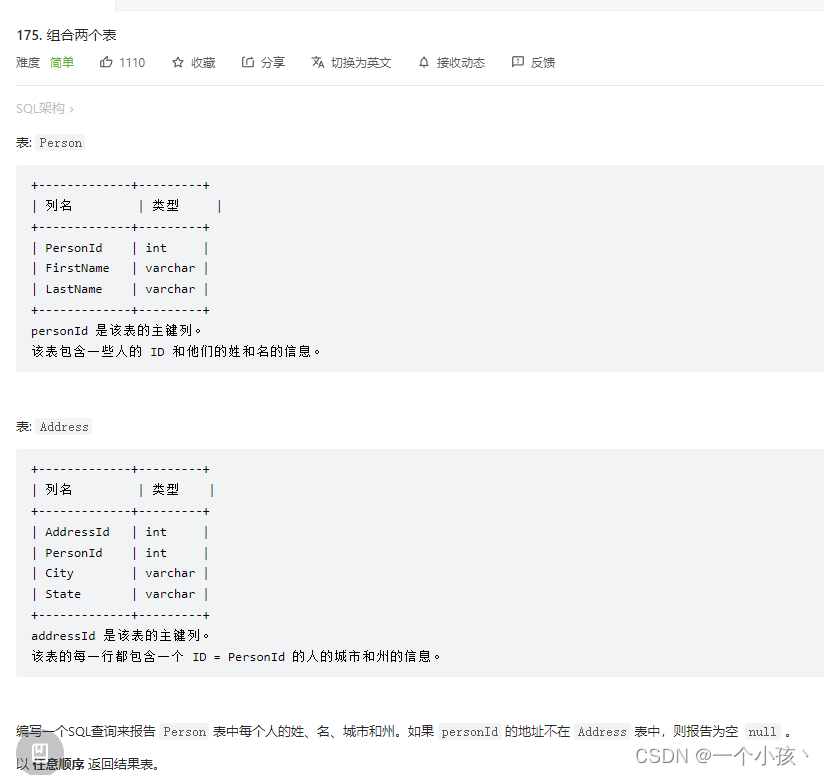
#连接后这两个就是一个表了
select firstName, lastName, city, state
from Person left join Address
on Person.PersonId = Address.PersonId;
select p.firstName, p.lastName, a.city, a.state
from Person as p left join Address as a
on p.PersonId = a.PersonId;?
?
?
?
#5.5
select ifnull((select distinct salary
from Employee
order by salary desc
limit 1 offset 1), null) as SecondHighestSalary;
?
?
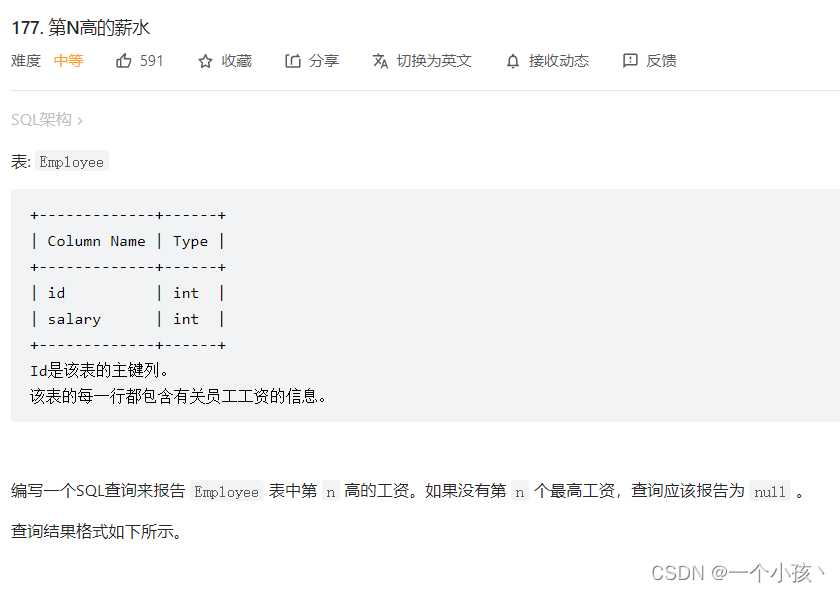
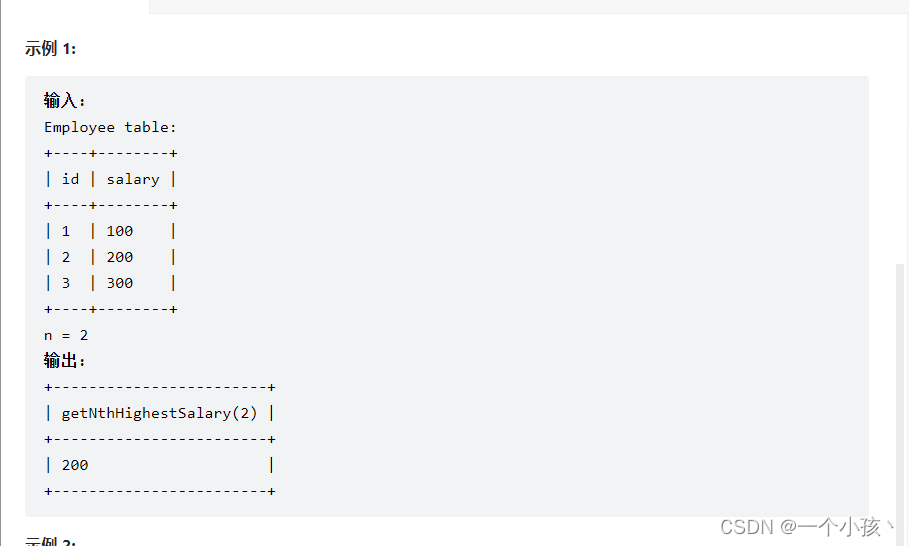
#编写一个函数
CREATE FUNCTION getNthHighestSalary(N INT) RETURNS INT
BEGIN
RETURN (
# Write your MySQL query statement below.
select distinct salary
#临时表必须命名,窗口函数的使用dense_rank()
from (select salary, dense_rank() over (order by salary desc) as a from employee) as temp
where a = N
);
END

?
# Write your MySQL query statement below
#命名的时候使用反引号,它是为了区分MYSQL的保留字(就和java中的关键字一样)与普通字符而引入的符号
#加上partition by是指定分组,比如各种学科的时候,这个不需要指定分组啊
select score, dense_rank() over (order by score desc) as `rank`
from Scores;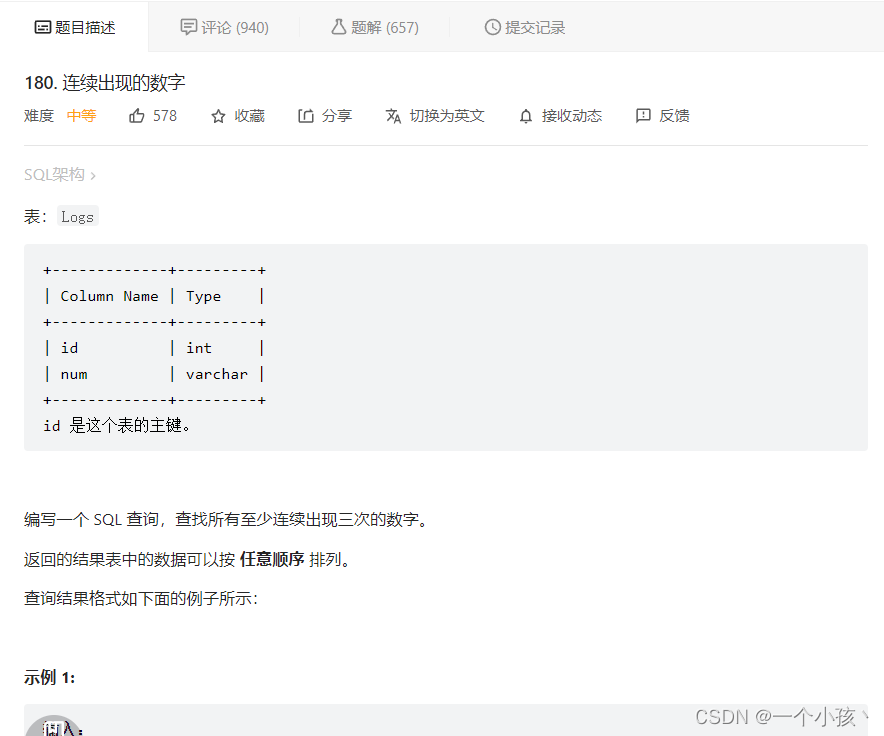
?
# Write your MySQL query statement below
#在业务层进行筛选
#非要用数据库的话就查3个表
select *
from Logs l1, Logs l2, Logs l3
where l1.Id = l2.Id - 1
and l2.Id = l3.Id - 1
and l1.Num = l2.Num
and l2.Num = l3.Num;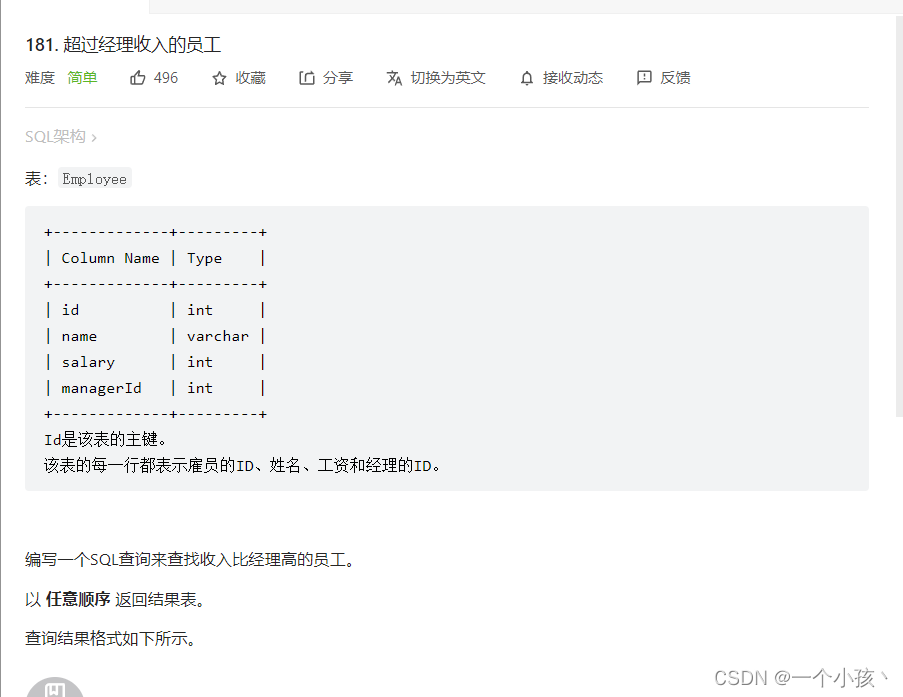
?
# Write your MySQL query statement below
# SELECT
# a.NAME AS Employee
# FROM Employee AS a JOIN Employee AS b
# ON a.ManagerId = b.Id
# AND a.Salary > b.Salary
# ;
#一个表中的查询,换个名字又是一样的新表,用自连接
#左连接返回左边全部,已经两者都有的部分
select a.name as `Employee`
from Employee as a join Employee as b on a.managerId = b.id and a.salary > b.salary;
# Write your MySQL query statement below
#先查找电子邮箱出现的次数, 在查询大于一的个数,这是临时表的方式
select Email
from (select Email, count(Email) as `num`
from Person
group by Email) as temp
where num > 1;
#优先顺序: where>group by>having>order by
select Email
from Person
group by Email
having count(Email) > 1;?
?
# Write your MySQL query statement below
#连接查询五种情况的第一种
select c.Name as Customers
from Customers as c left join Orders as o on c.Id = o.CustomerId
where o.Id is null
#子查询的方式
select customers.name as 'Customers'
from customers
where customers.id not in
(
select customerid from orders
);
?
?
# Write your MySQL query statement below
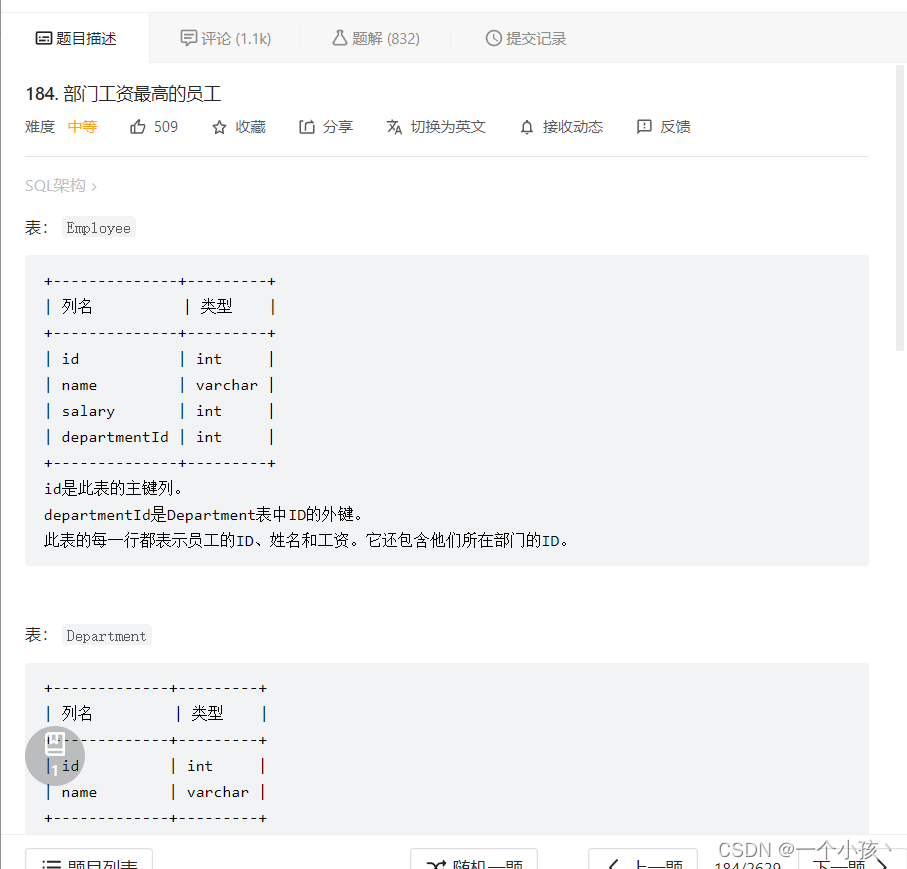
#部门工资最高的员工,不同分组中最高或着最低的问题
#真要是写起来细节很多,要记住前面带上哪个表在.
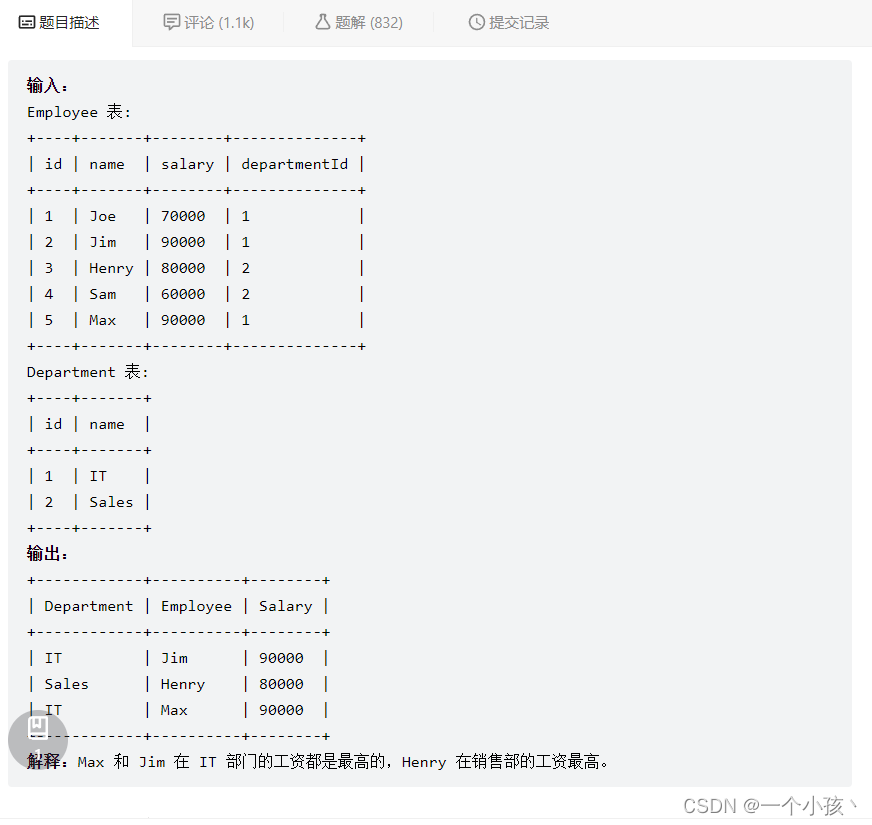
select temp.Department, temp.Employee, temp.Salary
from (select d.name as `Department`, e.name as `Employee`, e.salary as `Salary`,
#得按照原两个表中字段值多的一列写,e.department改为d.Department是错误的
dense_rank() over (partition by e.departmentId order by e.Salary desc) as `dense`
from Employee as e join Department as d on e.departmentId = d.id ) as temp
where temp.dense = 1;
?
# Write your MySQL query statement below
select temp.Department, temp.Employee, temp.Salary
from (select d.name as `Department`, e.name as `Employee`, e.salary as `Salary`,
#得按照原两个表中字段值多的一列写,e.department改为d.Department是错误的
dense_rank() over (partition by e.departmentId order by e.Salary desc) as `dense`
from Employee as e join Department as d on e.departmentId = d.id ) as temp
where temp.dense < 4;

?
# Write your MySQL query statement below
#某种意义上,p2作为临时表了,然后p1中的数据一条一条去对比
delete p1 from Person p1, Person p2 where p1.Email = p2.Email and p1.Id > p2.Id;
?
# Write your MySQL query statement below
# SELECT
# weather.id AS 'Id'
# FROM
# weather
# JOIN
# weather w ON DATEDIFF(weather.date, w.date) = 1
# AND weather.Temperature > w.Temperature
# ;
# SELECT DATEDIFF('2008-12-30','2008-12-29') AS DiffDate 结果为1; SELECT DATEDIFF('2008-12-29','2008-12-30') AS DiffDate 结果为-1。
# MySQL 使用 DATEDIFF 来比较两个日期类型的值。
select w.id
from weather as w join weather as wt on
datediff(w.recordDate, wt.recordDate) = 1 and w.Temperature > wt.Temperature;