文章目录
GlusterFS分布式文件系统
GlusterFS简介
开源分布式文件系统
PB级容量
高可用性
读/写性能
基于文件系统级别共享
? GlusterFS(GNU ClusterFile System)是一种全对称的开源分布式文件系统,所谓全对称是指GlusterFS采用弹性哈希算法,没有中心节点,所有节点全部平等。GlusterFS配置方便,稳定性好,可轻松达到PB级容量,数千个节点。
? 2011年被红帽收购,之后推出了基于GlusterFS的Red Hat Storage Server,增加了针对KVM的许多特性。可用作为KVM存储image存储集群,也可以为LB或HA提供存储。
GlusterFS术语:
Brick
Volume
Fuse
VFS
Glusterd
GlusterFS重要特性:
全对称架构
支持多种卷类型(类似RAID0/1/5/10/01)
支持卷级别的压缩
支持NFS
支持SMB
支持Hadoop
支持Openstack
支持kubernetes
GlusterFS重要概念:
brick: GlusterFS的基本单元,以节点服务器目录形式展现。
Volume: 多个 bricks 的逻辑集合
Metadata: 元数据,用于描述文件、目录等的信息。
Self-heal: 用于后台运行检测复本卷中文件和目录的不一致性并解决这些不一致。
GlusterFS Server: 数据存储服务器,即组成GlusterFs存储集群的节点。
GlusterFS Client: 使用GlusterFS存储服务器的服务器,例如KVM、Openstack、LB RealServer、HA node。
准备机器
5台虚拟机(当然可以更多节点)
操作系统 IP 主机名
Centos7.4 192.168.62.203 node1
Centos7.4 192.168.62.204 node2
Centos7.4 192.168.62.135 node3
Centos7.4 192.168.62.166 node4
所有机器关闭防火墙
systemctl stop firewalld && setenforce 0
同步时间重要
yum -y install ntp //时间服务 都下载
[root@mysql-1 ~]# vim /etc/ntp.conf //将下面两行添加进去
选取一个主机同步即可
server 127.127.1.0 # local clock
fudge 127.127.1.0 stratum 10
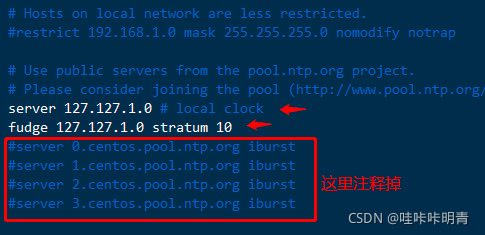
[root@node1 ~]# systemctl restart ntpd
其余3台客户端同步时间:
[root@node2 ~]# yum -y install ntp
[root@node2 ~]# ntpdate node1
分别修改主机名称:
[root@192 ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname node1
[root@192 ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname node2
[root@192 ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname node3
[root@192 ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname node4
配置解析,所有机器:
[root@192 yum.repos.d]# cat /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
192.168.62.131 node01
192.168.62.231 node02
192.168.62.168 node03
192.168.62.166 node04
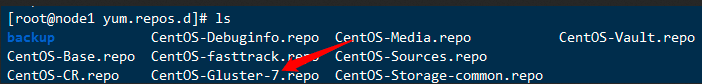
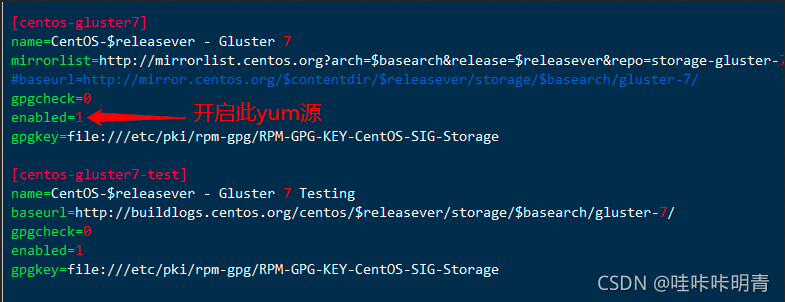
安装glusterfs服务(所有主机)
这条命令需要敲两遍,重点
yum install centos-release-gluster glusterfs-server samba rpcbind -y
如果下载失败,修改glusterfs的yum源配置文件
所有节点启动服务并设置为开机自启
[root@node1 ~]# systemctl start glusterd.service
[root@node1 ~]# systemctl enable glusterd.service
 ## 创建Glusterfs集群
## 创建Glusterfs集群
添加节点的过程就是创建集群的过程,在node01一台上操作就可以,不需要添加本节点
[root@node1 yum.repos.d]# gluster peer probe node02
peer probe: success.
[root@node1 yum.repos.d]# gluster peer probe node03
peer probe: success.
[root@node1 yum.repos.d]# gluster peer probe node04
查看状态
[root@node1 yum.repos.d]# gluster peer status
Number of Peers: 3
Hostname: node02
Uuid: c5c38696-787b-48f9-a4b8-9a38d0cef54f
State: Peer in Cluster (Connected)
Hostname: node03
Uuid: 5cf46129-304a-48c4-b354-4b7f661ed3bb
State: Peer in Cluster (Connected)
Hostname: node04
Uuid: 2d325694-953c-45c6-a284-68816c9e9cdc
State: Peer in Cluster (Connected)
从集群中删除节点
[root@node1 yum.repos.d]# gluster peer detach node04
All clients mounted through the peer which is getting detached need to be remounted using one of the other active peers in the trusted storage pool to ensure client gets notification on any changes done on the gluster configuration and if the same has been done do you want to proceed? (y/n) y
peer detach: success
[root@node1 yum.repos.d]# gluster peer status
Number of Peers: 2
Hostname: node02
Uuid: c5c38696-787b-48f9-a4b8-9a38d0cef54f
State: Peer in Cluster (Connected)
Hostname: node03
Uuid: 5cf46129-304a-48c4-b354-4b7f661ed3bb
State: Peer in Cluster (Connected)
重新添加
[root@node1 ~]# gluster peer probe node04 //重新添加回来
glusgerfs卷的类型*
基本类型:条带,复制,哈希。然后还有两两组合和三种类型同时使用,总共加起来共7种,新版的还有冗余卷
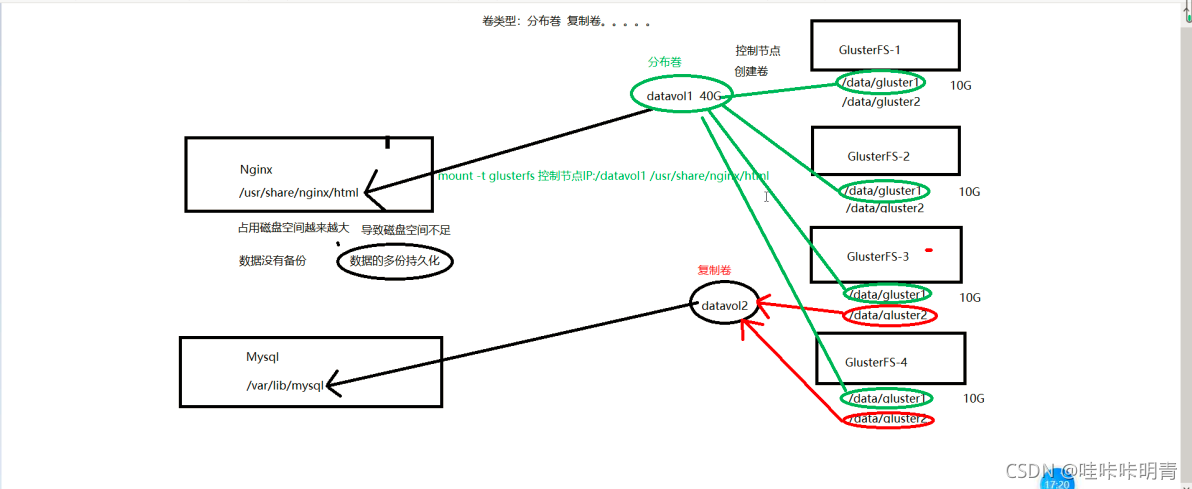
分布卷
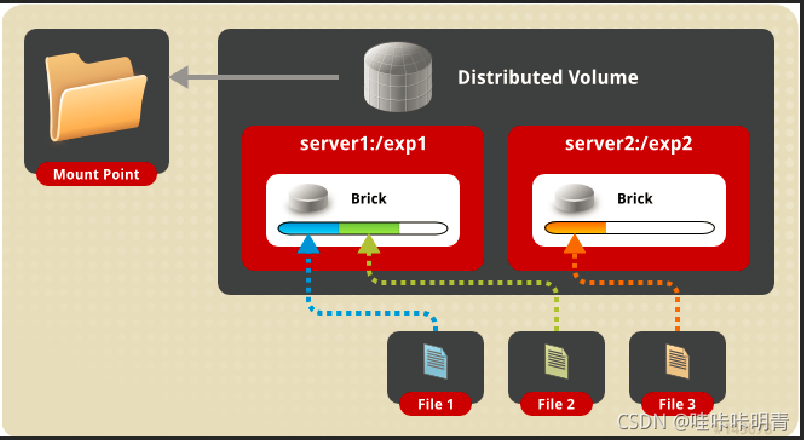
分布巻
分布卷也称为哈希卷,多个文件在多个 brick 上使用哈希算法随机存储。
哈希卷类似与负载均衡(实际上不是很均衡),他会将完整的数据分成几个部分,分别存储在每一个brick上
应用场景: 大量小文件
优点: 读/写性能好
缺点: 如果存储或服务器故障,数据将丢失
创建数据分区
所有server节点分别创建/data0/gluster目录,所谓brick的位置,用于存储数据
mkdir -pv /data0/gluster
创建volume,在控制节点上操作
[root@node1 yum.repos.d]# gluster
Welcome to gluster prompt, type 'help' to see the available commands.
gluster> volume create datavol1 transport tcp node01:/data0/gluster/data1 node02:/data0/gluster/data1 node03:/data0/gluster/data1 node04:/data0/gluster/data1 force
volume create: datavol1: success: please start the volume to access data
启动volume
因为默认是分布巻(哈希卷),所以卷的类型没有指定,datavol1 这个volume拥有4个brick,分布在4个peer节点
gluster> volume start datavol1
volume start: datavol1: success
查看卷信息
gluster> volume info datavol1
Volume Name: datavol1
Type: Distribute
Volume ID: 45ca6286-f622-4902-b10d-ccc38febe137
Status: Started
Snapshot Count: 0
Number of Bricks: 4
Transport-type: tcp
Bricks:
Brick1: node01:/data0/gluster/data1
Brick2: node02:/data0/gluster/data1
Brick3: node03:/data0/gluster/data1
Brick4: node04:/data0/gluster/data1
Options Reconfigured:
transport.address-family: inet
nfs.disable: on
查看卷状态
gluster> volume status datavol1
删除卷
需要提前停止卷运行
gluster> volume stop datavol1 //停止
Stopping volume will make its data inaccessible. Do you want to continue? (y/n) y
volume stop: datavol1: success
gluster> volume delete datavol1 //删除
Deleting volume will erase all information about the volume. Do you want to continue? (y/n) y
volume delete: datavol1: success
找台虚拟机作为客户端,去挂载
[root@node4 ~]# mount -t glusterfs node01:/datavol1 /mnt
[root@node4 ~]# touch /mnt/fenbu1.txt #会随机分配到某个节点上
================================================================
去各个节点查看,不一定分布到哪个节点
[root@node1 ~]# ls /data0/gluster/data1/
fenbu1.txt
[root@node4 ~]# touch /mnt/fenbu2.txt
去各个节点查看,发现最终在node3节点上发现
[root@node3 ~]# ls /data0/gluster/data1/
fenbu2.txt
以上是volume的状态信息,可以看到在每一个节点上启动一个volume后,gluster会自动的启动相关的进程,Port机监听的端口。在使用ps去查看的时候此时会有3个进程:
glusterd #管理进程
glusterfsd #brick进程,因为本机上只有一个brick
glusterfs #默认启动的nfs的协议进程,是可以关闭的
在另外一个节点上会启动相同的进程。
卷的扩容和缩容
收缩卷
注意:收缩之前数据会自动迁移
[root@node1 glusterfs]# ls /data0/gluster/data1
fenbu1.txt
[root@node3 ~]# ls /data0/gluster/data1/
fenbu2.txt fenbu3.txt
[root@node1 glusterfs]# gluster
gluster> volume remove-brick datavol1 node03:/data0/gluster/data1 start //开启迁移
gluster> volume remove-brick datavol1 node03:/data0/gluster/data1 status //查看迁移状态
gluster> volume remove-brick datavol1 node03:/data0/gluster/data1 commit //提交
gluster> volume info datavol1 //再次查看状态,就看不到node03了
数据也会自动迁移到其他节点的brick上
[root@node1 glusterfs]# ls /data0/gluster/data1 //随机移动到了这里
fenbu1.txt fenbu2.txt fenbu3.txt
[root@node3 mmm]# ls /data0/gluster/data1/ //就是空的了
[root@node3 mmm]#
卷的扩容
gluster> volume add-brick datavol1 node03:/data0/gluster/data1 force //扩容,但是数据自动分布上去
gluster> volume info datavol1 //再次查看卷信息,就会有node03节点
卷的重新均衡
扩容之后,应当再做一次数据的重新均衡
gluster> volume rebalance datavol1 start
gluster> volume rebalance datavol1 status
gluster> volume rebalance datavol1 stop
复制卷
 `多个文件在多个brick上复制多份,brick的数目要与需要复制的份数相等,建议brick分布在不同的服务器上。
`多个文件在多个brick上复制多份,brick的数目要与需要复制的份数相等,建议brick分布在不同的服务器上。
复制卷和条带卷必须要指定卷的类型,复制卷就是每一个brick中的数据都是一样的,都是写入数据的完整备份,相当raid1。
所以容量会减少一半,当然性能上也会有所消耗.
应用场景: 对可靠性和读性能要求高的场景
优点: 读性能好
缺点: 写性能差`
[root@node4 data1]# gluster
Welcome to gluster prompt, type 'help' to see the available commands.
创建复制卷
gluster> volume create datavol2 replica 2 transport tcp node01:/data0/gluster/data2 node02:/data0/gluster/data2 force
启动volume
gluster> volume start datavol2
查看volume状态
gluster> volume status
查看卷信息
gluster> volume info datavol2
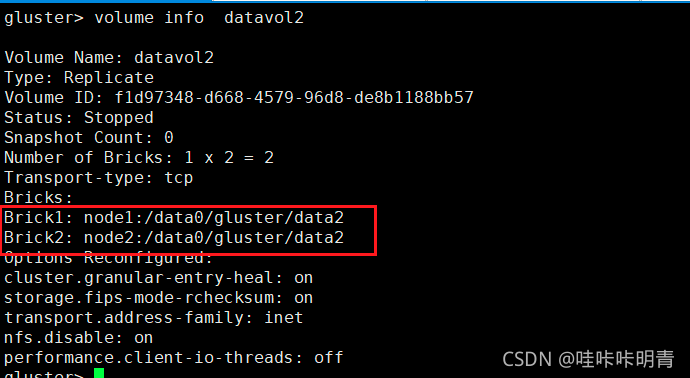
想要看到需要挂载
关于数据,存储节点会同步控制节点的数据,控制节点不会同步存储节点的数据
[root@node3 data2]# mount -t glusterfs node01:/datavol2 /mnt
[root@node3 data2]# ls /mnt/
[root@node3 data2]# cd /mnt/
[root@node3 mnt]# touch d.txt
[root@node1 mnt]# ls /data0/gluster/data2/
d.txt
[root@node2 data2]# cd /data0/gluster/data2/
[root@node2 data2]# ls
d.txt