概述
存储数据的方式
- Java程序存储数据(变量、对象、数组、集合),其实数据保存在内存中,属于瞬时状态存储
- 文件存储数据,保存在硬盘上,属于持久化存储
分类
DDL:数据定义语言
创建数据库 创建表 修改表 删除表
DML:数据操作语言
数据新增 删除 修改
DQL:数据查询语言
查询数据 表单查询 多表查询 子查询 关联查询
TCL:事务控制语言
比如:新增一个管理员(admin基本信息 admin_role管理员对应的角色信息)
addAdmin();成功
addAdminRole();失败
涉及到DML操作时需要添加事务控制,事务管理方式:commit();[数据提交,永久性入库] rollback();
[数据回滚]
DCL:数据控制语言
给用户分配权限,回收权限(保护隐私)
grant 授权
revoke 回收权限
连接数据库
mysql -h host -u user -p -- host是主机名,user是mysql的用户名
mysql -u user -p -- 连接本地数据库
DDL
-- 创建数据库
create database 库名;
create database 库名 default character set utf8; -- 创建数据库并且规定编码方式
create database 库名 default character set utf8 collate utf8_bin; -- 创建数据库,并且规定编码方式、是否区分大小写
-- 查询所有数据库
show databases;
-- 查询数据库创建语句
show create database 库名; -- CREATE DATABASE `db05` /*!40100 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8 */
-- 修改数据库编码格式
alter database 库名 character set utf8;
-- 删除库
drop database 库名;
-- 使用库
use 库名;
-- 查看当前使用库
select database();
-- 创建表
create table 表名(
字段名 字段类型[约束],
字段名 字段类型[约束]
);
-- 示例
create table user(
name varchar (20),
age int (4)
);
-- 查看表设计
describe 表名;
-- 简写
desc 表名;
-- 添加列
alter table 表名 add 列名 类型;
-- 修改列类型
alter table 表名 modify [column] 列名 类型;
-- 修改列名
alter table 表名 change 原列名 新列名 新类型;
-- 删除列
alter table 表名 drop [column] 列名;
-- 修改表名
rename table 原表名 to 新表名;
-- 修改表字符集
alter table 表名 character set 字符集;
-- 删除表
drop table 表名;
DML
-- 新增
insert into 表名 values();-- 插入所有列数据
insert into 表名 (列名) values ('数据'); -- 在指定列插入数据
insert into 表名 (列名) values ('数据'),('数据'); -- 一次性插入多条数据
-- 示例
-- insert into user (username,gender,salary,birthday,introduce) values ('rose','F',8888,'2018-07-06','good girl');
-- insert into user (username,gender,salary,birthday,introduce) values ('lucy','F',4985,'2014-03-16','good girl'), ('tom','T',6988,'2019-01-06','good boy');
-- 修改
update user set 字段名=字段值; -- 修改该列的所有值为指定值
update 表名 set 字段名=字段值 where 字段名=字段值; -- 根据where条件修改某一些记录
-- 示例
-- update user set salary=5000;
-- update user set salary=5000 where id=4;
-- update user set salary=4000.00,id=1 where gender='F';
-- update user set salary=salary+500 where gender='F';
-- 删除
delete from 表名; -- 删除表中所有的记录
delete from 表名 where 列名=值; -- 根据条件删除记录
truncate table 表名; -- 删除表中所有的记录
DQL
简单查询
-- 单列查询
select id from 表名;
-- 多列查询
select 列名1,列名2... from 表名;
-- All查询
select * from 表名;
select 所有列名 from 表名; -- 推荐使用
-- 定义列别名
select 列名 [as] 新列名 from 表名; -- select username '姓名' from user;
-- 查询结果去重
select distinct 列名 from 表名;
select distinct 列名1,列名2 from 表名; -- 联合(列名1,列名2)去重,distinct要放在select后面
-- 排序
select 列名 from 表名 order by 列名 asc/desc;
asc:升序(默认)
desc:降序
-- select * from user order by salary desc,id asc;优先薪资降序查询,然后id升序查询
条件查询
-- where查询
select 列名 from 表名 where 条件;
-- 区间判断 and 在...和...之间
select * from user where salary between 5000 and 10000; -- 闭区间
select * from user where salary not between 5000 and 10000; -- 开区间
-- 判断是否为null null值参与运算还是null
select * from user where birthday is null;
select * from user where birthday is not null;
-- in查询 可以多个数据 需要排除空,不然如果not in里面的数据有null,结果没有数据
select * from user where id=1 or id=2; -- 等价于下面
select * from user where id in (1,2);
select * from user where id!=1 and id!=2; -- 等价于下面
select * from user where id not in (1,2);
select * from emp_ju where deptno in (select deptno from dept_ju);
select * from emp_ju where deptno not in (select deptno from dept_ju where deptno is not null);
-- 模糊查询 %任意长度的任意字符 _一个字符
select * from 表名 where 列名 like '%条件%';
select * from 表名 where 列名 like '小_';
-- ifnull 判断第一个表达式是否为 NULL,如果为 NULL 则返回第二个参数的值,如果不为 NULL 则返回第一个参数的值
select IFNULL(deptno,0) from dept_ju; -- 查看deptno不为空的数据,如果为空,返回0
-- 和select * from emp_ju where deptno not in (select deptno from dept_ju where deptno is not null);作用一致
select * from emp_ju where deptno in (SELECT IFNULL(deptno,0)FROM dept_ju);
常用函数
数字函数
-- round(数字,位数) :四舍五入
select round(bnum,1) from math where num=15;
-- truncate(数字,位数) 返回被舍去至小数点后D位的数字X。D为 0, 则结果不带有小数点或不带有小数部分。
select truncate(bnum,1)from math where num=54454;
-- abs(数字):返回数据的绝对值
select abs(bnum)from math where num=54454;
-- rand() 返回一个随机浮点值 v ,范围在 0 到1 之间 (即, 其范围为 0 ≤ v ≤ 1.0)。
select rand();
-- sqrt(数字) 平方根
select sqrt(num) from math where bnum=3.29;
-- pow(x,y) x的y次方
select pow(num,2) from math where bnum=3.29;
-- mod(x,y) x/y的余数
select mod(num,2) from math where bnum=3.29;
字符串函数
-- trim(str);去除首尾的空格
select trim(str) from math where num=20;
-- concat();字符串拼接
select concat('First name',str,'Last Name')from math where num=20;
-- upper(str):转成大小
select upper(str)from math where num=16;
-- lower(str):转换小写
select lower(str)from math where num=16;
-- substring(str,1,2);-->下标从1开始(java是0),截取2个
select substring(str,2,5)from math where num=16;
时间函数
-- date(now());返回当前日期
select date(now());
-- time(now());返回当前时间
select time(now());
-- 上面两个拼接
select concat(date(now()),' ',time(now()));
-- -- date_format(时间,'%x-%m-%d %h:%i:%s'); yyyy-MM-dd
select date_format('2020-11-11 18:16:10','%x-%m-%d %h:%i:%s');
-- adddate('2020-10-10',-5);-->往前推5天 5往后推 interval:间隔
select adddate('2020-11-11 18:16:10',-5);
select date_add('2020-11-11 18:16:10',interval 3 day);
组函数
-- count()求记录数,如果count(列名)会忽略空值 COUNT(*) 函数返回表中的记录数
select count(num) from math;
-- sum():求和,忽略空值无影响
select sum(num) from math;
-- avg():求平均数,忽略空值,对结果有影响
select avg(num) from math;
-- max():求最大,忽略空值无影响
select max(num) from math;
-- min():求最小,忽略空值无影响
select min(num) from math;
分组查询
-- 查询每一个部门的最高薪水和最低薪水,要求没有部门的不在计算范围内
select deptno,max(salary),min(salary) from emp_ju where deptno is not null group by deptno;
-- 查询每一个部门下有哪一些员工
select deptno,group_concat(ename) from emp_ju where deptno is not null group by deptno;
-- 查询每一个部门的薪水总和与平均薪水,没有部门的员工不在计算范围内
select sum(salary) '薪资总和',avg(ifnull(salary,0)) '平均薪资' from emp_ju where deptno is not null group by deptno;
-- 查询平均薪水大于5000的部门
select deptno,avg(ifnull(salary,0)) avg from emp_ju where deptno is not null group by deptno having avg>5000;
-- 查询哪些部门的人数超过2个人,计算部门的平均薪水,且按照薪水的升序排序
select deptno, count(deptno)as c ,avg(ifnull(salary,0)) avg from emp_ju where deptno is not null group by deptno having c>2 order by avg;
? 注:凡是和组函数(聚合函数)同时出现的列名,则一定要写在group by之后或者使用 group_concat(列名 separator ‘:’)拼接,否则数据会有遗漏。
-- 查询-----表----条件----分组------筛选-----排序-----分页
select->from->where->group by->having->order by->limit
where与having的区别
1.where在分组前对数据进行过滤,而having是在分组后对数据进行过滤
2.having后面可以使用聚合函数,而where不可以
分页查询
-- limit(当前页,每页显示的记录数);
-- 从第几条记录开始抓取,下标(从0开始)(page-1)*pageSize pageSiz:抓取几条记录
select * from emp_ju limit ?,?;
-- 比如:查询第一页的数据,每页展示10条记录 limit 0,10
-- 查询第二页的数据,每页展示10条记录 limit 10,10
子查询
- 子查询可以区分为关联子查询和非关联子查询,他们的外层查询之间的执行顺序和关系不同
- 一个select语句中包含另外一个完整的select语句,即如果一条语句中包含两个或两个以上的select,则是子查询。
- from:主表查询 where:子表查询
非关联子查询
- 不依赖于主查询可以单独执行,并且只执行1次
- 执行过程:先执行子查询(独立的sql)->返回查询结果作为主查询的条件->最后执行主查询
- 非关联子查询比较运算符,根据子查询的结果而定:
- 单值(一条记录):> < =…
- 多值(多条记录):>any() >all() in() 将子查询记录使用组函数处理
-- 查询哪些部门的人数比30号部门人数多 先查询每个部门的人数,然后查询30号部门的人数,最后拼接
select deptno, count(deptno) c from emp_ju group by deptno having c > (select count(*) from emp_ju where deptno=30);
-- 查询哪些部门的平均薪水比20号部门的平均薪水高
select deptno,avg(ifnull(salary,0)) a from emp_ju group by deptno having a > (select avg(ifnull(salary,0)) from emp_ju where deptno=20);
-- 查询员工所在部门的平均薪水大于5000的员工姓名和职位
select deptno,ename,position,avg(ifnull(salary,0)) from emp_ju where deptno in (select deptno from emp_ju)group by deptno having avg(ifnull(salary,0))>5000;
-- 查询每个部门拿最高薪水的人是谁? (a,b)in(a,b)
select * from emp where (deptno,salary) in (select deptno,max(salary) from emp group by deptno);
关联子查询
- 子查询不是独立的语句,依赖主查询执行
- 执行过程:–>先执行主查询–>结果传递给子查询–>执行子查询–>主查询筛选子查询返回的结果
-- 查询哪些员工的薪水比本部门的平均薪水低
select * from emp e where salary < (select avg(ifnull(salary,0)) from emp where deptno=e.deptno);
-- 查询哪些人有下属
select * from emp_ju where empno in (select distinct leader from emp_ju)
-- exists:用于判断子查询有没有数据返回,如果满足关系则有数据返回,不满足则没有数据返回。exists不关心子查询返回的值,只关心是否有数据返回,因此子查询select后面写什么都可以,通常直接用1表示
select * from emp_ju e where not exists (select 1 from emp_ju where leader=e.empno);
in和exisit的使用
- 非关联子查询:in
- 关联子查询:exsist
- left 大 right 小 in
表关联查询
- 内连接:表1 [inner] join 表2 on 条件;
内连接的结果集中的数据一定是在两张表中都能找到匹配的记录 - 左连接:表1 left join 表2 on 条件;
以左边为驱动表,驱动表中的数据在结果集中都有对应的记录 - 右连接:表1 right join 表2 on 条件;
以右边为驱动表 - 全连接:不支持full out join,使用 left join union right join 实现相同的效果
外连接特点(左外/右外):
结果集=内连接结果集(匹配上)+驱动表在匹配表中匹配不上的记录(匹配不上)
如果驱动表在匹配表中找不到匹配的记录,则匹配一行空行
-- 内连接 查询员工姓名及其部门的名称(数据在两张表,deptno为共有数据)
select ename,dname from emp e inner join dept d on e.deptno=d.deptno;
-- 左连接 查询员工姓名及其部门的名称,要求没有部门的员工也要被查询出来
select ename,dname from emp e left join dept d on e.deptno=d.deptno;
-- 右外连接 以右边的表为主表,所有信息都会显示
select e.ename,d.dname from emp e right join dept d on e.deptno=d.deptno;
-- 全连接
select e.ename,d.dname from emp e left join dept d on e.deptno=d.deptno
union
select e.ename,d.dname from emp e right join dept d on e.deptno=d.deptno;
DCL
数据控制语言:控制不同用户对于数据库、表访问权限和安全级别
-- 创建用户 username:自定义账号用户名 host:数据库地址 pwssword:自定义用户密码
create user 'username'@'host' identified by 'password';
-- create user 'jack'@'localhost' identified by '1234';
-- 分配权限
grant privileges on database.table to 'username'@'host';
-- grant select,insert,update,delete on db2105.emp_ju to 'jack'@'localhost'; 全部权限可以使用 *
-- 回收权限
revoke privileges on database.table from 'username'@'host';
-- revoke all on db2105.emp_ju from 'jack'@'localhost';
-- 删除用户
drop user 'username'@'host';
-- drop user 'jack'@'localhost';
约束
-
主键约束
-- 创建表并且添加主键约束 primary key auto_increment : 主键 自动增长 如果设置成自动增长,主键无法删除 create table aa( id int primary key, name varchar(20) ); -- 新增主键约束 alter table 表名 add primary key (列名); -- 删除主键约束 alter table aa add primary key (列名); -- 修改字段为主键约束 (先将原来的主键删除,然后将字段设置为主键) alter table aa add primary key (列名); -
唯一约束
-- 添加唯一约束 alter table 表名 add unique(列名); alter table aa add unique(name); -- 删除唯一约束 alter tbale 表名 drop index 列名; alter table aa drop index name; -
非空约束
-- 添加非空约束 not null alter table aa modify name varchar(30) not null; -
默认约束
-- 添加默认约束 default '默认值' alter table aa modify name varchar(30) default 'jack'; -
外键约束
-- 添加外键约束 alter table 表名1 add foreign key(列名1) reference 表名2(列名2); alter table bb add foreign key (a_id) references aa(id);
TCL
-
事务控制
? 一组(DML:操作数据)操作的逻辑单元,需要保证数据的一致,要么一起成功,要不一起失败。
比如:转账:A转给B 100,那么A-100,B+100
-
mysql引擎
-
主要引擎如下:
? myisam :mysql 5.5之前,data文件是三个文件:.frm(存储表结构) .myd(存储数据) .myi(存储索引)
? innodb:data文件是两个:.frm(存储表结构) .idb(数据、索引)
-
事务的基本命令
-- 查看mysql数据库的默认引擎 show engines; -- 开启事务:两种方式 当事务被提交、事务回滚或者断开连接时,事务结束,否则一直处于开启事务状态 begin; start transaction; -- 提交事务 commit; --回滚事务 rollback
-
-
事务的四个特性: ACID
- 原子性(Atomicity):每项操作都是一次执行,只有两个状态:成功、失败
- 一致性(Consistency):不能破话数据的安全性,需要数据一致,比如转账的业务
- 隔离性(Isolation):并发环境中,事务是相互隔离的,事务之间不能相互影响
- 持久性(Durability):事务提交后,数据将被永久保存
-
数据库的隔离级别
-
? 查看和设置隔离级别
-- 查看隔离级别 select @@tx_isolation; -- 设置隔离级别 set session transaction isolation level 隔离级别; -
sql支持的隔离级别
-
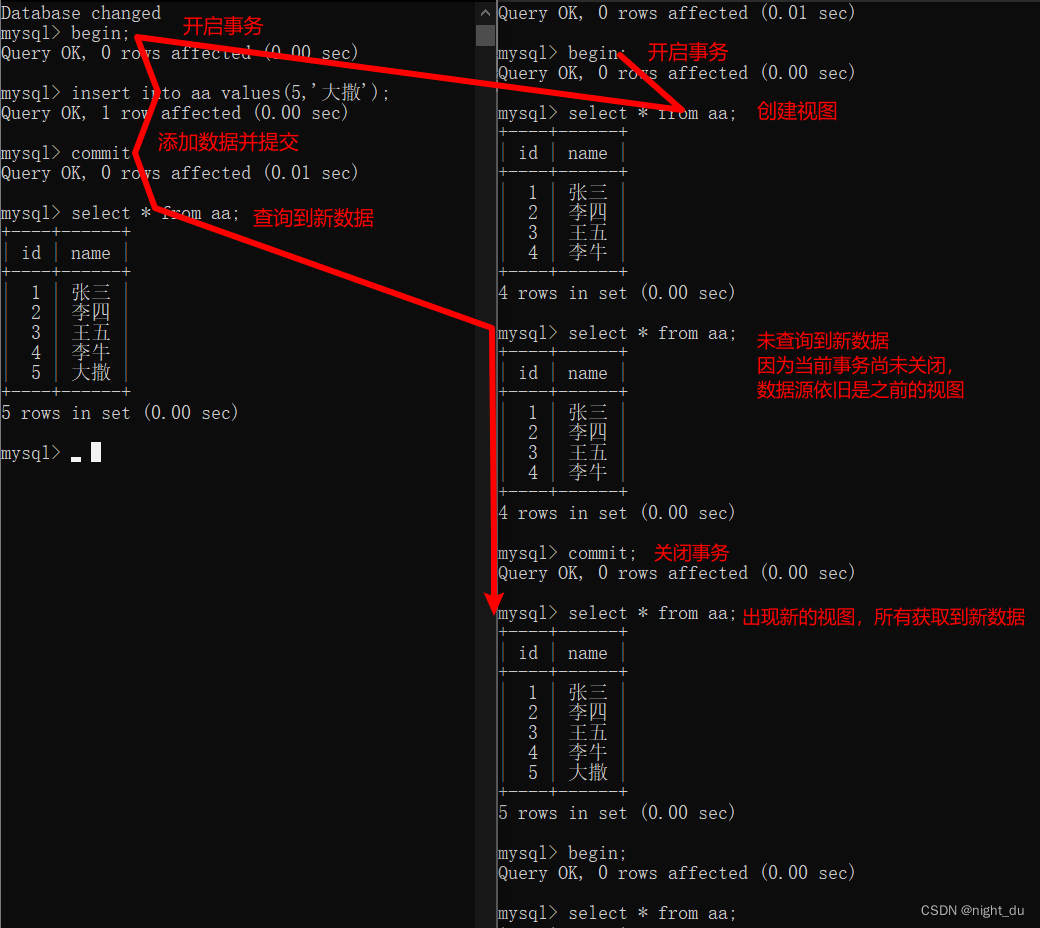
读未提交(read uncommitted):事务B读到了事务A未提交的数据 --------> 脏读
-
读提交(read committed):事务B读到了事务A提交的数据 Oracle -------->不可重复读
-
重复读(repeatable read):事务B读不到事务A提交的数据 —>幻读
-
串行化(serializable):使用锁的方式保证数据读写,写写都是串行(等先写的写完再写后面的)
下面是重复读的演示图:
-
-
如何实现数据的隔离?
? 数据会创建一个视图,访问的时候以视图的逻辑为准。
- 可重复读:启动事务并执行一个sql语句时创建视图,会一直使用这个视图的数据,直到视图结束
- 读提交:每一个sql语句执行都会创建视图
- 读未提交:直接返回记录的最新值,无视图
- 串行化:使用锁避免并行访问
-
索引
-
为什么有索引:提升查询效率,主要减少的是IO的读取次数
-
基本命令
-- 查看内部执行 explain select * from emp where empno=1002; -- 添加索引 create index 索引名称 on 表(列); create index empno_index on emp(empno); -- 删除索引 alter table 表名 drop index 索引名称; alter table emp drop index empno_index;

-
为什么添加索引之后查询效率提高
? 背景:A表10条记录,查找col2=89记录
? 如果不加索引,查找数据的次数是6次I/O,加了索引之后,查询列按照特定的数据结构保存索引值,查找次数是2次I/O,减少了查询次数。 -
mysql数据索引用的是什么数据结构保存的
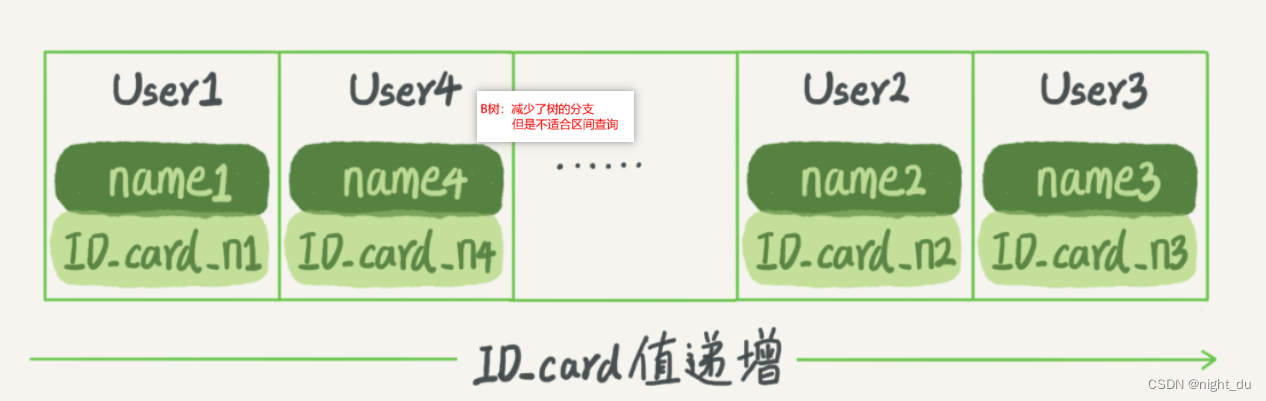
有序数组、hash表、搜索树
-
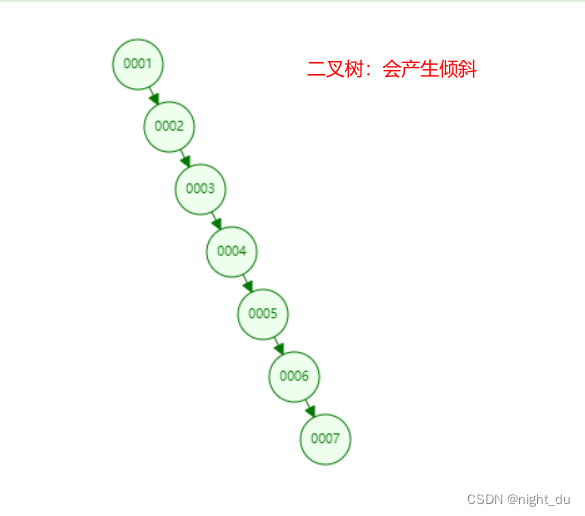
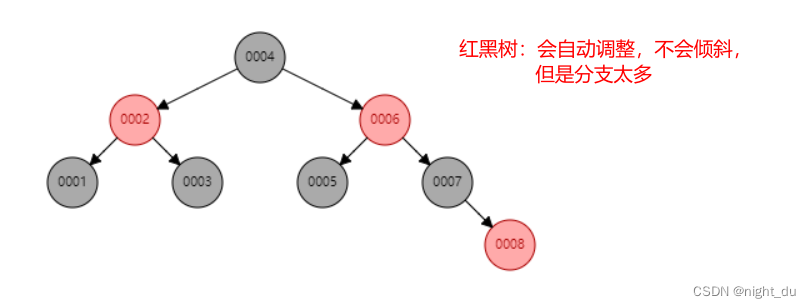
采用的是b+树数据结构,不是二叉树(树高太高,特殊情况会发生数据倾斜),红黑树(特殊的平衡二叉树,会自动平衡,当数据量比较大时,数据的高度会很高,I/O查找的次数就会很多);
-
b树与b+树
- b+树非叶子节点不存储data,只存储key(可以增大节点中存储的索引值)
-
b+树叶子节点与叶子节点之间有链指向,提升范围查找的效率
有序数组:
-
二叉树
红黑树:
B树
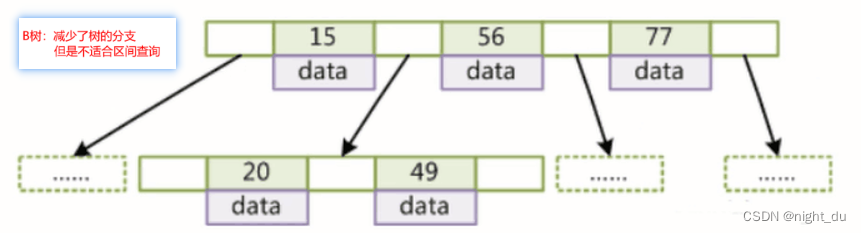
B+树
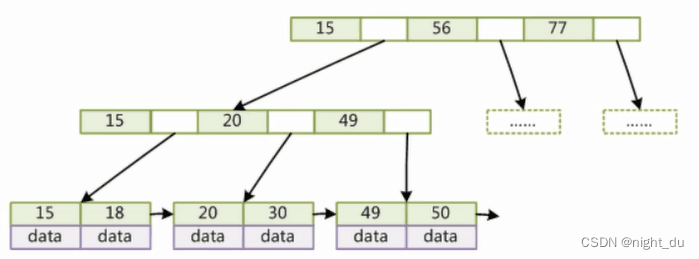
-
索引分类
- 聚集索引:数据和指针在一起 innodb
- 普通索引(二级索引):除主键外的索引
-
索引使用场景
-
经常出现在where子句中的字段,特别是大表的字段,应该建立索引
-
索引应该建在小字段上,对于大的字段甚至超长字段不要建立索引
-
经常与其他表建立连接的字段上
-
索引应该建在选择性高的字段上(离散度越高越好)
-
某些字段经常以and方式出现在where子句中,单子段查询极少甚至没有,考虑创建复合索引
select * from A where a=? and b=? --对于上面的情况使用复合索引 create index a_b_index on 表名(a,b); create index empno_sal_index on emp_ju (empno,salary); -- 创建复合索引 -
频繁进行数据操作的表,不要建立太多的索引
-
-
索引失效场景
-
where中索引字段列使用了运算符!=
-
模糊查询like以%开头
-
where中索引字段使用了函数
-
需要类型转换,包括隐式转换
-
复合索引未遵循最左原则
-- c1,c2,c3 select * from emp where c1=1 and c2=2; -- 走 select * from emp where c2=2 and c1=1; -- 走 select * from emp where c2=2 and c3=3; -- 不走 -
mysql觉得全表扫描更快时
-
-
索引创建的越多越好吗?
- 索引越多,占用的空间越
- DML操作时,会增加索引的开销,不好维护