任务控制
一、编写循环和条件任务
1. 循环简介
-
Ansible支持使用
loop关键字对一组项目迭代任务(旧版本使用with_items,与loop用法一致)- 循环过程:
loop关键字添加到任务中,将应对其迭代任务的项目列表取为值- 循环变量
item保存每个迭代过程中使用的值(内部原理有机会RHCA再研究吧)
-
示例
# 如下示例除了参数name不一致,其余都一致,就可以写成循环
- name: Postfix is running
service:
name: postfix
state: started
- name: Dovecot is running
service:
name: dovecot
state: started
# 改写为简单循环
- name: Postfix and Dovecot are running
service:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: started
loop:
- postfix
- dovecot
# 简单来说就是将loop下的列表依次迭代的赋值给item
# loop下的列表也可以写成变量的形式(下面给出完整写法)
---
- name:
vars:
mail_services:
- postfix
- dovecot
tasks:
- name: Postfix and Dovecot are running
service:
name: "{{ item }}"
state: started
loop: "{{ mail_services }}"
2. 循环字典列表
- 在上例中我们循环的是列表中的纯量
- loop列表中的项也可以是散列或字典,使用
item.xx的形式调用 - 示例
# zhangsan存在且为wheel组,lisi存在且为root组
- name: Users exist and are in the correct groups
user:
name: "{{ item.name }}"
state: present
group: "{{ item.groups }}"
loop:
- name: zhangsan
groups: wheel
- name: lisi
groups: root
3、将Register变量与Loop一起使用
- register关键字也可以捕获循环任务的输出
- 示例
vim loop_register.yml
---
- name: Loop Register Test
gather_facts: no # 不收集事实,上一篇有讲
hosts: localhost
tasks:
- name: Looping Echo Task
shell: "echo This is my item: {{ item }}"
loop:
- one
- two
register: echo_results # 注册运行结果echo_results变量
- name: Show echo_results variable
debug:
var: echo_results
- 分析结果
- 查看
Task[Show echo_results variable]下的"echo_results"变量
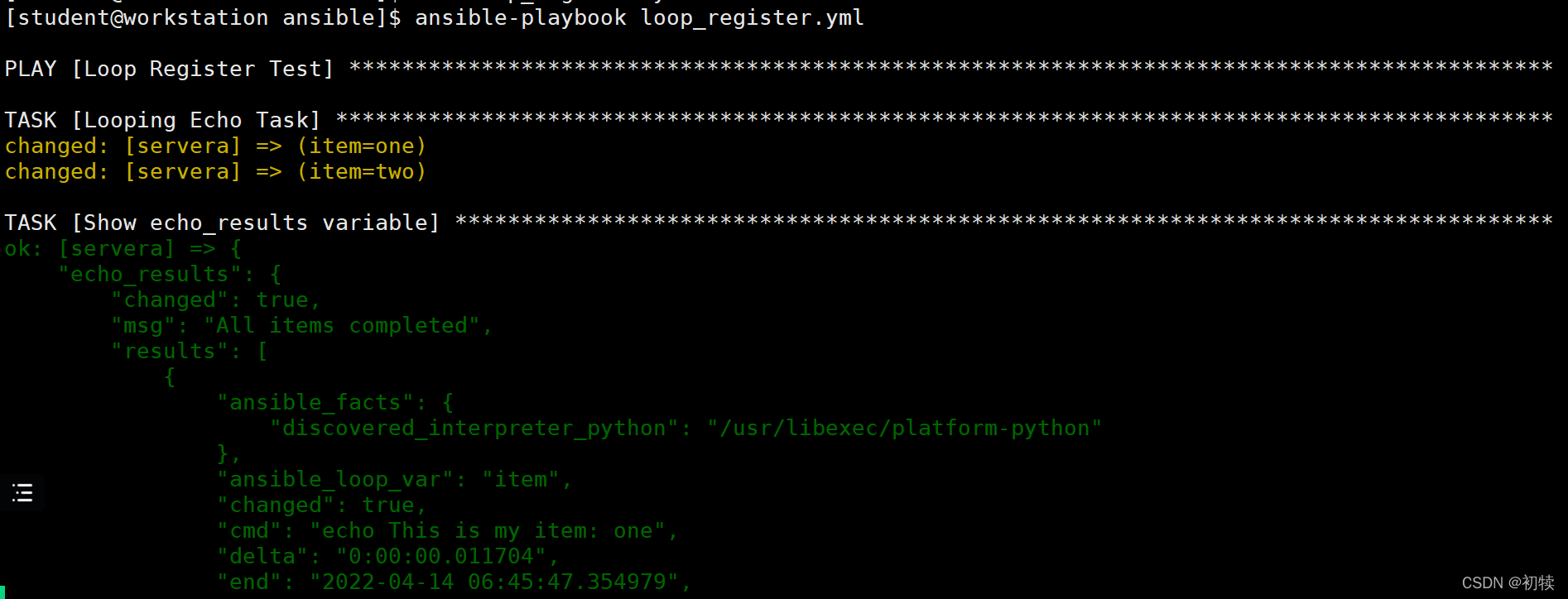
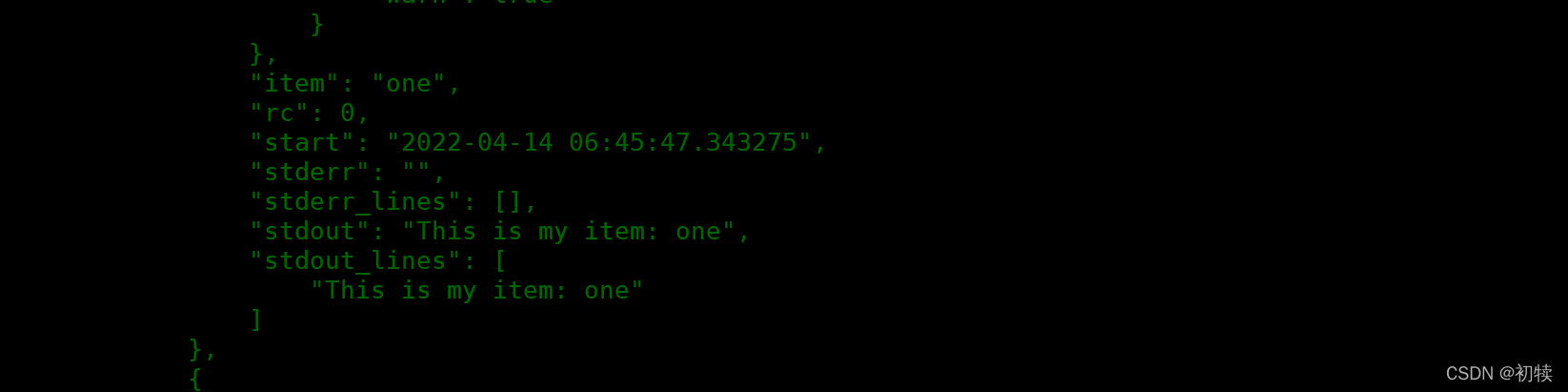
- 常用字段
"注册变量.rc/注册变量['results'].rc"、"注册变量.stdout/注册变量.['results'].stdout"等- 可利用循环
echo_results字典中的results列表来打印某些信息(虽然考试绝对不会考…不过也不难理解) - 示例打印输出结果
- 可利用循环
---
- name: Loop Register Test
gather_facts: no # 不收集事实,上一篇有讲
hosts: localhost
tasks:
- name: Looping Echo Task
shell: "echo This is my item: {{ item }}"
loop:
- one
- two
register: echo_results
- name: Show echo_results variable
debug:
msg: "STDOUT from previous task: {{ item.stdout }}" # 即迭代打印echo_results['results']列表中的stdout对象的值
loop: "{{ echo_results['results'] }}"
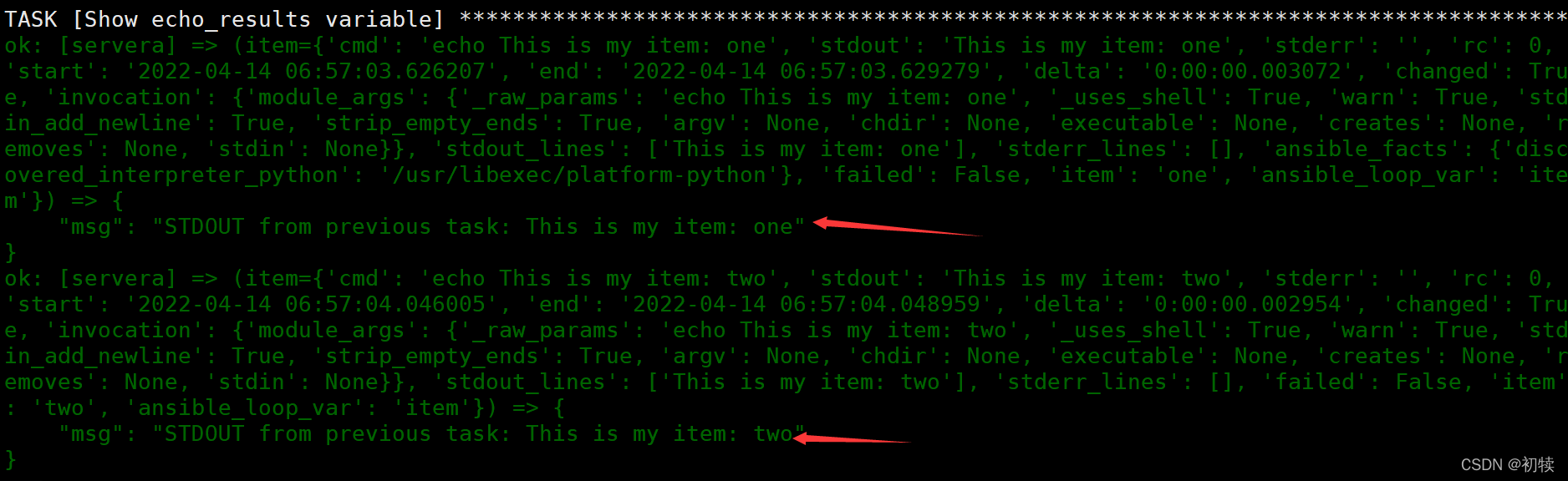
4. 条件简介
- Ansible可使用
conditionals在符合特定条件时执行任务或play - 可以作为条件的变量
- Playbook变量
- 注册变量
- Ansible事实等
- 可能的应用场景
- 可以在变量中定义硬限制(如min_memory)并将它与受管主机上的可用内存进行比较。
- Ansible可以捕获并评估命令的输出,以确定某一任务在执行进一步操作前是否已经完成。例如,如果某一程序失败,则将跳过批处理。
- 可以利用 Ansible 事实来确定受管主机网络配置,并且决定要发送的模板文件〈如,网络绑定或中继)。
- 可以评估 CPU 的数量,来确定如何正确调节某一 Web 服务器。
- 将注册的变量与预定义的变量进行比较,以确定服务是否已更改。例如,测试服务配置文件的 MD5 校验和以查看服务是否已更改。
5、条件任务
when语句用于有条件的运行任务,类似if- 简单示例
# 直接使用布尔变量作为条件
---
- name: simple Boolean Task Demo
hosts: all
vars:
run_my_task: true
tasks:
- name: httpd package is installed
yum:
name: httpd
when: run_my_task
# is defined是否定义作为条件
---
- name: Test Variable is Defined Demo
hosts: all
vars:
my_service: httpd
tasks:
- name: "{{ my_service }} package is installed"
yum:
name: "{{ my_service }}"
when: my_service is defind
- 书上的可用条件
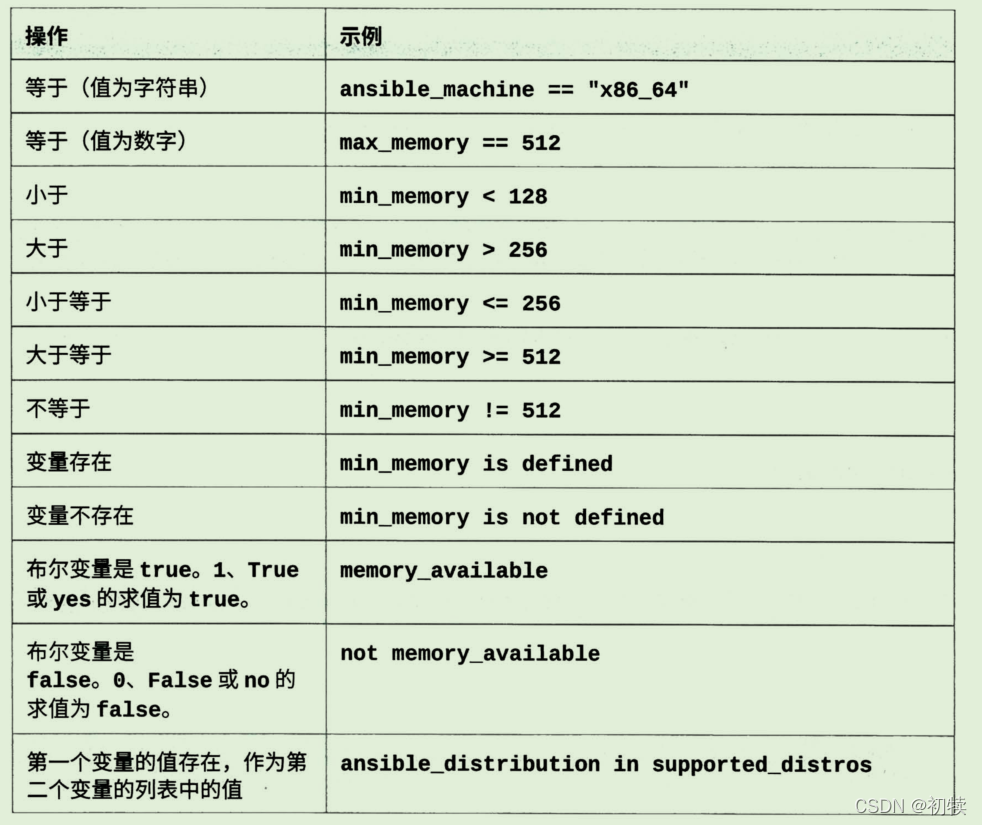
-
最后一个条件成立的要求
- 第一个变量和第二个列表存在
- 第一个变量是第二个列表中的某个值
- 以上两个条件同时成立
-
简单示例
---
- name: Demonstrate the "in" keyword
hosts: all
gather_facts: yes
vars:
supported_distros:
- RedHat
- Fedora
tasks:
- name: Install httpd using yum,where supported
yum:
name: http
state: present
# ansible_distribution是一个事实变量,可以setup模块查看
when: ansible_distribution in supported_distros
6. 多条件任务
- 一个when语句可用于评估多个条件。为此,可以使用and或 or关键字组合条件,并使用括号分组条件。
- when关键字还支持使用列表来描述条件列表,此时效果相当于and
- 使用大于字符(>),可以让长条件在playbook中分成多行,以便于阅读
# 使用列表来描述条件列表,相当于and
# 如果远程主机是红帽企业Linux7.5主机,并且安装的内核是指定版本,则下述条件语句得到满足。
when:
- ansible_distribution_version == "7.5"
- ansible_kernel == "3.10.0-327.el7.x86_64"
# 大于字符分行长条件
# 如果计算机上运行的是红帽企业Linux7或Fedora 28,则下述条件语句得到满足。
when: >
( ansible_distribution == "RedHat" and
ansible_distribution_major_version == "7" )
or
( ansible_distribution == "Fedora" and
ansible_distribution_major_version == "28" )
7. 结合循环和有条件任务
例1:
在下例中,yum模块将安装 mariadb-server软件包,只要/上挂载的文件系统具有超过300MB的可用空间。ansible_mounts事实是一组字典,各自代表一个已挂载文件系统的相关事实。循环迭代列表中的每一字典,只有找到了代表两个条件都为真的已挂载文件系统的字典时,条件语句才得到满足。
- name: install mariadb-server if enough space on root
yum:
name: mariadb-server
state: latest
# ansible_mounts是一个事实的字典列表的变量
loop: "{{ ansible_mounts }}"
# 迭代此列表,筛选满足条件
when: item.mount == "/" and item.size_available > 300000000
- 此例中通过事实来判断是否执行
例2:
下面是组合使用条件和注册变量的另一个示例。下方标注的playbook只有在postfix服务处于运行状态时才会重新启动httpd服务。
- name: Restart HTTPD if Postfix is Running
hosts: all
tasks:
- name: Get Postfix server status
command: /usr/bin/systemctl is-active postfix
ignore_errors: yes
# 保存结果信息
register: result
- name: Restart Apache HTTPD based on Postfix status
service:
name: httpd
state: restarted
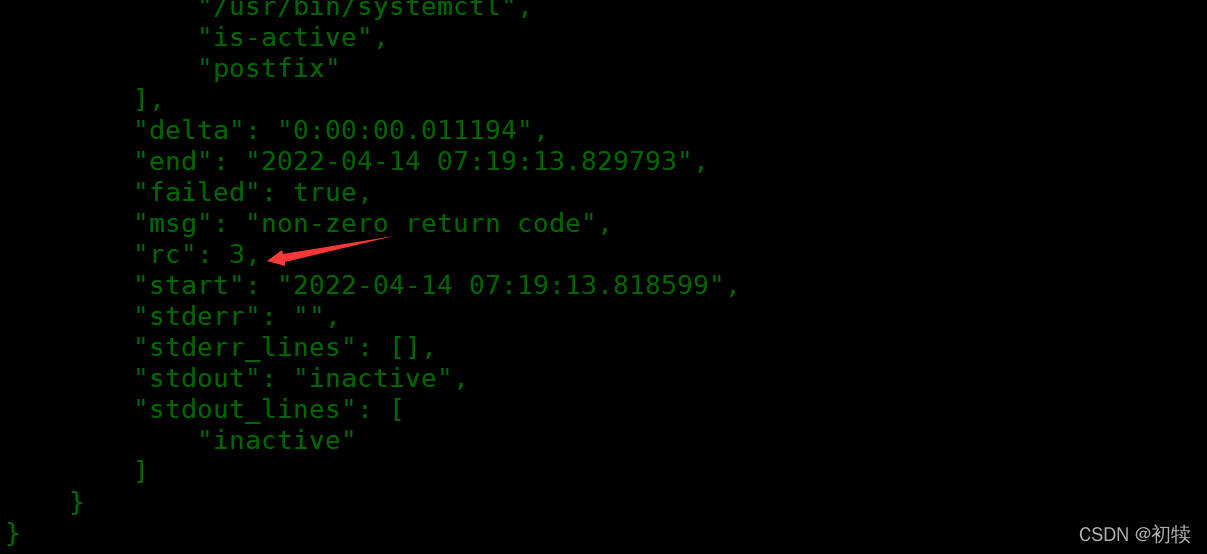
# 根据结果信息中的rc判断是否执行成功
when: result.rc == 0
- 此例中通过register注册变量来判断是否执行
二、实施处理程序
1. 简介
- Ansible模块设计为具有幂等性。即在正确编写的playbook中,playbook及其任务可以运行多次而不会改变受管主机,除非需要进行更改使受管主机进入所需的状态。
- 处理程序是响应由其他任务触发的通知的任务。
- 仅当任务在受管主机上更改了某些内容时(changed),任务才通知其处理程序。
- 每个处理程序具有全局唯一的名称,在playbook中任务块的末尾触发。如果没有任务通过名称通知处理程序,处理程序就不会运行。
- 如果一个或多个任务通知处理程序,处理程序就会在play中的所有其他任务完成后运行一次。
2. 语法
-
处理程序可视为非活动任务,只有在使用notify语句显式调用时才会被触发。
-
handlers以数组的形式定义notify调用的处理函数。
-
简单示例
tasks:
- name: copy demo.example.conf configuration template
template:
src: /var/lib/templates/demo.example.conf.template
dest: letc/httpd/conf.d/demo.example.conf
# 配置文件更新则显示调用restart apache
notify:
- restart apache
# 与tasks处于同一层级
# restart apache处理函数
handlers:
- name: restart apache
service:
name: httpd
state: restarted
# 注意点:
# 1.notify和handlers的名字必须一一对应
# 2.可将其写成数组的形式迭代的调用多个处理函数
3. 描述处理程序的好处
- 处理程序始终按照play的handlers部分指定的顺序运行。它们不按在任务中由notify语句列出的顺序运行,或按任务通知它们的顺序运行。
- 处理程序通常在相关 play中的所有其他任务完成后运行。playbook的tasks部分中某一任务调用的处理程序,将等到tasks下的所有任务都已处理后才会运行。
- 处理程序名称存在于各play命名空间中。如果两个处理程序被错误地给予相同的名称,则仅会运行一个。
- 即使有多个任务通知处理程序,该处理程序依然仅运行一次。如果没有任务通知处理程序,它就不会运行。
- 如果包含notify语句的任务没有报告changed结果(例如,软件包已安装并且任务报告ok),则处理程序不会获得通知。处理程序将被跳过,直到有其他任务通知它。只有相关任务报告了changed状态,Ansible才会通知处理程序。
三、处理任务失败
1. 简介
- Ansible评估各任务的返回代码,从而确定任务是成功还是失败
- 通常而言,当任务失败时,Ansible将立即在该主机上中止 play的其余部分并且跳过所有后续任务
- 如果想即使在任务失败时也继续执行play。可以使用如下三种方法处理任务失败
- 相当于程序设计的异常处理
2. 忽略任务失败
- 通过忽略失败的任务覆盖中止的行为,在任务中使用
ignore_errors来实现 - 简单示例
- name: Latest version of notapkg is installed
yum:
# 即使notapkg软件包不存在也会继续执行此playbook
name: notapkg
state: latest
# 忽略错误
ignore_errors: yes
3. 任务失败后强制执行处理程序
-
通常而言,如果任务失败并且 play在该主机上中止,则收到play中早前任务通知的处理程序将不会运行
-
设置
force_handlers: yes参数,即使play因为后续任务失败而中止也会调用被通知的处理程序 -
简单示例
---
- hosts: all
# 注意是在此处加
force_handlers: yes
tasks:
- name: a task which always notifies its handler
command: /bin/true
notify: restart the database
- name: a task which fails because the package doesn't exist
yum:
name: notapkg
state: latest
# 即使上面安装失败,处理程序照样执行
handlers:
- name : restart the database
service:
name: mariadb
state: restarted
# 注
# 处理程序会在任务报告changed结果时获得通知,而在任务报告ok或failed结果时不会获得通知。
4. 指定任务失败条件
failed_when:指定任务失败的条件效果同fail....when(可以理解为何时raise一个异常)
# failed_when
tasks:
- name: Run user creation script
shell: /usr/local/bin/create_users.sh
register: command_result
failed_when: "'Password missing' in command_result.stdout"
#fail....when
tasks:
- name: Run user creation script
shell: /usr/ local/bin/create_users.sh
register: command_result
ignore_errors: yes
- name: Report script failure
fail:
msg: "The password is missing in the output"
when: "'Password missing' in command_result.stdout"
5. 指定何时任务报告“Changed”结果
-
人为指定任务是否报告changed状态,通常和处理程序handlers一起使用
-
示例
tasks:
- shell:
cmd: /usr/local/bin/upgrade-database
register: command_result
changed_when: " 'Success' in command_result.stdout"
notify:
- restart_database
handlers:
- name: restart_database
service:
name: mariadb
state: restarted
6. Ansible块和错误处理
-
非常类似程序的异常处理
- 方式一:使用when进行条件判断(类比if)
- 方式二:使用专门的错误处理语句(类比
try...catch/except...finally)
-
这里重点讲方式二
- block:定义要运行的主要任务。(类比try)
- rescue:定义要在block子句中定义的任务失败时运行的任务。(类比catch/except)
- always:定义始终都独立运行的任务,不论block和rescue子句中定义的任务是成功还是失败。(类比finally)
-
简单示例
tasks:
- name: upgrade DB
block:
- name: upgrade the database
shell:
cmd: /usr/loca1/lib/upgrade-database
rescue:
- name: revert the database upgrade
shell:
cmd: /usr/local/lib/revert-database
always:
- name: always restart the database
service:
name: mariadb
state: restarted
