消息发送流程
DefaultMQProducer-发送入口
消息发送的入口在DefaultMQProducer类中的send方法。这个方法有很多重载方法,对应的方法参数也各不一样。
SendResult send(Message msg);
SendResult send(Message msg,long timeout);
SendResult send(Message msg,SendCallback sendCallback,long timeout);
SendResult send(Message msg, MessageQueue mq, SendCallback sendCallback, long timeout);
SendResult send(Message msg,MessageQueueSelector selector, Object arg,SendCallback sendCallback,long timeout);
......省略更多
重点参数说明一下:
| 参数 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| msg | Message | 消息对象 |
| mq | MessageQueue | 目标消息队列,通过它获得要传递消息到指定的消息队列 |
| sendCallback | SendCallback | 异步模式在发送完成(成功或不成功)时的回调 |
| selector | MessageQueueSelector | 消息队列选择器 |
| arg | Object | 该参数与消息队列选择器配合使用 |
| timeout | long | 发送超时时间 |
DefaultMQProduceImpl-消息发送实现类
send 方法对应的实现直接委托给DefaultMQProduceImpl来实现具体细节。具体有两种默认的发送消息的实现,一个是同步发送,一个是异步发送。两者区别很简单,异步相对于同步方法来说多了一个自定义回调SendCallback实现。看一下两者的对比如下:
/**
* DEFAULT SYNC
*/
public SendResult send(
Message msg) throws MQClientException, RemotingException, MQBrokerException, InterruptedException {
return send(msg, this.defaultMQProducer.getSendMsgTimeout());
}
/**
* DEFAULT ASYNC
*/
public void send(Message msg,
SendCallback sendCallback) throws MQClientException, RemotingException, InterruptedException {
send(msg, sendCallback, this.defaultMQProducer.getSendMsgTimeout());
}
上面两个方法调用的底层都是一个,即sendDefaultImpl。重点参数说明一下。
| 参数 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| msg | Message | 消息对象 |
| communicationModemq | CommunicationMode | 通信方式,同步或者异步 |
| sendCallback | SendCallback | 异步模式在发送完成(成功或不成功)时的回调 |
| timeout | long | 发送超时时间 |
sendDefaultImpl-发送消息底层方法
private SendResult sendDefaultImpl(
Message msg,
final CommunicationMode communicationMode,
final SendCallback sendCallback,
final long timeout) {
//确认Producer客户端状态是否ok-(ServieceState.RUNNING)
this.makeSureStateOK();
/**
* 消息校验,包含消息的topic校验和消息体的校验。
* topic校验包含以下几点,topic的名字,长度以及是否为不准用的topic(SCHEDULE_TOPIC_XXXX)
* 消息体校验 消息体是不是空和消息体的长度
*/
Validators.checkMessage(msg, this.defaultMQProducer);
//本次调用的id
final long invokeID = random.nextLong();
//本地调用开始时间
long beginTimestampFirst = System.currentTimeMillis();
long beginTimestampPrev = beginTimestampFirst;
long endTimestamp = beginTimestampFirst;
/**
* 尝试去查找Topic的订阅信息
* 1.从topicPublishInfoTable缓存中查找
* 2.如果缓存为空,则从nameserver拉取配置
*/
TopicPublishInfo topicPublishInfo = this.tryToFindTopicPublishInfo(msg.getTopic());
if (topicPublishInfo != null && topicPublishInfo.ok()) {
boolean callTimeout = false;
MessageQueue mq = null;
Exception exception = null;
SendResult sendResult = null;
//若通信模式为同步模式,则失败重试次数=3次(默认2次+1)。若为异步模式则为1次
int timesTotal = communicationMode == CommunicationMode.SYNC
? 1 + this.defaultMQProducer.getRetryTimesWhenSendFailed() : 1;
int times = 0;
//记录每一次重试时候发送消息目标Broker名字的数组
String[] brokersSent = new String[timesTotal];
//进行重试次数循环发送消息逻辑
for (; times < timesTotal; times++) {
//获取broker名字,第一次为null,第二次为上次选择的broker名字
String lastBrokerName = null == mq ? null : mq.getBrokerName();
//根据Topic订阅信息+上一次broker名字选择一个消息队列
// 有失败重试策略,默认使用 RoundRobin 算法,可以通过 DefaultMQProducer#setSendLatencyFaultEnable 设置启用 LatencyFault 策略
MessageQueue mqSelected = this.selectOneMessageQueue(topicPublishInfo, lastBrokerName);
//如果队列不为空
if (mqSelected != null) {
mq = mqSelected;
//将本次选中的消息队列的broker名字添加到数组中
brokersSent[times] = mq.getBrokerName();
//重新赋值调用开始时间
beginTimestampPrev = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (times > 0) {
//Reset topic with namespace during resend.
msg.setTopic(this.defaultMQProducer.withNamespace(msg.getTopic()));
}
//发送消息的花费时间
long costTime = beginTimestampPrev - beginTimestampFirst;
//如果设置的超时时间小于花费时间,则进行超时标记,并break中断,超时时间默认是3000毫秒
if (timeout < costTime) {
callTimeout = true;
break;
}
//发送消息到选中的队列中
sendResult = this.sendKernelImpl(msg, mq, communicationMode, sendCallback, topicPublishInfo,
timeout - costTime);
endTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 当设置启用 LatencyFault 策略时,更新 FaultItem
//根据发送所耗费的时间决定是不是要将该broker加入到故障列表中
this.updateFaultItem(mq.getBrokerName(), endTimestamp - beginTimestampPrev, false);
//如果是SYNC同步模式下发送失败可进行重试,ASYNC/ONEWAY模式下直接返回null
switch (communicationMode) {
case ASYNC:
return null;
case ONEWAY:
return null;
case SYNC:
if (sendResult.getSendStatus() != SendStatus.SEND_OK) {
if (this.defaultMQProducer.isRetryAnotherBrokerWhenNotStoreOK()) {
continue;
}
}
return sendResult;
default:
break;
}
} else {
break;
}
}
if (sendResult != null) {
return sendResult;
}
String info = String.format("Send [%d] times, still failed, cost [%d]ms, Topic: %s, BrokersSent: %s",
times,
System.currentTimeMillis() - beginTimestampFirst,
msg.getTopic(),
Arrays.toString(brokersSent));
info += FAQUrl.suggestTodo(FAQUrl.SEND_MSG_FAILED);
MQClientException mqClientException = new MQClientException(info, exception);
if (callTimeout) {
throw new RemotingTooMuchRequestException("sendDefaultImpl call timeout");
}
}
validateNameServerSetting();
}
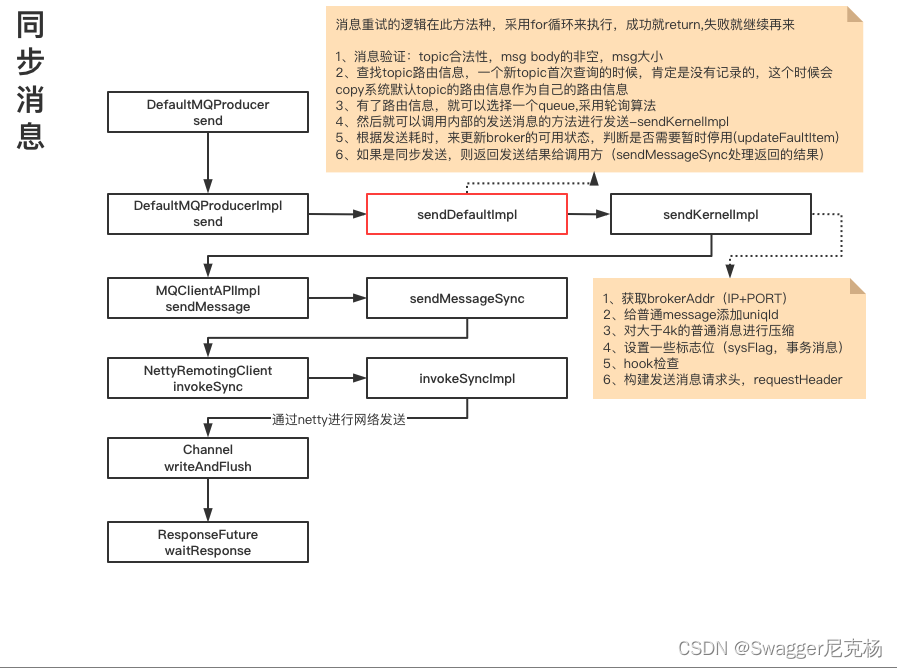
这里对整个方法的逻辑步骤进行一个梳理:
- 检查Producer客户端状态是否是运行状态,校验消息的合法性,生成全局调用id(用于打日志)和相关的时间戳。
- 根据消息的Topic获取对应的消息订阅信息,获取逻辑在
tryToFindTopicPublishInfo,这里会从缓存map里获取,如果没有则回去namerServer拉取相应的订阅信息。稍后也会对该方法进行分析。 - 根据不同的消息发送模式,计算消息失败重试的次数(同步模式是2+1,异步模式是1次,客户端默认为
retryTimesWhenSendFailed=2) - 根据选择的brokerName,选择一个消息队列
MessageQueue。这里选择队列的方法是selectOneMessageQueue,稍后进行分析。 - 选择好队列之后,记录对应的brokerName,对重试次数范围内以及发送超时时间之内进行进行消息发送,发送的逻辑在
sendKernelImpl。 - 发送之后进行容错策略的更新,更新逻辑在
updateFaultItem,之后进行分析。 - 根据不同的消息通信模式进行处理,只有同步模式有处理逻辑,在同步逻辑发送失败的时候如果开启了
retryAnotherBrokerWhenNotStoreOK(失败重试发送到另外的broker),则进行重试。这里的重试还是跟上面的重试有区别的,这里是调用内部发送实现并且有返回SendResult的情况,但是发送结果不是成功。
下面针对上述重要步骤的重要逻辑分别进行分析
1.尝试去查找Topic订阅信息tryToFindTopicPublishInfo
//Topic订阅信息缓存Map
private final ConcurrentMap<String/* topic */, TopicPublishInfo> topicPublishInfoTable =
new ConcurrentHashMap<String, TopicPublishInfo>();
private TopicPublishInfo tryToFindTopicPublishInfo(final String topic) {
//从Topic缓存Map中根据topic获取相应的订阅信息
TopicPublishInfo topicPublishInfo = this.topicPublishInfoTable.get(topic);
//如果缓存为空或者订阅信息messageQueueList为空
if (null == topicPublishInfo || !topicPublishInfo.ok()) {
//创建一个TopicPublishInfo放入缓存中
this.topicPublishInfoTable.putIfAbsent(topic, new TopicPublishInfo());
//根据topic从nameServer拉取最新的topic路由信息,并更新缓存
this.mQClientFactory.updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(topic);
//从缓存中获取订阅信息
topicPublishInfo = this.topicPublishInfoTable.get(topic);
}
//如果topic订阅信息包含路由信息并且messageQueueList不为空,则直接返回
if (topicPublishInfo.isHaveTopicRouterInfo() || topicPublishInfo.ok()) {
return topicPublishInfo;
} else {
//重新从nameServer拉取最新的topic路由信息,并直接返回
this.mQClientFactory.updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer(topic, true, this.defaultMQProducer);
topicPublishInfo = this.topicPublishInfoTable.get(topic);
return topicPublishInfo;
}
}
方法中关于updateTopicRouteInfoFromNameServer方法解析可以参考我上一篇的文章()。
2.选择消息队列selectOneMessageQueue
该方法设计延迟故障的逻辑,下一篇进行详细分析,逻辑简单过一下。
public MessageQueue selectOneMessageQueue(final TopicPublishInfo tpInfo, final String lastBrokerName) {
//调用mq故障策略的selectOneMessageQueue
return this.mqFaultStrategy.selectOneMessageQueue(tpInfo, lastBrokerName);
}
public MessageQueue selectOneMessageQueue(final TopicPublishInfo tpInfo, final String lastBrokerName) {
//省略延迟故障的逻辑
return tpInfo.selectOneMessageQueue(lastBrokerName);
}
public MessageQueue selectOneMessageQueue(final String lastBrokerName) {
//如果lastBrokerName为空,说明第一次正常发送
if (lastBrokerName == null) {
return selectOneMessageQueue();
} else {
//如果lastBrokerName不为空,说明进行了重试
for (int i = 0; i < this.messageQueueList.size(); i++) {
//获取一个队列(brokerName!=lastBrokerName)的消息队列
int index = this.sendWhichQueue.incrementAndGet();
int pos = Math.abs(index) % this.messageQueueList.size();
if (pos < 0)
pos = 0;
MessageQueue mq = this.messageQueueList.get(pos);
if (!mq.getBrokerName().equals(lastBrokerName)) {
return mq;
}
}
//如果还没有获取到消息对接,则再进行一次选择
return selectOneMessageQueue();
}
}
public MessageQueue selectOneMessageQueue() {
//获取一个随机数,并进行取模
int index = this.sendWhichQueue.incrementAndGet();
int pos = Math.abs(index) % this.messageQueueList.size();
if (pos < 0)
pos = 0;
//获取MessageQueue
return this.messageQueueList.get(pos);
}
3.发送消息准备工作sendKernelImpl
sendKernelImpl方法内主要是构建发送网络请求的请求头和一些钩子方法。
private SendResult sendKernelImpl(final Message msg,
final MessageQueue mq,
final CommunicationMode communicationMode,
final SendCallback sendCallback,
final TopicPublishInfo topicPublishInfo,
final long timeout) {
long beginStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
//根据brokerName从broker集群信息brokerAddrTable缓存中获取brokerId=0的地址
String brokerAddr = this.mQClientFactory.findBrokerAddressInPublish(mq.getBrokerName());
//如果缓存不存在
if (null == brokerAddr) {
//尝试去从nameServer拉取配置,更新brokerAddrTable缓存Map,并返回地址
tryToFindTopicPublishInfo(mq.getTopic());
brokerAddr = this.mQClientFactory.findBrokerAddressInPublish(mq.getBrokerName());
}
SendMessageContext context = null;
if (brokerAddr != null) {
//是否使用vip端口
brokerAddr = MixAll.brokerVIPChannel(this.defaultMQProducer.isSendMessageWithVIPChannel(), brokerAddr);
//消息内容
byte[] prevBody = msg.getBody();
try {
//for MessageBatch,ID has been set in the generating process
//MessageBatch批量消息生成时已经设置uniqId,如果是单个消息,则再生成一次
if (!(msg instanceof MessageBatch)) {
MessageClientIDSetter.setUniqID(msg);
}
boolean topicWithNamespace = false;
//获取clientConfig的nameSpace信息
if (null != this.mQClientFactory.getClientConfig().getNamespace()) {
msg.setInstanceId(this.mQClientFactory.getClientConfig().getNamespace());
topicWithNamespace = true;
}
//消息标识
int sysFlag = 0;
boolean msgBodyCompressed = false;
//尝试对消息进行压缩,批量消息不支持压缩
if (this.tryToCompressMessage(msg)) {
sysFlag |= MessageSysFlag.COMPRESSED_FLAG;
msgBodyCompressed = true;
}
//获取消息的失误属性
final String tranMsg = msg.getProperty(MessageConst.PROPERTY_TRANSACTION_PREPARED);
//如果是事务消息,则添加标记
if (tranMsg != null && Boolean.parseBoolean(tranMsg)) {
sysFlag |= MessageSysFlag.TRANSACTION_PREPARED_TYPE;
}
//钩子方法调用
if (hasCheckForbiddenHook()) {
//......省略准备逻辑
this.executeCheckForbiddenHook(checkForbiddenContext);
}
if (this.hasSendMessageHook()) {
//......省略准备逻辑
this.executeSendMessageHookBefore(context);
}
//构建发送消息请求投
SendMessageRequestHeader requestHeader = new SendMessageRequestHeader();
requestHeader.setProducerGroup(this.defaultMQProducer.getProducerGroup());
requestHeader.setTopic(msg.getTopic());
requestHeader.setDefaultTopic(this.defaultMQProducer.getCreateTopicKey());
requestHeader.setDefaultTopicQueueNums(this.defaultMQProducer.getDefaultTopicQueueNums());
requestHeader.setQueueId(mq.getQueueId());
requestHeader.setSysFlag(sysFlag);
requestHeader.setBornTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
requestHeader.setFlag(msg.getFlag());
requestHeader.setProperties(MessageDecoder.messageProperties2String(msg.getProperties()));
requestHeader.setReconsumeTimes(0);
requestHeader.setUnitMode(this.isUnitMode());
requestHeader.setBatch(msg instanceof MessageBatch);
//如果消息是重试消息
if (requestHeader.getTopic().startsWith(MixAll.RETRY_GROUP_TOPIC_PREFIX)) {
//获取消息重新消费次数
String reconsumeTimes = MessageAccessor.getReconsumeTime(msg);
if (reconsumeTimes != null) {
//将重新消费次数set到请求头中
requestHeader.setReconsumeTimes(Integer.valueOf(reconsumeTimes));
MessageAccessor.clearProperty(msg, MessageConst.PROPERTY_RECONSUME_TIME);
}
//获取消息的最大重试次数
String maxReconsumeTimes = MessageAccessor.getMaxReconsumeTimes(msg);
if (maxReconsumeTimes != null) {
// 将重试次数set到请求头中,并清空属性
requestHeader.setMaxReconsumeTimes(Integer.valueOf(maxReconsumeTimes));
MessageAccessor.clearProperty(msg, MessageConst.PROPERTY_MAX_RECONSUME_TIMES);
}
}
SendResult sendResult = null;
//消息通信模式,同步模式/异步模式/oneway
switch (communicationMode) {
//异步模式
case ASYNC:
Message tmpMessage = msg;
boolean messageCloned = false;
if (msgBodyCompressed) {
tmpMessage = MessageAccessor.cloneMessage(msg);
messageCloned = true;
msg.setBody(prevBody);
}
if (topicWithNamespace) {
if (!messageCloned) {
tmpMessage = MessageAccessor.cloneMessage(msg);
messageCloned = true;
}
msg.setTopic(NamespaceUtil.withoutNamespace(msg.getTopic(), this.defaultMQProducer.getNamespace()));
}
long costTimeAsync = System.currentTimeMillis() - beginStartTime;
if (timeout < costTimeAsync) {
throw new RemotingTooMuchRequestException("sendKernelImpl call timeout");
}
//异步的方式发送消息
sendResult = this.mQClientFactory.getMQClientAPIImpl().sendMessage(
brokerAddr,
mq.getBrokerName(),
tmpMessage,
requestHeader,
timeout - costTimeAsync,
communicationMode,
sendCallback,
topicPublishInfo,
this.mQClientFactory,
this.defaultMQProducer.getRetryTimesWhenSendAsyncFailed(),
context,
this);
break;
case ONEWAY:
case SYNC:
long costTimeSync = System.currentTimeMillis() - beginStartTime;
if (timeout < costTimeSync) {
throw new RemotingTooMuchRequestException("sendKernelImpl call timeout");
}
//同步的方式发送消息
sendResult = this.mQClientFactory.getMQClientAPIImpl().sendMessage(
brokerAddr,
mq.getBrokerName(),
msg,
requestHeader,
timeout - costTimeSync,
communicationMode,
context,
this);
break;
default:
assert false;
break;
}
//如果有发送消息的钩子,则进行调用
if (this.hasSendMessageHook()) {
context.setSendResult(sendResult);
this.executeSendMessageHookAfter(context);
}
return sendResult;
} finally {
msg.setBody(prevBody);
msg.setTopic(NamespaceUtil.withoutNamespace(msg.getTopic(), this.defaultMQProducer.getNamespace()));
}
}
throw new MQClientException("The broker[" + mq.getBrokerName() + "] not exist", null);
}
4.发送消息MQClientAPIImpl#sendMessage
发送消息的逻辑最后是通过MQClientAPIImpl来实现的,这个类之前在将MQClientInstance启动时创建。这个类是MQ内部一些操作的api的实现,包括发送,消费消息和admin控制台的一些操作指令的实现,以及一些网络请求的处理。直接看最终实现逻辑。
public SendResult sendMessage(
final String addr,
final String brokerName,
final Message msg,
final SendMessageRequestHeader requestHeader,
final long timeoutMillis,
final CommunicationMode communicationMode,
final SendCallback sendCallback,
final TopicPublishInfo topicPublishInfo,
final MQClientInstance instance,
final int retryTimesWhenSendFailed,
final SendMessageContext context,
final DefaultMQProducerImpl producer
) throws RemotingException, MQBrokerException, InterruptedException {
long beginStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
//根据消息的类型和模式选择不同的请求code,然后封装到RemotingCommand
RemotingCommand request = null;
//获取消息的类型
String msgType = msg.getProperty(MessageConst.PROPERTY_MESSAGE_TYPE);
//是否为reply消息
boolean isReply = msgType != null && msgType.equals(MixAll.REPLY_MESSAGE_FLAG);
if (isReply) {
if (sendSmartMsg) {
SendMessageRequestHeaderV2 requestHeaderV2 = SendMessageRequestHeaderV2.createSendMessageRequestHeaderV2(requestHeader);
request = RemotingCommand.createRequestCommand(RequestCode.SEND_REPLY_MESSAGE_V2, requestHeaderV2);
} else {
request = RemotingCommand.createRequestCommand(RequestCode.SEND_REPLY_MESSAGE, requestHeader);
}
} else {
if (sendSmartMsg || msg instanceof MessageBatch) {
// 该类的 field 全为 a,b,c,d 等,可以加速 FastJson 反序列化
SendMessageRequestHeaderV2 requestHeaderV2 = SendMessageRequestHeaderV2.createSendMessageRequestHeaderV2(requestHeader);
// 根据 request code 创建 RPC 请求对象
// 该设计是通过类型码的形式,来标识不同类型的请求
request = RemotingCommand.createRequestCommand(msg instanceof MessageBatch ? RequestCode.SEND_BATCH_MESSAGE : RequestCode.SEND_MESSAGE_V2, requestHeaderV2);
} else {
request = RemotingCommand.createRequestCommand(RequestCode.SEND_MESSAGE, requestHeader);
}
}
//设置消息体
request.setBody(msg.getBody());
//消息通信模式,同步模式/异步模式/oneway
switch (communicationMode) {
//单向,没有返回
case ONEWAY:
this.remotingClient.invokeOneway(addr, request, timeoutMillis);
return null;
//异步
case ASYNC:
final AtomicInteger times = new AtomicInteger();
//消息准备时间
long costTimeAsync = System.currentTimeMillis() - beginStartTime;
//如果超时了,就报错
if (timeoutMillis < costTimeAsync) {
throw new RemotingTooMuchRequestException("sendMessage call timeout");
}
this.sendMessageAsync(addr, brokerName, msg, timeoutMillis - costTimeAsync, request, sendCallback, topicPublishInfo, instance,
retryTimesWhenSendFailed, times, context, producer);
return null;
//同步
case SYNC:
//消息准备时间
long costTimeSync = System.currentTimeMillis() - beginStartTime;
//如果超时了,就报错
if (timeoutMillis < costTimeSync) {
throw new RemotingTooMuchRequestException("sendMessage call timeout");
}
return this.sendMessageSync(addr, brokerName, msg, timeoutMillis - costTimeSync, request);
default:
assert false;
break;
}
return null;
}
这里只对同步方法的逻辑进行简单的分析:
private SendResult sendMessageSync(
final String addr,
final String brokerName,
final Message msg,
final long timeoutMillis,
final RemotingCommand request
) throws RemotingException, MQBrokerException, InterruptedException {
//同步发送的逻辑,这里就是通过对Netty客户端的调用来发送消息
RemotingCommand response = this.remotingClient.invokeSync(addr, request, timeoutMillis);
assert response != null;
//返回信息的处理,包含事务消息相关事务id,消息的偏移量等的解析
return this.processSendResponse(brokerName, msg, response,addr);
}
invokeSync的逻辑是在NettyRemotingClient类中进行实现和扩展的,该类主要是对Netty的一些扩展实现和内部逻辑封装,作用是对网络请求的一些操作。
@Override
public RemotingCommand invokeSync(String addr, final RemotingCommand request, long timeoutMillis)
throws InterruptedException, RemotingConnectException, RemotingSendRequestException, RemotingTimeoutException {
//消息发送时间戳
long beginStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
//根据broker的地址获取Netty的channel对象
final Channel channel = this.getAndCreateChannel(addr);
//如果channel不为空并且活跃的
if (channel != null && channel.isActive()) {
try {
//事前钩子方法调用
doBeforeRpcHooks(addr, request);
//花费时间
long costTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - beginStartTime;
//如果超时了,则报错
if (timeoutMillis < costTime) {
throw new RemotingTimeoutException("invokeSync call timeout");
}
//调用Netty进行消息发送
RemotingCommand response = this.invokeSyncImpl(channel, request, timeoutMillis - costTime);
//事后钩子方法调用
doAfterRpcHooks(RemotingHelper.parseChannelRemoteAddr(channel), request, response);
return response;
} catch (RemotingSendRequestException e) {
log.warn("invokeSync: send request exception, so close the channel[{}]", addr);
this.closeChannel(addr, channel);
throw e;
} catch (RemotingTimeoutException e) {
if (nettyClientConfig.isClientCloseSocketIfTimeout()) {
this.closeChannel(addr, channel);
log.warn("invokeSync: close socket because of timeout, {}ms, {}", timeoutMillis, addr);
}
log.warn("invokeSync: wait response timeout exception, the channel[{}]", addr);
throw e;
}
} else {
this.closeChannel(addr, channel);
throw new RemotingConnectException(addr);
}
}
整个消息发送逻辑已经大概的讲完,因细节比较多,可自行查看对应源码。