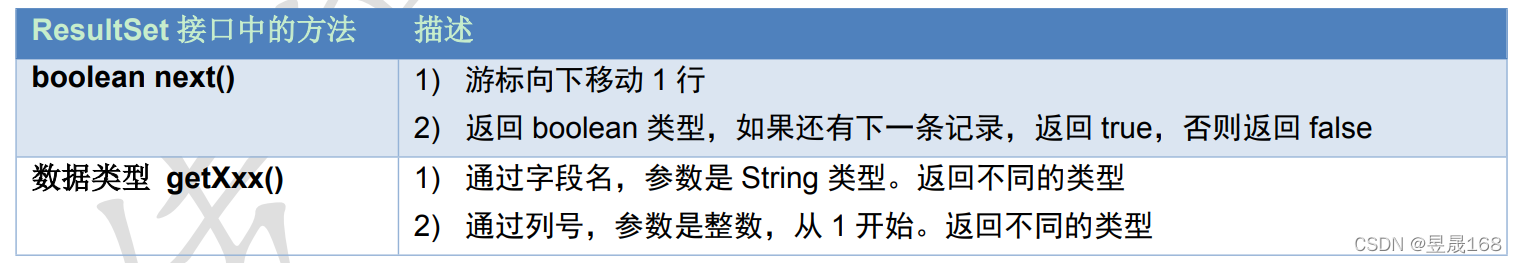
ResultSet:结果集对象,封装结果对象,注意只有executeQuery方法执行才返回ResultSet对象

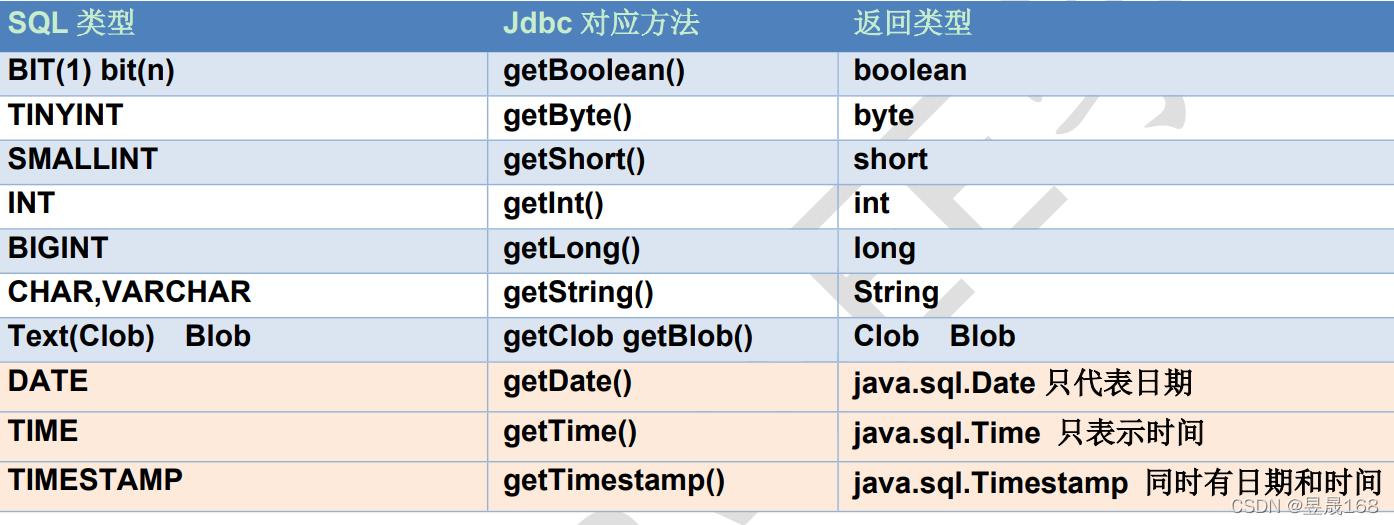
注意: java.sql.Date、Time、Timestamp(时间戳),三个共同父类是:java.util.Date
ResultSet类中常用的方法:
1.next():游标向下移动一行,判断当前行是否是最后一行之后(是否有数据),如果是,则返回false,如果不是则返回true
2.getXxx(参数):获得表中列的数据
Xxx:代表是数据类型,如:int getInt(),String getString()
参数:
1.int 代表是列的编号,注意编号是从1开始的,如:getString(1)
2.String 代表列名称,如:getDouble("balance"),getInt("id")
注意:在使用ResultSet(对象)时应该先判断是否有数据
使用的步骤
1.游标向下移动一行
2.判断是否有数据
3.获取数据
package com.haikang.jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
public class JDBCQuery {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection =null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
//1.导入Jar包
try {
//2.注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//3.获得数据库连接对象
connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/user4","root","root");
//4.定义Sql语句;查询account表中所有数据
String sql = "select * from account";
//5.获得执行Sql对象
statement = connection.createStatement();
//6.执行Sql语句
resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
//7.处理返回的结果集
//7.1使光标向下移
resultSet.next();
//7.2获得第一行的内容
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String name = resultSet.getString("name");
double aDouble = resultSet.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id+"\t"+name+"\t"+aDouble);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//先开的后关
if (resultSet!=null){
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement!=null){
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection!=null){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
优化代码区
package com.haikang.jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
public class JDBCQuery02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection connection =null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
//1.导入Jar包
try {
//2.注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//3.获得数据库连接对象
connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/user4","root","root");
//4.定义Sql语句
String sql = "select * from account";
//5.获得执行Sql对象
statement = connection.createStatement();
//6.执行sql语句
resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
//处理返回的结果
while(resultSet.next()!=false){
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String name = resultSet.getString("name");
double aDouble = resultSet.getDouble(3);
System.out.println(id+"\t"+name+"\t"+aDouble);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally{
//关流
if (resultSet!=null){
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement!=null){
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection!=null){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
练习:定义一个定义方法,查询emp表的数据将其封装为对象,然后装载集合,返回集合
1.定义Employee类
2.定义public List<Employee> findAll(){}
3.实现方法,select * from employee
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Employee {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String gender;
private double salary;
private Date join_date;
private Integer dept_id;
}
package com.haikang.jdbc;
import com.haikang.pojo.Employee;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class JDBCQuery03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Employee> all = findAll();
int size = findAll().size();
System.out.println(size);
System.out.println(all);
}
public static List<Employee> findAll(){
Connection connection = null;
Statement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
Employee employee = null;
List<Employee> lists = new ArrayList<>();;
try {
//1.注册驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获得数据库连接对象
connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test", "root", "root");
//3.定义Sql语句
String sql = "select * from emp";
//4.获得执行Sql对象
statement = connection.createStatement();
//5.执行Sql语句
resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
while (resultSet.next()!=false){
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String name = resultSet.getString("name");
String gender = resultSet.getString("gender");
double salary = resultSet.getDouble("salary");
Date join_date = resultSet.getDate("join_date");
int dept_id = resultSet.getInt("dept_id");
//封装对象
employee = new Employee(id,name,gender,salary,join_date,dept_id);
// 向集合中添加数据
lists.add(employee);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
//关流
if (resultSet!=null){
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (statement!=null){
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (connection!=null){
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return lists;
}
}
练习:登录
需要:
1.通过键盘录入用户名和密码
2.判断用户是否登录成功
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS USER(
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
username VARCHAR(32),
PASSWORD VARCHAR(32)
);
INSERT INTO USER VALUES(NULL,'zs','123'),(NULL,'li','456');
package com.haikang.login;
/**
* 1.导入驱动Jar包
* 2.注册驱动
* 3.获取数据库连接对象Connection
* 4.定义Sql
* 注意:Sql的参数使用?作为占位符:如select * from user where username=? and password=?
* 5.获取执行Sql语句对象PreparedStatement,同时并Sql语句传入
* 如:connection.prepareStatement(sql);
*
* 6.给?赋值
* a.方法:SetXxx(参数1,参数2)
* 参数1:?的位置编号 ,注意编号是从1开始的
* 参数2:?的值
* 7.执行Sql语句,处理返回结果,不需要传入Sql语句了(注意由于上面已经传入了)
* 8.释放资源
*/
public class JDBCLogin02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
for (int i=0;i<3;i++){
System.out.println("请输入用户名:");
String username = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入密码:");
String password = sc.nextLine();
boolean login = login(username, password);
if (login){
System.out.println("登录成功:");
break;
}else {
System.out.println("用户名或密码错误"+(2-i)+"次机会:");
}
}
}
public static boolean login(String username,String password){
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
if (username==null||password==null){
return false;
}
try {
//注册驱动和获得数据库连接对象
connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//定义Sql语句
String sql = "select * from user where username=? and password=?";
//获得Sql执行对象
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//给占位符赋值
preparedStatement.setString(1,username);
preparedStatement.setString(2,password);
//执行Sql语句,注意不需要传入Sql语句了,如果传入那就是使用父类Statement的方法了
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
//处理返回结果
boolean next = resultSet.next();
return next;
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
//关流
JDBCUtils.close(resultSet,preparedStatement,connection);
return false;
}
}