一、以下测试程序包含两个类? com.suntown.Main 和 com.suntown.EmbedMySqlServer,依赖的jar包有?mysql-connector-mxj-gpl-6-0-11-db-files.jar 对应的mysql版本为 6.0.11-alpha-community
package com.suntown;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.util.Properties;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
try {
new EmbedMySqlServer(EmbedMySqlServer.genenalProp(),"f:\\mysqlfile").startup();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package com.suntown;
import com.mysql.management.MysqldResource;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
public class EmbedMySqlServer {
private MysqldResource mysqlInstance;
public final Properties props;
private String port;
private String embedMySqlHome;
public static Properties genenalProp(){
Properties pro = new Properties();
try{
pro.load(EmbedMySqlServer.class.getResourceAsStream("/MySql_general.properties"));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return pro;
}
public EmbedMySqlServer(Properties props) {
this.props = props;
}
public EmbedMySqlServer(Properties props, String embedMySqlHome) {
this.embedMySqlHome = embedMySqlHome;
this.props = props;
}
public final String getEmbedMySqlHome() {
return null == this.embedMySqlHome ? getPlatformBaseDir() : this.embedMySqlHome;
}
public static String getPlatformBaseDir() {
return System.getProperty("user.dir");
}
public static boolean isBlank(String str) {
int strLen;
if (str != null && (strLen = str.length()) != 0) {
for(int i = 0; i < strLen; ++i) {
if (!Character.isWhitespace(str.charAt(i))) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
} else {
return true;
}
}
public void startup() {
File baseDir = new File(this.getEmbedMySqlHome(), "mysql-em");
this.mysqlInstance = new MysqldResource(baseDir);
this.port = this.props.getProperty("port");
if (isBlank(this.port)) {
this.props.put("port", this.port = String.valueOf((int)(Math.random() * 40000.0D)));
}
Set<Object> keys = this.props.keySet();
Map<String, String> options = new HashMap(keys.size());
Iterator var4 = keys.iterator();
while(var4.hasNext()) {
Object key = var4.next();
String val = this.props.getProperty(key.toString());
if ("".equals(val)) {
options.put(key.toString(), null);
} else {
options.put(key.toString(), val.replace("{$contextPath}", getPlatformBaseDir()));
}
}
if (!this.mysqlInstance.isRunning()) {
this.mysqlInstance.start("Em_MySQL", options, false, keys.contains("defaults-file"));
}
}
public String getPort() {
return this.port;
}
public boolean isRunning() {
return null == this.mysqlInstance ? false : this.mysqlInstance.isRunning();
}
public void shutdown() {
if (this.mysqlInstance != null) {
this.mysqlInstance.shutdown();
}
}
public void cleanup() {
if (this.mysqlInstance != null) {
this.mysqlInstance.cleanup();
}
}
}
配置文件?MySql_general.properties?内容如下
# MySQL Server Instance Configuration File # ---------------------------------------------------------------------- # Generated by the MySQL Server Instance Configuration Wizard # # # Installation Instructions # ---------------------------------------------------------------------- # # On Linux you can copy this file to /etc/my.cnf to set global options, # mysql-data-dir/my.cnf to set server-specific options # (@localstatedir@ for this installation) or to # ~/.my.cnf to set user-specific options. # # On Windows you should keep this file in the installation directory # of your server (e.g. C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server X.Y). To # make sure the server reads the config file use the startup option # "--defaults-file". # # To run run the server from the command line, execute this in a # command line shell, e.g. # mysqld --defaults-file="C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server X.Y\my.ini" # # To install the server as a Windows service manually, execute this in a # command line shell, e.g. # mysqld --install MySQLXY --defaults-file="C:\Program Files\MySQL\MySQL Server X.Y\my.ini" # # And then execute this in a command line shell to start the server, e.g. # net start MySQLXY # # # Guildlines for editing this file # ---------------------------------------------------------------------- # # In this file, you can use all long options that the program supports. # If you want to know the options a program supports, start the program # with the "--help" option. # # More detailed information about the individual options can also be # found in the manual. # # # CLIENT SECTION # ---------------------------------------------------------------------- # # The following options will be read by MySQL client applications. # Note that only client applications shipped by MySQL are guaranteed # to read this section. If you want your own MySQL client program to # honor these values, you need to specify it as an option during the # MySQL client library initialization. # port=3336 default-character-set=utf8 # The default storage engine that will be used when create new tables when default-storage-engine=INNODB # Set the SQL mode to strict sql-mode="STRICT_TRANS_TABLES,NO_AUTO_CREATE_USER,NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION" # The maximum amount of concurrent sessions the MySQL server will # allow. One of these connections will be reserved for a user with # SUPER privileges to allow the administrator to login even if the # connection limit has been reached. max_connections=800 # Query cache is used to cache SELECT results and later return them # without actual executing the same query once again. Having the query # cache enabled may result in significant speed improvements, if your # have a lot of identical queries and rarely changing tables. See the # "Qcache_lowmem_prunes" status variable to check if the current value # is high enough for your load. # Note: In case your tables change very often or if your queries are # textually different every time, the query cache may result in a # slowdown instead of a performance improvement. query_cache_size=200M # The number of open tables for all threads. Increasing this value # increases the number of file descriptors that mysqld requires. # Therefore you have to make sure to set the amount of open files # allowed to at least 4096 in the variable "open-files-limit" in # section [mysqld_safe] table_cache=1520 # Maximum size for internal (in-memory) temporary tables. If a table # grows larger than this value, it is automatically converted to disk # based table This limitation is for a single table. There can be many # of them. tmp_table_size=66M # How many threads we should keep in a cache for reuse. When a client # disconnects, the client's threads are put in the cache if there aren't # more than thread_cache_size threads from before. This greatly reduces # the amount of thread creations needed if you have a lot of new # connections. (Normally this doesn't give a notable performance # improvement if you have a good thread implementation.) thread_cache_size=38 #*** MyISAM Specific options # The maximum size of the temporary file MySQL is allowed to use while # recreating the index (during REPAIR, ALTER TABLE or LOAD DATA INFILE. # If the file-size would be bigger than this, the index will be created # through the key cache (which is slower). myisam_max_sort_file_size=128M # If the temporary file used for fast index creation would be bigger # than using the key cache by the amount specified here, then prefer the # key cache method. This is mainly used to force long character keys in # large tables to use the slower key cache method to create the index. myisam_sort_buffer_size=128M # Size of the Key Buffer, used to cache index blocks for MyISAM tables. # Do not set it larger than 30% of your available memory, as some memory # is also required by the OS to cache rows. Even if you're not using # MyISAM tables, you should still set it to 8-64M as it will also be # used for internal temporary disk tables. key_buffer_size=384M # Size of the buffer used for doing full table scans of MyISAM tables. # Allocated per thread, if a full scan is needed. read_buffer_size=64K read_rnd_buffer_size=256K # This buffer is allocated when MySQL needs to rebuild the index in # REPAIR, OPTIMZE, ALTER table statements as well as in LOAD DATA INFILE # into an empty table. It is allocated per thread so be careful with # large settings. sort_buffer_size=1M #*** INNODB Specific options *** # Use this option if you have a MySQL server with InnoDB support enabled # but you do not plan to use it. This will save memory and disk space # and speed up some things. #skip-innodb # Additional memory pool that is used by InnoDB to store metadata # information. If InnoDB requires more memory for this purpose it will # start to allocate it from the OS. As this is fast enough on most # recent operating systems, you normally do not need to change this # value. SHOW INNODB STATUS will display the current amount used. innodb_additional_mem_pool_size=12M # If set to 1, InnoDB will flush (fsync) the transaction logs to the # disk at each commit, which offers full ACID behavior. If you are # willing to compromise this safety, and you are running small # transactions, you may set this to 0 or 2 to reduce disk I/O to the # logs. Value 0 means that the log is only written to the log file and # the log file flushed to disk approximately once per second. Value 2 # means the log is written to the log file at each commit, but the log # file is only flushed to disk approximately once per second. innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit=0 # The size of the buffer InnoDB uses for buffering log data. As soon as # it is full, InnoDB will have to flush it to disk. As it is flushed # once per second anyway, it does not make sense to have it very large # (even with long transactions). innodb_log_buffer_size=8M # InnoDB, unlike MyISAM, uses a buffer pool to cache both indexes and # row data. The bigger you set this the less disk I/O is needed to # access data in tables. On a dedicated database server you may set this # parameter up to 80% of the machine physical memory size. Do not set it # too large, though, because competition of the physical memory may # cause paging in the operating system. Note that on 32bit systems you # might be limited to 2-3.5G of user level memory per process, so do not # set it too high. innodb_buffer_pool_size=256M # Size of each log file in a log group. You should set the combined size # of log files to about 25%-100% of your buffer pool size to avoid # unneeded buffer pool flush activity on log file overwrite. However, # note that a larger logfile size will increase the time needed for the # recovery process. innodb_log_file_size=64M # Number of threads allowed inside the InnoDB kernel. The optimal value # depends highly on the application, hardware as well as the OS # scheduler properties. A too high value may lead to thread thrashing. innodb_thread_concurrency=10
配置文件?platform-map.properties?内容如下
#String key = System.getProperty("os.name") + "-" + System.getProperty("os.arch");
#key = key.replace(' ', '_').replace('/', '_').replace('\\', '_');
Linux-i386=Linux-i386
Linux-x86=Linux-i386
Linux-i686=Linux-i386
Linux-x86_64=Linux-i386
Linux-amd64=Linux-i386
Linux-ia64=Linux-i386
#Linux-ppc=Linux-ppc
#Linux-ppc64=Linux-ppc
Mac_OS_X-i386=Mac_OS_X-i386
Mac_OS_X-x86_64=Mac_OS_X-i386
Mac_OS_X-ppc=Mac_OS_X-ppc
Rhapsody-PowerPC=Mac_OS_X-ppc
#Mac_OS-PowerPC=
#macos-PowerPC=
#MacOS-PowerPC=
SunOS-sparc=SunOS-sparc
Solaris-sparc=SunOS-sparc
SunOS-sparcv9=SunOS-sparc
SunOS-x86=SunOS-x86
Solaris-x86=SunOS-x86
SunOS-amd64=SunOS-x86
FreeBSD-x86=FreeBSD-x86
#For x86 only
Windows_7-x86=Win-x86
Windows_Vista-x86=Win-x86
Windows_2003-x86=Win-x86
Windows_XP-x86=Win-x86
Windows_2000-x86=Win-x86
Windows_NT-x86=Win-x86
Windows_NT_(unknown)-x86=Win-x86
Windows_Server_2008-x86=Win-x86
#For x64 only
Windows_7-amd64=Win-x64
Windows_10-amd64=Win-x64
Windows_Vista-amd64=Win-x64
Windows_2003-amd64=Win-x64
Windows_XP-amd64=Win-x64
Windows_2000-amd64=Win-x64
Windows_NT-amd64=Win-x64
Windows_NT_(unknown)-amd64=Win-x64
Windows_Server_2008-amd64=Win-x64
#Windows_98-x86=
#Windows_95-x86=
#Windows_95-Pentium=
#Windows_CE-Unknown=
启动main类后
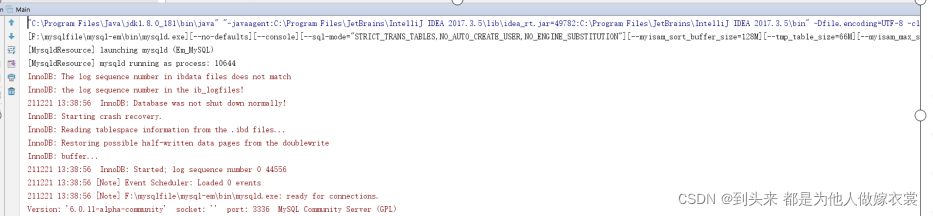
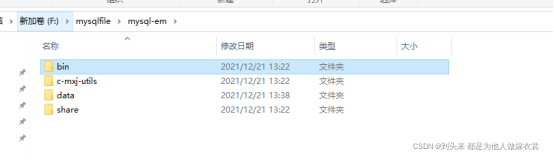
执行后会在f:\mysqlfile目录释放一个150M大小的mysql免安装包
?
?
实质上是启动一个独立的mysqld进程,端口为3336(可在配置文件中指定)。使用navicat连接的时候
初始用户名密码是root/空密码。