Ehcache缓存
说道缓存,大家想到的是一定是Redis,确实在国内Redis被大量应用,推上了新的高度!但是不一定所有的场合都要使用Redis,例如服务器资源紧缺,集成不方便的时候就可以考虑使用本地缓存。
1、Ehcache简介
1.1、概述
缓存应该是每个系统都要考虑的架构,缓存不仅可以加速系统的访问速度还可以提升系统的性能。如我们需要经常访问的高频热点数据,如果把它缓存起来就能有效减少数据库服务器的压力。手机验证码等有一定的失效时间,我们就可以考虑使用缓存,等失效时间过了,就删掉验证码。因此市面上缓存组件也层出不进,常见的有
JCache:Java缓存API。由JSR107定义,定义了5个核心接口,分别是CachingProvider,CacheManager,Cache,Entry和ExpriyEhCache:纯Java的进程内缓存框架,jvm虚拟机中缓存、速度快,效率高,是Hibernate中默认的CacheProvider,但是共享缓存与集群分布式应用整合不方便Redis:生态完善,通过socket访问缓存服务,效率上是比EhCache低的,但是在集群模式、分布式应用上就比较成熟,是大型应用首先中间件Caffeine:Caffeine是使用Java8对Guava缓存的重写版本,有人称它为缓存之王
本文也是主要介绍Ehcache本地缓存的使用,相对来说使用还是比较广泛,出现时间也比较早,拥有的优点也不少,能满足大多数场景,非常适合做本地缓存。
主要的特性有:
- 快速
- 简单
- 多种缓存策略(设置有效期等)
- 缓存数据有两级:内存和磁盘,因此无需担心容量问题
- 缓存数据会在虚拟机重启的过程中写入磁盘
- 可以通过RMI、可插入API等方式进行分布式缓存
- 具有缓存和缓存管理器的侦听接口
- 支持多缓存管理器实例,以及一个实例的多个缓存区域
- 提供Hibernate的缓存实现
jar包获取方式:
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/net.sf.ehcache/ehcache -->
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sf.ehcache</groupId>
<artifactId>ehcache</artifactId>
<version>2.10.6</version>
</dependency>
1.2、Spring缓存抽象
在Spring中使用缓存,就不得不说Spring中的缓存抽象。为了简化缓存的开发Spring从3.1开始定义了org.springframework.cache.Cache和org.springframework.cache.CacheManager接口来统一不同的缓存技术或组件。例如 JCache、 EhCache、 Hazelcast、 Guava、 Redis 等,具体规范如下:
- Cache接口为缓存的组件规范定义,包含缓存的各种操作集合
- Cache接口下Spring提供了各种xxxCache的实现。如RedisCache,EhCacheCache ,ConcurrentMapCache等
- 每次调用需要缓存功能的方法时,Spring会检查检查指定参数的指定的目标方法是否已经被调用过。如果有就直接从缓存中获取方法调用后的结果,如果没有就调用方法并缓存结果后返回给用户。下次调用直接从缓存中获取。
因此我们在使用这些缓存组件的时候,一定要告诉Spring我们使用的是哪一种(注册实现CacheManager接口的Bean,都不注册则会使用ConcurrentMapCacheManager默认缓存实现)。
在缓存抽象中也支持使用JCache(JSR-107)的注解去大大简化我们的开发。
| 相关注解或概念 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Cache | 缓存接口,定义缓存操作。实现有:RedistCache、EhCacheCache、ConcurrentMapCache等 |
| CacheManager | 缓存管理器,管理各种缓存(Cache)组件 |
| @Cacheable | 主要针对方法配置,能够根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存 |
| @CacheEvict | 清空缓存 |
| @CachePut | 保证方法被调用,又希望结果被缓存 |
| @EnableCaching | 开启基于注解的缓存 |
| keyGenerator | 缓存数据时key生成策略 |
| serialize | 缓存数据时value序列化策略 |
2、SpringBoot集成Ehcache
2.1、缓存效果初体验
使用SpringBoot的初始化向导或Maven快速搭建一个工程,并添加如下依赖pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.laizhenghua</groupId>
<artifactId>cache-sample</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework.boot/spring-boot-starter-web -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<version>2.5.5</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework.boot/spring-boot-starter-test -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<version>2.5.5</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.alibaba/fastjson -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.75</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/net.sf.ehcache/ehcache -->
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sf.ehcache</groupId>
<artifactId>ehcache</artifactId>
<version>2.10.6</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework.boot/spring-boot-starter-cache -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
<version>2.5.5</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
我们暂时先添加这些依赖,等往后用到什么添加什么即可。
1、编写主程序,添加@EnableCaching注解
/**
* @description: 主程序
* @author: laizhenghua
* @date: 2022/5/4 17:06
*/
@EnableCaching // 开启基于注解的缓存
@SpringBootApplication
public class ApplicationMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ApplicationMain.class, args);
}
}
2、在resources目录下,编写ehcache.xml配置文件(配置文件一般放在resources目录下),这个文件怎么编写呢?在ehcache依赖jar包中找到ehcache-failsafe.xml文件,如下图所示:

把文件内容复制到ehcache.xml,注释内容去掉,新增一个Cache标签并改造文件内容(注意Cache标签配置信息不能为空否则启动程序会报错(不能只有默认的defaultCache缓存组件),标签属性先按照以下配置后面会讲具体含义),如下所示
ehcache.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://ehcache.org/ehcache.xsd">
<diskStore path="java.io.tmpdir"/>
<!-- defaultCache -->
<defaultCache
maxElementsInMemory="10000"
eternal="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="120"
timeToLiveSeconds="120"
maxElementsOnDisk="10000000"
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU">
<persistence strategy="localTempSwap"/>
</defaultCache>
<!-- userEntityCache(有效期5min) -->
<cache name="userEntityCache" maxElementsInMemory="10" eternal="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="60"
timeToLiveSeconds="300"
overflowToDisk="true"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/>
</ehcache>
3、编写application.properties配置文件与EhCacheCacheManager类型的bean实例(指定Spring缓存抽象Cache接口和CacheManager实现是什么)
application.properties
# 指定缓存组件类型与配置文件
spring.cache.ehcache.config=classpath:cache/ehcache.xml
EhCacheConfiguration.class(注意这个类是我们自己新增的)
/**
* @description: EhCache的配置类
* @author: laizhenghua
* @date: 2022/5/4 20:08
*/
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(CacheProperties.class) // 这样写的好处就是与配置文件的配置信息进行绑定
public class EhCacheConfiguration {
private final CacheProperties cacheProperties;
public EhCacheConfiguration(CacheProperties cacheProperties) {
this.cacheProperties = cacheProperties;
}
@Bean
public EhCacheManagerFactoryBean ehCacheManagerFactory() {
EhCacheManagerFactoryBean ehCacheManagerFactory = new EhCacheManagerFactoryBean();
ehCacheManagerFactory.setConfigLocation(cacheProperties.resolveConfigLocation(cacheProperties.getEhcache().getConfig()));
ehCacheManagerFactory.setShared(true);
return ehCacheManagerFactory;
}
@Bean
public EhCacheCacheManager ehCacheCacheManager(EhCacheManagerFactoryBean ehCacheManagerFactory) {
return new EhCacheCacheManager(ehCacheManagerFactory.getObject());
}
}
4、编写控制层业务代码
/**
* @description:
* @author: laizhenghua
* @date: 2022/5/4 17:54
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@RequestMapping(value = "/getList", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public R getList() {
return R.ok().put("data", userService.getList());
}
}
5、编写业务层测试代码(注意@Cacheable注解的使用value属性就是ehcache.xml配置文件上配置的缓存名称)
/**
* @description:
* @author: laizhenghua
* @date: 2022/5/4 17:55
*/
@Service(value = "userService")
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
private static final org.apache.logging.log4j.Logger log = org.apache.logging.log4j.LogManager.getLogger(UserServiceImpl.class);
@Override
@Cacheable(value = "userEntityCache", key = "#root.method.name") // 使用方法名作为缓存的key
public List<String> getList() {
log.info("query user list start"); // 启动项目 多次请求接口 观察此日志的输出情况就能看到效果
List<String> dataList = new ArrayList<>();
dataList.add("Java");
dataList.add("Python");
dataList.add("C/C++");
dataList.add("PHP");
return dataList;
}
}
6、发起多次请求,观察日志输出情况!就能看到效果。
需要注意的是不是所有的方法加上@Cacheable注解后方法结果就会被缓存。Spring缓存抽象中注解@Cacheable也是基于面向切面的思想做的,在执行目标方法之前处理缓存逻辑!实际上就是使用动态代理,创建实例的时候注入的是代理对象,在代理对象里面调用目标方法,顺便处理缓存逻辑。因此目标方法一定是能被Spring代理到,缓存才会生效。很多初学者遇到缓存不生效也是这个原因。
后面在介绍怎么优化这种情况。
2.2、验证缓存组件走的是EhCacheCache
我们发现前面给方法加上@Cacheable注解后,如果方法参数相同,再次调用方法时,SpringBoot将不再执行目标方法,而是直接返回了结果,实现这一过程的原理又是什么呢?
/**
* {@link ImportSelector} to add {@link CacheType} configuration classes.
*/
// 这个静态类是 CacheAutoConfiguration 自动配置类旗下的一个静态类
static class CacheConfigurationImportSelector implements ImportSelector {
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
CacheType[] types = CacheType.values();
String[] imports = new String[types.length];
for (int i = 0; i < types.length; i++) {
imports[i] = CacheConfigurations.getConfigurationClass(types[i]);
}
return imports;
}
}
一切都要从自动配置类CacheAutoConfiguration的静态类CacheConfigurationImportSelector加载缓存配置类说起,SpringBoot启动的时候,加载所有缓存自动配置类,如下图所示
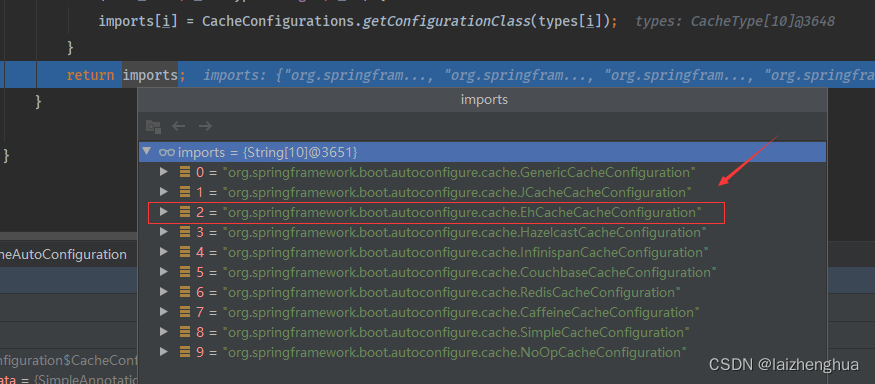
那么这么多自动缓存配置类,最终哪一个类会生效或注入IOC容器中呢?在没有导入Redis、Ehcache等配置类时,默认生效的是SimpleCacheConfiguration这个配置类时,这个默认生效的Cache实现类是ConcurrentMapCache本地map缓存。而上面案例我们是导入Ehcach了配置信息,此时生效的应该是EhCacheCacheConfiguration这个自动缓存配置类。
验证如下(主程序中打印IOC容器bean的Id):
/**
* @description: 主程序
* @author: laizhenghua
* @date: 2022/5/4 17:06
*/
@EnableCaching // 开启基于注解的缓存
@SpringBootApplication
public class ApplicationMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext = SpringApplication.run(ApplicationMain.class, args);
String[] beanDefinitionNames = applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : beanDefinitionNames) {
if (name.startsWith("eh")) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
}
}
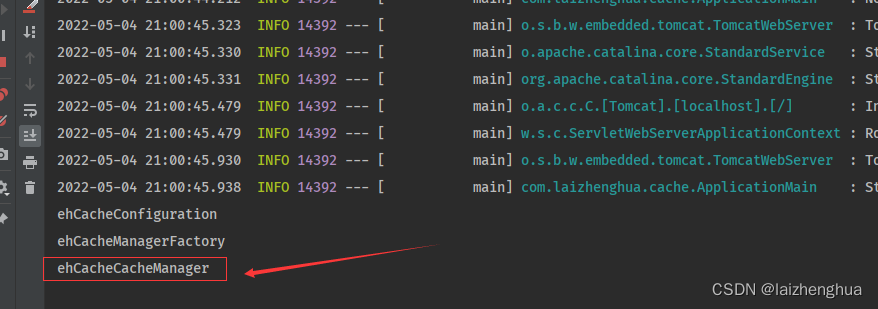
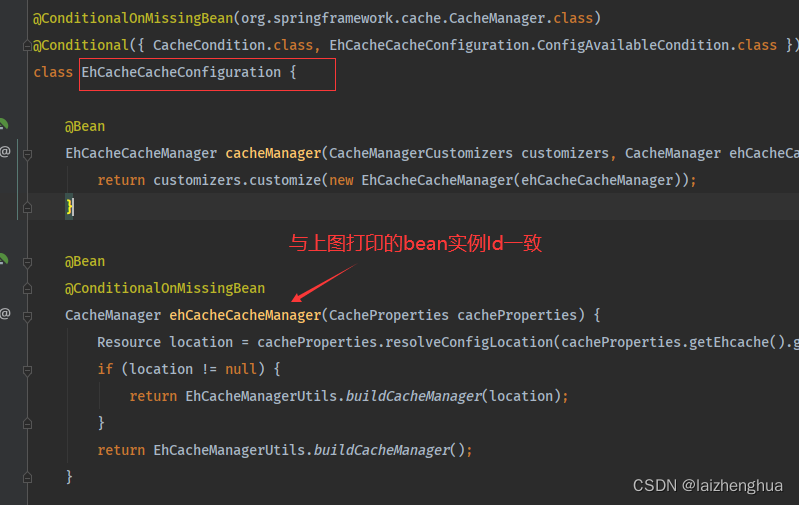
到这里大家可能会有一个疑问,为什么仅凭这样我就敢断定缓存组件CacheManager或Spring缓存抽象Cache接口的实现类走的是EhCacheCache?就是我们加入ehcache配置类后,EhCacheCacheConfiguration缓存配置类就生效了
2.3、ehcache.xml配置文件详解
这个文件只有一个作用,就是通过cache标签声明一个个缓存组件,我们可以在这里指定缓存的一些属性和缓存策略如有效期、是否保存到磁盘等,详细属性含义如下
<!-- userEntityCache(有效期5min) -->
<cache name="userEntityCache" maxElementsInMemory="10" eternal="false"
timeToIdleSeconds="60"
timeToLiveSeconds="300"
overflowToDisk="true"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/>
<!--
name 缓存名称
eternal true表示对象永不过期,此时会忽略timeToIdleSeconds和timeToLiveSeconds属性,默认为false
timeToIdleSeconds 设定允许对象处于空闲状态的最长时间,以秒为单位。当对象自从最近一次被访问后,如果处于空闲状态的时间超过了timeToIdleSeconds属性值,这个对象就会过期,EHCache将把它从缓存中清空。只有当eternal属性为false,该属性才有效。如果该属性值为0,则表示对象可以无限期地处于空闲状态
timeToLiveSeconds 设定对象允许存在于缓存中的最长时间,以秒为单位。当对象自从被存放到缓存中后,如果处于缓存中的时间超过了 timeToLiveSeconds属性值,这个对象就会过期,EHCache将把它从缓存中清除。只有当eternal属性为false,该属性才有效。如果该属性值为0,则表示对象可以无限期地存在于缓存中。timeToLiveSeconds必须大于timeToIdleSeconds属性,才有意义
maxElementsInMemory 内存中最大缓存对象数;maxElementsInMemory界限后,会把溢出的对象写到硬盘缓存中。注意:如果缓存的对象要写入到硬盘中的话,则该对象必须实现了Serializable接口才行
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy 当达到maxElementsInMemory限制时,Ehcache将会根据指定的策略去清理内存。可选策略有:LRU(最近最少使用,默认策略)、FIFO(先进先出)、LFU(最少访问次数)
maxElementsOnDisk 硬盘中最大缓存对象数,若是0表示无穷大
overflowToDisk 是否保存到磁盘,当系统宕机时
diskPersistent 是否缓存虚拟机重启期数据,是否持久化磁盘缓存,当这个属性的值为true时,系统在初始化时会在磁盘中查找文件名为cache名称,后缀名为index的文件,这个文件中存放了已经持久化在磁盘中的cache的index,找到后会把cache加载到内存,要想把cache真正持久化到磁盘,写程序时注意执行net.sf.ehcache.Cache.put(Element element)后要调用flush()方法
diskSpoolBufferSizeMB 这个参数设置DiskStore(磁盘缓存)的缓存区大小。默认是30MB。每个Cache都应该有自己的一个缓冲区
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds 磁盘失效线程运行时间间隔,默认为120秒
clearOnFlush 内存数量最大时是否清除
-->
在项目中我们集成Ehcache时配置缓存组件根据实际情况进行调整与配置即可。
