1、使用sqoop直接导入
(1)创建Hbase表
-- 1、如果用户表存在先删除
hbase(main):013:0> disable 'tbl_users' hbase(main):014:0> drop 'tbl_users'
-- 或者清空表
hbase(main):015:0> truncate 'tbl_users'
-- 2、创建用户表
hbase(main):016:0> create 'tbl_users','detail'
hbase(main):019:0> desc "tbl_users"
Table tbl_users is ENABLED tbl_users COLUMN FAMILIES DESCRIPTION {NAME => 'detail', BLOOMFILTER => 'ROW', VERSIONS => '1', IN_MEMORY => 'false', KEEP_DELETED_CELLS => 'FALSE', DATA_BLOCK_ENCODING => 'NONE', TTL => 'FOREVER', COMPRESSION => 'NONE', MIN_VERSIONS => '0', BLOCKCACHE => 'true', BLOCKSIZE => '65536', REPLICATION_SCOPE => '0'}
(2)sqoop全量导入Hbase中
可以使用SQOOP将MySQL表的数据导入到HBase表中,指定 表的名称、列簇及RowKey
/export/servers/sqoop/bin/sqoop import \
-D sqoop.hbase.add.row.key=true \
--connect jdbc:mysql://bigdata-cdh01:3306/tags_dat \
--username root \
--password 123456 \
--table tbl_users \
--hbase-create-table \
--hbase-table tbl_users \
--column-family detail \
--hbase-row-key id \
--num-mappers 2
参数含义解释:
1、-D sqoop.hbase.add.row.key=true 是否将rowkey相关字段写入列族中,默认为false,默认情况下你将在列族中看不到任何row key中的字段。注意,该参数必须放在import之后。
2、--hbase-create-table 如果hbase中该表不存在则创建
3、--hbase-table 对应的hbase表名
4、--hbase-row-key hbase表中的rowkey,注意格式 5、--column-family hbase表的列族
(3)sqoop增量导入Hbase中
/export/servers/sqoop/bin/sqoop import \
-D sqoop.hbase.add.row.key=true \
--connect jdbc:mysql://bigdata-cdh01.itcast.cn:3306/tags_dat \
--username root \
--password 123456 \
--table tbl_logs \
--hbase-create-table \
--hbase-table tag_logs \
--column-family detail \
--hbase-row-key id \
--num-mappers 20 \
--incremental lastmodified \
--check-column log_time \
--last-value '2019-08-13 00:00:00' \
相关增量导入参数说明:
1、--incremental lastmodified 增量导入支持两种模式 append 递增的列;lastmodified 时间戳。
2、--check-column 增量导入时参考的列
3、--last-value 最小值,这个例子中表示导入2019-08-13 00:00:00到今天的值
注意:
使用SQOOP导入数据到HBase表中,有一个限制:
需要指定RDBMs表中的某个字段作为HBase表的ROWKEY,如果HBase表的ROWKEY为多
个字段组合,就无法指定,所以此种方式有时候不能使用。
2、Hbase自带工具—HBase ImportTSV
HBase ImportTSV将tsv(也可以是csv,每行数据中各个字段使用分隔符分割)格式文本数据,加载到HBase表中。
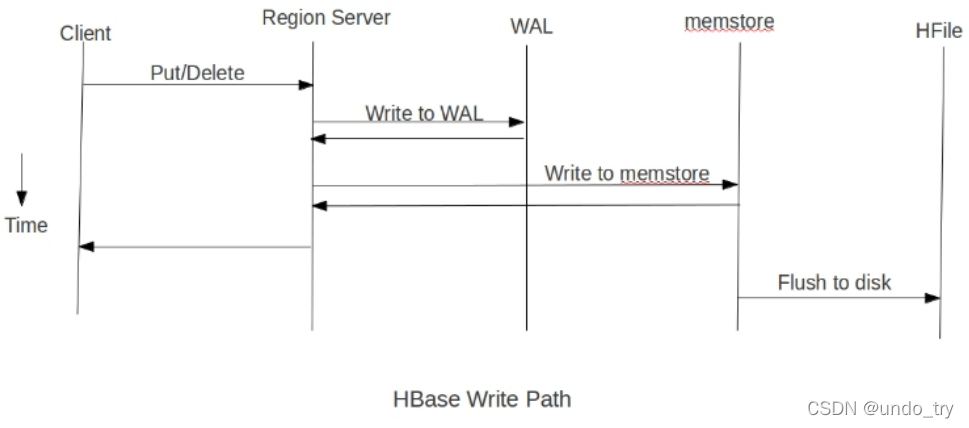
(1) 采用Put方式加载导入
采用Put方式向HBase表中插入数据流程:
Put
-> WAL 预写日志
-> MemStore(内存) ,当达到一定大写Spill到磁盘上:
1) 先导入数据至Hive表
使用Sqoop将MySQL数据库表中的数据导入到Hive表中(本质就是存储在HDFS上)
/export/servers/sqoop/bin/sqoop import \
--connect jdbc:mysql://bigdata-cdh01:3306/tags_dat \
--username root \
--password 123456 \
--table tbl_users \
--direct \
--hive-overwrite \
--delete-target-dir \
--fields-terminated-by '\t' \
--lines-terminated-by '\n' \
--hive-table tags_dat.tbl_users \
--hive-import \
--num-mappers 1
2) 从Hive表到Hbase
HADOOP_HOME=/export/servers/hadoop
HBASE_HOME=/export/servers/hbase
HADOOP_CLASSPATH=`${HBASE_HOME}/bin/hbase mapredcp`:${HBASE_HOME}/conf ${HADOOP_HOME}/bin/yarn jar ${HBASE_HOME}/lib/hbase-server-1.2.0- cdh5.14.0.jar \
importtsv \
-
Dimporttsv.columns=HBASE_ROW_KEY,detail:log_id,detail:remote_ip,detail:site_global_ticket,detail:site_global_session,detail:global_user_id,detail:cookie_text,detail:user_agent,detail:ref_url,detail:loc_url,detail:log _time \
tbl_logs \
/user/hive/warehouse/tags_dat.db/tbl_logs
(2) 将数据直接保存为HFile文件,然后加载到HBase表中
# 1. 生成HFILES文件
HADOOP_HOME=/export/servers/hadoop
HBASE_HOME=/export/servers/hbase
HADOOP_CLASSPATH=`${HBASE_HOME}/bin/hbase mapredcp`:${HBASE_HOME}/conf ${HADOOP_HOME}/bin/yarn jar ${HBASE_HOME}/lib/hbase-server-1.2.0- cdh5.14.0.jar \
importtsv \
-Dimporttsv.bulk.output=hdfs://bigdata-cdh01:8020/datas/output_hfile/tbl_logs \
-
Dimporttsv.columns=HBASE_ROW_KEY,detail:log_id,detail:remote_ip,detail:site_global_ticket,detail:site_global_session,detail:global_user_id,detail:cookie_text,detail:user_agent,detail:ref_url,detail:loc_url,detail: log_time \
tbl_logs \
/user/hive/warehouse/tags_dat.db/tbl_logs
# 2. 将HFILE文件加载到表中
HADOOP_CLASSPATH=`${HBASE_HOME}/bin/hbase mapredcp`:${HBASE_HOME}/conf ${HADOOP_HOME}/bin/yarn jar ${HBASE_HOME}/lib/hbase-server-1.2.0- cdh5.14.0.jar \
completebulkload \
hdfs://bigdata-cdh01:8020/datas/output_hfile/tbl_logs \
tbl_logs
注意:
1)、ROWKEY不能是组合主键 只能是某一个字段
2)、当表中列很多时,书写-Dimporttsv.columns值时很麻烦,容易出错
3、HBase Bulkload
在大量数据需要写入HBase时,通常有 put方式和bulkLoad 两种方式。
1、put方式为单条插入,在put数据时会先将数据的更新操作信息和数据信息 写入WAL ,
在写入到WAL后, 数据就会被放到MemStore中 ,当MemStore满后数据就会被 flush到磁盘
(即形成HFile文件) ,在这种写操作过程会涉及到flush、split、compaction等操作,容易造
成节点不稳定,数据导入慢,耗费资源等问题,在海量数据的导入过程极大的消耗了系统
性能,避免这些问题最好的方法就是使用BulkLoad的方式来加载数据到HBase中。
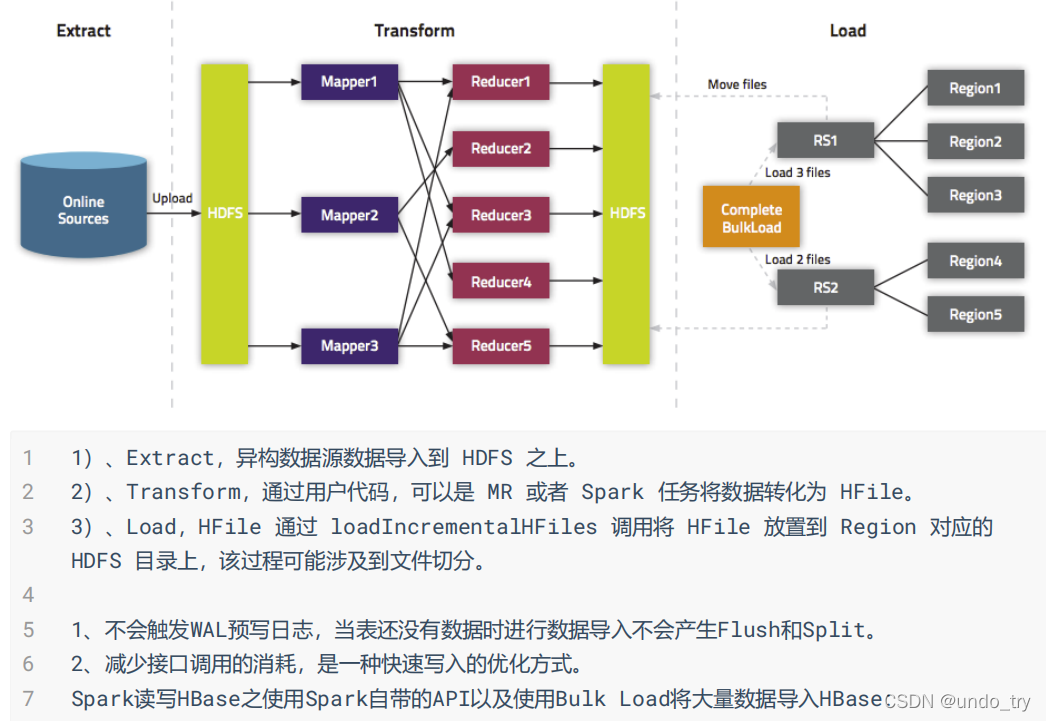
2、BulkLoader利用HBase数据按照HFile格式存储在HDFS的原理,使用MapReduce直接批量
生成HFile格式文件后,RegionServers再将HFile文件移动到相应的Region目录下。
(1)编写MR程序
package com.yyds.tags.mr.etl;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Bytes;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* 定义常量
*/
interface Constants {
// hive表数据目录
String INPUT_PATH = "hdfs://bigdata-cdh01:8020/user/hive/warehouse/tags_dat.db/tbl_logs";
// 生成的hfile目录
String HFILE_PATH = "hdfs://bigdata-cdh01:8020/datas/output_hfile/tbl_logs";
// 表名
String TABLE_NAME = "tbl_logs";
// 列簇名称
byte[] COLUMN_FAMILY = Bytes.toBytes("detail");
// 表字段
List<byte[]> list = new ArrayList<byte[]>() {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6125158551837044300L;
{
add(Bytes.toBytes("id"));
add(Bytes.toBytes("log_id"));
add(Bytes.toBytes("remote_ip"));
add(Bytes.toBytes("site_global_ticket"));
add(Bytes.toBytes("site_global_session"));
add(Bytes.toBytes("global_user_id"));
add(Bytes.toBytes("cookie_text"));
add(Bytes.toBytes("user_agent"));
add(Bytes.toBytes("ref_url"));
add(Bytes.toBytes("loc_url"));
add(Bytes.toBytes("log_time"));
}
};
}
package com.yyds.tags.mr.etl;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configured;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.HBaseConfiguration;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.TableName;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.*;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.io.ImmutableBytesWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.HFileOutputFormat2;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.LoadIncrementalHFiles;
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Bytes;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.Tool;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.ToolRunner;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 将Hive表数据转换为HFile文件并移动HFile到HBase
*/
public class LoadLogsToHBaseMapReduce extends Configured implements Tool {
// 连接HBase Connection对象
private static Connection connection = null;
/**
* 定义Mapper类,读取CSV格式数据,转换为Put对象,存储HBase表
*/
static class LoadLogsToHBase extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, ImmutableBytesWritable, Put> {
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// 按照分隔符分割数据,分隔符为 逗号
String[] split = value.toString().split("\\t");
if (split.length == Constants.list.size()) {
// 构建Put对象,将每行数据转换为Put
Put put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes(split[0]));
for (int i = 1; i < Constants.list.size(); i++) {
put.addColumn(
Constants.COLUMN_FAMILY,
Constants.list.get(i),
Bytes.toBytes(split[i])
);
}
// 将数据输出
context.write(new ImmutableBytesWritable(put.getRow()), put);
}
}
}
@Override
public int run(String[] strings) throws Exception {
// a. 获取配置信息对象
Configuration configuration = super.getConf() ;
// b. 构建Job对象Job
Job job = Job.getInstance(configuration);
job.setJobName(this.getClass().getSimpleName());
job.setJarByClass(LoadLogsToHBaseMapReduce.class);
// c. 设置Job
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(Constants.INPUT_PATH));
job.setMapperClass(LoadLogsToHBase.class);
// 设置输出格式为HFileOutputFormat2
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(ImmutableBytesWritable.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Put.class);
job.setOutputFormatClass(HFileOutputFormat2.class);
// 判断输出目录是否存在,如果存在就删除
FileSystem hdfs = FileSystem.get(configuration) ;
Path outputPath = new Path(Constants.HFILE_PATH) ;
if(hdfs.exists(outputPath)){
hdfs.delete(outputPath, true) ;
}
// d. 设置输出路径
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, outputPath);
// 获取HBase Table,对HFileOutputFormat2进行设置
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(Constants.TABLE_NAME));
HFileOutputFormat2.configureIncrementalLoad(
job,
table,
connection.getRegionLocator(TableName.valueOf(Constants.TABLE_NAME)) );
// 提交运行Job,返回是否执行成功
boolean isSuccess = job.waitForCompletion(true);
return isSuccess ? 0 : 1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 获取Configuration对象,读取配置信息
Configuration configuration = HBaseConfiguration.create();
// 获取HBase 连接Connection对象
connection = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(configuration);
// 运行MapReduce将数据文件转换为HFile文件
int status = ToolRunner.run(configuration, new LoadLogsToHBaseMapReduce(), args);
System.out.println("HFile文件生成完毕!~~~");
// 运行成功时,加载HFile文件数据到HBase表中
if (0 == status) {
// 获取HBase Table句柄
Admin admin = connection.getAdmin();
Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(Constants.TABLE_NAME));
// 加载数据到表中
LoadIncrementalHFiles load = new LoadIncrementalHFiles(configuration);
load.doBulkLoad(
new Path(Constants.HFILE_PATH),
admin,
table,
connection.getRegionLocator(TableName.valueOf(Constants.TABLE_NAME))
);
System.out.println("HFile文件移动完毕!~~~");
}
}
}
(2)编写spark程序
package com.yyds.tags.mr.etl.hfile
import scala.collection.immutable.TreeMap
/**
* HBase 中各个表的字段名称,存储在TreeMap中
*/
object TableFieldNames{
// 使用TreeMap为qualifier做字典序排序
// 行为日志数据表的字段
val LOG_FIELD_NAMES: TreeMap[String, Int] = TreeMap(
("id", 0),
("log_id", 1),
("remote_ip", 2),
("site_global_ticket", 3),
("site_global_session", 4),
("global_user_id", 5),
("cookie_text", 6),
("user_agent", 7),
("ref_url", 8),
("loc_url", 9),
("log_time", 10)
)
}
package com.yyds.tags.mr.etl.hfile
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.{FileSystem, Path}
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.{ConnectionFactory, Table}
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.io.ImmutableBytesWritable
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.{HFileOutputFormat2, LoadIncrementalHFiles, TableOutputFormat}
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.util.Bytes
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.{HBaseConfiguration, KeyValue, TableName}
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job
import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
import scala.collection.immutable.TreeMap
/**
* @DESC: 将数据存储文本文件转换为HFile文件,加载到HBase表中
*
* HBase数据库提供批量导入数据至表功能,相关知识点如下:
* 1、Hbase 中LoadIncrementalHFiles 支持向Hbase 写入HFile 文件
* 2、写入的HFile 文件要求是排序的(rowKey,列簇,列)
* 3、关键是绕过Hbase regionServer,直接写入Hbase文件
* 4、Spark RDD的 repartitionAndSortWithinPartitions 方法可以高效地实现分区并排序
* 5、JAVA util.TreeMap 是红黑树的实现,能很好的实现排序的要求
*/
object HBaseBulkLoader {
/**
* 依据不同表的数据文件,提取对应数据,封装到KeyValue对象中
* 提取数据字段,构建二元组(RowKey, KeyValue)
* Key: rowkey + cf + column + version(timestamp)
* Value: ColumnValue
*
* @param line
* @param family
* @param fieldNames
* @return
*/
def getLineToData(line: String, family: String, fieldNames: TreeMap[String, Int]): List[(ImmutableBytesWritable, KeyValue)] = {
val length = fieldNames.size
// 分割字符串
val fieldValues: Array[String] = line.split("\\t", -1)
if (null == fieldValues || fieldValues.length != length) return Nil
// 获取id,构建RowKey
val id: String = fieldValues(0)
val rowKey = Bytes.toBytes(id)
val ibw: ImmutableBytesWritable = new ImmutableBytesWritable(rowKey)
// 列簇
val columnFamily: Array[Byte] = Bytes.toBytes(family)
// 构建KeyValue对象
fieldNames.toList.map { case (fieldName, fieldIndex) =>
// KeyValue实例对象
val keyValue = new KeyValue(
rowKey, //
columnFamily, //
Bytes.toBytes(fieldName), //
Bytes.toBytes(fieldValues(fieldIndex)) //
)
// 返回
(ibw, keyValue)
}
}
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// 应用执行时传递5个参数:数据类型、HBase表名称、表列簇、输入路径及输出路径
/**
* args = Array ("1", "tbl_tag_logs", "detail", "/user/hive/warehouse/tags_dat.db/tbl_logs", "/datas/output_hfile/tbl_tag_logs")
*/
if (args.length != 5) {
println("Usage: required params: <DataType> <HBaseTable> <Family> <InputDir> <OutputDir>")
System.exit(-1)
}
// 将传递赋值给变量, 其中数据类型:1Log、2Good、3User、4Order
val Array(dataType, tableName, family, inputDir, outputDir) = args
// 依据参数获取处理数据schema
val fieldNames = dataType.toInt match {
case 1 => TableFieldNames.LOG_FIELD_NAMES
case 2 => TableFieldNames.GOODS_FIELD_NAMES
case 3 => TableFieldNames.USER_FIELD_NAMES
case 4 => TableFieldNames.ORDER_FIELD_NAMES
}
// 1. 构建SparkContext实例对象
val sc: SparkContext = {
// a. 创建SparkConf,设置应用配置信息
val sparkConf = new SparkConf()
// .setMaster("local[2]")
.setAppName(this.getClass.getSimpleName.stripSuffix("$"))
.set("spark.serializer", "org.apache.spark.serializer.KryoSerializer")
// b. 传递SparkContext创建对象
SparkContext.getOrCreate(sparkConf)
}
// 2. 读取文本文件数据,转换格式
val keyValuesRDD: RDD[(ImmutableBytesWritable, KeyValue)] = sc.textFile(inputDir)
.filter(line => null != line) // 过滤数据
.flatMap { line => getLineToData(line, family, fieldNames) }
.sortByKey()
// TODO:构建Job,设置相关配置信息,主要为输出格式
// a. 读取配置信息
val conf: Configuration = HBaseConfiguration.create()
// Configuration parameter hbase.mapreduce.hfileoutputformat.table.name cannot be empty
conf.set("hbase.mapreduce.hfileoutputformat.table.name", tableName)
// b. 如果输出目录存在,删除
val dfs = FileSystem.get(conf)
val outputPath: Path = new Path(outputDir)
if (dfs.exists(outputPath)) {
dfs.delete(outputPath, true)
}
dfs.close()
// TODO:c. 配置HFileOutputFormat2输出
val conn = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(conf)
val htableName = TableName.valueOf(tableName)
val table: Table = conn.getTable(htableName)
HFileOutputFormat2.configureIncrementalLoad(
Job.getInstance(conf), //
table, //
conn.getRegionLocator(htableName) //
)
// TODO: 3. 保存数据为HFile文件
keyValuesRDD
.sortBy(x => (x._1, x._2.getKeyString), true) //要保持 整体有序
.saveAsNewAPIHadoopFile(
outputDir, //
classOf[ImmutableBytesWritable], //
classOf[KeyValue], //
classOf[HFileOutputFormat2], //
conf //
)
// TODO:4. 将输出HFile加载到HBase表中
val load = new LoadIncrementalHFiles(conf)
load.doBulkLoad(outputPath, conn.getAdmin, table,
conn.getRegionLocator(htableName))
// 应用结束,关闭资源
sc.stop()
}
}