第03章 使用PreparedStatement实现CRUD操作
创作日期:2021-12-07
3.1 操作和访问数据库
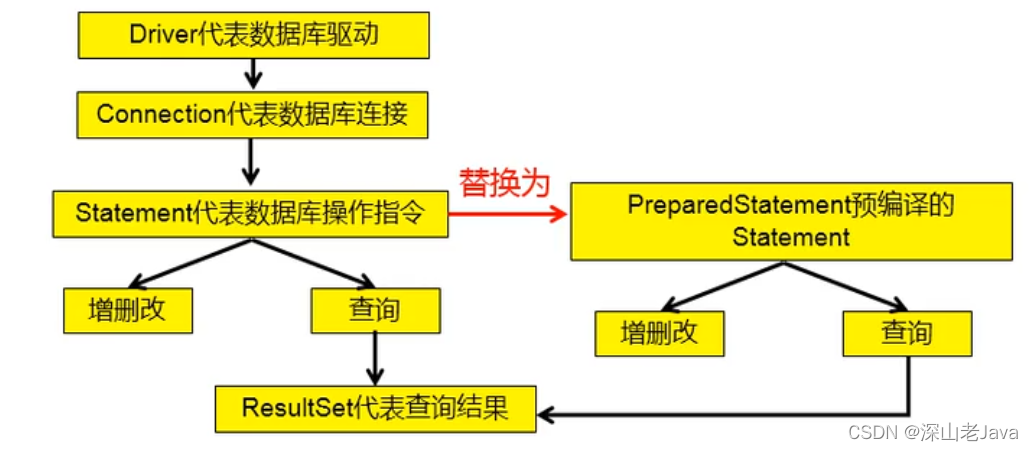
- 数据库连接被用于向数据库服务器发送命令和SQL语句,并接受数据库服务器返回的结果。其实一个数据库连接就是一个Socket连接。
- 在 java.sql 包中有3个接口分别定义了对数据库的调用的不同方式:
- Statement:用于执行静态 SQL 语句并返回它所生成结果的对象。
- PrepatedStatement:SQL 语句被预编译并存储在此对象中,可以使用此对象多次高效的执行该语句。
- CallableStatement:用于执行 SQL 存储过程。
3.2 使用Statement操作数据表的弊端
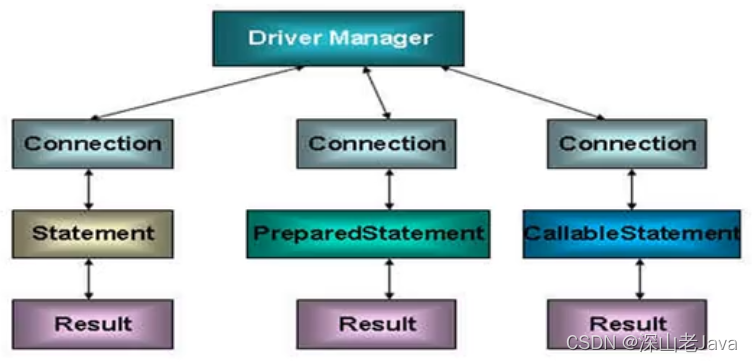
- 通过调用 Connection 对象的 createStatement() 方法创建该对象。该对象用于执行静态的SQL语句,并且返回执行结果。
- Statement 接口中定义了下列方法用于执行 SQL 语句:
int excuteUpdate(String sql):执行更新操作INSERT,UPDATE,DELETE
ResultSet executeQuery(String sql):执行查询操作SELECT
- 但是使用Statement操作数据表存在弊端:
- 问题一:存在拼串操作,繁琐
- 问题二:存在SQL注入问题
- SQL 注入是利用某些系统没有对用户输入的数据进行充分的检查,而在用户输入数据中注入非法的 SQL 语句段或命令(如:SELECT user,password FROM user_table WHERE user='a' OR 1 = 'AND password = ' OR '1' = '1'),从而利用系统的SQL引擎完成恶意行为的做法。
- 对于 java 而言,要防范 SQL 注入,只需用 PreparedStatement(从Statement扩展而来)取代 Statement 就可以了。
3.3 PreparedStatement的使用
3.3.1?PreparedStatement介绍
- 可以通过调用 Connection 对象的 preparedStatement(String sql)?方法获取 PreparedStatement 对象
- PreparedStatement 接口是?Statement 的子接口,它表示一条预编译过的 SQL 语句
- PreparedStatement 对象所代表的 SQL语句中的参数用(?)来表示,调用?PreparedStatement 对象的 setXxx() 方法来设置这些参数,setXxx() 方法有两个参数,第一个参数是要设置的 SQL 语句中的参数的索引(从1开始),第二个是设置的 SQL 语句中的参数的值
3.3.2?PreparedStatement vs Statement
- 代码的可读性和可维护性。
- PreparedStatement 能最大可能提高性能:
- DBServer会对预编译语句提供性能优化。因为预编译语句有可能被重复调用,所以语句在被DBServer的编译器编译后的执行代码被缓存下来,那么下次调用时只要是相同的预编译语句就不需要编译,只要将参数直接传入编译过的语句执行代码就会得到执行。
- 在 statement 语句中,即使是相同操作但因为数据内容不一样,所以整个语句本身不能匹配,没有缓存语句的意义,事实是没有数据库会对普通语句编译后的执行代码缓存。这样每执行一次都要对传入的语句编译一次。
- (语法检查,语义检查,翻译成二进制命令,缓存)
- PreparedStatement ?可以防止 SQL 注入
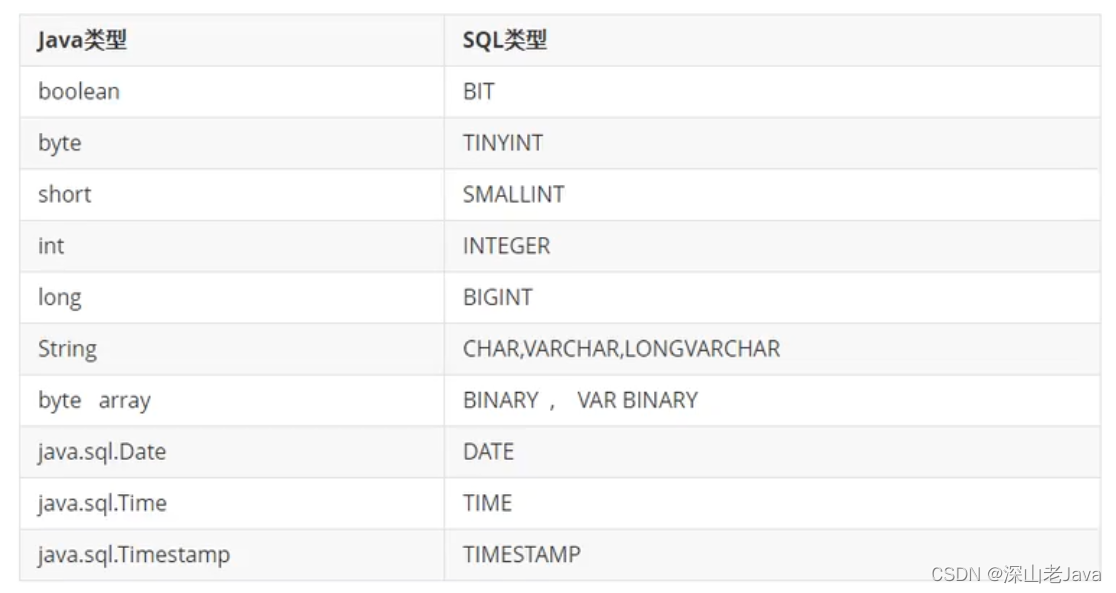
3.3.3 Java与SQL对应数据类型转换表
3.3.4 使用PreparedStatement实现增,删,改操作
package com.lmq.preparedstatement_curd;
/*
* 使用PreparedStatement来替换Statement,实现对数据表的增删改查操作
*/
import com.lmq.util.JDBCUtils;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
public class PreparedStatementUpdateTest1 {
//向表中添加一条记录
@Test
public void testInsert() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
//1.获取数据库连接
connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//2.预编译sql语句,返回PreparedStatement的实例
@SuppressWarnings("SqlResolve") String sql = "insert into sales(city,county,sales_value)values (?,?,?)";//?:占位符
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//3.填充占位符
preparedStatement.setString(1, "河南");
preparedStatement.setString(2, "郑州");
preparedStatement.setInt(3, 55);
//4.执行操作
preparedStatement.execute();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//5.关闭资源
JDBCUtils.closeResource(connection, preparedStatement);
}
}
//修改表中的一条记录
@Test
public void testRevise() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
//1.获取数据库连接
connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//2.预编译sql语句,返回PreparedStatement的实例
@SuppressWarnings("SqlResolve") String sql = "update sales set sales_value = ? where city = ?";//?:占位符
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//3.填充占位符
preparedStatement.setInt(1, 25);
preparedStatement.setString(2, "河南");
//4.执行操作
preparedStatement.execute();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//5.关闭资源
JDBCUtils.closeResource(connection, preparedStatement);
}
}
//删除表中的一条记录
@Test
public void testDelete() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
try {
//1.获取数据库连接
connection = JDBCUtils.getConnection();
//2.预编译sql语句,返回PreparedStatement的实例
@SuppressWarnings("SqlResolve") String sql = "DELETE from sales where city = ?";//?:占位符
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//3.填充占位符
preparedStatement.setString(1, "河南");
//4.执行操作
preparedStatement.execute();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//5.关闭资源
JDBCUtils.closeResource(connection, preparedStatement);
}
}
}
package com.lmq.util;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* @Description:操作数据库的工具类
* @author: XFDQ.lmq
* @create: 2022-04-23 10:51
*/
public class JDBCUtils {
//获取数据库连接
public static Connection getConnection() throws Exception {
//1.读取配置文件
InputStream inputStream = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(inputStream);
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String driverClass = properties.getProperty("driverClass");
//2.加载驱动
Class.forName(driverClass);
//3.获取连接
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
return connection;
}
//资源的关闭
public static void closeResource(Connection connection, PreparedStatement preparedStatement) {
try {
if (connection != null)
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (preparedStatement != null)
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//jdbc.properties 配置文件
user=root
password=123456
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/dbtest3_9
driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver3.3.5 使用PreparedStatement实现查询操作
package com.lmq.preparedstatement_curd;
import com.lmq.customer.Customer1;
import com.lmq.util.JDBCUtils;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* @Description:针对于表的查询操作
* @author: XFDQ.lmq
* @create: 2022-04-23 14:52
*/
public class PreparedStatementQuery1 {
@Test
public void testQuery1() {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
try {
//1.创建数据库连接
InputStream inputStream = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(inputStream);
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String password = properties.getProperty("password");
String url = properties.getProperty("url");
String driverClass = properties.getProperty("driverClass");
Class.forName(driverClass);
connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
//2.编译sql语句
@SuppressWarnings("SqlResolve") String sql = "select city,county,sales_value from sales where id = ?";
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
preparedStatement.setInt(1,4);
//3.执行sql语句,并返回结果集
resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
//4.处理结果集
if (resultSet.next()) {
//获取当前数据的各个字段的值
String city = resultSet.getString(1);
String county = resultSet.getString(2);
int sales_value = resultSet.getInt(3);
//方式一:直接输出
System.out.println("city = " + city + "," + "county = " + county + "," + "sales_value = " + sales_value);
//方式二:转换成数组
Object[] data = new Object[]{city, county, sales_value};
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
System.out.print(data[i] + ",");
}
System.out.println();
//方式三:将数据封装为一个对象
Customer1 customer1 = new Customer1(city, county, sales_value);
System.out.println(customer1);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//5.关闭资源
try {
if (connection != null)
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (preparedStatement != null)
preparedStatement.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (resultSet != null)
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
3.5 资源的释放
- 释放ResultSet,PreparedStatement,Connection。
- 数据库连接(Connection)是非常稀有的资源,用完后必须马上释放,如果Connection不能及时正确的关闭将导致系统宕机。Connection的使用原则是尽量晚创建,尽量早的释放。
- 可以在finally中关闭,保证及时其他代码出现异常,资源也一定能被关闭。
#资源的释放
connection.close();
preparedStatement.close();
resultSet.close();3.6 JDBC API小结
上一节:
下一节: