一、Mybatis的各种查询功能
1.若查询结果只有一条时
(1)可以使用实体类对象接收
(2)也可以使用list和map集合接收;
2.若查询结果有多条
(1)使用实体类类型的的list集合接收
(2)使用map类型的list集合接收
(3)可以在mapper接口的方法上添加@MapKey注解,此时可以将map集合作为值,以某个唯一字段的值作为键,放在同一个map集合中
二、特殊SQL的执行
1.模糊查询
<!--三种方式都可以实现模糊查询,推荐使用方式3-->
<select id="getUserByLike" resultType="com.jd.wds.pojo.User">
<!--select * from user where username like '%${username}%'-->
<!--select * from user where username like concat ('%',#{username},'%')-->
select * from user where username like "%"#{username}"%"
</select>
2.批量删除
<!--批量删除的特殊情况-->
<delete id="deleteMore">
<!--此处只能使用${}的形式,因为#{}的方式会添加引号,而id的字段名是int-->
<!--delete from user where id in (#{id})-->
delete from user where id in (${id})
</delete>
3.动态设置表名
<select id="getUserByTableName" resultType="com.jd.wds.pojo.User">
<!--此处只能使用${},不能使用#{}-->
<!--select * from #{tableName}-->
select * from ${tableName}
</select>
4.字段名和属性名不一致
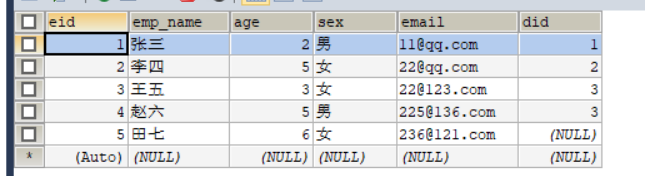
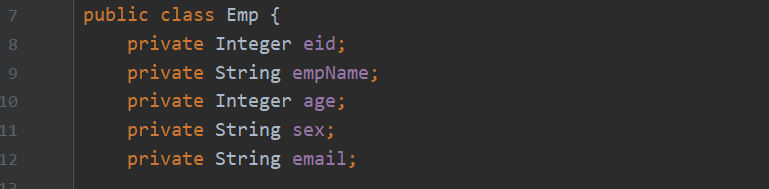
根据不同的规范,创建表时字段选用下划线命名,创建类的属性名选用小驼峰命名,此时就会出现字段名和属性名不完全对应,三种解决方法:
<select id="getAllEmp" resultType="com.jd.wds.pojo.Emp">
<!--方法1:给对应的字段名设置别名-->
select eid,emp_name empName,age,sex,email from t_emp
</select>
<!--mybatis的核心配置文件中配置如下,此时sql语句:select * from t_emp-->
<!--方法2:设置全局配置:驼峰命名转下划线命名-->
<settings>
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
</settings>
<!--方法3:使用resultmap设置自定义的映射-->
<resultMap id="empResultMap" type="com.jd.wds.pojo.Emp">
<!--id设置的是主键名,result设置的是非主键名,column是属性名-->
<id property="eid" column="eid"></id>
<result property="empName" column="emp_name"></result>
<result property="age" column="age"></result>
<result property="sex" column="sex"></result>
<result property="email" column="email"></result>
</resultMap>
<select id="getAllEmp" resultMap="empResultMap">
<!--解决字段名和属性名方法1:给对应的字段名设置别名-->
select * from t_emp
</select>
5.多对一的映射关系
多对一对应对象,一对多对应集合
举个栗子:查询某个员工信息及所在的部门信息(多个员工对应一个部门,典型的多对一)
方法1:resultMap通过级联属性赋值处理
<resultMap id="empAndDeptOne" type="com.jd.wds.pojo.Emp">
<id property="eid" column="eid"></id>
<result property="empName" column="emp_name"></result>
<result property="age" column="age"></result>
<result property="sex" column="sex"></result>
<result property="email" column="email"></result>
<!--需要在Emp类中声明dept属性,resultMap通过级联属性赋值-->
<result property="dept.did" column="did"></result>
<result property="dept.deptName" column="dept_name"></result>
</resultMap>
<select id="getEmpAndDept" resultMap="empAndDeptOne">
SELECT * FROM t_emp LEFT JOIN t_dept ON t_emp.did = t_dept.did WHERE t_emp.eid = #{eid}
</select>
方法2:使用association专门处理级联属性赋值
<resultMap id="empAndDeptTwo" type="com.jd.wds.pojo.Emp">
<id property="eid" column="eid"></id>
<result property="empName" column="emp_name"></result>
<result property="age" column="age"></result>
<result property="sex" column="sex"></result>
<result property="email" column="email"></result>
<!--需要在Emp类中声明dept属性,使用association专门处理级联属性赋值
javaType:需要处理的属性的类型;
property:需要处理的属性名-->
<association javaType="com.jd.wds.pojo.Dept" property="dept">
<result property="did" column="did"></result>
<result property="deptName" column="dept_name"></result>
</association>
</resultMap>
<select id="getEmpAndDept" resultMap="empAndDeptTwo">
SELECT * FROM t_emp LEFT JOIN t_dept ON t_emp.did = t_dept.did WHERE t_emp.eid = #{eid}
</select>
方法3:使用分步查询解决
<!--<mapper resource="com/jd/wds/mapper/EmpMapper.xml"/>-->
<!--分步查询员工所对应的部门信息-->
<!--第一步:查询员工信息-->
<resultMap id="EmpAndDeptByStepOne" type="com.jd.wds.pojo.Emp">
<id property="eid" column="eid"></id>
<result property="empName" column="emp_name"></result>
<result property="age" column="age"></result>
<result property="sex" column="sex"></result>
<result property="email" column="email"></result>
<!--association标签中property:属性名,select:第二步的sql查询语句,column:第二步的查询条件-->
<association property="dept" select="com.jd.wds.mapper.DeptMapper.getEmpAndDeptByStepTwo" column="did"></association>
</resultMap>
<select id="getEmpAndDeptByStepOne" resultMap="EmpAndDeptByStepOne">
select * from t_emp where eid=#{eid}
</select>
<!--<mapper resource="com/jd/wds/mapper/DeptMapper.xml"/>-->
<!--步骤2:根据查询道德did查询t_dept表中的数据-->
<select id="getEmpAndDeptByStepTwo" resultType="com.jd.wds.pojo.Dept">
select * from t_dept where did = #{did}
</select>
分步查询的好处:可以实现延迟加载,提高SQL的复用,必须在配置文件中开启才可使用,默认不开启延时加载。
6.一对多的映射关系
多对一对应对象,一对多对应集合
举个栗子:查询某个部门以及部门中员工的信息(一个部门可以有多个员工,典型的一对多)
方法1:使用collection处理一对多的结果映射
<resultMap id="DeptAndEmp" type="com.jd.wds.pojo.Dept">
<id property="did" column="did"></id>
<result property="deptName" column="dept_name"></result>
<!--collection:处理一对多的结果映射,emps:一对多的集合名,ofType:集合emps所对应的集合类型-->
<collection property="emps" ofType="com.jd.wds.pojo.Emp">
<id property="eid" column="eid"></id>
<result property="empName" column="emp_name"></result>
<result property="age" column="age"></result>
<result property="sex" column="sex"></result>
<result property="email" column="email"></result>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="getDeptAndEmp" resultMap="DeptAndEmp">
select * from t_dept left join t_emp on t_dept.did = t_emp.did where t_dept.did = #{did}
</select>
方法2:使用分步查询处理一对多的结果映射
<!--分步查询-->
<!--<mapper resource="com/jd/wds/mapper/DeptMapper.xml"/>-->
<resultMap id="getDeptAndEmpByStep" type="com.jd.wds.pojo.Dept">
<id property="did" column="did" ></id>
<result property="deptName" column="dept_name"></result>
<collection property="emps" select="com.jd.wds.mapper.EmpMapper.getDeptAndEmpByStepTwo" column="did">
</collection>
</resultMap>
<!--第一步:根据did查询所在的部门信息-->
<select id="getDeptAndEmpByStepOne" resultMap="getDeptAndEmpByStep">
select * from t_dept where did = #{did}
</select>
<!--<mapper resource="com/jd/wds/mapper/EmpMapper.xml"/>-->
<!--第二步:根据第一步查询结果的did查询所在的员工信息-->
<select id="getDeptAndEmpByStepTwo" resultType="com.jd.wds.pojo.Emp">
select * from t_emp where did = #{did}
</select>
三、动态SQL
1.< if > 元素
根据标签中test属性所对应的表达式来确定标签中的内容是否要拼接到SQL中。
<!--通过多个条件精确查询某一条数据-->
<select id="getEmpDynamicCondition" resultType="com.jd.wds.pojo.Emp">
select * from t_emp where 1=1
<!--test属性的值是属性名-->
<if test="empName != null and empName !=''">
and emp_name = #{empName}
</if>
<if test="age != null and age !=''">
and age = #{age}
</if>
<if test="sex != null and sex != ''">
and sex = #{sex}
</if>
<if test="email != null and email != ''">
and email = #{email}
</if>
</select>
2.< where >元素
当标签中有内容时,将自动生成where关键字,将内容之前的and或or去掉;当标签中没有内容时,where没有任何效果。(and或or在内容之后会报错)
<select id="getEmpDynamicCondition" resultType="com.jd.wds.pojo.Emp">
select * from t_emp
<where>
<if test="empName != null and empName !=''">
and emp_name = #{empName}
</if>
<if test="age != null and age !=''">
and age = #{age}
</if>
<if test="sex != null and sex != ''">
and sex = #{sex}
</if>
<if test="email != null and email != ''">
and email = #{email}
</if>
</where>
</select>
3.< trim >元素
若标签中有内容:
prefix/suffix:将trim标签中内容前面或后面添加指定内容
suffixoverrides /prefixoverrides : 将trim标签中内容前面或后面去掉指定内容
若标签中没有内容,trim标签没有任何效果。
<select id="getEmpDynamicCondition" resultType="com.jd.wds.pojo.Emp">
select * from t_emp
<!--此时在内容之前添加where,条件前面加and|or-->
<trim prefix="where" prefixOverrides="and|or">
<if test="empName != null and empName !=''">
and emp_name = #{empName}
</if>
<if test="age != null and age !=''">
and age = #{age}
</if>
<if test="sex != null and sex != ''">
and sex = #{sex}
</if>
<if test="email != null and email != ''">
and email = #{email}
</if>
</trim>
</select>
4.< choose > < when > < otherwise >元素
相当于if,else if,else if,else
<select id="getEmpDynamicCondition" resultType="com.jd.wds.pojo.Emp">
select * from t_emp where 1=1
<choose>
<when test="empName != null and empName !=''">
and emp_name = #{empName}
</when>
<when test="age != null and age !=''">
and age = #{age}
</when>
<when test="sex != null and sex != ''">
and sex = #{sex}
</when>
<when test="email != null and email != ''">
and email = #{email}
</when>
<otherwise>
did = 1
</otherwise>
</choose>
</select>
5.< foreach >元素
foreach用于遍历操作,经常用于批量删除、批量添加等操作。
<!--批量删除操作-->
<delete id="deleteMoreUser">
<!--方法1:使用in集合的方式-->
delete from t_emp where eid in
<foreach collection="eids" open="(" close=")" separator="," item="eid">
#{eid}
</foreach>
<!--方法2:使用or连接条件-->
delete from t_emp where
<foreach collection="eids" item="eid" separator="or">
eid = #{eid}
</foreach>
</delete>
<!--批量插入操作-->
<insert id="insertMoreUser">
insert into t_emp values
<foreach collection="emps" separator="," item="emp">
(null,#{emp.empName},#{emp.age},#{emp.sex},#{emp.email},#{emp.did})
</foreach>
</insert>
6.SQL标签
用于设置SQL片段,在需要的位置进行引用即可。
<!--设置sql片段-->
<sql id="columns">eid,emp_name,age,sex,email</sql>
<select id="selectAllUser" resultType="com.jd.wds.pojo.Emp">
<!--使用sql片段-->
select <include refid="colums"></include> from t_emp where eid = #{eid}
</select>
四、Mybatis缓存
1.Mybatis的一级缓存
缓存只是针对查询功能,一级缓存是SqlSession级别的,默认开启,下次使用相同的SqlSession查询相同的数据时,直接从缓存中获取,不会从数据库中查询(只执行一次SQL语句,有两个相同的结果)。
一级缓存失效的4种情况:
(1)不同的SqlSession对应的一级缓存
(2)同一个SqlSession对应的查询条件不同
(3)同一个SqlSession两次查询之间执行了任何一次增删改操作
(4)同一个SqlSesion两次查询之间手动清理了缓存
//手动清空缓存
sqlSession.clearCache();
2.Mybatis的二级缓存
二级缓存是SqlSessionFactory级别,通过同一个SqlSessionFactory创建的SqlSession的查询结果会被缓存,此后若执行相同的查询语句,结果就会从缓存中获取。
(1)二级缓存开启的条件:
① 在核心配置文件中,设置全局配置属性cacheEnabled=“true”
<setting name="cachedEnable" value="true"/>
② 在映射文件中设置标签< cache />
③ 二级缓存必须在SqlSession关闭或提交后生效、
④ 查询的数据所转换的实体类类型必须实现序列化接口
(2)二级缓存失效的条件
两次查询之间执行了任意的增删改操作,会使一二级缓存同时失效。
(3)二级缓存的相关配置

(4)缓存查询的顺序
