我们经常在网站搜索输入时,会帮我们提醒自动完成的功能,比如:
 当我们在百度上搜索 Elasticsearch 时,它会自动弹出一些可以让我们进行搜索的条目。在很多的情况下,用户可能直接选择其中的一个进行输入,而不需要打入全部的文字。
当我们在百度上搜索 Elasticsearch 时,它会自动弹出一些可以让我们进行搜索的条目。在很多的情况下,用户可能直接选择其中的一个进行输入,而不需要打入全部的文字。
在我之前的文章里,有关 autocomplete,也即自动补全的内容,我有几篇文章可以供大家来进行参考:
在今天的文章中,我将使用几种方法来展示自动完成是如何实现的。为了方便大家理解下面的代码,请在 github 上下载我的代码:
git clone https://github.com/liu-xiao-guo/AutoComplete-Input-Elastic-Search-Python$ pwd
/Users/liuxg/python/AutoComplete-Input-Elastic-Search-Python
$ tree -L 2
.
├── Backend
│?? └── api.py
├── Frontend
│?? ├── app.py
│?? └── templates
├── README.md
└── games.json整个项目的代码非常简单。?
- Backend:处理前端发送来的请求,并转发至 Elasticsearch
- Frontend:处理网页发送的搜索请求
- games.json:这是一个实验的数据
准备数据
我们首先把 games.json 这个 JSON 数据摄入到 Elasticsearch 中:
?
我们接下来选择下载的 games.json 文件:
 ?我们输入索引的名称为 games:
?我们输入索引的名称为 games:
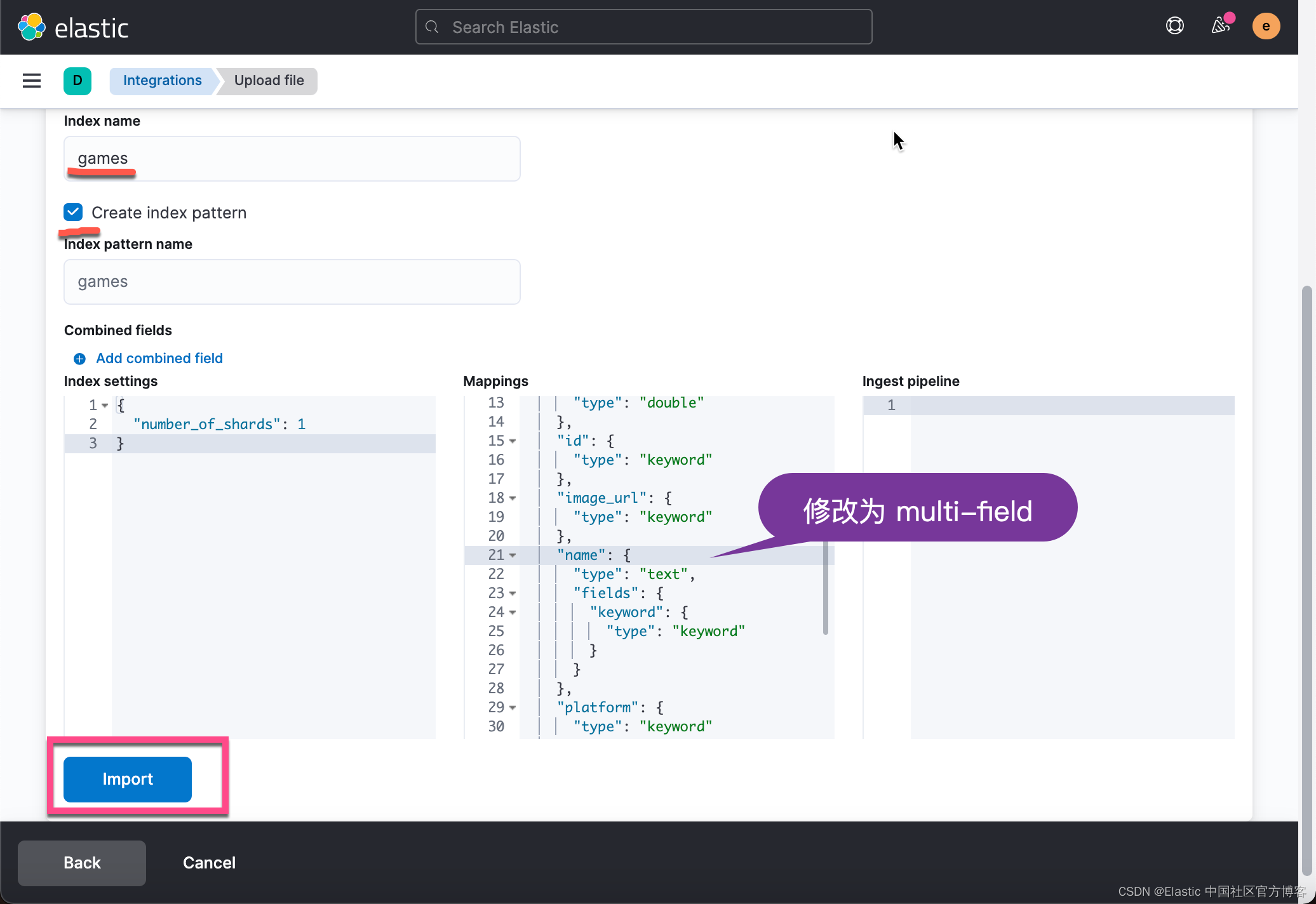
?在上面,我们需要修改 mappings 为:
{
"properties": {
"critic_score": {
"type": "long"
},
"developer": {
"type": "text"
},
"genre": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"global_sales": {
"type": "double"
},
"id": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"image_url": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"name": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
},
"platform": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"publisher": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"user_score": {
"type": "long"
},
"year": {
"type": "long"
}
}
}?把 name 字段修改为一个 multi-field 的字段。点击上面的 Import。这样就完成了我们的 games 索引的摄入。
运行 Backend
我们接下来运行 Backend 应用。这是一个基于 Flask 的 Python 应用。我们需要安装它所需要的 Python 包:
pip3 install flask
pip3 install flask_restful
pip3 install Api
pip3 install reqparse
pip3 install Elasticsearch?我们的 api.py 的设计非常简单:
api.py
try:
from flask import app,Flask
from flask_restful import Resource, Api, reqparse
import elasticsearch
from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch
import datetime
import concurrent.futures
import requests
import json
except Exception as e:
print("Modules Missing {}".format(e))
app = Flask(__name__)
api = Api(app)
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
INDEX_NAME = 'games'
es = Elasticsearch([{'host': 'localhost', 'port': 9200, 'http_auth':('elastic', 'password')}])
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
class Controller(Resource):
def __init__(self):
self.query = parser.parse_args().get("query", None)
self.baseQuery ={
"_source": [],
"size": 0,
"min_score": 0.5,
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match_phrase_prefix": {
"name": {
"query": "{}".format(self.query)
}
}
}
],
"filter": [],
"should": [],
"must_not": []
}
},
"aggs": {
"auto_complete": {
"terms": {
"field": "name.keyword",
"order": {
"_count": "desc"
},
"size": 25
}
}
}
}
def get(self):
res = es.search(index=INDEX_NAME, size=0, body=self.baseQuery)
return res
parser = reqparse.RequestParser()
parser.add_argument("query", type=str, required=True, help="query parameter is Required ")
api.add_resource(Controller, '/autocomplete')
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True, port=4000)
在上面,我的集群的访问用户名及密码为:elastic/password。在上面,它做了一个很简单的 match_phrase_prefix 搜索:
GET games/_search
{
"size": 0,
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match_phrase_prefix": {
"name": "final fan"
}
}
],
"must_not": [],
"filter": [],
"should": []
}
},
"aggs": {
"auto_complete": {
"terms": {
"field": "name.keyword",
"size": 25
}
}
}
}它的返回值为:
{
"took" : 3,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 11,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"auto_complete" : {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound" : 0,
"sum_other_doc_count" : 0,
"buckets" : [
{
"key" : "Crisis Core: Final Fantasy VII",
"doc_count" : 1
},
{
"key" : "Dissidia: Final Fantasy",
"doc_count" : 1
},
{
"key" : "Final Fantasy IX",
"doc_count" : 1
},
{
"key" : "Final Fantasy Tactics",
"doc_count" : 1
},
{
"key" : "Final Fantasy VII",
"doc_count" : 1
},
{
"key" : "Final Fantasy VIII",
"doc_count" : 1
},
{
"key" : "Final Fantasy X",
"doc_count" : 1
},
{
"key" : "Final Fantasy X-2",
"doc_count" : 1
},
{
"key" : "Final Fantasy XII",
"doc_count" : 1
},
{
"key" : "Final Fantasy XIII",
"doc_count" : 1
},
{
"key" : "Final Fantasy XIII-2",
"doc_count" : 1
}
]
}
}
}从上面的结果中,我们可以看出来搜索的结果。
我们使用如下的命令来运行 Backend 的应用:
$ pwd
/Users/liuxg/python/AutoComplete-Input-Elastic-Search-Python/Backend
$ python api.py
* Serving Flask app "api" (lazy loading)
* Environment: production
WARNING: This is a development server. Do not use it in a production deployment.
Use a production WSGI server instead.
* Debug mode: on
* Running on http://127.0.0.1:4000/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)
* Restarting with fsevents reloader
* Debugger is active!
* Debugger PIN: 119-780-958这样我们的 Backend 就运行起来了。我们在下面来运行 Frontend 的应用。
运行 Frontend
我们进入到 Frondend 的子目录中,并使用如下的命令来进行运行:
$ pwd
/Users/liuxg/python/AutoComplete-Input-Elastic-Search-Python/Frontend
$ ls
app.py templates
$ python app.py
* Serving Flask app "app" (lazy loading)
* Environment: production
WARNING: This is a development server. Do not use it in a production deployment.
Use a production WSGI server instead.
* Debug mode: on
* Running on http://127.0.0.1:5000/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)
* Restarting with fsevents reloader
* Debugger is active!
* Debugger PIN: 119-780-958如上所示,前端运行于地址?http://127.0.0.1:5000/。我们在浏览器中打开它:
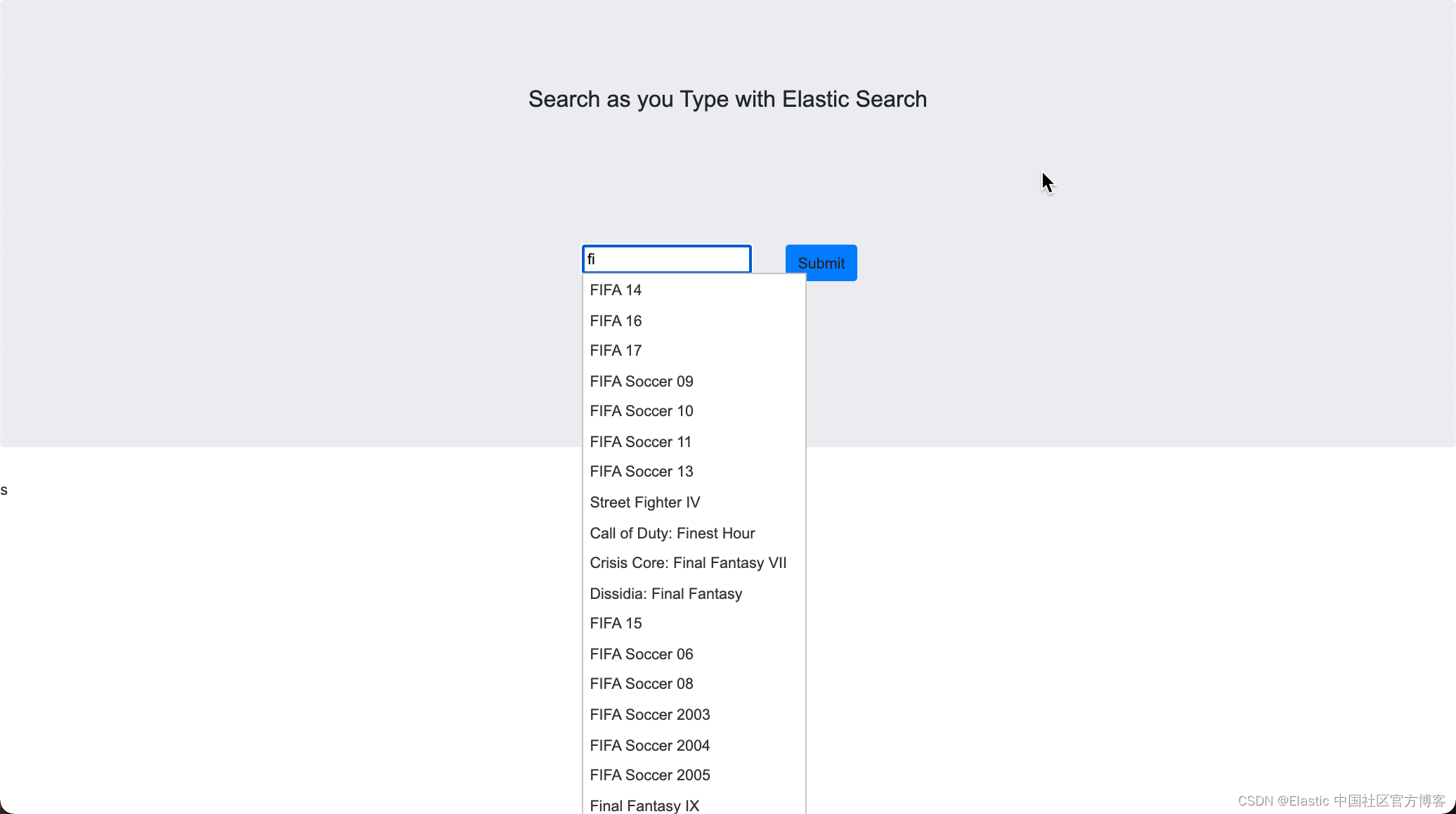
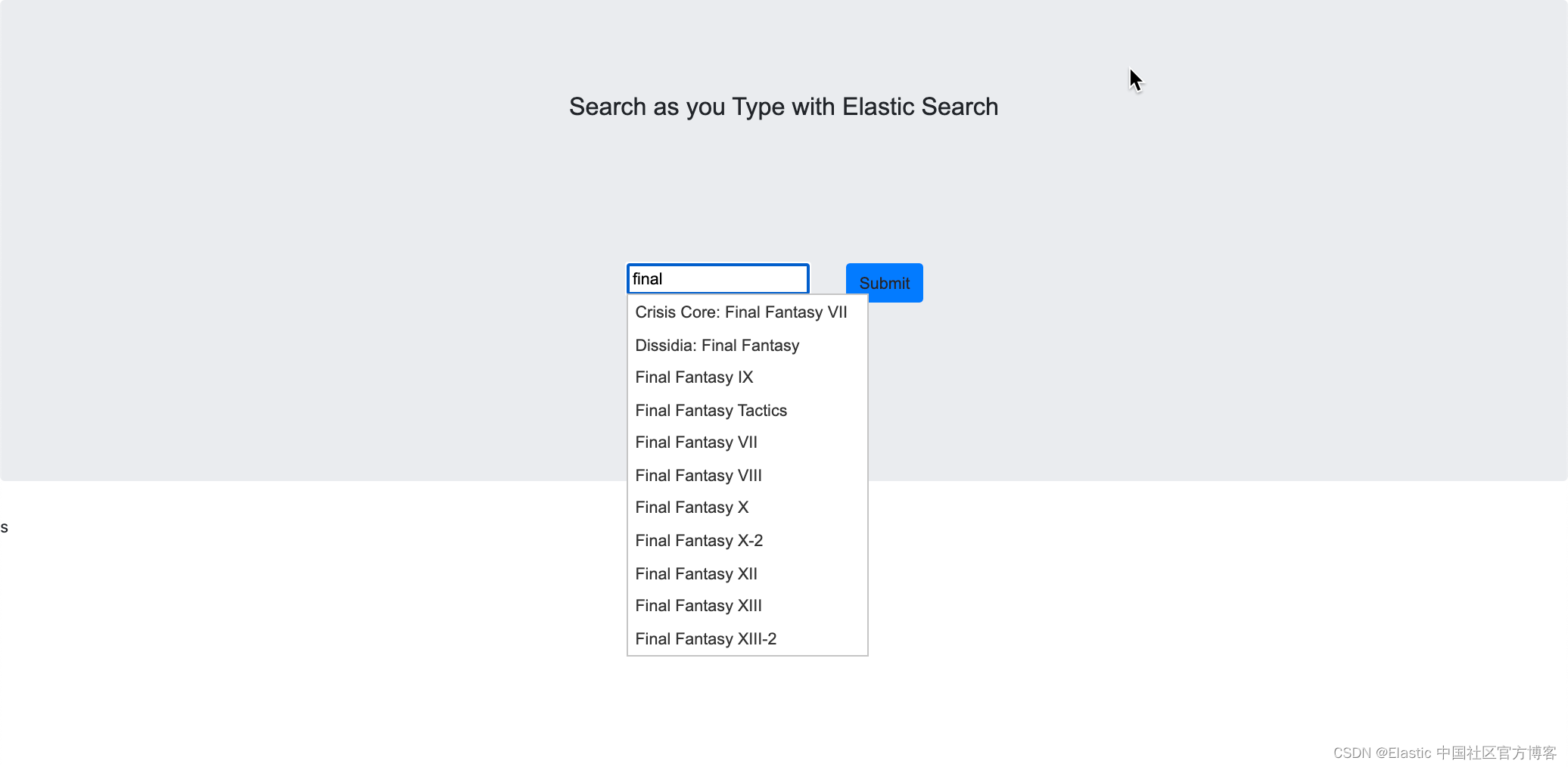
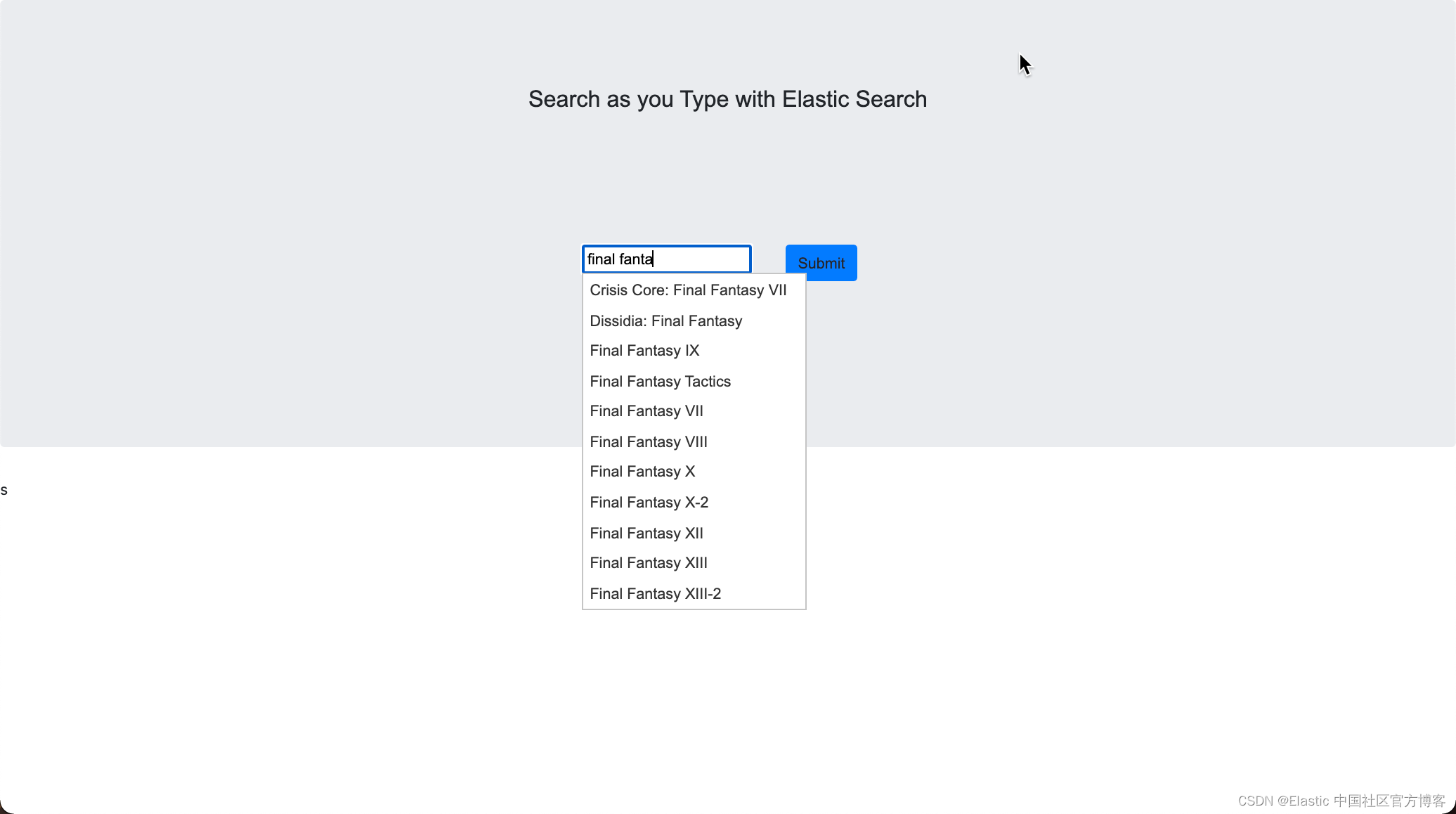
?当我们在输入框中打入 final 时,我们可以看到候选的名单出现了。它可以让我们很方便地进行输入。我们甚至可以选择其中的一个进行输入:
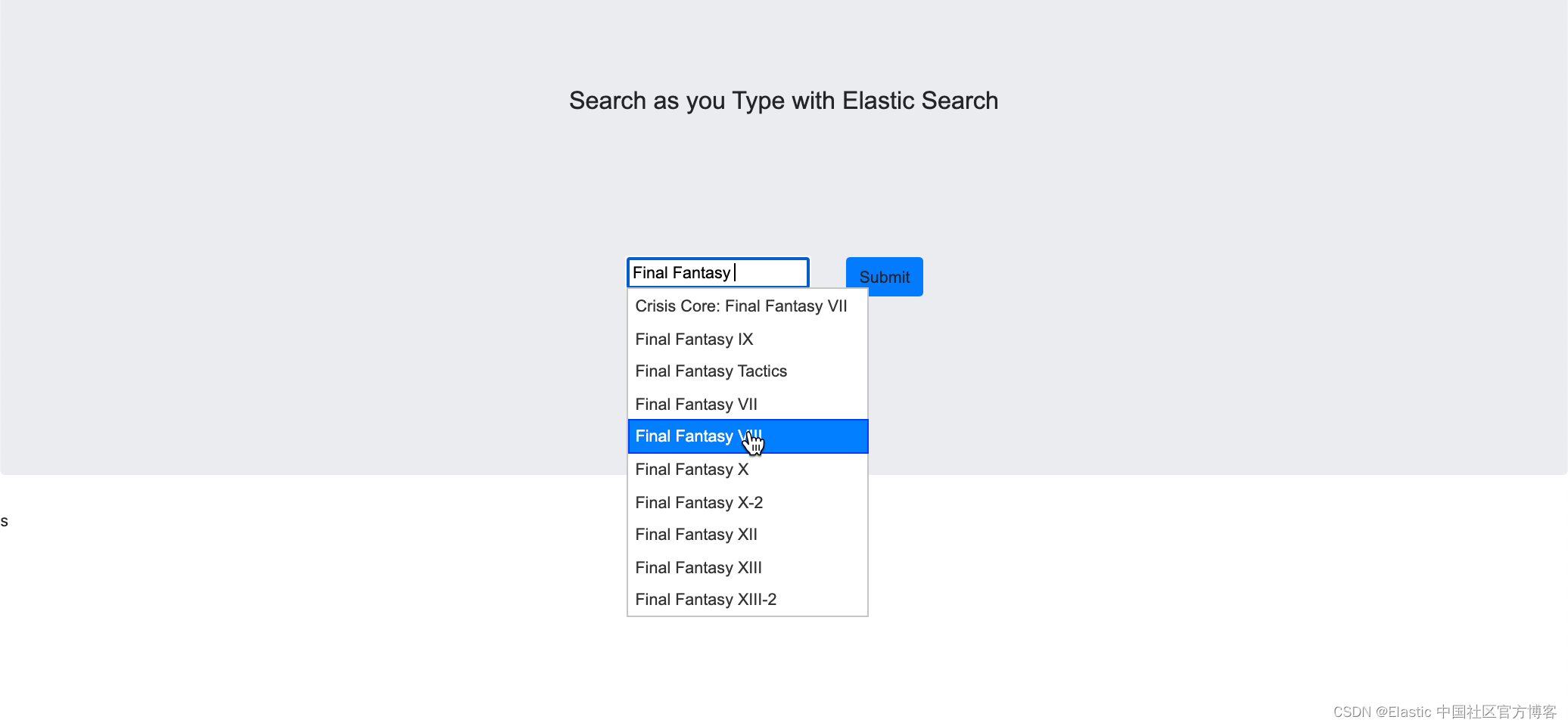
在客户端的设计中,它使用了 ajax 技术。当我们的输入发生改变时自动补全窗口的里的名单也会自动发生变化。
更进一步改进?
在某种程度上,上面的设计还是不错的。它满足了许多情况下的需求。接下来,我们来使用 search-as-you-type 字段类型来完成我们的设计。我们可以参考我之前的文章 “?Elasticsearch:Search-as-you-type 字段类型”。我们首先来删除之前导入的 games 索引以及被创建的索引模式?games*。然后,我们在摄入数据时:
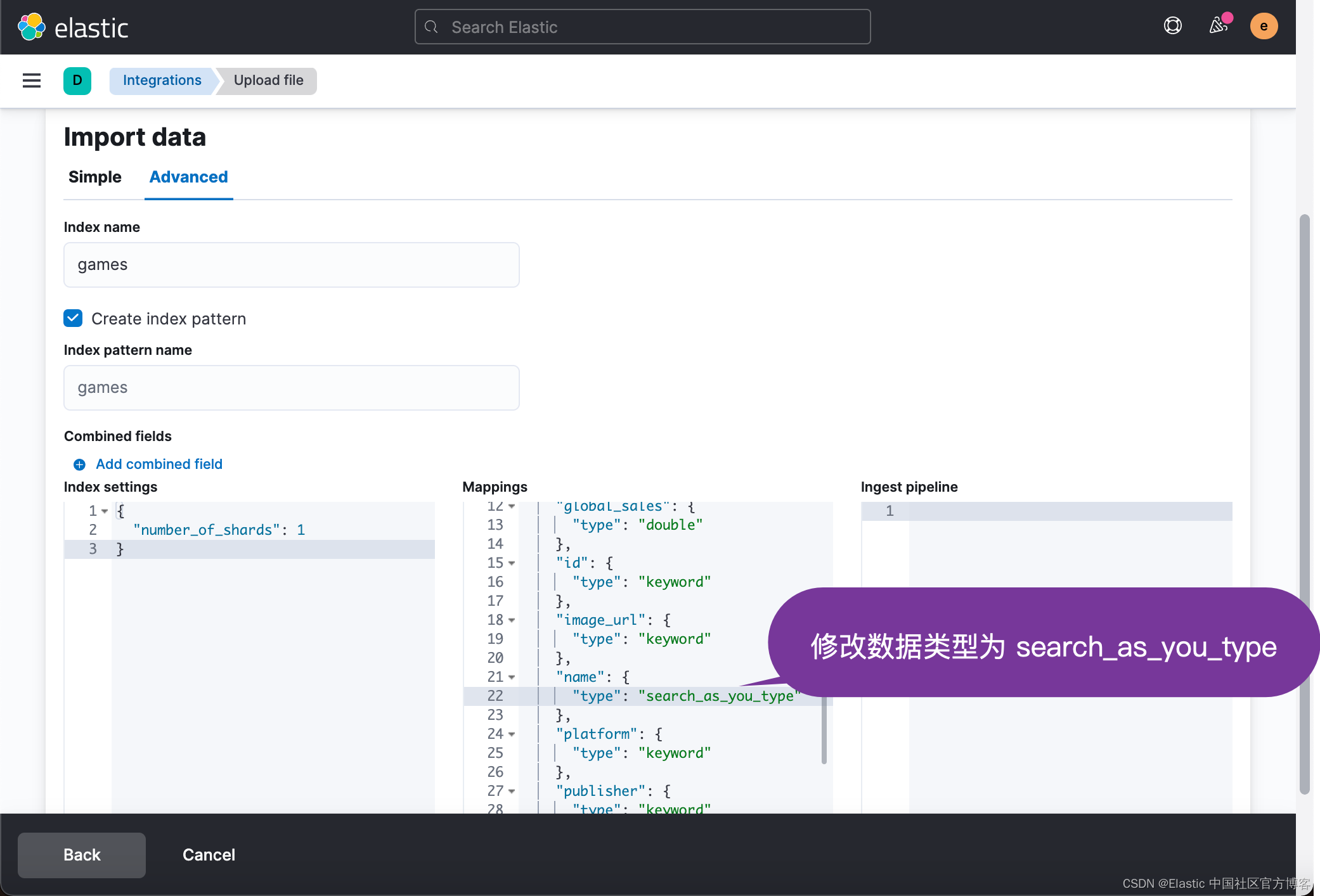
点击当前页面的 Import 按钮,并完成 games 索引的创建:
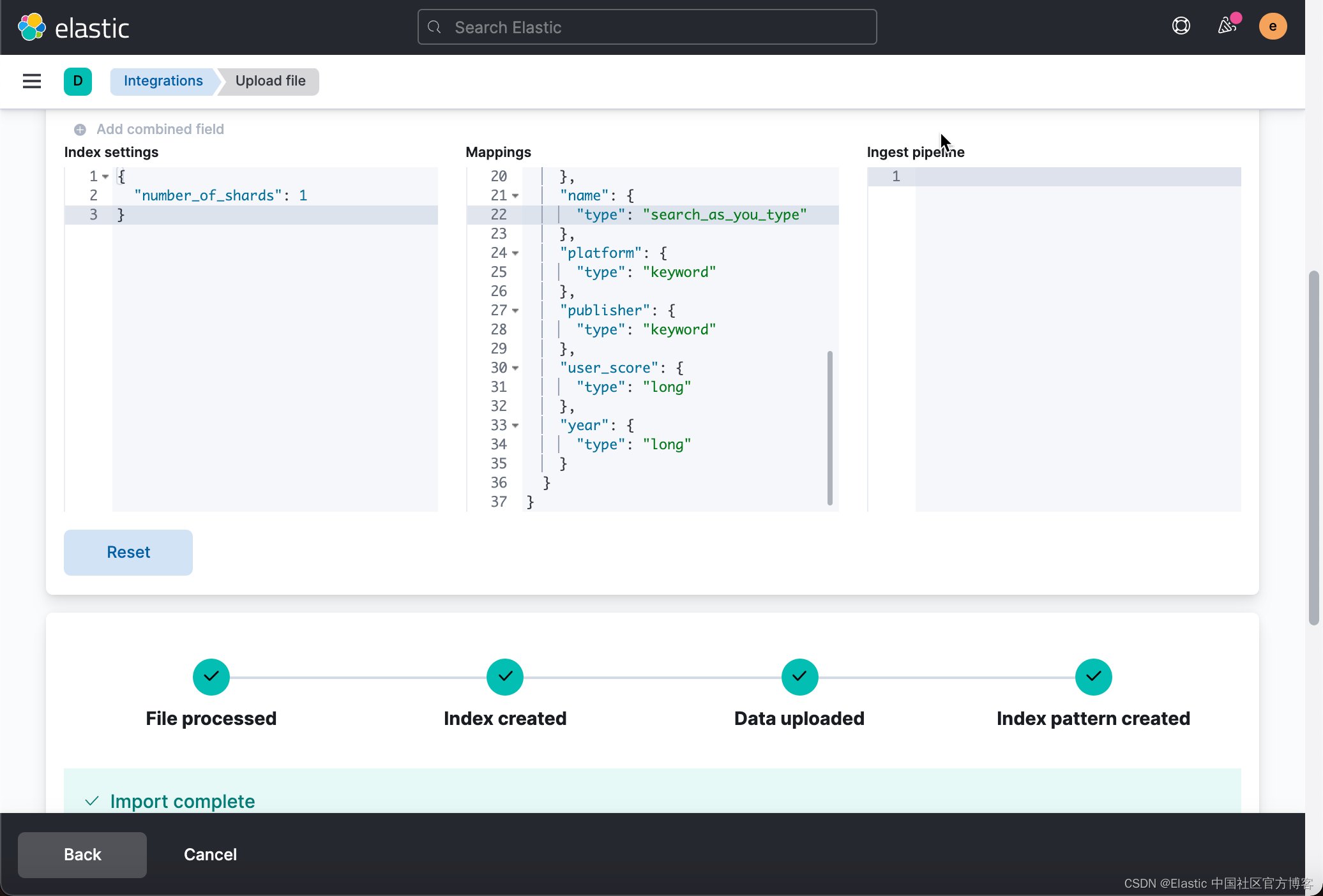
这样我们的 name 字段为?search_as_you_type 类型。由于一些原因,search_as_you_type 类型的数据目前还不能定义 multi-field,我们不能为这个字段添加 keyword 字段。在?https://github.com/elastic/elasticsearch/issues/56326?issue 里,有一个解决方案就是把 search_as_you_type 作为一个 multi-field,而把 keyword 作为一个主要的字段。在本文章中就不做展开了。留给开发者自己研究。
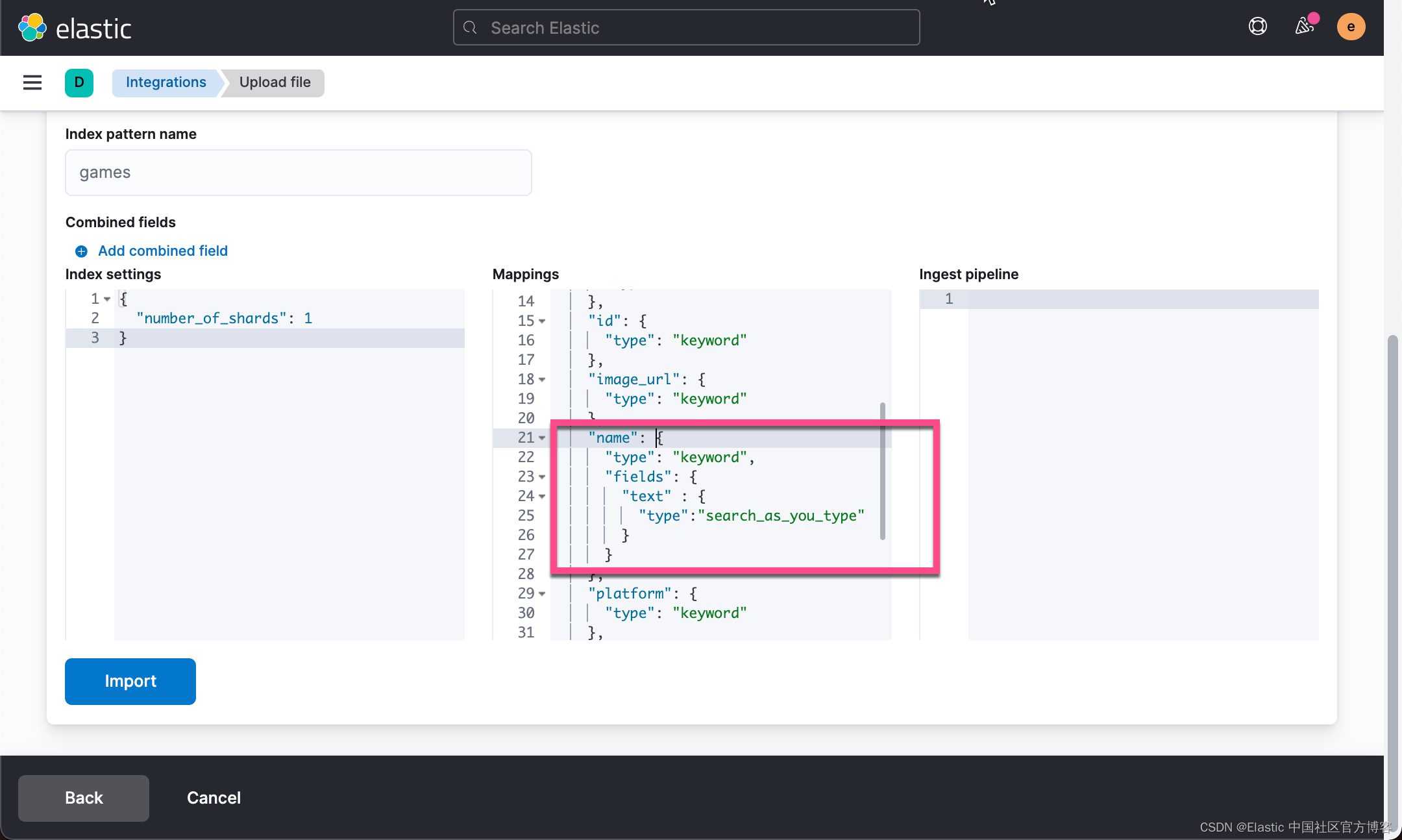
请注意在下面的练习中,我使用的不是这个含有 multi-field 的定义。
我们需要修改我们的 Backend 才能使得它起作用。我们修改 api.py 如下:
Backend/api.py
try:
from flask import app,Flask
from flask_restful import Resource, Api, reqparse
import elasticsearch
from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch
import datetime
import concurrent.futures
import requests
import json
except Exception as e:
print("Modules Missing {}".format(e))
app = Flask(__name__)
api = Api(app)
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
INDEX_NAME = 'games'
es = Elasticsearch([{'host': 'localhost', 'port': 9200, 'http_auth':('elastic', 'password')}])
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
class Controller(Resource):
def __init__(self):
self.query = parser.parse_args().get("query", None)
print(self.query)
self.baseQuery ={
# "_source": [],
"size": 10,
"min_score": 0.5,
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match_phrase_prefix": {
"name": {
"query": "{}".format(self.query)
}
}
}
],
"filter": [],
"should": [],
"must_not": []
}
}
}
def get(self):
res = es.search(index=INDEX_NAME, size=25, body=self.baseQuery)
return res
parser = reqparse.RequestParser()
parser.add_argument("query", type=str, required=True, help="query parameter is Required ")
api.add_resource(Controller, '/autocomplete')
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True, port=4000)在上面,我们使用了?match_phrase_prefix 来完成我们的搜索。它相当于如下的搜索:
GET games/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase_prefix": {
"name": "final fan"
}
}
}由于我们没有使用 aggs 来返回结果,取而代之的是搜索的文档,那么我们需要修改相应的 home.html 文档:
Frontend/templates/home.html
我们把 typeHandler 修改为:
const typeHandler = function(e) {
$result.innerHTML = e.target.value;
console.log(e.target.value);
$.ajax({
url: "/pipe",
type : 'POST',
cache: false,
data:{'data': e.target.value},
success: function(html)
{
console.log(html)
var data = html.hits.hits
var _ = []
$.each(data, (index, value)=>{
_.push(value._source.name)
});
console.log(_)
$( "#source" ).autocomplete({
source: _
});
}
});
}这个是由于我们的响应格式的变化:
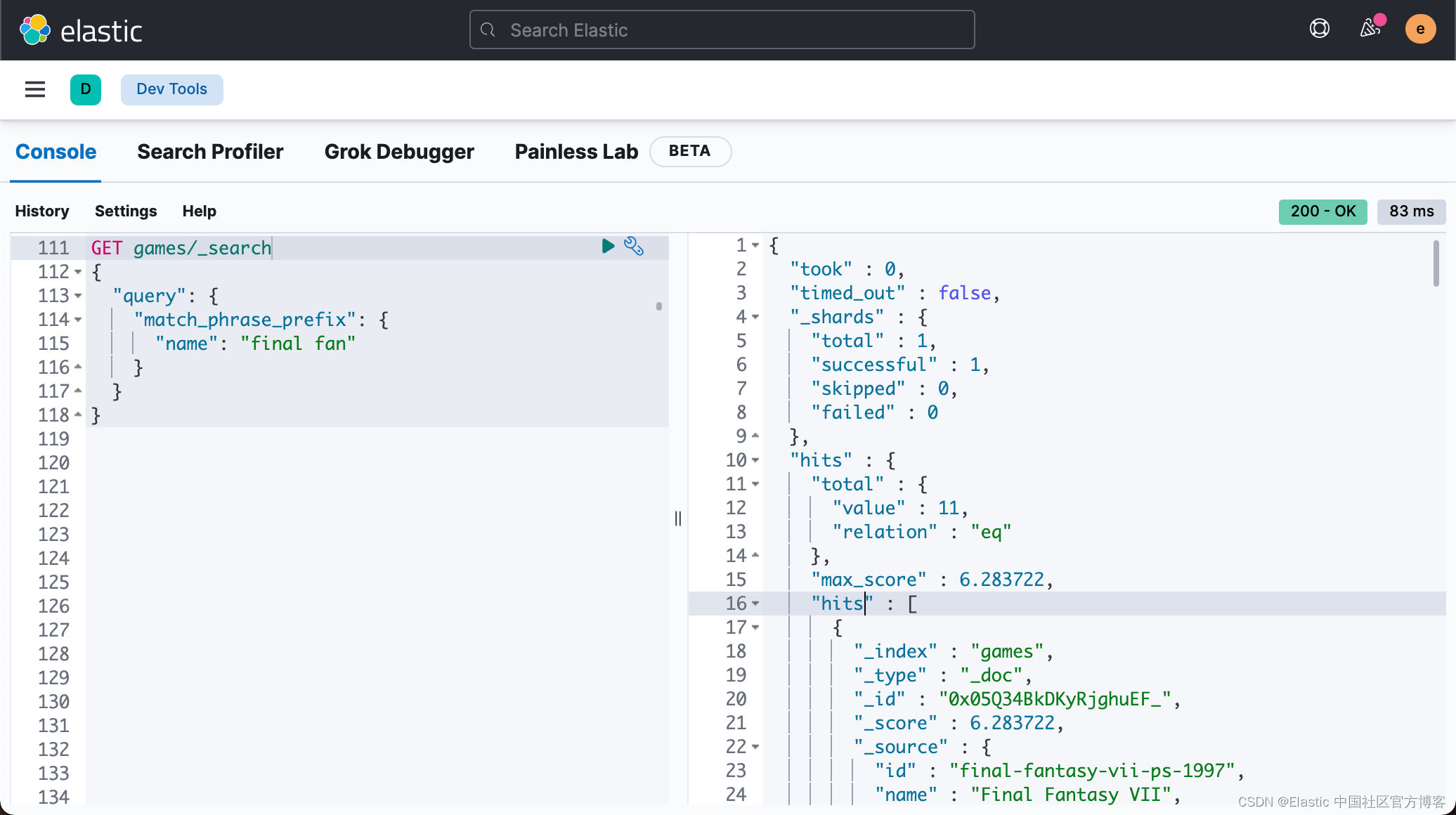
我们重新运行 Backend 和 Frontend,那么我们可以看到和之前一模一样的结果:
?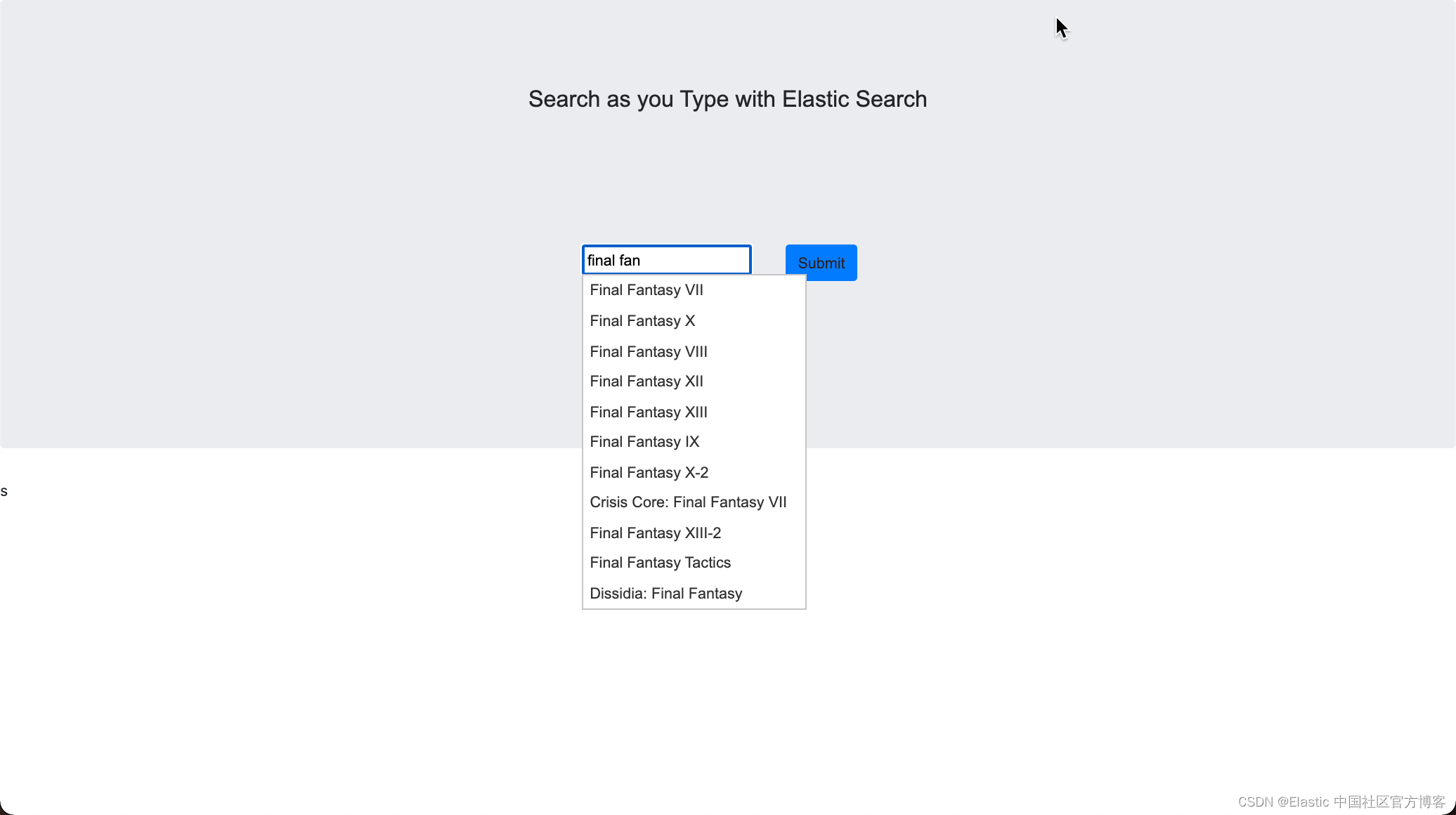
你是不是觉得把 name 字段的类型修改后也没有什么特别的,对吧? 但是我们可以尝试一下如下的搜索:
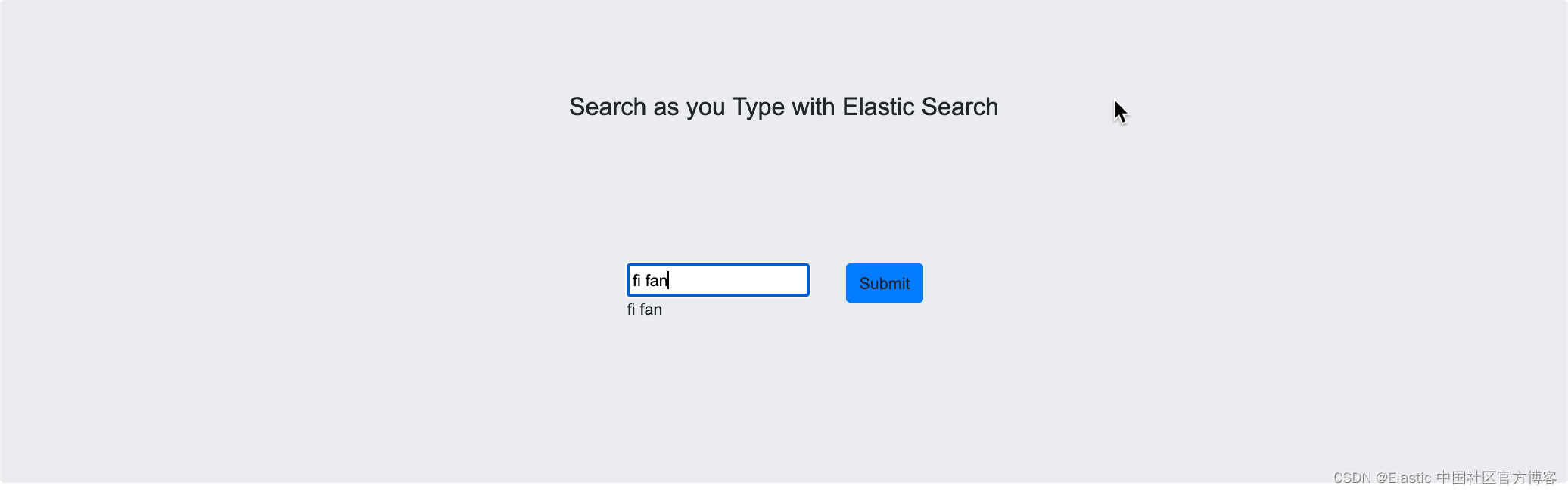
?在上面,我们输入 fi 及 fan,我们没有看到任何的结果。我们没有充分利用?search_as_you_type 给我们带来的好处。
我们重新修改 Backend 中的 api.py 为如下的代码:
Backend/api.py
try:
from flask import app,Flask
from flask_restful import Resource, Api, reqparse
import elasticsearch
from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch
import datetime
import concurrent.futures
import requests
import json
except Exception as e:
print("Modules Missing {}".format(e))
app = Flask(__name__)
api = Api(app)
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
INDEX_NAME = 'games'
es = Elasticsearch([{'host': 'localhost', 'port': 9200, 'http_auth':('elastic', 'password')}])
#------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
class Controller(Resource):
def __init__(self):
self.query = parser.parse_args().get("query", None)
print(self.query)
self.baseQuery ={
"_source": [],
"size": 0,
"min_score": 0.5,
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"multi_match": {
"query": "{}".format(self.query),
"type": "bool_prefix",
"operator": "or",
"fields": [
"name",
"name._2gram",
"name._3gram"
]
}
}
],
"filter": [],
"should": [],
"must_not": []
}
}
}
def get(self):
res = es.search(index=INDEX_NAME, size=25, body=self.baseQuery)
return res
parser = reqparse.RequestParser()
parser.add_argument("query", type=str, required=True, help="query parameter is Required ")
api.add_resource(Controller, '/autocomplete')
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True, port=4000)
在上面,我使用了 multi-match。上面的搜索相当于这样的命令:
GET games/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "fi fan",
"type": "bool_prefix",
"operator": "or",
"fields": [
"name",
"name._2gram",
"name._3gram"
]
}
}
}上面的命令,可以搜索出来前缀为 fi 及 fan 的文档。
我们也同时把? typeHandler 修改为:
const typeHandler = function(e) {
$result.innerHTML = e.target.value;
console.log(e.target.value);
$.ajax({
url: "/pipe",
type : 'POST',
cache: false,
data:{'data': e.target.value},
success: function(html)
{
console.log(html)
var data = html.hits.hits
var _ = []
console.log("nice")
$.each(data, (index, value)=>{
_.push(value._source.name)
});
console.log("list:")
console.log(_)
$( "#source" ).autocomplete({
source: _
});
$( "#result" ).text(_)
}
});
}在上面,我们使用 result 来显示结果。我们重新运行 Backend 及 Frontend:
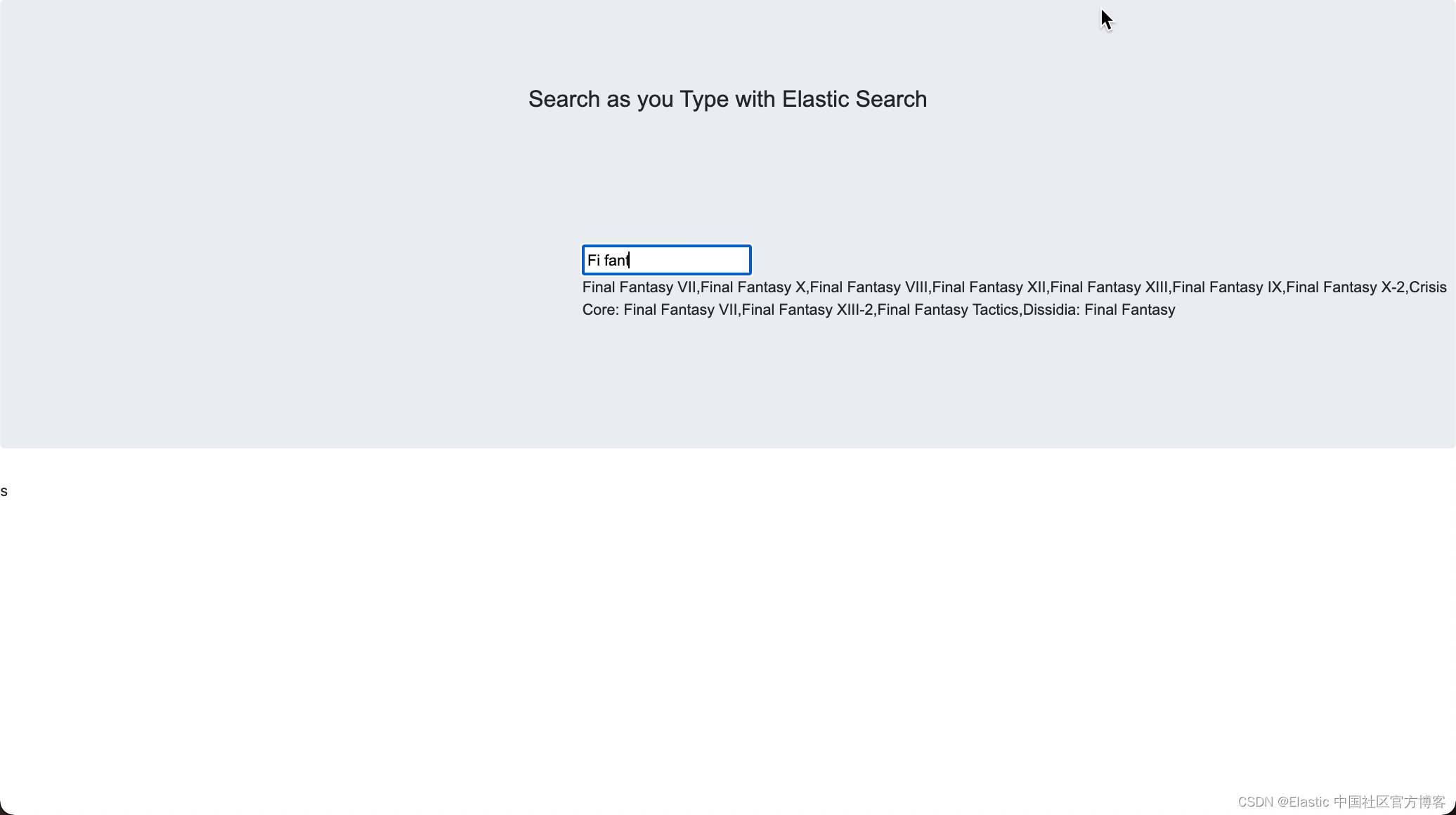
尽管画面不是很美,但是,当我们输入诸如 "fi fan" 这样的词,我们可以看到我们想要的搜索的结果。