JDBC入门![]() https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_47514459/article/details/121719450
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_47514459/article/details/121719450
小编相信,通过对上文的阅读,让各位对jdbc(Java对数据库的操作)已经有一定的认识,下面我们就来看看SQL注入的问题与PreparedStatement(对数据库的增删查改)的内容吧!
目录
主要因素:程序先进行sql语句的拼接,在进行sql语句的编译,再进行注入
PreparedStatement (预编译数据库操作对象)
PreparedStatement的使用(先进行编译,再进行传值,关键字不进行编译了)
Statement 与PreparedStatement的比较
SQL注入
?模拟用户登录(来方便观看现象)
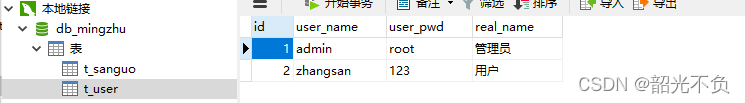
创建表存储用户
CREATE TABLE t_user( id int primary key auto_increment comment '用户主键',
user_name varchar(20) not null unique comment '用户名称',
user_pwd varchar(20) ,
real_name varchar(255)
);
INSERT INTO t_shuihuo VALUES(null,"admin","root","管理员");
INSERT INTO t_shuihuo VALUES(null,"zhangsan","123456","管理员");
创建登录类
public class Jdbc_login {
public static void main(String[]args){
//初始化界面,返回用户名与密码
Map<String ,String> userLogin = initUI();
//验证用户名与密码
Boolean ok = checkNameAndPwd(userLogin.get("user_name"),userLogin.get("user_pwd"));
System.out.println(ok ? "登录成功" : "登陆失败");
}
}实现类中方法
//初始界面,获取用户名和密码
public static Map<String,String> initUI(){
//存储输入账户,密码
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
System.out.println("***************欢迎登录****************");
//获取输入输出
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("用户名:");
//nextLine接收是接收一行
String user_name = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.print("密码: ");
String user_pwd = scanner.nextLine();
//将获取的账户密码,输入到集合中
map.put("user_name",user_name);
map.put("user_pwd",user_pwd);
//返回集合
return map;
}
//生成用户名与密码检测方法
private static Boolean checkNameAndPwd(String user_name, String user_pwd) {
boolean ok = false;//判断登录是否正确
Connection conn = null;
Statement stat = null;
ResultSet res = null;
try {
//1,创建驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2,链接数据库
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3333/db_mingzhu?charset=utf-8","root","root");
//3,获取数据库对象
stat = conn.createStatement();
//4,执行sql语句
String sql = "select * from t_user where user_name = '"+user_name+"' and user_pwd = '"+user_pwd+"'";
System.out.println(sql);
res = stat.executeQuery(sql);
//5,处理查询结果集(判断数据库释放)
if (res.next()){
ok = true;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//6,释放资源
if ( res != null ){
try {
res.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (stat != null){
try {
stat.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return ok;
}完整的代码(我懂你的,如果想自己测试,记得修改数据库接口与数据库名称)
package com.luosf.jdbc;
import com.sun.jmx.snmp.SnmpNull;
import java.awt.*;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Jdbc_login {
public static void main(String[]args){
//初始化界面,返回用户名与密码
Map<String ,String> userLogin = initUI();
//验证用户名与密码
Boolean ok = checkNameAndPwd(userLogin.get("user_name"),userLogin.get("user_pwd"));
System.out.println(ok ? "登录成功" : "登陆失败");
}
//初始界面,获取用户名和密码
public static Map<String,String> initUI(){
//存储输入账户,密码
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
System.out.println("***************欢迎登录****************");
//获取输入输出
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("用户名:");
//nextLine接收是接收一行
String user_name = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.print("密码: ");
String user_pwd = scanner.nextLine();
//将获取的账户密码,输入到集合中
map.put("user_name",user_name);
map.put("user_pwd",user_pwd);
//返回集合
return map;
}
//生成用户名与密码检测方法
private static Boolean checkNameAndPwd(String user_name, String user_pwd) {
boolean ok = false;//判断登录是否正确
Connection conn = null;
Statement stat = null;
ResultSet res = null;
try {
//1,创建驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2,链接数据库
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3333/db_mingzhu?charset=utf-8","root","root");
//3,获取数据库对象
stat = conn.createStatement();
//4,执行sql语句
String sql = "select * from t_user where user_name = '"+user_name+"' and user_pwd = '"+user_pwd+"'";
System.out.println(sql);
//程序执行到这,才会将sql语句编译发送给DBMS,DBMS才进行编译
res = stat.executeQuery(sql);
//5,处理查询结果集(判断数据库释放)
if (res.next()){
ok = true;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//6,释放资源
if ( res != null ){
try {
res.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (stat != null){
try {
stat.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return ok;
}
}
现象
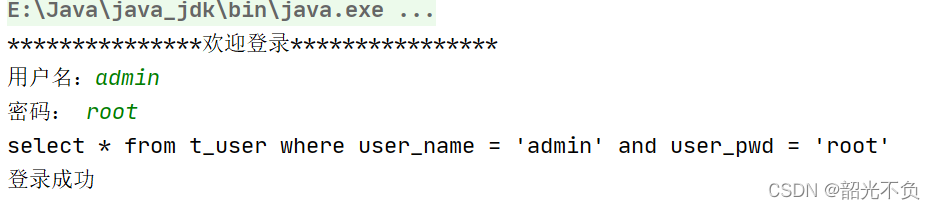
?sql注入
当我们随便输入一个用户名和密码时(让sql语句恒成立)
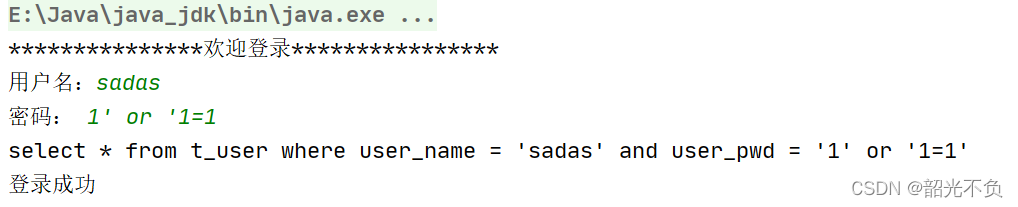
?发现登录成功了(这种现象称为sql注入)
导致sql注入的根本原因:
当用户输入的信息中含有sql的关键字,在字符串的拼接过程中导致sql语句发生了变化(sql语句恒成立)。
根本原因:用户提供信息参与了sql语句的编译。
主要因素:程序先进行sql语句的拼接,在进行sql语句的编译,再进行注入
解决sql注入方法
Statement?
在Java.sql.statement接口中:先进行字符串的拼接,在进行sql语句的编译
优点:Statement 可以进行sql语句的拼接。
缺点:因为拼接存在,存在sql注入
PreparedStatement (预编译数据库操作对象)
在Java.sql.PreparedStatement?接口中:先进行sql语句的编译,然后在进行sql语句的传值。
优点:避免了sql注入
缺点:不能进行sql的拼接只能传值。
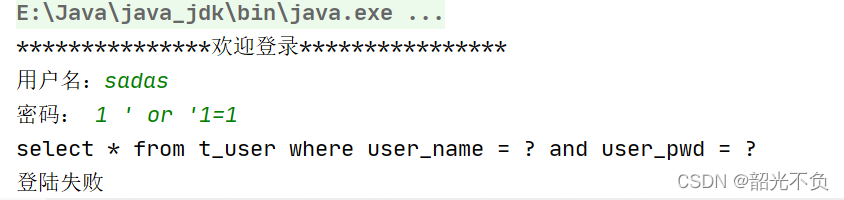
在PreparedStatement的sql语句中一个?表示一个占位符,一个占位符只能接受一个值(如下)
String sql = "select * from t_user where user_name = ? and user_pwd = ? ";PreparedStatement的使用(先进行编译,再进行传值,关键字不进行编译了)
PreparedStatement stat = null;
//3,获取预编译数据库操作对象
String sql = "select * from t_user where user_name = ? and user_pwd = ? ";
//此时发送sql语句给DBMS,进行sql语句的编译
stat = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//给占位符传值
//JDBC下标从1开始的
stat.setString(1,user_name); //1,代表第一个问号
stat.setString(2,user_pwd); //2,代表第二个问号
System.out.println(sql);
//程序执行到这,才会将sql语句编译发送给DBMS,DBMS才进行编译
res = stat.executeQuery(); //不用在进行sqld的传入了修改后全部代码
package com.luosf.jdbc;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Jdbc_sql {
public static void main(String[]args){
//初始化界面,返回用户名与密码
Map<String ,String> userLogin = initUI();
//验证用户名与密码
Boolean ok = checkNameAndPwd(userLogin.get("user_name"),userLogin.get("user_pwd"));
System.out.println(ok ? "登录成功" : "登陆失败");
}
//初始界面,获取用户名和密码
public static Map<String,String> initUI(){
//存储输入账户,密码
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
System.out.println("***************欢迎登录****************");
//获取输入输出
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("用户名:");
//nextLine接收是接收一行
String user_name = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.print("密码: ");
String user_pwd = scanner.nextLine();
//将获取的账户密码,输入到集合中
map.put("user_name",user_name);
map.put("user_pwd",user_pwd);
//返回集合
return map;
}
//生成用户名与密码检测方法
private static Boolean checkNameAndPwd(String user_name, String user_pwd) {
boolean ok = false;//判断登录是否正确
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement stat = null;
ResultSet res = null;
try {
//1,创建驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2,链接数据库
conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3333/db_mingzhu?charset=utf-8","root","root");
//3,获取预编译数据库操作对象
String sql = "select * from t_user where user_name = ? and user_pwd = ? ";
//此时发送sql语句给DBMS,进行sql语句的编译
stat = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
//给占位符传值
//JDBC下标从1开始的
stat.setString(1,user_name); //1,代表第一个问号
stat.setString(2,user_pwd); //2,代表第二个问号
System.out.println(sql);
//程序执行到这,才会将sql语句编译发送给DBMS,DBMS才进行编译
res = stat.executeQuery();
//5,处理查询结果集(判断数据库释放)
if (res.next()){
ok = true;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//6,释放资源
if ( res != null ){
try {
res.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (stat != null){
try {
stat.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (conn != null){
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return ok;
}
}
Statement 与PreparedStatement的比较
关系:Statement是PreparedStatement的父类。
Statement(使用,与使用场景)
进行字符串的拼接
使用场景:(当需要使用关键字(升序或降序)进行拼接时,就使用statement)
PreparedStatement(使用与使用场景)
先编译进行字符串的传值
使用场景(当你进行输入防止sql注入时,就使用PreparedStatement)