问题
消费者启动的时候,去哪拿的消息呢?
问题答案
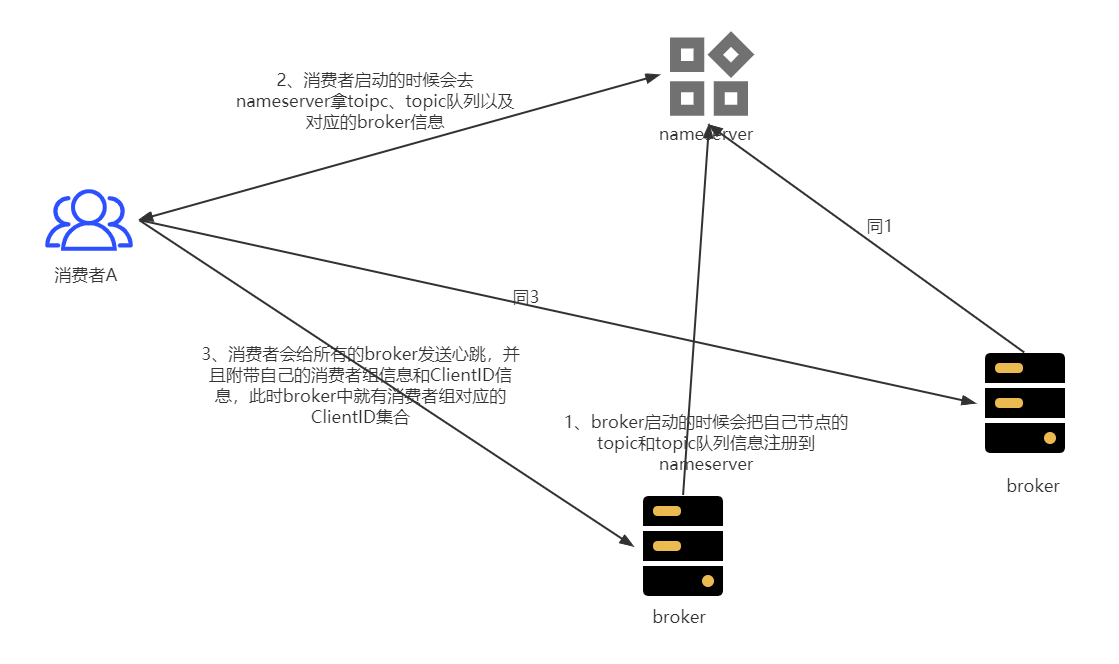
(1)当broker启动的时候,会把broker的地址端口、broker上的主题信息、主题队列信息发送到nameserver(如图中1)
(2)消费者Client启动的时候会去nameserver拿toipc、topic队列以及对应的broker信息,拿到以后把信息存储到本地(如图中2)
(3)消费者会给所有的broker发送心跳,并且附带自己的消费者组信息和ClientID信息,此时broker中就有消费者组对应的ClientID集合(如图中3)
(4)消费者启动后会reblance,有订阅的主题队列列表,并且通过broker可以拿到消费者组的ClientID集合,两个集合做rebalance,就可以拿到当前消费者对应消费的主题队列
(5) 消费者知道自己消费的主题队列,就可以根据队列信息通过Netty发送消息
跟源码
注意
本文是消费者启动流程,所以不去关注broker和nameserver的启动流程,这样关注点比较集中,因此步骤(1)本文不做描述。
消费者启动时怎么拿到toipc的信息
消费者启动的时候会调用
MQClientInstance###start()方法,start()方法里有会调用
MQClientInstance###startScheduledTask()方法,里面的一段代码如下,会每隔一段时间更新一下topic路由信息
//MQClientInstance###startScheduledTask()
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
MQClientInstance.this.updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("ScheduledTask updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer exception", e);
}
}
}, 10, this.clientConfig.getPollNameServerInterval(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
会把路由信息保存到本地的一个HashMap里,这样消费者就拿到了topic的信息并且会把broker的信息保存下来
//MQClientInstance###updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(final String topic, boolean isDefault,DefaultMQProducer defaultMQProducer)
//根据主题从nameserver获取topic信息
topicRouteData = this.mQClientAPIImpl.getTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(topic, 1000 * 3);
//MQClientInstance###updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(final String topic, boolean isDefault,DefaultMQProducer defaultMQProducer)
//把主题和主题队列相关的broker保存下来
TopicRouteData cloneTopicRouteData = topicRouteData.cloneTopicRouteData();
for (BrokerData bd : topicRouteData.getBrokerDatas()) {
this.brokerAddrTable.put(bd.getBrokerName(), bd.getBrokerAddrs());
}
总结:消费者拿到主题的队列列表和broker信息
消费者给broker发现心跳的作用
MQClientInstance###startScheduledTask()方法,里面的一段代码如下,会每隔一段时间给所有的broker发送心跳消息
//MQClientInstance###startScheduledTask()
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
MQClientInstance.this.cleanOfflineBroker();
MQClientInstance.this.sendHeartbeatToAllBrokerWithLock();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("ScheduledTask sendHeartbeatToAllBroker exception", e);
}
}
}, 1000, this.clientConfig.getHeartbeatBrokerInterval(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
那么发送的心跳包中携带什么信息呢?如代码中所示,携带clientID和组名称
//MQClientInstance###prepareHeartbeatData
private HeartbeatData prepareHeartbeatData() {
HeartbeatData heartbeatData = new HeartbeatData();
// clientID
//放入了当前消费者的clientID
//放入了当前消费者的clientID
//放入了当前消费者的clientID
heartbeatData.setClientID(this.clientId);
// Consumer
for (Map.Entry<String, MQConsumerInner> entry : this.consumerTable.entrySet()) {
MQConsumerInner impl = entry.getValue();
if (impl != null) {
ConsumerData consumerData = new ConsumerData();
//放入了当前消费者的组名称
//放入了当前消费者的组名称
//放入了当前消费者的组名称
//放入了当前消费者的组名称
consumerData.setGroupName(impl.groupName());
consumerData.setConsumeType(impl.consumeType());
consumerData.setMessageModel(impl.messageModel());
consumerData.setConsumeFromWhere(impl.consumeFromWhere());
consumerData.getSubscriptionDataSet().addAll(impl.subscriptions());
consumerData.setUnitMode(impl.isUnitMode());
heartbeatData.getConsumerDataSet().add(consumerData);
}
}
// Producer
for (Map.Entry<String/* group */, MQProducerInner> entry : this.producerTable.entrySet()) {
MQProducerInner impl = entry.getValue();
if (impl != null) {
ProducerData producerData = new ProducerData();
producerData.setGroupName(entry.getKey());
heartbeatData.getProducerDataSet().add(producerData);
}
}
return heartbeatData;
}
此时broker拿到心跳消息怎么处理的呢?有一部分逻辑如下面代码所示,记录一下消费者信息
//ClientManageProcessor###heartBeat(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RemotingCommand request)
```java
public RemotingCommand heartBeat(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RemotingCommand request) {
//省略
for (ConsumerData data : heartbeatData.getConsumerDataSet()) {
//省略
boolean changed = this.brokerController.getConsumerManager().registerConsumer(
data.getGroupName(),
clientChannelInfo,
data.getConsumeType(),
data.getMessageModel(),
data.getConsumeFromWhere(),
data.getSubscriptionDataSet(),
isNotifyConsumerIdsChangedEnable
);
//省略
}
//省略
}
消费者怎么做reblance
MQClientInstance的start的方法里会开启一个rebalance的线程,如下面代码所示
//MQClientInstance###start()
public void start() throws MQClientException {
//省略
// Start rebalance service
this.rebalanceService.start();
//省略
}
跟RebalanceService的run()方法一直跟下去最后跟到RebalanceImpl的rebalanceByTopic方法,如下面代码所示。根据主题队列列表和消费者组集合去做一个Rebalance,最后的返回结果是当前消费者需要消费的主题队列。
//RebalanceImpl##rebalanceByTopic
private void rebalanceByTopic(final String topic, final boolean isOrder) {
//获取订阅的主题的队列
//获取订阅的主题的队列
//获取订阅的主题的队列
Set<MessageQueue> mqSet = this.topicSubscribeInfoTable.get(topic);
//获取同消费者组的ClientID集合
//获取同消费者组的ClientID集合
//获取同消费者组的ClientID集合
List<String> cidAll = this.mQClientFactory.findConsumerIdList(topic, consumerGroup);
if (mqSet != null && cidAll != null) {
List<MessageQueue> mqAll = new ArrayList<MessageQueue>();
mqAll.addAll(mqSet);
//排序
//排序
//排序
Collections.sort(mqAll);
Collections.sort(cidAll);
AllocateMessageQueueStrategy strategy = this.allocateMessageQueueStrategy;
List<MessageQueue> allocateResult = null;
try {
//rebalance算法核心实现,最后的结果是返回应该消费的队列
//rebalance算法核心实现,最后的结果是返回应该消费的队列
//rebalance算法核心实现,最后的结果是返回应该消费的队列
allocateResult = strategy.allocate(
this.consumerGroup,
this.mQClientFactory.getClientId(),
mqAll,
cidAll);
} catch (Throwable e) {
}
Set<MessageQueue> allocateResultSet = new HashSet<MessageQueue>();
if (allocateResult != null) {
//rebalance算法核心实现,最后的结果是返回应该消费的队列
//rebalance算法核心实现,最后的结果是返回应该消费的队列
//rebalance算法核心实现,最后的结果是返回应该消费的队列
allocateResultSet.addAll(allocateResult);
}
//此处看下面的消费者怎么去拉消息
//此处看下面的消费者怎么去拉消息
//此处看下面的消费者怎么去拉消息
boolean changed = this.updateProcessQueueTableInRebalance(topic, allocateResultSet, isOrder);
}
}
总结:消费者拿到主题的队列列表和消费者组中ClientID集合,通过在消费者这变做rebalance,从而确定被分配的主题队列集合
消费者怎么拉取消息
此处还是继续跟上面的代码,,然后执行到下面的代码,当消费者确定自己被分配的主题队列后,会把主题队列封装成PullRequest 并进行dispatch
//RebalanceImpl###updateProcessQueueTableInRebalance
private boolean updateProcessQueueTableInRebalance(final String topic, final Set<MessageQueue> mqSet,
final boolean isOrder) {
//省列
List<PullRequest> pullRequestList = new ArrayList<PullRequest>();
for (MessageQueue mq : mqSet) {
//省略
PullRequest pullRequest = new PullRequest();
pullRequest.setConsumerGroup(consumerGroup);
pullRequest.setNextOffset(nextOffset);
pullRequest.setMessageQueue(mq);
pullRequest.setProcessQueue(pq);
pullRequestList.add(pullRequest);
changed = true;
}
}
//省略
//派发请求任务
this.dispatchPullRequest(pullRequestList);
return changed;
}
下面跟RebalanceImpl###dispatchPullRequest方法,最后跟到下面的代码,就是把PullRequest放入到一个阻塞队列里。
//PullMessageService###executePullRequestImmediately
public void executePullRequestImmediately(final PullRequest pullRequest) {
try {
this.pullRequestQueue.put(pullRequest);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("executePullRequestImmediately pullRequestQueue.put", e);
}
}
那么谁取阻塞队列里的数据谁就是消费消息了?
PullMessageService是一个线程,他的run方法里会取上面阻塞队列里的PullRequest,如下面代码所示
//PullMessageService###run()
public void run() {
log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service started");
while (!this.isStopped()) {
try {
PullRequest pullRequest = this.pullRequestQueue.take();
this.pullMessage(pullRequest);
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Pull Message Service Run Method exception", e);
}
}
log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service end");
}
从PullMessageService###pullMessage方法一直往下跟,就跟到下面的代码
//DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl###pullMessage(final PullRequest pullRequest)
public void pullMessage(final PullRequest pullRequest) {
//省略
final long beginTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
PullCallback pullCallback = new PullCallback() {
//省略,但是重要,后面会说
//省略,但是重要,后面会说
//省略,但是重要,后面会说
//省略,但是重要,后面会说
};
//省略
try {
//发送数据并且执行回调方法,下面我们看一下回调方法的内容就好好了
//发送数据并且执行回调方法,下面我们看一下回调方法的内容就好好了
//发送数据并且执行回调方法,下面我们看一下回调方法的内容就好好了
this.pullAPIWrapper.pullKernelImpl(
pullRequest.getMessageQueue(),
subExpression,
subscriptionData.getExpressionType(),
subscriptionData.getSubVersion(),
pullRequest.getNextOffset(),
this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getPullBatchSize(),
sysFlag,
commitOffsetValue,
BROKER_SUSPEND_MAX_TIME_MILLIS,
CONSUMER_TIMEOUT_MILLIS_WHEN_SUSPEND,
CommunicationMode.ASYNC,
pullCallback
);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("pullKernelImpl exception", e);
this.executePullRequestLater(pullRequest, pullTimeDelayMillsWhenException);
}
}
那么回调方法是什么逻辑呢?代码如下所示,发现数据并且submitConsumeRequest
PullCallback pullCallback = new PullCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(PullResult pullResult) {
if (pullResult != null) {
pullResult = DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.pullAPIWrapper.processPullResult(pullRequest.getMessageQueue(), pullResult,
subscriptionData);
switch (pullResult.getPullStatus()) {
//发现数据
//发现数据
//发现数据
case FOUND:
long prevRequestOffset = pullRequest.getNextOffset();
pullRequest.setNextOffset(pullResult.getNextBeginOffset());
long pullRT = System.currentTimeMillis() - beginTimestamp;
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.getConsumerStatsManager().incPullRT(pullRequest.getConsumerGroup(),
pullRequest.getMessageQueue().getTopic(), pullRT);
long firstMsgOffset = Long.MAX_VALUE;
if (pullResult.getMsgFoundList() == null || pullResult.getMsgFoundList().isEmpty()) {
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.executePullRequestImmediately(pullRequest);
} else {
firstMsgOffset = pullResult.getMsgFoundList().get(0).getQueueOffset();
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.getConsumerStatsManager().incPullTPS(pullRequest.getConsumerGroup(),
pullRequest.getMessageQueue().getTopic(), pullResult.getMsgFoundList().size());
boolean dispatchToConsume = processQueue.putMessage(pullResult.getMsgFoundList());
//跟进去
//跟进去
//跟进去
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.consumeMessageService.submitConsumeRequest(
pullResult.getMsgFoundList(),
processQueue,
pullRequest.getMessageQueue(),
dispatchToConsume);
if (DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getPullInterval() > 0) {
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.executePullRequestLater(pullRequest,
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getPullInterval());
} else {
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.executePullRequestImmediately(pullRequest);
}
}
//省略
break;
case NO_NEW_MSG:
case NO_MATCHED_MSG:
//省略
}
}
}
};
跟上面submitConsumeRequest方法的到下面的代码,封装成ConsumeRequest,其实ConsumerRequest是一个线程
//ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyService###submitConsumeRequest
public void submitConsumeRequest(
final List<MessageExt> msgs,
final ProcessQueue processQueue,
final MessageQueue messageQueue,
final boolean dispatchToConsume) {
final int consumeBatchSize = this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumeMessageBatchMaxSize();
if (msgs.size() <= consumeBatchSize) {
ConsumeRequest consumeRequest = new ConsumeRequest(msgs, processQueue, messageQueue);
try {
this.consumeExecutor.submit(consumeRequest);
} catch (RejectedExecutionException e) {
this.submitConsumeRequestLater(consumeRequest);
}
} else {
//省略
}
}
}
ConsumeRequest的run方法就会执行我们注册的listener方法,此时就消费到数据
```java
@Override
public void run() {
//省略
status = listener.consumeMessage(Collections.unmodifiableList(msgs), context);
//省略
}
}
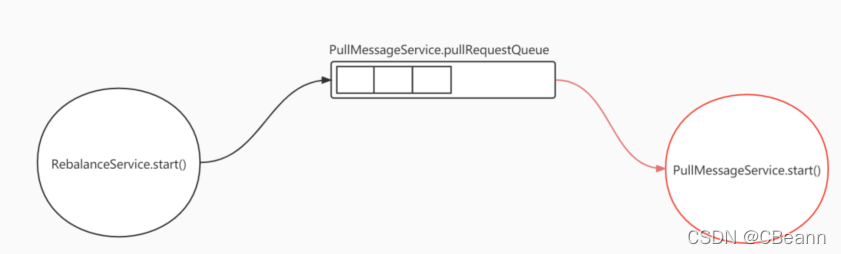
总结:
如下图所示,RebalanceService线程会根据情况把请求放在PullMessageService的pullRequestQueue阻塞队列队列里,队列的每一个节点就是拉请求;PullMessageService线程就是不断去pullRequestQueue里拿任务然后去看一下broker中有没有数据,如果有数据就消费。
总结
(1)忽然发现nameserver在整个过程中的作用感觉不是很大,其实我感觉这种设计还挺好的,因为把所有的压力都放在nameserver返回减少系统的健壮性。
(2)RocketMQ的rebalance是在消息消费者这边实现的,这样有一个很大的优势是减少nameserver和broker的压力。那消费者是怎么实现rebalance的呢?通过一个参数为当前消费者ID、主题队列、消费者组ClientID列表的匹配算法,每次只要保证算法的幂等性就可以了。
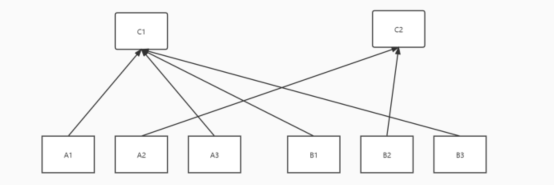
(3)RocketMQ的rebalance的rebalance是根据单个主题去实现的,这样的一个缺点是容易出现消费不平衡的问题。如下图所示。
(4)RocketMQ是AP的,因为他的很操作都是都是通过线程池的定时任务去做的。
参考
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1fE411V7Ho?p=8