MySQL
MySQL是一个关系型数据库管理系统。
安装配置
下载网址:https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/installer/
安装:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34444097/article/details/82315587
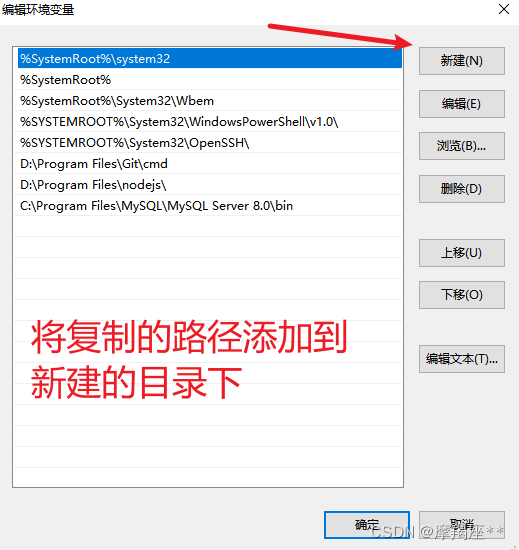
安装完成后,配置环境变量:
找到mysql的安装目录,默认:C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server 8.0\bin。如果修改了,则自己找到修改的目录。一定要定位到bin目录下。复制路径。
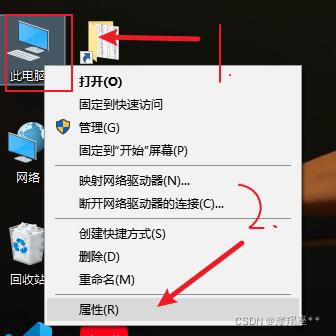
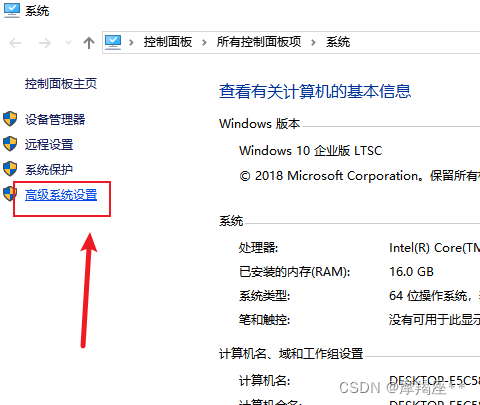
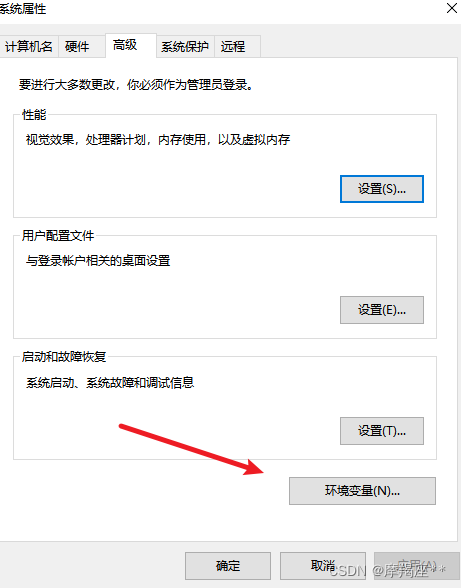
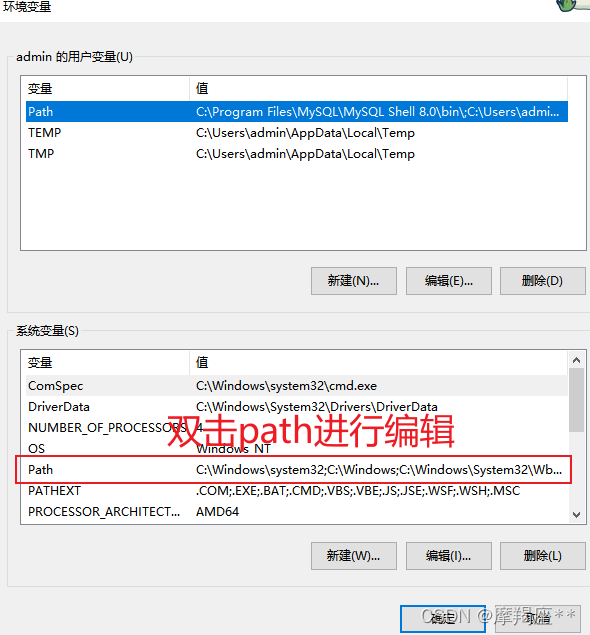
进入命令窗口
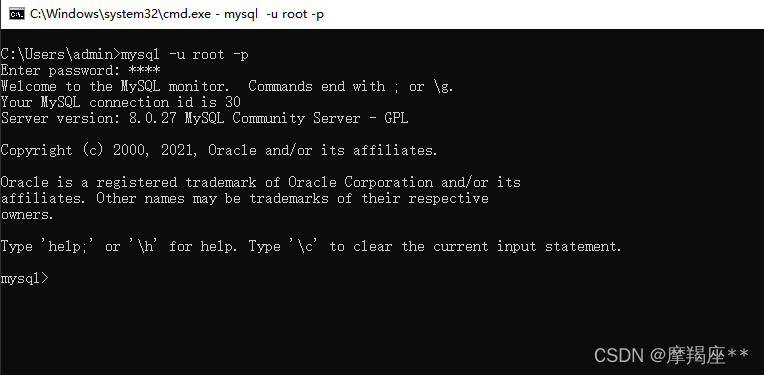
win+r 输入cmd 进入命令窗口, 输入 mysql -u root -p 回车 再输入密码 进入mysql的命令窗口
概念
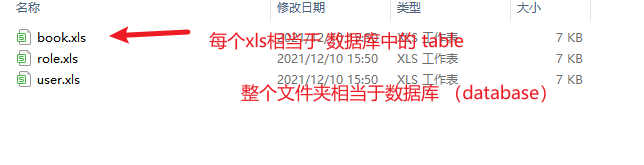
数据库(database)
mysql里面存储了很多数据库,我们可以理解为 电脑上的一个 文件夹。 一般情况下,一个项目对应一个数据库。
每一个数据库是由多张表组成的。
表(table)
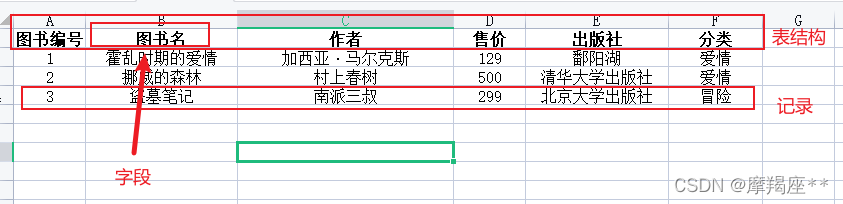
字段
相当于表格中的表头
记录
一条记录相当于表格中的一条内容
数据库的操作
# 查看所有的数据库
show databases;
#创建一个数据库
create database py;
#查看一个数据库的编码格式
show create database py;
#设置数据库的编码格式
alter database py default character set utf8mb4;
#删库
drop database py;
#创建指定字符串的数据库
create database py default character set utf8mb4;
表的操作
表的操作之前,请确认已经选中了数据库
# 选中py这个数据库
use py;
#创建表
create table book (
id int(11) not null,
name varchar(20),
author varchar(20),
price double(5,2),
category varchar(10)
);
#查看表
show tables;
#修改表名 将book表重命名为books
alter table book rename books
#添加字段
alter table books add press varchar(20);
#查看表的字段信息
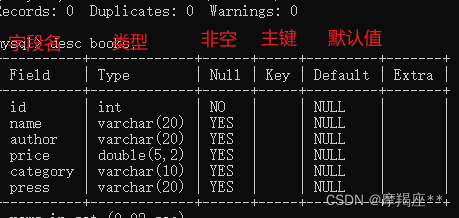
desc books;
#删除字段 删除books表中的press字段。
alter table books drop press
#删除表 删除books表
drop table books
操作记录
# 添加记录 (指定字段)
insert into book(id,name,author,price,category) values (1,'诛仙','萧鼎',99,'仙侠');
#添加记录(所有字段,添加的值要一一对应)
insert into book values (1,'诛仙','萧鼎',99,'仙侠');
#查询所有记录
select * from book;
#修改记录
update book set price = 239; #将所有书的价格修改为239元。
#修改指定条件的记录
update book set price = 29 where id = 1;#将id为1的书籍的价格修改为29元。
#一次修改多个字段的值。
update book set name = "三体(系列)",category = "科幻" where id = 4; #将id等于4的书籍的名字修改为三体(系列),同时将分类修改为 科幻。
#删除一条记录
delete from book where id = 4 #删除id为4的书籍
delete from book; #删除所有书籍
#查询符合条件的记录
select * from book where category = '爱情';#查询所有分类为爱情的书籍
where子句
where子句用于过滤记录。
单条件
#查询id等于1的记录
select * from book where id = 1;
#查询price大于100的记录
select * from book where price > 100;
#查询price小于100的记录
select * from book where price < 100;
#查询price大于等于100的记录
select * from book where price >= 100;
#查询price小于等于100的记录
select * from book where price <= 100;
# 空值判断 查询分类是空的记录
select * from book where category is null;
#模糊匹配 查询作者的名字中带‘三’的记录 %表示任意个字符
select * from book where author like '%三%';
#查询作者的名字以‘三’开头的记录
select * from book where author like '三%';
#查询作者的名字以‘三’开头的记录
select * from book where author like '三%';
#查询书名以‘笔记’结尾的记录
select * from book where name like '%笔记';
多条件
and & or 运算符用于一个以上的条件,对记录的过滤。
如果多个条件都要成立,则使用 and 运算符。
# 查询 价格在50-150之间的书籍
select * from book where price >= 50 and price <=150;
如果多个条件只要有一个成立,则使用or运算符。
# 查询 分类是仙侠 或价格大于150 或价格小于50 的书籍。
select * from book where category = '仙侠' or price>150 or price <50;
#查询 价格在100-150之间的书籍 或 分类是 爱情的 书籍
select * from book where category = '爱情' or price >= 100 and price <= 150;
#查询 价格大于100,分类是 爱情或者冒险的书籍。 注意,and与or同时出现的,将视为整体的部分用小括号包裹。
select * from book where price >100 and (category = '冒险' or category = '爱情');
in 符合范围中某一个值。
#查询 分类是 爱情,冒险,仙侠 中的一个的书籍
select * from book where category in ('爱情','冒险','仙侠');
聚合函数
#查询个数
select count(*) from book;
#查询价格大于100的有几本
select count(*) from book where price >100;
#求和 全买下来要花多少钱
select sum(price) from book;
#求最大值 价格最大值是多少
select max(price) from book;
#求最小值 价格最小值是多少
select max(price) from book;
# 查询最贵的那本书 (子查询)
select * from book where price = (select max(price) from book);
#求平均值
select avg(price) from book;
排序
order by 可以对记录进行排序。
#按照价格从小到大排序
select * from book order by price;
#按照价格从大到小排序
select * from book order by price desc;
#与where联合使用。 where要在order by的前面。 id大于3的值,按照价格排序。
select * from book where id >3 order by price;
分页
使用limit可以限制 查询结果的数量。
#查询 前4本书籍
select * from book limit 4;
#查询第二页的书籍,每页显示4本。
select * from book limit 4,4;
#公示, 查询第n页,每页m本。 limit (n-1)*m, m
#查询最贵的三本书。
select * from book order by price desc limit 3;
#查询最贵的那本书
select * from book order by price desc limit 1;
Navicat使用步骤
1.安装 ,安装完成后,先不要打开navicat。
2.破解:选择安装的目录中,navicat.exe文件!!!
3.如果mysql的版本是8以上,修改以下加密规则:
3.1 cmd命令行下登录mysql。
3 2 还原用户登录密码加密规则
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'password' PASSWORD EXPIRE NEVER;
3.3 重新设置用户密码为root。
ALTER USER 'root'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED WITH mysql_native_password BY 'root';
4.新建连接
执行SQL
或者按下快捷键:ctrl+Q
多表关联查询
数据库表有三种关联关系,分别为:一对多,一对一,多对多。
以学生表,老师表,班级表为例,学生与班级的关系就是多对一。 学生请了家教,一个学生对应一个老师,就是一对一。老师与班级之间是多对多的关系,一个班级有多个任课老师,每个任课老师带多个班级。
新建两张表
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `classroom`;
CREATE TABLE `classroom` (
`id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT 'id',
`name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '教室名',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=5 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of classroom
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `classroom` VALUES ('1', '鄱阳湖');
INSERT INTO `classroom` VALUES ('2', '淀山湖');
INSERT INTO `classroom` VALUES ('3', '老君山');
INSERT INTO `classroom` VALUES ('4', '桐柏山');
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for student
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `student`;
CREATE TABLE `student` (
`id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '学生id',
`name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '学生姓名',
`gender` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '性别',
`age` int DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '年龄',
`score` int DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '成绩',
`c_id` int DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '教室id',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=5 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of student
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('1', '吴用', '男', '20', '4', '1');
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('2', '李逵', '男', '23', '22', '1');
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('3', '孙二娘', '女', '26', '103', '1');
INSERT INTO `student` VALUES ('4', '扈三娘', '女', '18', '59', '2');
在多的那一端添加一个字段,存储 一 那一端的id。 在上面的例子中,学生是多的一端,在student表添加一个字段,c_id 存储 教室 classroom表的id
内连接
#查询鄱阳湖的同学的信息。
SELECT
s.id 学生编号,
s. NAME 学生姓名,
c. NAME AS 教室
FROM
#我们可以为表添加别名。
student s
INNER JOIN classroom c ON c_id = c.id
WHERE
c. NAME = '鄱阳湖';
#内连接 另外一种写法。
SELECT
s.id,
s. NAME,
c.`name` AS classname
FROM
student s,
classroom c
WHERE
s.c_id = c.id
外连接
左外连接
#查询所有同学的信息,包括所属的班级名。
SELECT
s.id,
s. NAME,
c.`name` AS classname
FROM
student s LEFT JOIN
classroom c
ON #on后面跟两种表关联的条件。
s.c_id = c.id
右外连接
#查询所有教室的信息,包含它的学生信息。
SELECT
s.id,
s. NAME,
c.`name` AS classname
FROM
student s RIGHT JOIN
classroom c
ON
s.c_id = c.id