记录:281
场景:在实际开发中,开发文档中的建表信息以表格的方式提供,包括字段名称、字段类型、字段注释、是否为空等。本例就是先把表格信息转换为约定格式的txt文件,在使用Java代码生成完整的ODPS建表语句(MaxCompute建表语句)。
版本:Spring Boot 2.6.3
名词:
ODPS:Open Data Processing Service。
MaxCompute:云原生大数据计算服务(MaxCompute,原名ODPS)是一种快速、完全托管的TB/PB级数据仓库解决方案。MaxCompute向用户提供了完善的数据导入方案以及多种经典的分布式计算模型,能够更快速的解决用户海量数据计算问题,有效降低企业成本,并保障数据安全。
经历:
2018年,小北在项目中使用ODPS。感觉挺溜的,也用上大数据套件。
2022年,此刻,在官网找相关资料的话,搜索MaxCompute,可以比较快定位到相关文档。
我们使用了很多阿里云组件,算是深度用户了。众多组件之中,就ODPS(MaxCompute)这个组件,获得团队最多好的评价:这瓜真甜。
一、案例场景
1.常规表
1.1开发文档中以表格方式提供建表信息。
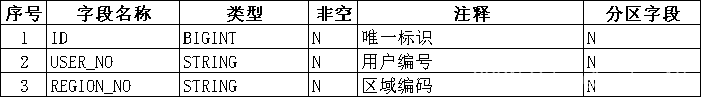
1.2.手动转换为txt文件,文件名:H_USER.txt,格式约定如下:
第一行为,表名##表名称#表类型。
第二行开始,每行:字段名称##字段类型##字段非空##字段注释##字段主键或者索引。
H_USER##用户信息##常规表
ID##BIGINT##N##唯一标识##N
USER_NO##STRING##N##用户编号##N
REGION_NO##STRING##N##区域编码##N?1.3执行代码,自动生成sql文件,文件名:H_USER.sql,生成结果。
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS H_USER (
ID BIGINT COMMENT '唯一标识',
USER_NO STRING COMMENT '用户编号',
REGION_NO STRING COMMENT '区域编码'
)
COMMENT '用户信息';2.分区表
2.1开发文档中以表格方式提供建表信息。
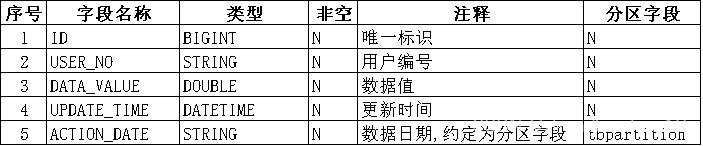
2.2 手动转换为txt文件,文件名:H_DATA.txt,格式约定如下:
第一行为,表名##表名称#表类型。
第二行开始,每行:字段名称##字段类型##字段非空##字段注释##字段主键或者索引。
H_DATA##数据表##分区表
ID##BIGINT##N##唯一标识##N
USER_NO##STRING##N##用户编号##N
DATA_VALUE##DOUBLE##N##数据值##N
UPDATE_TIME##DATETIME##N##更新时间##N
ACTION_DATE##STRING##N##数据日期,约定为分区字段##tbpartition?2.3 执行代码,自动生成sql文件,文件名:H_DATA.sql,生成结果。
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS H_DATA (
ID BIGINT COMMENT '唯一标识',
USER_NO STRING COMMENT '用户编号',
DATA_VALUE DOUBLE COMMENT '数据值',
UPDATE_TIME DATETIME COMMENT '更新时间'
)
COMMENT '数据表'
PARTITIONED BY (
ACTION_DATE STRING COMMENT '数据日期,约定为分区字段'
); 二、使用类
1.读文件操作
java.lang.AutoCloseable,接口。
java.io.Closeable,接口,继承AutoCloseable。
java.lang.Readable,接口。
java.io.Reader,抽象类,实现Readable接口和Closeable。
java.io.BufferedReader,实现类,实现Reader抽象类。
java.io.InputStreamReader,实现类,读输入流,Reader抽象类。
java.io.FileReader,实现类,读文件,继承InputStreamReader。
new BufferedReader(new FileReader(fileName))。
2.写文件操作
java.lang.AutoCloseable,接口。
java.io.Closeable,接口,继承AutoCloseable。
java.io.Flushable,接口。
java.lang.Appendable,接口。
java.io.Writer,抽象类,实现Appendable, Closeable, Flushable。
java.io.BufferedWriter,实现类,实现Writer抽象类。
java.io.OutputStreamWriter,实现类,写输出流,Writer抽象类。
java.io.FileWriter,实现类,写文件,继承OutputStreamWriter。
new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(fileName, true));
3.操作ArrayList
java.lang.Iterable,接口。
java.util.Collection,接口,继承Iterable。
java.util.List,接口,继承Collection。
java.util.AbstractCollection,抽象类,实现Collection。
java.util.AbstractList,抽象类,继承AbstractCollection,实现List。
java.util.ArrayList,一个Resizable-array。
4.Collections
java.util.Collections,对集合相关操作。
5.File操作
java.io.Serializable,接口。
java.lang.Comparable,接口。
java.io.File,实现类,实现Serializable和Comparable接口。
三、代码
1.读文件
读取文件,逐行读取,每读取一行,立即解析,根据分隔符##,分割成多个String字符串,存放在一个List<String>中。解析完成的一行数据List<String>,再放入List<List>中。
读取文件,逐行读取,每读取一行,立即解析,根据分隔符##,分割成多个String字符串,存放在一个List<String>中。解析完成的一行数据List<String>,再放入List<List>中。
public static ArrayList<ArrayList<String>> readFromTxt(String fileName) {
ArrayList<ArrayList<String>> listAll = new ArrayList<>();
try {
//1.读txt文件,一次读一行
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(fileName));
String oneLine = null;
//2.使用readLine方法,一次读一行
while ((oneLine = br.readLine()) != null) {
ArrayList<String> oneLineList = getOneLine(oneLine, "##");
listAll.add(oneLineList);
}
br.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("读异常.");
e.printStackTrace();
}
return listAll;
}
public static ArrayList<String> getOneLine(String content, String split) {
String[] strArr = content.split(split);
ArrayList<String> oneLine = new ArrayList<>(strArr.length);
Collections.addAll(oneLine, strArr);
return oneLine;
}2.写文件
逐行写文件,以追加方式写入,不覆盖已经写入的内容。
public static void writeFile(String fileName, String content) {
try {
// 设置为追加写入true
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(
new FileWriter(fileName, true));
bw.write(content);
bw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("写异常.");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}3.生成建表语句和注释
根据从txt读取的表字段信息,生成建表语句和注释,如果有分区则生成分区字段。
public static void createTable(String fileName, ArrayList<ArrayList<String>> content) {
List<String> firstOne = content.get(0);
String tableName = firstOne.get(0);
String tableComment = firstOne.get(1);
String tableType = firstOne.get(2);
String part1 = "CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS ";
String part2 = tableName;
String part3 = " ( ";
writeFile(fileName, part1 + part2 + part3 + "\n");
String part5 = ")\n";
String part6 = "COMMENT '" + tableComment + "'\n";
int size = content.size();
List<List<String>> parList = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> allLine = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
ArrayList<String> oneLine = content.get(i);
if (StringUtils.equals(tableName, oneLine.get(0))) continue;
if (StringUtils.equals("tbpartition", oneLine.get(4))) {
parList.add(oneLine);
continue;
}
String line = "";
int last = content.size() - 1;
String columnName = oneLine.get(0) + " ";
String dataType = oneLine.get(1) + " ";
String comment = " COMMENT '" + oneLine.get(3) + "'";
line = columnName + dataType + comment + ",\n";
allLine.add(line);
}
// 写入每行
writeAllLine(fileName, allLine);
String part7 = getPartition(tableType, parList);
writeFile(fileName, part5 + part6 + part7 + "\n");
}
public static void writeAllLine(String fileName, List<String> allLine) {
int size = allLine.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
int last = allLine.size() - 1;
String line = allLine.get(i);
if (i == last) {
line = line.replace(",", "");
writeFile(fileName, " " + line);
} else {
writeFile(fileName, " " + line);
}
}
}
// 建表类型
public static String getPartition(String tableType, List<List<String>> parList) {
String result = "";
switch (tableType) {
case "常规表":
result = ";";
break;
case "分区表":
String part01 = "PARTITIONED BY ( \n";
String part03 = "); \n";
String part02 = "";
int size = parList.size();
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
List<String> oneList = parList.get(i);
String columnName = oneList.get(0) + " ";
String dataType = oneList.get(1) + " ";
String comment = " COMMENT '" + oneList.get(3) + "'";
int last = parList.size() - 1;
if (i == last) {
String var1 = " " + columnName + dataType + comment + "\n";
sb.append(var1);
} else {
String var2 = " " + columnName + dataType + comment + "," + "\n";
sb.append(var2);
}
}
part02 =sb.toString();
result = part01 + part02 + part03;
break;
}
return result;
}4.在main函数调用
在main函数调用测试,从指定目录下读取txt文件名称,逐个生成SQL文件。
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("开始...");
String baseDir = "D:\\example\\";
List<String> listFile = getAllTxtFile(baseDir);
for (String fileName : listFile) {
singleFile(baseDir, fileName);
}
System.out.println("结束...");
}
public static List<String> getAllTxtFile(String path) {
File dirFile = new File(path);
File[] subFiles = dirFile.listFiles();
List<String> fileList = new ArrayList<>();
if (subFiles != null) {
for (File subFile : subFiles) {
if (subFile.isDirectory()) continue;
else {
if (subFile.isFile() && subFile.getName().endsWith(".txt")) {
fileList.add(subFile.getName().substring(0, subFile.getName().length() - 4));
}
}
}
}
return fileList;
}
public static void singleFile(String baseDir, String fileName) {
String srcFileName = baseDir + fileName + ".txt";
String tarFileName = baseDir + fileName + ".sql";
ArrayList<ArrayList<String>> read = readFromTxt(srcFileName);
// 表结构与注释
createTable(tarFileName, read);}以上,感谢。
2022年7月3日