- 谷粒商城-分布式基础篇【环境准备】
- 谷粒商城-分布式基础【业务编写】
- 谷粒商城-分布式高级篇【业务编写】持续更新
- 谷粒商城-分布式高级篇-ElasticSearch
- 谷粒商城-分布式高级篇-分布式锁与缓存
- 项目托管于gitee
一、异步复习
1.1、线程回顾
初始化线程的4种方式
- 继承 Thread
- 实现 Runnable 接口
- 实现 Callable接口 + FutureTask (可以拿到返回结果,可以处理异常)
- 线程池
- Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
- ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue workQueue, ThreadFactory threadFactory, RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
区别:
-
方式1和方式2:主进程无法获取线程的运算结果。不适合当前场景
-
方式3:主进程可以获取线程的运算结果,但是不利于控制服务器中的线程资源。可以导致服务器资源耗尽。
-
方式4:可以控制资源,系统性能稳定
通过线程池性能稳定,也可以获取执行结果,并捕获异常。但是,在业务复杂情况下,一个异步调用可能会依赖于另一个异步调用的执行结果。
我们以后在业务代码里面,以上三种启动线程的方式都不用。【将所有的多线程异步任务都交给线程池执行】
public class ThreadTest {
// 当前系统池只有一两个,每个异步任务直接提交给线程池,让他自己去执行
public static ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
System.out.println("main...start....");
/**
* 1. 继承 Thread
* Thread01 thread = new Thread01();
* thread.start();
* 2. 实现 Runnable 接口
* Runable01 runable01 = new Runable01();
* new Thread(runable01).start();
* 3. 实现 Callable接口 + FutureTask (可以拿到返回结果,可以处理异常)
* FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(new Callable01());
* new Thread(futureTask).start();
* // 阻塞等待整个线程执行完成,获取返回结果
* Integer integer = futureTask.get();
* 4. 线程池
* 给线程池直接提交任务.
* 我们以后在业务代码里面,以上三种启动线程的方式都不用。【将所有的多线程异步任务都交给线程池执行】
* 区别:
* 1、2不能得到返回值,3可以获取返回值
* 1、2、3都不能控制资源
* 4 可以控制资源,系统性能稳定
*/
service.execute(new Runable01());
}
public static class Thread01 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("当前线程: " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10/2;
System.out.println("运行结果:" + i);
}
}
public static class Runable01 implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("当前线程: " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10/2;
System.out.println("运行结果:" + i);
}
}
public static class Callable01 implements Callable<Integer> {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("当前线程: " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10/2;
System.out.println("运行结果:" + i);
return i;
}
}
}
1.2、线程池
线程池[ExecutorService]
- 给线程池直接提交任务.
- 我们以后在业务代码里面,以上三种启动线程的方式都不用。【将所有的多线程异步任务都交给线程池执行】
- 原生:service.execute(new Runable01());
- 创建
1)、Executors
2)、new ThreadPoolExecutor() - 好处:
- 降低资源的消耗:通过重复利用已经创建好的线程降低线程的创建和销毁带来的损耗
- 提高响应速度 :因为线程池中的线程数没有超过线程池的最大上限时,有的线程处于等待分配任务的状态,当任务来时无须创建新的线程就能执行
- 提高线程的可管理性 :线程池会根据当前系统特点对池内的线程进行优化处理,减少创建和销毁线程带来的系统开销。无限的创建和销毁线程不仅消耗系统资源,还降低系统的稳定性,使用线程池进行统一分配
1.2.1、七大参数
七大参数
-
corePoolSize :
核心线程数[一直存在,除非设置(allowCoreThreadTimeOut)],创建好以后就准备的线程数量,就等待来接受异步任务去执行 -
maximumPoolSize :
最大线程数量;控制资源 -
keepAliveTime :
存活时间,如果当前线程数量大于核心线程数,只要线程空闲大于指定的时间(keepAliveTime),就会释放空闲的核心线程外的线程(maximumPoolSize - corePoolSize)。 -
unit :
时间单位 -
BlockingQueue workQueue
阻塞队列,如果任务很多,线程都在工作,将目前多的任务放在队列里面。只要有线程空闲,就会去队列里面取出新的任务继续执行 -
ThreadFactory
线程创建的工厂 -
RejectedExecutionHandler
如果队列满了,按照我们指定的拒绝策略,拒绝执行任务
- AbortPolicy :抛出运行时异常RejectedExecutionException。这种策略丢弃任务,并抛出异常。(jdk默认策略)
- CallerRunsPolicy : 线程调用运行该任务的 execute 本身。此策略提供简单的反馈控制机制,能够减缓新任务的提交速度。
- DiscardOldestPolicy(弃老策略)jdk:如果执行程序尚未关闭,则位于工作队列头部的任务将被删除,然后重试执行程序。
- DiscardPolicy :发生拒绝策略时,不触发任何动作
1.2.2、线程的工作顺序
工作顺序
-
线程池创建,准备好core数量的核心线程,准备接受任务
-
新的任务进来,用core准备好的空闲线程执行
2.1、core满了,就将再进来的任务放入阻塞队列中。空闲的core就会自己去阻塞队列获取任务执行
2.2、阻塞队列满了,就直接开新线程执行,最大只能开到max指定的数量
2.3、max满了就用RejectedExecutionHandler拒绝任务2.4、max都执行完成,有很多空闲,在指定的时间keepAliveTime以后,释放空闲的线程(max-core)。
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>():默认是Integer的最大值,可能会导入内存不够
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5,
200,
10,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(100000),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy()
);
面试题:一个线程池 core 7, max 20, queue 50, 100并发进来怎么分配的
- 7个会立即执行
- 50个进入阻塞队列
- 再开13个线程进行执行
- 剩下的30个就使用拒绝策略
1.2.3、常见的4种线程池
常见的4种线程池
- newCachedThreadPool
创建一个可缓存线程池,如果线程池长度超过处理需要,可灵活回收空闲线程,若无可回收,则新建线程。core是0,所有都可以回收 - newFixedThreadPool
创建一个定长线程池,可控制线程最大并发数,超出的线程会在对队列中等待。固定大小,core=max。都不可回收 - newScheduledThreadPool
创建一个定长线程池。支持定势及周期性人去执行。定时任务的线程池 - newSingleThreadExecutor
创建一个单线程化的线程池,他只会用唯一的工作线程来执行任务,保证所有任务。后台从队列里面获取任务,挨个执行
二、CompletableFuture 组合式异步编排
业务场景:
查询商品详情页的逻辑比较复杂,有些数据还需要远程调用,必然需要话费更多的时间:
- 获取sku的基本信息 0.5s
- 获取sku的图片信息 0.5s
- 获取sku的促销信息 1s
- 获取spu的所有销售属性 1s
- 获取规格参数组及组下的规格参数 1.5s
- spu详情 1s
假如商品详情页的每个查询,需要如下标注的时间才能完成。那么,用户需要5.5s后才能看到商品详情页的内容。很显然是不能接受的。如果有多个线程同时完成这6步操作,也许只需要1.5s即可完成响应
2.1、创建异步对象
创建异步对象
CompletableFuture 提供了四个静态方法来创建一个异步操作。
- runAsync方法不支持返回值。
- supplyAsync可以支持返回值。
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable)
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor)
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier)
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor)
没有指定Executor的方法会使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool() 作为它的线程池执行异步代码。如果指定线程池,则使用指定的线程池运行。以下所有的方法都类同。
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
System.out.println("main...start....");
/**
* 方法完成之后的感知
*/
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程: " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 0;
System.out.println("运行结果:" + i);
return i;
}, executor).whenComplete((result,exception)->{
// 虽然能得到异常信息,但是没法修改返回数据
System.out.println("异步任务成功完成了...结果是:" + result+";异常是:"+exception);
}).exceptionally(throwable -> {
// 可以感知异常同时返回指定默认值
System.out.println(throwable);
return 10;
});
System.out.println(future2.get());
System.out.println("main...end....");
}
2.2、计算完成时回调方法
计算完成时回调方法
当CompletableFuture的计算结果完成,或者抛出异常的时候,可以执行特定的Action。主要是下面的方法:
//可以处理异常,无返回值
public CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action)
public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action)
public CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T,? super Throwable> action, Executor executor)
//可以处理异常,有返回值
public CompletableFuture<T> exceptionally(Function<Throwable,? extends T> fn)
whenComplete 可以处理正常和异常的计算结果【感知】,exceptionally 处理异常情况【修改】
whenComplete 和 whenCompleteAsync 的区别:
- whenComplete :是执行当前任务的线程继续执行 whenComplete 的任务
- whenCompleteAsync : 是执行把 whenCompleteAsync 这个任务继续提交给线程池来进行执行
方法不以 Async 结尾,意味着 Action 使用相同的线程执行,而 Async 可能会使用其他线程执行(如果是使用相同的线程池,也可能会被同一个线程选中执行)
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
System.out.println("main...start....");
/*
CompletableFuture<Void> future1 = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程: " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 2;
System.out.println("运行结果:" + i);
}, executor);*/
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程: " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 0;
System.out.println("运行结果:" + i);
return i;
}, executor).whenComplete((result,exception)->{
// 虽然能得到异常信息,但是没法修改返回数据
System.out.println("异步任务成功完成了...结果是:" + result+";异常是:"+exception);
}).exceptionally(throwable -> {
// 可以感知异常同时返回指定默认值
return 10;
});
System.out.println(future2.get());
System.out.println("main...end....");
}
2.3、handle 方法
handle 方法
handle 是执行任务完成时对结果的处理。 handle 方法和 thenApply 方法处理方式基本一样。不同的是:
- handle 是在任务完成后再执行,还可以处理异常的任务。
- thenApply 只可以执行正常的任务,任务出现异常则不执行 thenApply 方法。
public <U> CompletionStage<U> handle(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn,Execut
/**
* 方法执行完成后的处理
*/
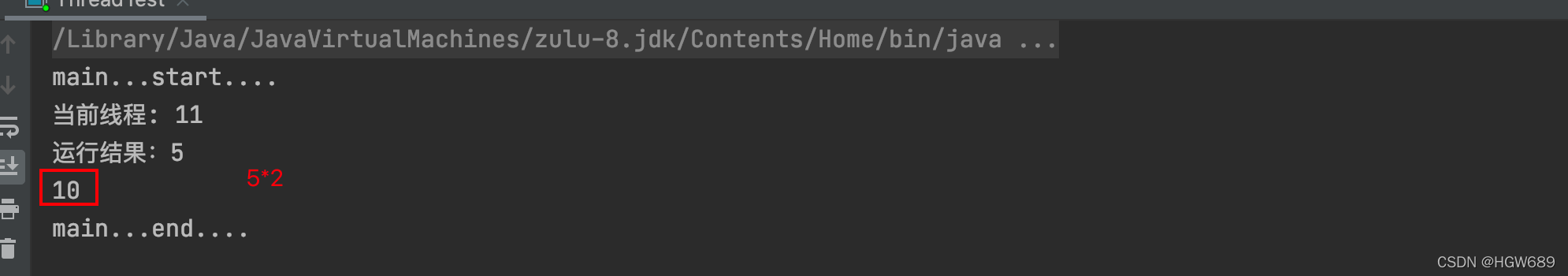
CompletableFuture<Integer> future3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程: " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 2;
System.out.println("运行结果:" + i);
return i;
}, executor).handle((res,thr)->{
if (res != null) {
return res *2;
}
if (thr != null) {
return 0;
}
return 0;
});
System.out.println(future3.get());
2.4、线程串行化
线程串行化
- thenRun 方法:
只要上面的任务执行完成,就开始执行 thenRun,只要处理完任务后,执行 thenRun 的后续操作 - thenAccept 方法:
消费处理结果。接收任务的处理结果,并消费处理,无返回结果。 - thenApply 方法:
当一个线程依赖另一个线程时,获取上一个任务返回的结果,并返回当前任务的返回值。
带有 Async 默认是异步执行的。同之前
- 不带 Asycn :共同同一个线程
- 带 Asycn : 交给线程池来进行执行
// thenRun
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRun(Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action,
Executor executor);
// thenAccept
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action);
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action);
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action,
Executor executor);
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> thenApplyAsync
(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> thenApplyAsync
(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn,
Executor executor);
测试代码:
/**
* 线程串行化
* 1)、thrnRun :不能获取到上一步的执行结果,并无返回值
* 2)、thenAccept : 能接收上一步结果,但是无返回值
* 3)、thenApply :能接收上一步结果,并有返回值
*/
CompletableFuture<Void> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程1: " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 2;
System.out.println("运行结果:" + i);
return i;
}, executor).thenRunAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务2启动了...");
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<Void> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程2: " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 2;
System.out.println("运行结果:" + i);
return i;
}, executor).thenAcceptAsync(res->{
System.out.println("任务2启动了..." + res);
},executor);
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("当前线程2: " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 2;
System.out.println("运行结果:" + i);
return i;
}, executor).thenApplyAsync(res -> {
System.out.println("任务2启动了..." + res);
return "Hello" + res;
}, executor);
System.out.println("返回值:"+future.get());
2.5、两任务组合-都要完成
两任务组合-都要完成
thenCombine 会把两个 CompletionStage 的任务都执行完成后,把两个任务的结果一块交给 thenCombine 来处理。
-
runAfterBoth
组合两个 future,不需要获取 future 的结果,只需两个 future 处理完任务后,处理该任务。两个CompletionStage,都完成了计算才会执行下一步的操作(Runnable)
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterBoth(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action); public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action); public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action,Executor -
thenAcceptBoth
组合两个 future,获取两个 future 任务的返回结果,然后处理任务,没有返回值
当两个CompletionStage都执行完成后,把结果一块交给thenAcceptBoth来进行消耗public <U> CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBoth(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action); public <U> CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action); public <U> CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action, Executor executor); -
thenCombine
组合两个 future,获取两个 future 的返回结果,并返回当前任务的返回值
thenCombine 会把 两个 CompletionStage 的任务都执行完成后,把两个任务的结果一块交给 thenCombine 来处理。public <U,V> CompletionStage<V> thenCombine(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn); public <U,V> CompletionStage<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn); public <U,V> CompletionStage<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn,Executor executor);
测试代码:
/**
* 两个异步任务都完成
*/
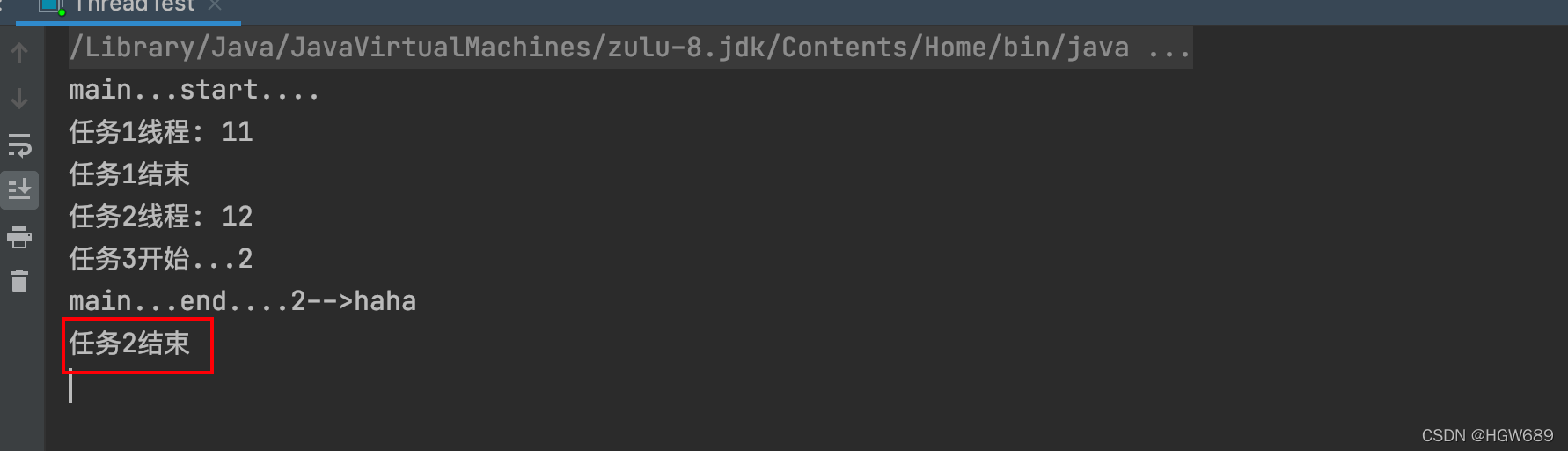
CompletableFuture<Integer> future01 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务1线程: " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 4;
System.out.println("任务1结束");
return i;
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<String> future02 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务2线程: " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
System.out.println("任务2结束");
return "Hello";
}, executor);
future01.runAfterBothAsync(future02, ()->{
System.out.println("任务3开始...");
},executor);
future01.thenAcceptBothAsync(future02, (f1,f2)->{
System.out.println("任务3开始,之前的结果:f1="+f1+";f2="+f2);
},executor);
CompletableFuture<String> future = future01.thenCombineAsync(future02, (f1, f2) -> {
return f1 + ":" +f2 +"->HaHa";
}, executor);
System.out.println("方法3的返回结果:" + future.get());
2.6、两任务组合-只要有一个任务完成就执行第三个
两任务组合-只要有一个任务完成就执行第三个
两个 CompletionStage 的返回类型要一致
-
runAfterEither 方法
两个任务有一个任务完成,不需要获取 future 的结果,处理任务,也没有返回值
两个CompletionStage,任何一个完成了都会执行下一步的操作(Runnable)public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterEither(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action); public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action); public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage<?> other,Runnable action,Executor executor); -
acceptEither 方法
两个任务有一个执行完成,获取它的返回值,处理任务,没有新的返回值
两个CompletionStage,谁执行返回的结果快,我就用那个CompletionStage的结果进行下一步的消耗操作。public CompletionStage<Void> acceptEither(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Consumer<? super T> action); public CompletionStage<Void> acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Consumer<? super T> action); public CompletionStage<Void> acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Consumer<? supe -
applyToEither 方法
两个任务有一个执行完成,获取它的返回值,处理任务并有新的返回值
两个CompletionStage,谁执行返回的结果快,我就用那个CompletionStage的结果进行下一步的转化操作。public <U> CompletionStage<U> applyToEither(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Function<? super T, U> fn); public <U> CompletionStage<U> applyToEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Function<? super T, U> fn); public <U> CompletionStage<U> applyToEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,Function<? sup
测试代码:
/**
* 两个异步任务只要有一个完成,我们就执行任务3
* runAfterEither: 不感知结果,自己也没有返回值
* acceptEither : 感知结果,自己没有返回值
*/
CompletableFuture<Object> future01 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务1线程: " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
int i = 10 / 4;
System.out.println("任务1结束");
return i;
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<Object> future02 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("任务2线程: " + Thread.currentThread().getId());
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("任务2结束");
return "Hello";
}, executor);
// CompletableFuture<Void> future3 = future01.runAfterEitherAsync(future02, () -> {
// System.out.println("任务3开始...");
// }, executor);
// CompletableFuture<Void> future4 = future01.acceptEitherAsync(future02, (res) -> {
// System.out.println("任务3开始..." + res);
// }, executor);
CompletableFuture<String> future = future01.applyToEitherAsync(future02, res -> {
System.out.println("任务3开始..." + res);
return res.toString() + "-->haha";
}, executor);
System.out.println("main...end...." + future.get());
}
2.7、多任务组合
- allOf : 等待所有任务完成
- anyOf :只有一个任务完成
public static CompletableFuture<Void> allOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs);
public static CompletableFuture<Object> anyOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs);
allOf 测试代码:
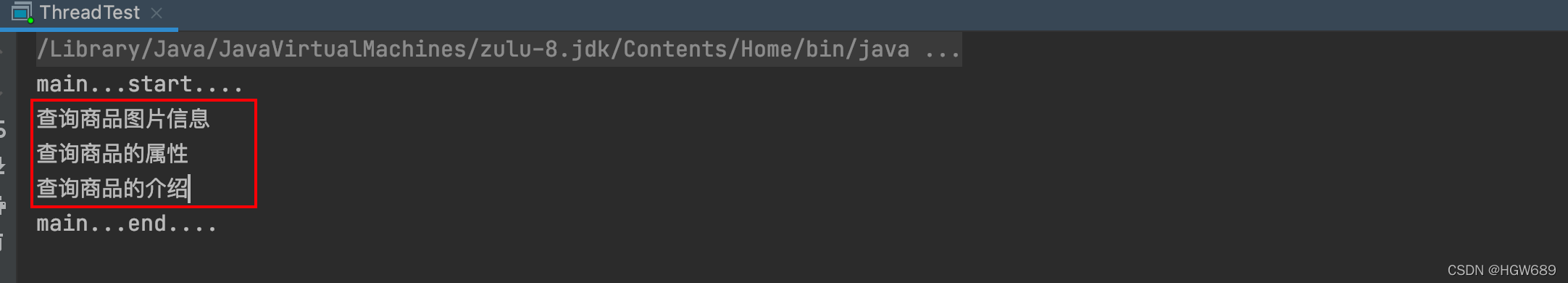
CompletableFuture<String> futureImg = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("查询商品图片信息");
return "hllo.jpg";
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<String> futureAttr = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("查询商品的属性");
return "星空白+256G";
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<String> futureDesc = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("查询商品的介绍");
return "苹果";
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<Void> allOf = CompletableFuture.allOf(futureImg, futureAttr, futureDesc);
allOf.get(); // 等待所有结果完成
System.out.println("main...end...." );
anyOf 测试代码:
CompletableFuture<String> futureImg = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("查询商品图片信息");
return "hllo.jpg";
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<String> futureAttr = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("查询商品的属性");
return "星空白+256G";
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<String> futureDesc = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("查询商品的介绍");
return "苹果";
}, executor);
CompletableFuture<Object> anyOf = CompletableFuture.anyOf(futureImg, futureAttr, futureDesc);
anyOf.get();
