一、导入驱动
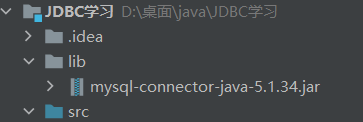
新建一个lib包,将驱动拖进去
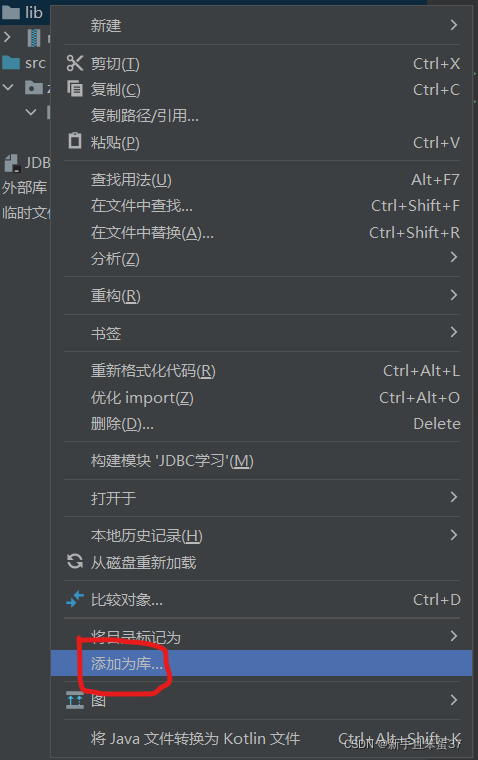
点击添加为库
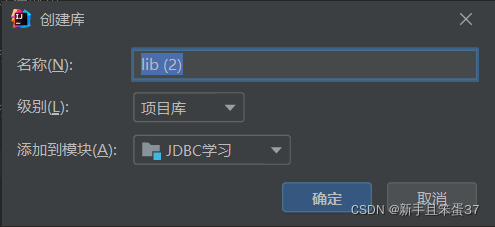
点击确定
二、JDBC程序
//1.加载驱动
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");//固定写法,加载驱动
//2.用户信息和url
//?连接参数,&并列条件
//设置参数:可用Unicode编码,字符集为utf-8,启用安全模式(useSSL=true,在高版本需要显式声明是否与要SSL连接)
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8";
String username = "root";
String password = "123456";
//3.连接成功
//connection代表数据库
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
//4.执行sql的对象
//statement是执行sql的对象
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
//5.执行sql
String sql = "select * from users";
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(sql);
while(resultSet.next()){
System.out.print("id=" + resultSet.getObject("id"));
System.out.print(",name=" + resultSet.getObject("name"));
System.out.print(",password=" + resultSet.getObject("password"));
System.out.print(",email=" + resultSet.getObject("email"));
System.out.print(",birthday=" + resultSet.getObject("birthday"));
System.out.println();
}
//6,释放连接
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();
步骤总结:
- 加载驱动
- 连接数据库 DriverManager
- 获取执行sql的对象 Statement
- 获得返回的结果集
- 释放连接
三、JDBC对象的解释
1、加载驱动
我们用的写法是
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
利用反射,将com.mysql.jdbc.Driver类加载。
而标准写法应该是
DriverManager.registerDriver(new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver());
不使用这个方法是因为,在Driver类内,有DriverManager.registerDriver(new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver());方法,这会使这个方法被调用两次。
2、URL
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8";
对比一下我们常见的url
https://www.baidu.com/s?wd=搜索内容
jdbc:mysql://就相当于https://
localhost:3306/就相当于www.baidu.com/
jdbcstudy就相当于s
后接?接参数
useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8就相当于wd=搜索内容
3、connection
代表数据库
可以设置数据库级别的东西:自动提交、事务回滚、获得信息、设置只读
3、statement
执行sql的类
还有个类是PreapareStatement也是执行sql的
statement.execute(sql);//执行任何的sql,效率相对低。
statement.executeQuery(sql);//返回ResultSet
statement.executeUpdate(sql);//更新、插入、删除,返回受影响的行数
statement.executeBatch(sql);//执行多个sql
4、ResultSet
封装了所有的查询结果
获取数据
resultSet.getObject("column_name");//不知道列的类型
resultSet.getString("column_name");
resultSet.getInt("column_name");
resultSet.getFloat("column_name");
resultSet.getDate("column_name");
遍历
resultSet.beforeFirst();//指针移至最前
resultSet.afterLast();//指针移至最后
resultSet.next();//移动到下一个
resultSet.previous();//移动到下一行
关于next()方法,指针一开始在第一行之前,也就是第一次在while()判断里调用next()方法会使指针指向第一行,这样就使得第二次调用next()方法才能获取到数据。
释放资源
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();//耗资源很多
四、StateMent对象详解
JDBC中的StateMent对象用于向数据库发送SQL语句,想完成对数据库的CRUD,只需要通过这个对象向数据库发送CRUD语句即可
executeQuery()方法返回结果集合
executeUpdate()返回受影响的行数
根据受影响的行数不为0,说明executeUpdate()语句执行成功
五、封装工具类
1、先设置配置文件
写入数据:
driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbcstudy?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
username=root
password=123456
2、封装
定义一个JdbcUtils类对数据进行获取,并封装连接和释放资源的方法:
public class JdbcUtils {
private static String driver = null;
private static String url = null;
private static String username = null;
private static String password = null;
static {
try{
InputStream in = JdbcUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("db.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(in);
driver = properties.getProperty("driver");
url = properties.getProperty("url");
username = properties.getProperty("username");
password = properties.getProperty("password");
//1.驱动只要加载一次
Class.forName(driver);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//2.获取链接
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
}
//3.释放资源
public static void release(Connection c, Statement s, ResultSet r){
if (r!=null){
try {
r.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (s!=null){
try {
s.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (c!=null){
try {
c.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
3、测试工具类
先用插入语句试试
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection c = null;
Statement s = null;
try {
c = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
s = c.createStatement();
String sql = "INSERT INTO `users` VALUE (5,'zhaoliu','123456','zl@sina.com','2000-07-13')";
int n = s.executeUpdate(sql);
if(n>0){
System.out.println("插入成功!");
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(c,s,null);
}
}
输出:插入成功!
利用sqlyog查看一下

确实插入成功了
再用查询语句试试
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection c = null;
Statement s = null;
ResultSet r = null;
try {
c = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
s = c.createStatement();
String sql = "SELECT * FROM `users` WHERE id=1";
r = s.executeQuery(sql);
while (r.next()){
System.out.print("id="+r.getObject("id"));
System.out.print(",name="+r.getObject("name"));
System.out.print(",password="+r.getObject("password"));
System.out.print(",email="+r.getObject("email"));
System.out.print(",birthday="+r.getObject("birthday"));
System.out.println();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.release(c,s,r);
}
}
对于执行完语句的数据处理,executeQuery()和executeUpdate()的处理稍有区别。