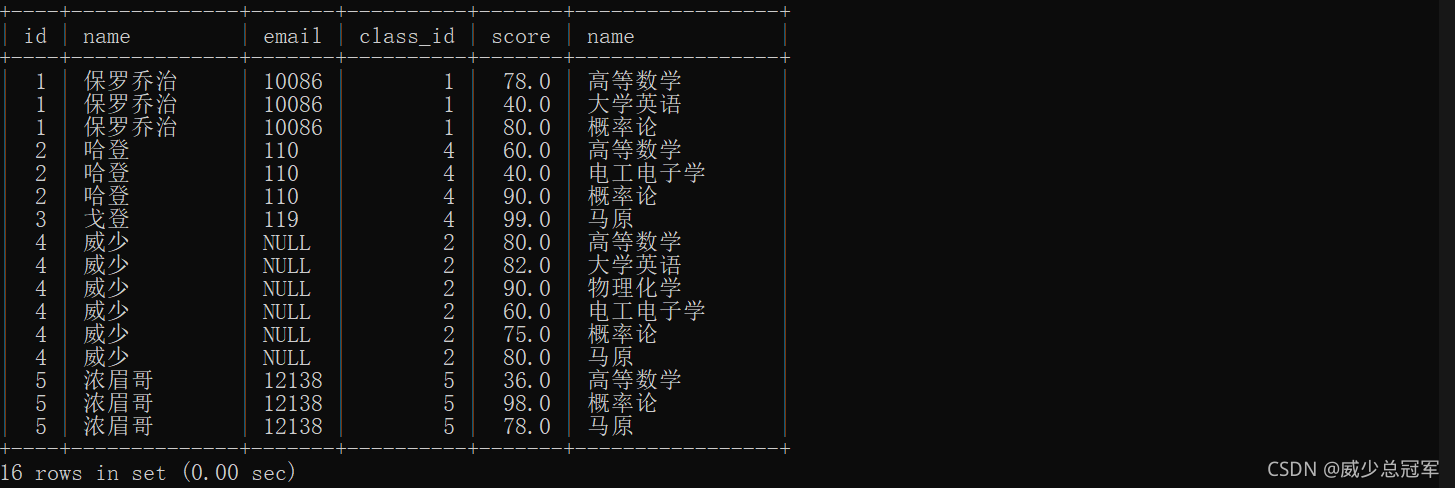
3.查询所有同学的成绩,及个人信息
三张表联合查询喽
select * from student,course,score;
select * from student,course,score where student.id = score.student_id and course.id = score.course_id;
select student.id,student.name,student.email,student.class_id,score.score,course.name from student,course,score where student.id = score.student_id and course.id = score.course_id;
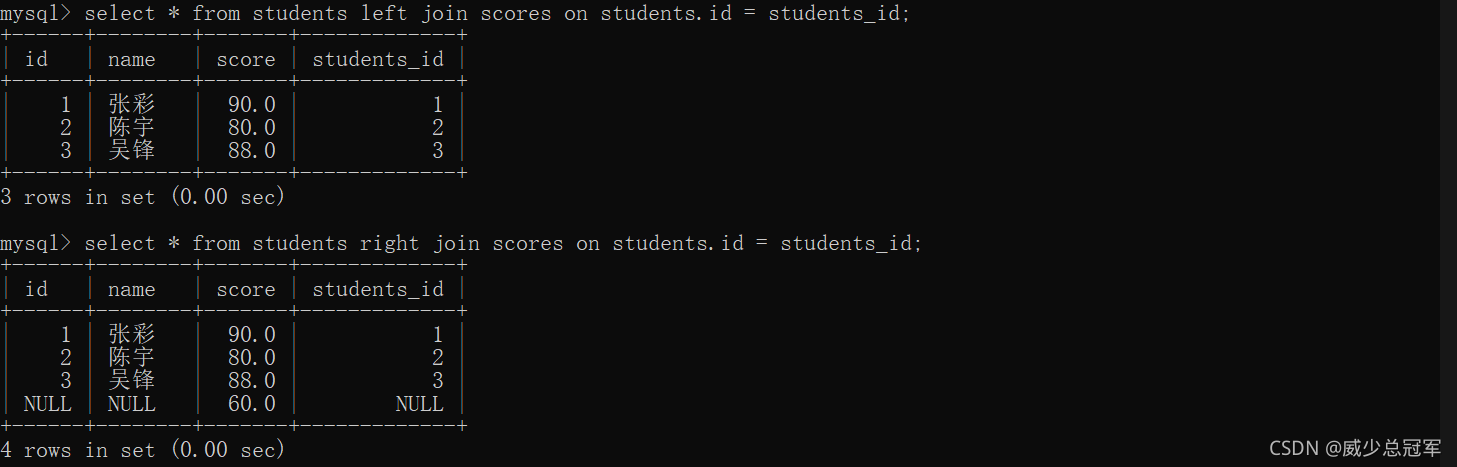
外连接
- 外连接和内连接的区别就在于对“空值”的处理方式不同,如果表中没有空值,那么内连接和外连接没有区别
- 此处的“空值”,不是单纯的指null,也指两个表中“数据不对应”
- 外连接分为左外连接和右外连接
select * from [表1] left join [表2] on ...
左外连接,表1全部+表1和表2的交集

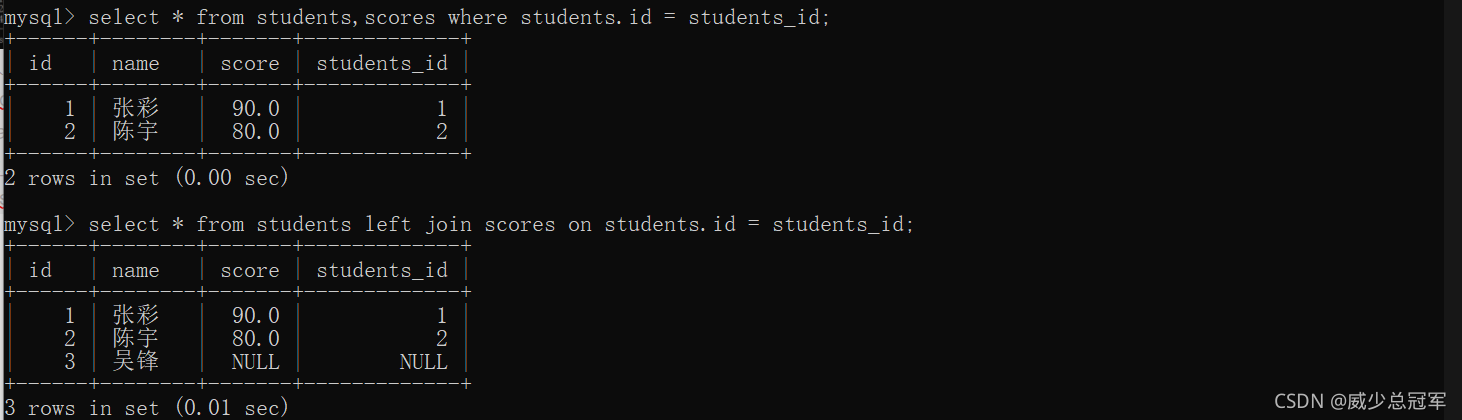
select * from [表1] right join [表2] on ...
右外连接 表2全部+表1和表2的交集

自连接
一张表自己和自己作笛卡尔积
用于行和行的比较
SQL语句只能进行列和列的比较,不能进行 行和行 的比较,使用自连接解决这一问题
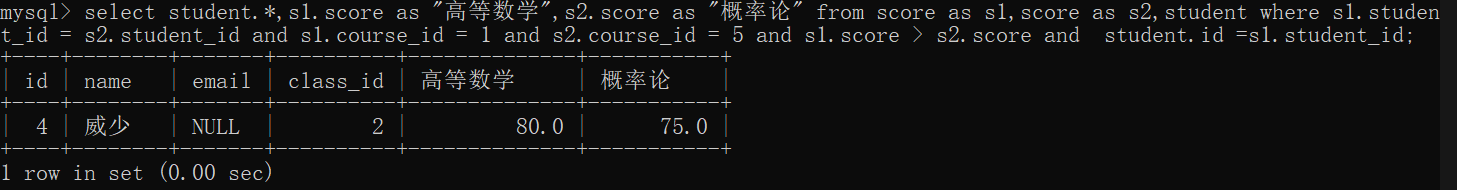
- 查找“高等数学”成绩比“概率论”成绩高的 成绩信息
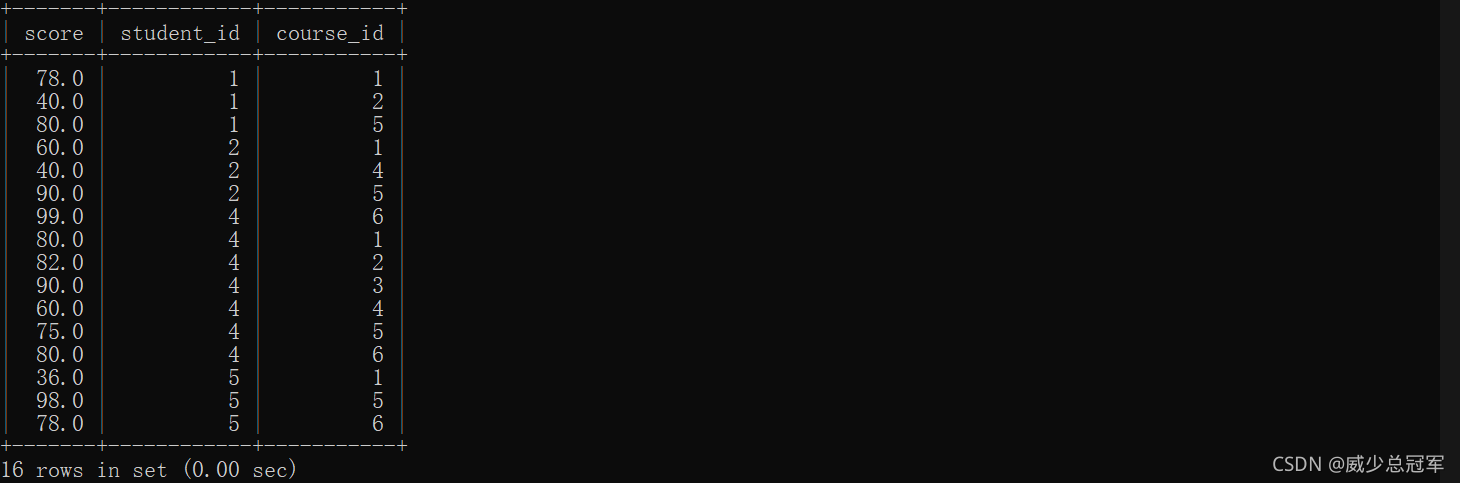


- 筛选出的每条记录都确定是一个同学的成绩,自连接时要设计别名
select * from score as s1,score as s2 where s1.student_id = s2.student_id;
- 筛选出的 记录中s1的score是高数的成绩,s2的score是概率论的成绩
select * from score as s1,score as s2 where s1.student_id = s2.student_id and s1.course_id = 1 and s2.course_id = 5;
- 比较
select * from score as s1,score as s2 where s1.student_id = s2.student_id and s1.course_id = 1 and s2.course_id = 5 and s1.score > s2.score;

子查询
先执行子查询,再执行外层查询
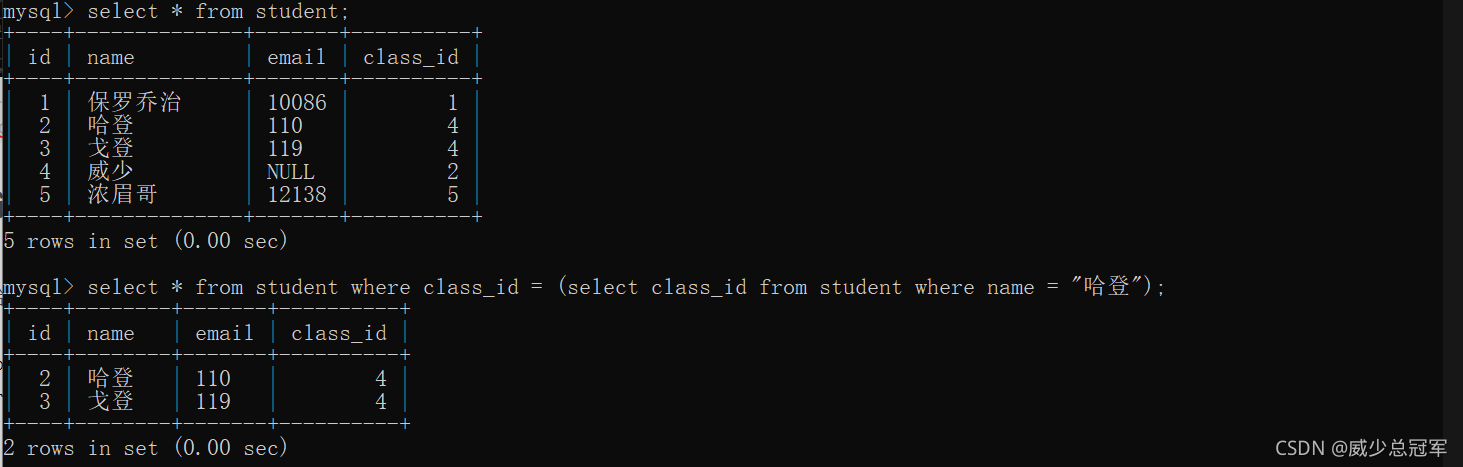
- 单行子查询:返回一行记录的子查询(=)
查询与 哈登 的同班同学的学生信息
select * from student where class_id = (select class_id from student where name = "哈登");
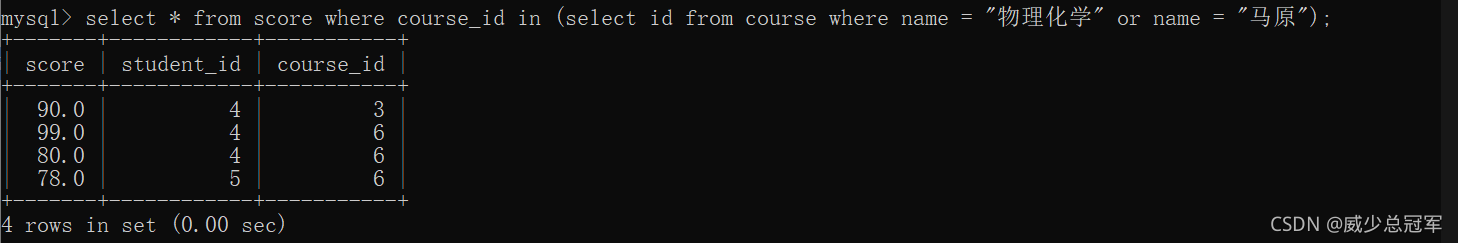
2. 多行子查询(in)
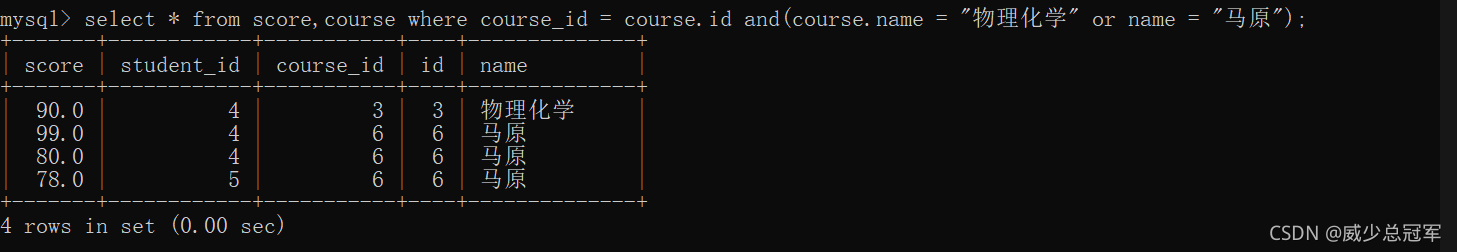
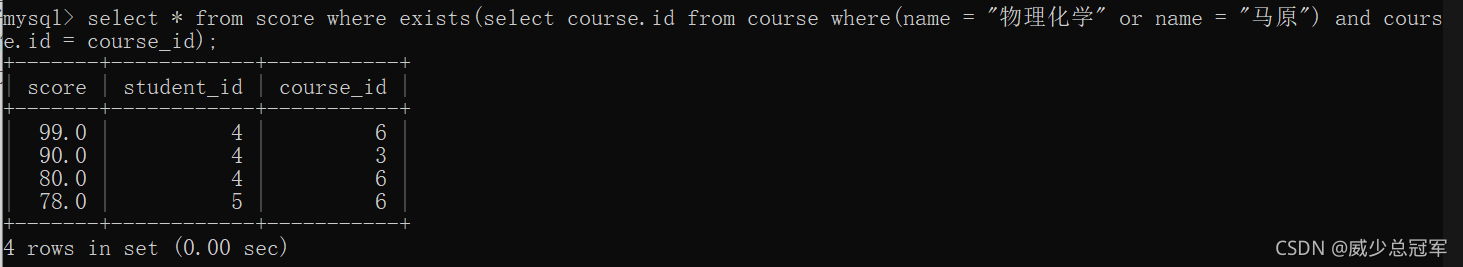
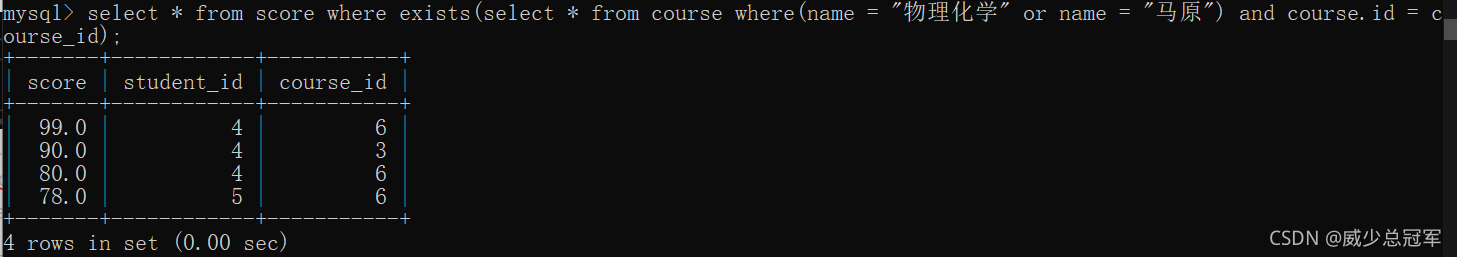
查询 “ 物理化学 ” 和 “ 马原 ” 的成绩信息
select * from score where course_id in (select id from course where name = "物理化学" or name = "马原");
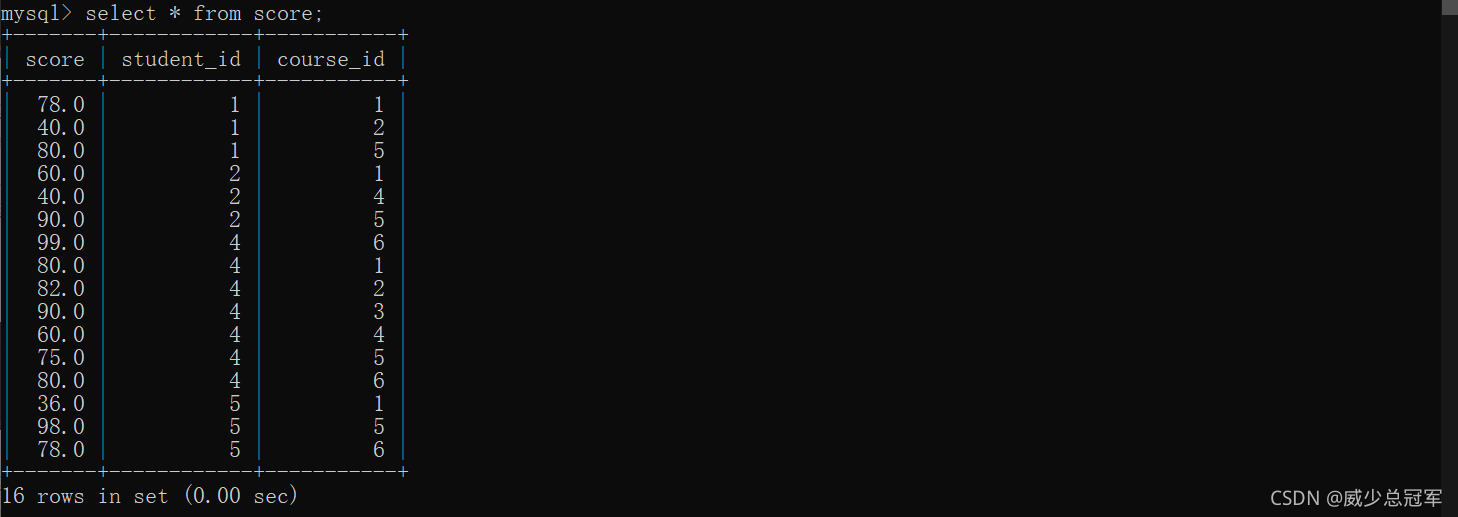


当然也可以用笛卡尔积
用 exists 关键字
- 先执行外层查询,需要遍历外层表中的每个记录,拿每条记录去执行子查询
- 子查询的此时=外层表的行数
- 前面 in 的写法中,子查询只执行依次一次,执行效率高,但是由于要把子查询的结果都放到内存中,导致内存占用过多
- 如果外表大 ,内表小 -----用in
- 外表小, 内表大-----用exists
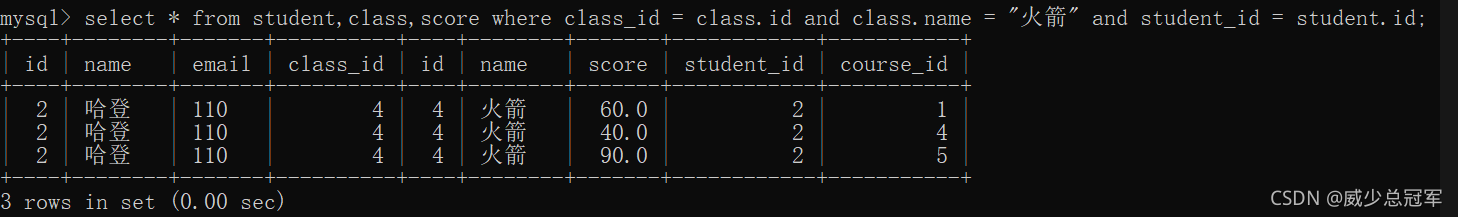
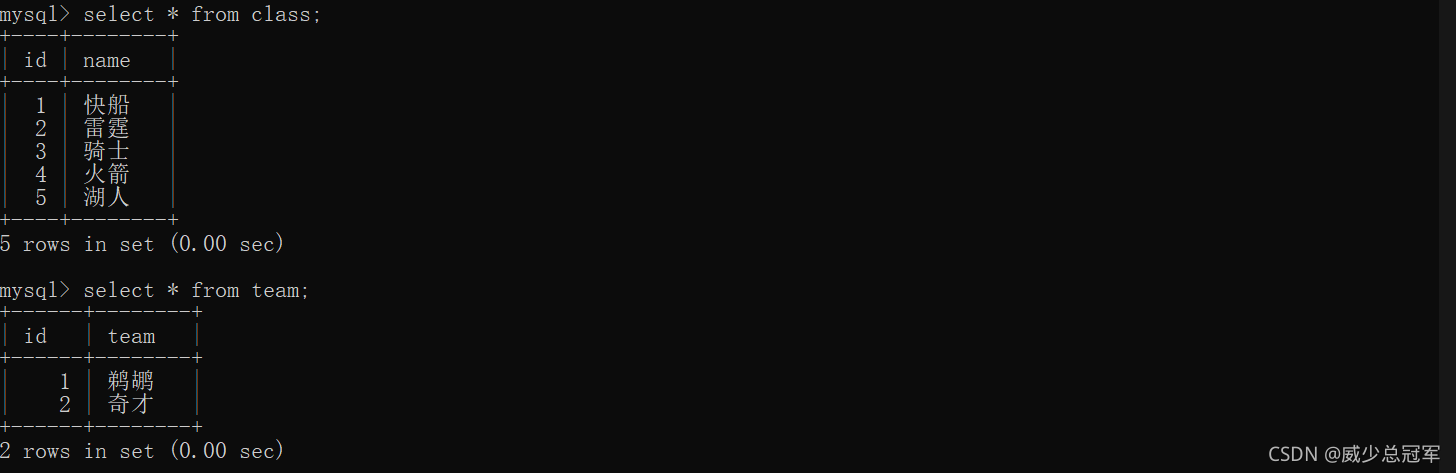
查找比“火箭”班的平均分高的成绩信息
1、 可以先查火箭班的平均分
(1)、先查火箭班的学生
select * from student,class where class_id = class.id and class.name = "火箭"
(2)、再查成绩
select * from student,class,score where class_id = class.id and class.name = "火箭" and student_id = student.id
(3)、求平均值
select student.*,avg(score) from student,class,score where class_id = class.id and class.name = "火箭" and student_id = student.id;
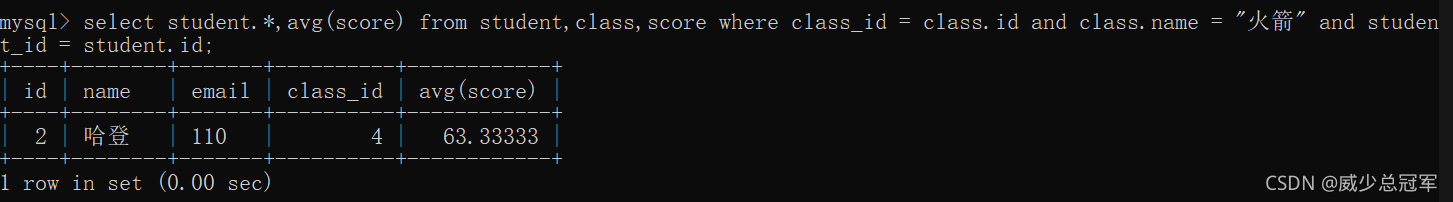
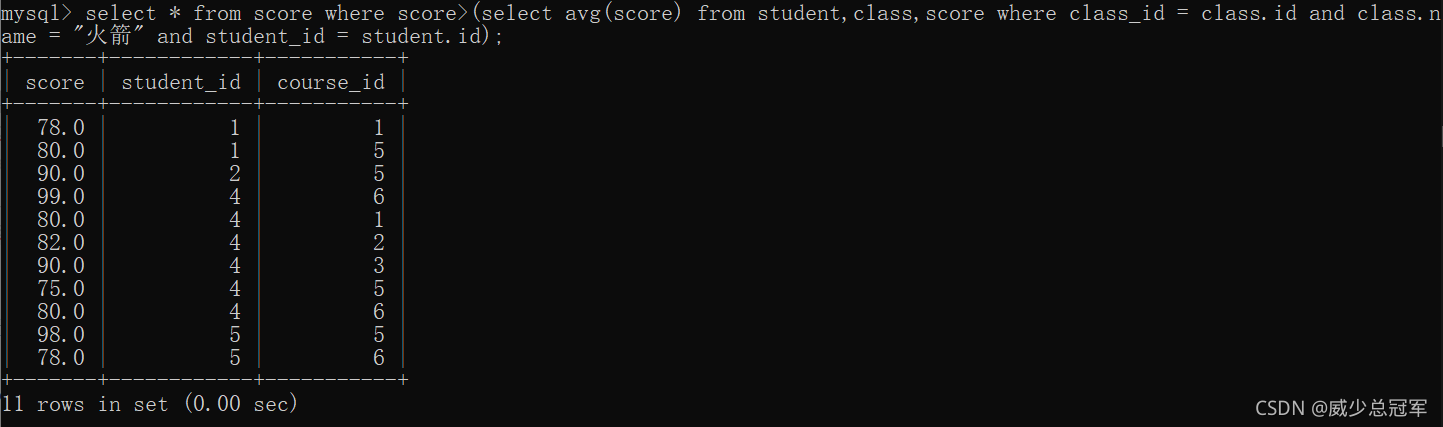
2、利用子查询
select * from score where score>(select avg(score) from student,class,score where class_id = class.id and class.name = "火箭" and student_id = student.id);
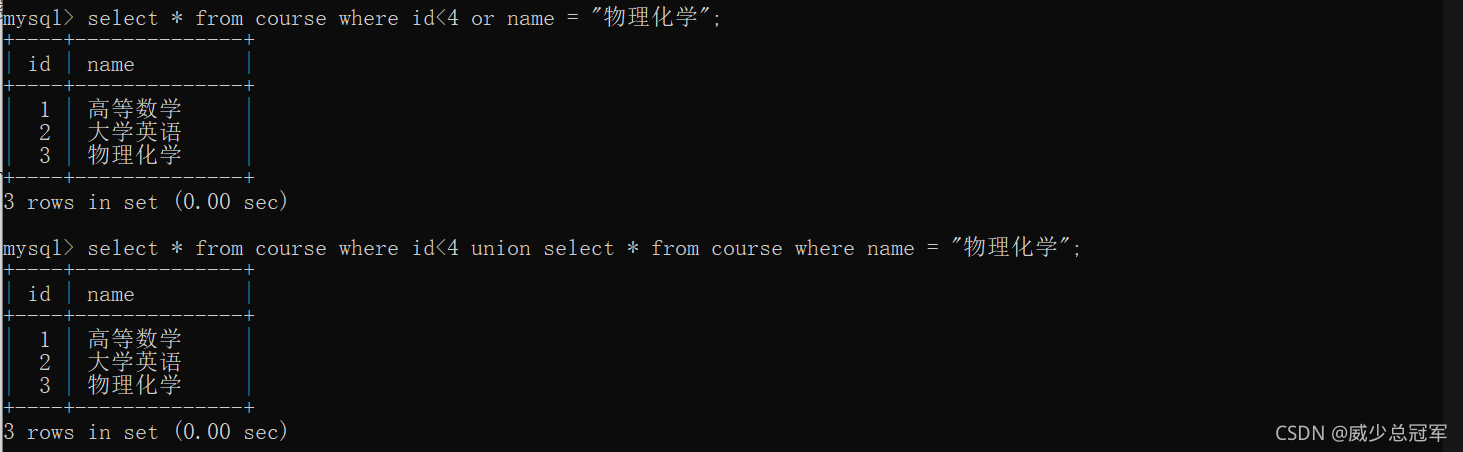
合并查询
把多个select查询的结果,合并成为一个结果
关键词 union
- 会自动去除结果集中的重复行
- 相当于 or ,但是 or 不能跨多张表进行数据合并,它可以哦
- 跨表进行数据合并时,要注意两边的查询得到的列是一致的,包括数量和类型;名字不同也没关系,沿用前面的表所查询的列名
select... from [表1] union select...from [表2]

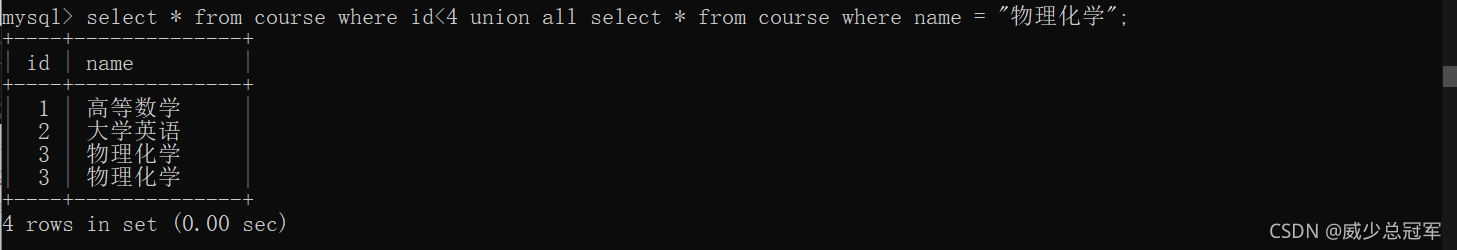
union all 会保留重复的行
跨表合并数据


露从今夜白,月是故乡明,中秋快乐!



