1、序言
????????数据持久化:把数据保存到可掉电式存储设备中以供之后使用。持久化的过程一般情况下通过各种关系数据库来完成。持久化主要应用是将内存中的数据存储到关系数据库中。
????????JDBC是接口,一组规范,JDBC以下连接的是子类(MySQL、Oracle,SQLServer、DB2等数据库),java应用程序通过JDBC(接口)连接数据库,面向接口编程。
????????JDBC底层的实现子类称为驱动。java.sql.Driver接口是所有JDBC驱动程序需要实现的接口。
????????在java程序中导入MySQL驱动:
????????(1)在项目下创建目录
????????(2)把相关的.jar文件复制到这个目录中
????????(3)再把mysql-connector-java-5.1.7-bin.jar、mysql-connector-java-5.1.7-src.zip两个文件导入到build-path中(在 IDEA 中 Build-path:File -- Project Structure -- Modules -- 选中需要添加 build-path 的项目 -- dependencies -- 点击右边的小加号 -- 选择JARs or directories -- 选择要添加的外部jar包)
? ? ? ? 数据库驱动程序下载:https://download.csdn.net/download/weixin_43923463/78395674
2、连接数据库
????????直接通过驱动程序连接本机数据库:
@Test
public void test() throws SQLException {
Driver driver = new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver();
//url:uniform resource locator 统一资源定位符
//主协议:子协议://MySQL服务器主机地址:MySQL服务器端口号/数据库名
String url = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/jdbc";
Properties info = new Properties();
info.setProperty("user","root"); //用户名
info.setProperty("password","hike");//密码
Connection connect = driver.connect(url,info); //直接通过驱动程序连接
System.out.println(connect);
}? ? ? ? 使用驱动程序管理器连接数据库:
@Test
public void test1() throws SQLException {
Driver driver = new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver();
DriverManager.registerDriver(driver);
String url = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/jdbc";
String user = "root";
String password = "hike";
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println(connection);
connection.close();
}? ? ? ? 通过反射使用驱动程序管理器连接数据库,标准做法:
@Test
public void test2() throws SQLException, ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
//Driver driver = new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver();
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); //在类的静态语句块中,会自动完成自我注册
//Driver driver = (Driver) clazz.newInstance();
//DriverManager.registerDriver(driver);
String url = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/jdbc";
String user = "root";
String password = "hike";
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println(connection);
connection.close();
}? ? ? ? 通过配置文件连接数据库
? ? ? ? 编写配置文件jdbc.properties。注意每一行的末尾不能有空格。
driverClassName = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url = jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/jdbc
user = root
password = hike @Test
public void test3() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
InputStream inputStream = getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(inputStream);
inputStream.close();
Class.forName(properties.getProperty("driverClassName"));
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(properties.getProperty("url"), properties);
System.out.println(connection);
}? ? ? ? 将连接、关闭数据库方法封装成工具类
public class JDBCUtil {
//如果连接失败,需要将问题报告给调用者,不能私自把问题压下来,所以需要抛出异常
public static Connection getConnection() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
InputStream inputStream = JDBCUtil.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(inputStream);
inputStream.close();
Class.forName(properties.getProperty("driverClassName"));
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(properties.getProperty("url"), properties);
return connection;
}
public static void close(Connection connection) {
if(connection != null){
try{
connection.close();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
@Test
public void test4(){
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtil.close(connection);
}
}3、JDBC的API Statement PreparedStatement
? ? ? ? 连接数据库后想要对数据库进行操作需要使用连接对象获取执行体对象。
? ? ? ??使用Statement创建表,向表中插入数据
@Test
public void test5(){
Connection connection = null; //连接对象
Statement statement = null; //执行体对象
try {
connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
statement = connection.createStatement(); //通过连接对象获取执行体对象
System.out.println(statement);
String sql = "create table if not exists user(id int auto_increment," +
"username varchar (20)," +
"password varchar (30)," +
"primary key (id)," +
"unique (username))";
int rows = statement.executeUpdate(sql);//update,delete,insert,DDL,DML
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected");
sql = "insert into user(username,password) values ('admin','admin')";
rows = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected");
sql = "insert into user(username,password) values ('root','root')";
rows = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected");
sql = "insert into user(username,password) values ('user','user')";
rows = statement.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtil.close(connection,statement);
}
}? ? ? ? Statemen缺点:statement有SQL注入的风险,并且效率低。?
? ? ? ? 一般使用PreparedStatement预编译,没有SQL注入风险,效率高。
? ? ? ? 创建表customer,包含属性id,name,gender,age,phone,并插入几条数据
@Test
public void test6(){
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "create table if not exists customer(" +
"id int auto_increment," +
"name varchar (20)," +
"gender enum('男','女')," +
"age int," +
"phone varchar (11)," +
"primary key(id)" +
")";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
int rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(rows +" rows affect");
sql = "insert into customer(name,gender,age,phone) values (?,?,?,?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//执行预编译前一定要先解决?
preparedStatement.setString(1,"李四");//把sql中的第一个?替换成参数2
preparedStatement.setString(2,"女");
preparedStatement.setInt(3,26);
preparedStatement.setString(4,"21111111111");
rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); //执行这个sql语句
System.out.println(rows +" rows affect");
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JDBCUtil.close(connection,preparedStatement);
}
}? ? ? ? 练习:创建teacher表,包含属性id,name,phone,gender,age,address,并插入几条数据
@Test
public void test7() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection(); //连接数据库
//准备sql语句
String sql = "create table if not exists teacher(" +
"id int auto_increment," +
"name varchar (20)," +
"phone char (11)," +
"gender enum('男','女')," +
"age int," +
"address varchar (50)," +
"primary key(id)" +
")";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); //预编译
int rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); //执行
System.out.println(rows + " rows afect");
JDBCUtil.close(null,preparedStatement); //关闭资源
sql = "insert into teacher(name,phone,gender,age,address) values (?,?,?,?,?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//插入第一条数据
preparedStatement.setString(1,"小张");
preparedStatement.setString(2,"12345678912");
preparedStatement.setString(3,"男");
preparedStatement.setInt(4,45);
preparedStatement.setString(5,"北京朝阳");
rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(rows + " rows affect");
//插入第二条数据
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1,"小张1");
preparedStatement.setString(2,"12345678912");
preparedStatement.setString(3,"男");
preparedStatement.setInt(4,45);
preparedStatement.setString(5,"北京朝阳");
rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(rows + " rows affect");
//插入第三条数据
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setString(1,"小张2");
preparedStatement.setString(2,"12345678912");
preparedStatement.setString(3,"男");
preparedStatement.setInt(4,45);
preparedStatement.setString(5,"北京朝阳");
rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(rows + " rows affect");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtil.close(connection, preparedStatement);
}
}
? ? ? ? 改进处理预编译后处理?的方式(使用Object数组处理问号)
@Test
public void test8(){
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "insert into customer(name,gender,age,phone) values (?,?,?,?)";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//使用Object数组处理问号
Object[] args = {"王五","女",23,"55555555555"};
for(int i = 0; i < args.length; i++){
preparedStatement.setObject(i + 1,args[i]);
}
int rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println(rows + " rows affect");
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JDBCUtil.close(connection,preparedStatement);
}
}? ? ? ? 除了sql语句和要插入的数据,程序的其他内容并不会变化,所以可以将通用的部分抽取出去,成为一个通用的方法。
public class CommonUtil {
//公共更新操作
//有了异常不要私自扣下,发送给调用者
public static int update(String sql,Object[] args) throws SQLException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
for(int i = 0; i < args.length; i++){
preparedStatement.setObject(i + 1,args[i]);
}
int rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
return rows;
}finally {
JDBCUtil.close(connection,preparedStatement);
}
}
}
@Test
public void test9(){
String sql = "insert into customer(name,gender,age,phone) values (?,?,?,?)";
Object[] args = {"赵六","男",28,"66666666666"};
try {
int rows = CommonUtil.update(sql, args);
System.out.println(rows + " rows affect");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}? ? ? ? 将Object数组变为可变参数Object...,使得程序更加灵活。
//有了异常不要私自扣下,发送给调用者
public static int update(String sql,Object... args) throws SQLException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection(); //从数据库获得连接
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql); //预编译传入的sql语句
for(int i = 0; i < args.length; i++){
preparedStatement.setObject(i + 1,args[i]); //处理?
}
int rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate(); //影响行数
return rows;
}finally {
JDBCUtil.close(connection,preparedStatement); //无论是否有异常,都能够实现资源的关闭
}
}
}
@Test
public void test9(){
String sql = "insert into customer(name,gender,age,phone) values (?,?,?,?)";
try {
int rows = CommonUtil.update(sql, "小七","女",27,"77777777777"); //可变参数直接传入想要操作的数据
System.out.println(rows + " rows affect");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}? ? ? ? ?在一段程序中插入两条数据,在以上程序中会连接两次数据库,造成资源的浪费,效率较低,在实际应用中,应避免connection的多次创建,这样也可以更好的支持事务性操作。改进Commonutil,将connection作为参数传入update方法中,避免在一段程序中多次连接数据库。
//有了异常不要私自扣下,发送给调用者
public static int update(Connection connection,String sql,Object... args) throws SQLException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
for(int i = 0; i < args.length; i++){
preparedStatement.setObject(i + 1,args[i]);
}
int rows = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
return rows;
}finally {
JDBCUtil.close(null,preparedStatement);
}
}
@Test
public void test10(){
String sql = "insert into customer(name,gender,age,phone) values (?,?,?,?)";
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
int rows = 0;
rows = CommonUtil.update(connection, sql,"小七1","女",27,"77777777777");
System.out.println(rows + " rows affect");
rows = CommonUtil.update(connection, sql,"小七2","女",27,"77777777777");
System.out.println(rows + " rows affect");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
JDBCUtil.close(connection);
}
}4、JDBC的API ResultSet
? ? ? ? 使用ResultSet执行对数据库的查询操作
@Test
public void test(){
String sql = "select id,name,gender,age,phone from customer where id > ?";
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setObject(1,1);
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); //结果集对象中内部的游标指向第一条数据之前
while(resultSet.next()){ //移动游标到下一行
int id = resultSet.getInt(1); //指向当前游标的第一列
String name = resultSet.getString(2);
String gender = resultSet.getString(3);
int age = resultSet.getInt(4);
String phone = resultSet.getString(5);
System.out.println(id + "\t" + name + "\t" + gender + "\t" + age + "\t" + phone);
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JDBCUtil.close(connection,preparedStatement,resultSet);
}
}
public class JDBCUtil {
public static void close(Connection connection, PreparedStatement preparedStatement, ResultSet resultSet) {
if(resultSet != null){
try{
resultSet.close();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(preparedStatement != null){
try{
preparedStatement.close();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(connection != null){
try{
connection.close();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}? ? ? ? 使用列标签获取每一列的值,列标签是指虚表的列名,也就是别名。
while(resultSet.next()){ //移动游标到下一行
int id = resultSet.getInt("id"); //指向当前游标的第一列
String name = resultSet.getString("name");
String gender = resultSet.getString("gender");
int age = resultSet.getInt("age");
String phone = resultSet.getString("phone");
System.out.println(id + "\t" + name + "\t" + gender + "\t" + age + "\t" + phone);
}? ? ? ? 给打印出来的所有数据添加表头(添加列名),并实现动态获取数据
@Test
public void test2(){
String sql = "select id,name,gender,age,phone from customer where id > ?";
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setObject(1,1);
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); //结果集对象中内部的游标指向第一条数据之前
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData(); //获取虚表表结构
int columnCount = metaData.getColumnCount(); //获取虚表的列数
//打印表头
for(int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++){
String label = metaData.getColumnLabel(i + 1); //获取列标签
System.out.print(label + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
//打印数据
while(resultSet.next()){ //移动游标到下一行
for(int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++){
String columnLabel = metaData.getColumnLabel(i + 1); //获取列标签
Object value = resultSet.getObject(columnLabel); //根据动态获取的列标签获取对应的数据值
System.out.print(value + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JDBCUtil.close(connection,preparedStatement,resultSet);
}
}? ? ? ? 将结果集对象化,需要提供相应的Customer类,此过程称为ORMapping,Object Relation DB Mapping。
public class Customer {
private int id;
private String name;
private String gender;
private int age;
private String phone;
public Customer() {
}
public Customer(int id, String name, String gender, int age, String phone) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.gender = gender;
this.age = age;
this.phone = phone;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Customer{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", gender='" + gender + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", phone='" + phone + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
@Test
public void test3(){
ArrayList<Customer> list = new ArrayList<>();
String sql = "select id,name,gender,age,phone from customer where id > ?";
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setObject(1,1);
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); //结果集对象中内部的游标指向第一条数据之前
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData(); //获取虚表表结构
int columnCount = metaData.getColumnCount(); //获取虚表的列数
//打印数据
while(resultSet.next()){ //移动游标到下一行
Customer customer = new Customer();
for(int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++){
String columnLabel = metaData.getColumnLabel(i + 1); //获取到的是列标签,同时也是属性名
Object value = resultSet.getObject(columnLabel); //根据动态获取的标签获取对应的数据值
Field field = Customer.class.getDeclaredField(columnLabel);//根据列标签获取到属性的定义
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(customer,value);
}
list.add(customer);
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JDBCUtil.close(connection,preparedStatement,resultSet);
}
for(Customer customer : list){
System.out.println(customer);
}
}????????练习:查询Teacher表,并将结果对象化。
public class Teacher {
private int id;
private String name;
private String phone;
private String gender;
private int age;
private String address;
public Teacher() {
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(String phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
public String getGender() {
return gender;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public Teacher(int id, String name, String phone, String gender, int age, String address) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.phone = phone;
this.gender = gender;
this.age = age;
this.address = address;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Teacher{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", phone='" + phone + '\'' +
", gender='" + gender + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", address='" + address + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
@Test
public void test4(){
ArrayList<Teacher> list = new ArrayList<>();
String sql = "select id,name,gender,age,phone from teacher where id > ?";
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setObject(1,1);
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); //结果集对象中内部的游标指向第一条数据之前
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData(); //获取虚表表结构
int columnCount = metaData.getColumnCount(); //获取虚表的列数
//打印数据
while(resultSet.next()){ //移动游标到下一行
Teacher teacher = new Teacher();
for(int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++){
String columnLabel = metaData.getColumnLabel(i + 1); //获取到的是列标签,同时也是属性名
Object value = resultSet.getObject(columnLabel); //根据动态获取的标签获取对应的数据值
Field field = Teacher.class.getDeclaredField(columnLabel);//根据列标签获取到属性的定义
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(teacher,value);
}
list.add(teacher);
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JDBCUtil.close(connection,preparedStatement,resultSet);
}
for(Teacher teacher : list){
System.out.println(teacher);
}
}
@Test
public void test1(){
String sql = "select id,name,gender,age,phone from customer where id > ?";
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setObject(1,1);
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); //结果集对象中内部的游标指向第一条数据之前
while(resultSet.next()){ //移动游标到下一行
int id = resultSet.getInt("id"); //指向当前游标的第一列
String name = resultSet.getString("name");
String gender = resultSet.getString("gender");
int age = resultSet.getInt("age");
String phone = resultSet.getString("phone");
System.out.println(id + "\t" + name + "\t" + gender + "\t" + age + "\t" + phone);
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JDBCUtil.close(connection,preparedStatement,resultSet);
}
}? ? ? ? 将公共的方法抽取出去,提示:类模板,泛型。
/**
* 通用的查询操作
* @param connection 数据库的连接对象
* @param clazz 类模板对象
* @param sql 需要执行的sql语句
* @param args 代替sql中的?的实参列表
* @param <T> 泛型
* @return 保存了所有对象的集合
* @throws Exception
*/
public static <T> List<T> getList(Connection connection, Class<T> clazz, String sql, Object... args) throws Exception{
ArrayList<T> list = new ArrayList<>();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//替换sql中的?
for(int i = 0; i < args.length; i++){
preparedStatement.setObject(i + 1, args[i]);
}
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery(); //结果集对象中内部的游标指向第一条数据之前
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData(); //获取虚表表结构
int columnCount = metaData.getColumnCount(); //获取虚表的列数
//打印数据
while(resultSet.next()){ //移动游标到下一行
T instance = clazz.newInstance();
for(int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++){
String columnLabel = metaData.getColumnLabel(i + 1); //获取到的是列标签,同时也是属性名
Object value = resultSet.getObject(columnLabel); //根据动态获取的标签获取对应的数据值
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField(columnLabel);//根据列标签获取到属性的定义
field.setAccessible(true); //暴力反射
field.set(instance,value); //通过反射的方式为目标对象的属性赋值
}
list.add(instance);
}
return list;
}finally {
JDBCUtil.close(null,preparedStatement,resultSet);
}
}
@Test
public void test6() throws Exception{
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
List<Teacher> list = CommonUtil.getList(connection,Teacher.class, "select * from teacher where id > ?", 1);
for(Teacher teacher : list){
System.out.println(teacher);
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JDBCUtil.close(connection);
}
}
5、JDBC的事务处理
? ? ? ??事务执行流程:关闭自动提交 -- 执行若干DML -- 成功commit,失败rollback -- 还原设置。
public static void main(String[] args){
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
List<Teacher> list = CommonUtil.getList(connection, Teacher.class, "select * from teacher");
for(Teacher teacher : list){
System.out.println(teacher);
}
System.out.println("&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&");
//1)关闭自动提交
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
//2)执行若干DML
int rows = CommonUtil.update(connection, "delete from teacher");
System.out.println(rows + " rows affected");
list = CommonUtil.getList(connection, Teacher.class, "select * from teacher");
for(Teacher teacher : list){
System.out.println(teacher);
}
//String string = null;
//System.out.println(string.length());
//3)成功commit
connection.commit();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
//4)失败rollback
try {
connection.rollback();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}finally {
//还原设置
try {
connection.setAutoCommit(true);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
JDBCUtil.close(connection);
}
}6、数据库连接池
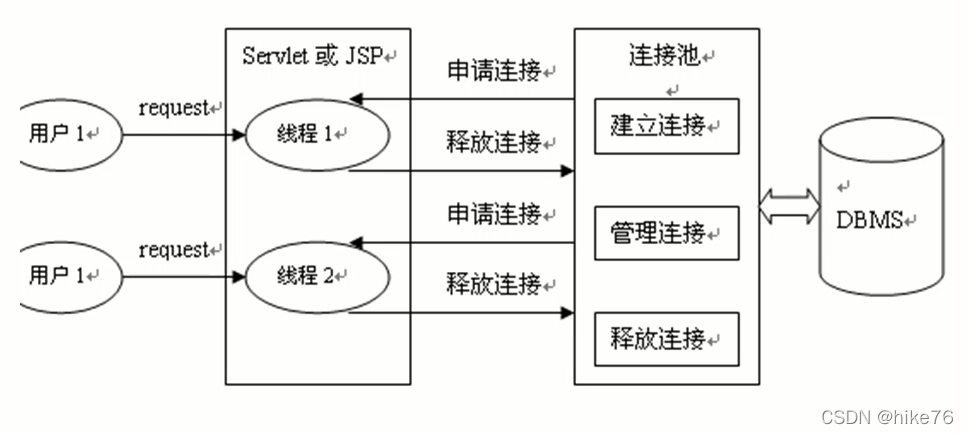
? ? ? ? 之间的所有操作每进行一次都会获取一次连接,造成效率较低。为了解决频繁进行数据库连接造成的低效率,使用连接池提前将数据库连接好,放在池子中。当用户请求时,将此资源分配给用户,用户使用后,归还到池子中即可。
? ? ? ? 数据库连接池的工作原理:
? ? ? ? 使用Druid驱动连接数据库
@Test
public void test() throws SQLException {
DruidDataSource druidDataSource = new DruidDataSource();
druidDataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
druidDataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/jdbc");
druidDataSource.setUsername("root");
druidDataSource.setPassword("hike");
Connection connection = druidDataSource.getConnection(); //代理对象
System.out.println(connection);
System.out.println(connection.getClass()); //获取到的是一个被包装过的对象
connection.close(); //只是把连接归还给连接池
}? ? ? ? 通过配置文件获取连接
? ? ? ? 编写配置文件Druid.properties
driverClassName = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url = jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/jdbc
username = root
password = hike @Test
public void test1() throws Exception{
InputStream inputStream = getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("Druid.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(inputStream);
assert inputStream != null;
inputStream.close();
DataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
}? ? ? ? 其他一些设置
druidDataSource.setInitialSize(5); //初始容量
druidDataSource.setMaxActive(40); //最大激活数
druidDataSource.setMinIdle(12); //最小空闲数? ? ? ? 在JDBCUtil中将连接抽取为公共方法
//只需要一个连接池就可以了
private static DataSource dataSource;
static { //类加载时就把池子建好
InputStream inputStream = JDBCUtil.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("Druid.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
properties.load(inputStream);
inputStream.close();
dataSource = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(properties);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static Connection getConnection() throws Exception {
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
return connection;
}? ? ? ? 测试:
@Test
public void test2() throws Exception {
Connection connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
}7、DBUtil 工具类
? ? ? ? 使用DBUtils插入数据
@Test
public void test() throws Exception {
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
Connection connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
int rows = queryRunner.update(connection, "insert into user(username,password) values (?,?)", "admin1", "admin1");
System.out.println(rows + "rows affected");
}? ? ? ? 查询数据
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception {
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
Connection connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "select id,name from customer where id > ?";
//结果集处理器,将结果集中的所有记录映射成Javabean对象,并放入list集合中
BeanListHandler<Customer> beanHandler = new BeanListHandler<>(Customer.class);
List<Customer> list = queryRunner.query(connection, sql, beanHandler, 1);
for(Customer customer : list) {
System.out.println(customer);
}
}? ? ? ? 标量处理器
@Test
public void test2() throws Exception {
QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
Connection connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
String sql = "select id,name from customer where id > ?";
//只取结果集中的第一行第一列
ScalarHandler scalarHandler = new ScalarHandler();
Object query = queryRunner.query(connection, sql, scalarHandler, 1);
System.out.println(query);
}8、DAO层编写逻辑? ? ? ??
????????编写TeacherDAO
????????DAO层专门管理数据库表与java对象之间的映射关系,data access object(DAO)。
public class TeacherDAO {
private QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
//获取批量对象
public List<Teacher> getList(String sql,Object... args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
return queryRunner.query(connection, sql, new BeanListHandler<Teacher>(Teacher.class), args);
}finally {
JDBCUtil.close(connection);
}
}
//获取一个对象
public Teacher getBean(String sql,Object... args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
return queryRunner.query(connection, sql, new BeanHandler<Teacher>(Teacher.class), args);
}finally {
JDBCUtil.close(connection);
}
}
//获取某一个值
public Object getValue(String sql,Object... args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
return queryRunner.query(connection, sql, new ScalarHandler(), args);
}finally {
JDBCUtil.close(connection);
}
}
//通用更新操作
public int updata(String sql,Object... args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
return queryRunner.update(connection, sql, args);
}finally {
JDBCUtil.close(connection);
}
}
@Test
public void test(){
TeacherDAO teacherDAO = new TeacherDAO();
try {
List<Teacher> list = teacherDAO.getList("select * from teacher");
for(Teacher teacher : list){
System.out.println(teacher);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}? ? ? ? 编写CustomerDAO
private QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
//获取批量对象
public List<Customer> getList(String sql, Object... args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
return queryRunner.query(connection, sql, new BeanListHandler<Customer>(Customer.class), args);
}finally {
JDBCUtil.close(connection);
}
}
//获取一个对象
public Customer getBean(String sql,Object... args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
return queryRunner.query(connection, sql, new BeanHandler<Customer>(Customer.class), args);
}finally {
JDBCUtil.close(connection);
}
}
//获取某一个值
public Object getValue(String sql,Object... args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
return queryRunner.query(connection, sql, new ScalarHandler(), args);
}finally {
JDBCUtil.close(connection);
}
}
//通用更新操作
public int updata(String sql,Object... args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
return queryRunner.update(connection, sql, args);
}finally {
JDBCUtil.close(connection);
}
}
@Test
public void test1(){
CustomerDAO customerDAO = new CustomerDAO();
try {
List<Customer> list = customerDAO.getList("select * from customer");
for(Customer customer : list){
System.out.println(customer);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
? ? ? ? 将CustomerDAO与TeacherDAO公共的部分抽取为JDBCDAO(泛型,类模板)。
public class JDBCDAO<T> {
private QueryRunner queryRunner = new QueryRunner();
private Class<T> clazz;
public JDBCDAO(Class<T> clazz){
this.clazz = clazz;
}
//获取批量对象
public List<T> getList(String sql, Object... args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
return queryRunner.query(connection, sql, new BeanListHandler<T>(clazz), args);
} finally {
JDBCUtil.close(connection);
}
}
//获取一个对象
public T getBean(String sql, Object... args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
return queryRunner.query(connection, sql, new BeanHandler<T>(clazz), args);
} finally {
JDBCUtil.close(connection);
}
}
//获取某一个值
public Object getValue(String sql, Object... args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
return queryRunner.query(connection, sql, new ScalarHandler(), args);
} finally {
JDBCUtil.close(connection);
}
}
//通用更新操作
public int updata(String sql, Object... args) throws Exception {
Connection connection = null;
try {
connection = JDBCUtil.getConnection();
return queryRunner.update(connection, sql, args);
} finally {
JDBCUtil.close(connection);
}
}
}
public class CustomerDAO extends JDBCDAO<Customer>{
public CustomerDAO() {
super(Customer.class);
}
}
public class TeacherDAO extends JDBCDAO<Teacher> {
public TeacherDAO() {
super(Teacher.class);
}
}