文章目录
一、常用查询
(增、删、改、查)
对MySQL数据库的查询,除了基本的查询外,有时候需要对查询的结果集进行处理。例如:只取10条数据、对查询结果进行排序或分组等
1.按关键字查询
使用select语句可以将需要的数据从MySQL数据库中查询出来,如果对查询的结果进行排序,可以使用order by 语句来对语句实现排序,并最终将排序后的结果返回给用户。这个语句的排序不光可以针对某一个字段,也可以针对多个字段
语法:
select column1,column2,... from table_name order by column1,column2,... asc
#查询结构以升序方式显示,asc可以省略
select column1,column2,... from table_name order by column1,column2,... desc
#查询结构以降序方式显示
ASC/DESC
- ASC是按照升序进行排序的,是默认的排序方式,即ASC可以省略。select语句中如果没有指定具体的排序方式,则默认按ASC方式进行排序
- desc是按降序方式进行排序。当然order by 前面也可以使用where子句对查询结果进一步过滤
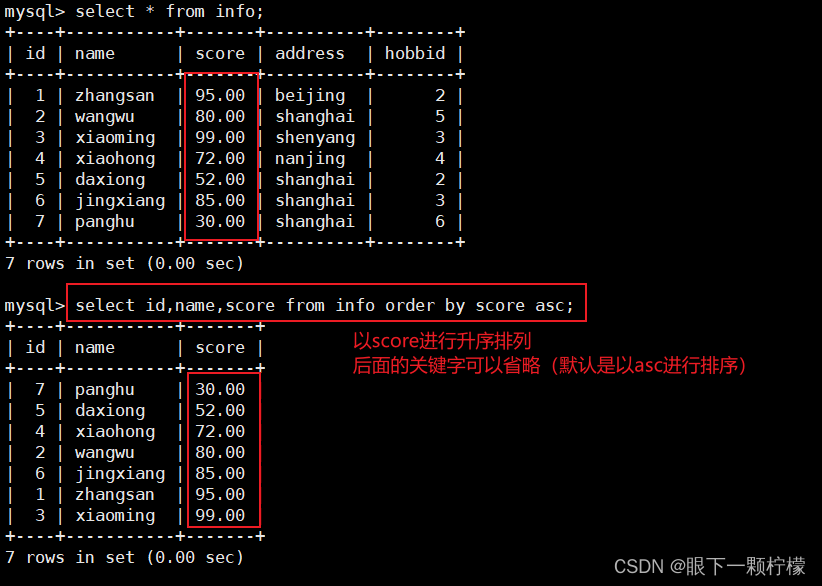
1.1升序排序
select id,name,score from info order by score asc;
#查询id,name,score字段的记录,并且以score进行升序排列
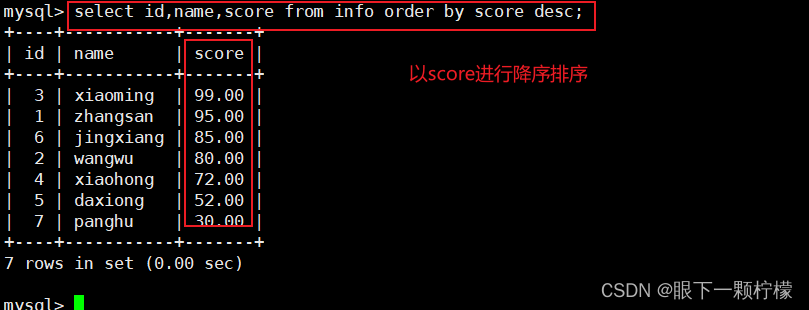
1.2降序排序
select id,name,score from info order by score desc;
#查找id,name,score字段的记录,以score进行降序排序
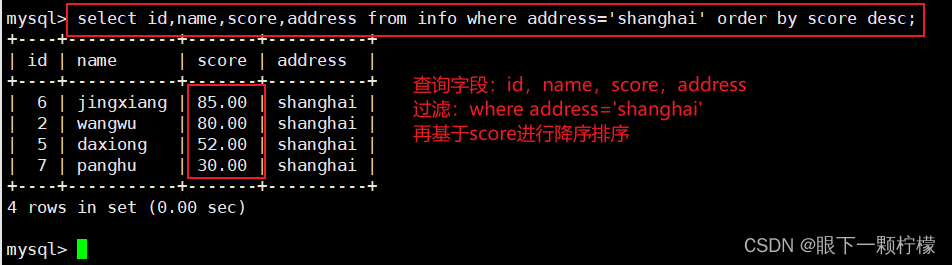
1.3结合where进行条件过滤
select id,name,score,address from info where address='shanghai' order by scroe desc;
#查询id,name,score,address字段,再进行过滤address为shnaghai的记录,并按照score进行降序排序
1.4多字段排序
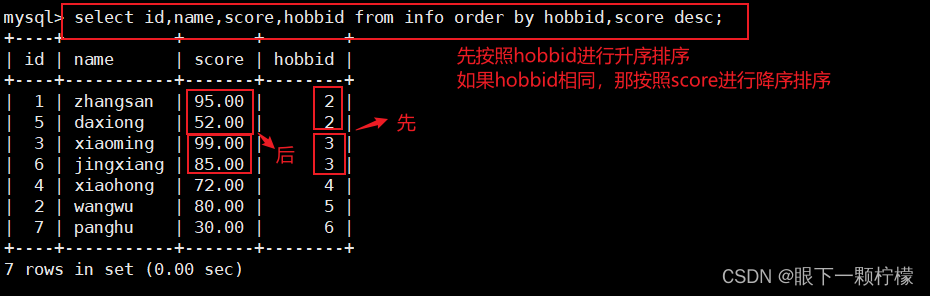
ORDER BY 语句也可以使用多个字段来进行排序,当排序的第一个字段相同的记录有多条的情况下,这些多条的记录再按照第二个字段进行排序,order by 后面跟多个字段时,字段之间使用英文逗号隔开,优先级是按先后顺序而定,但order by之后的第一个参数只有在出现相同值时,第二个字段才有意义
select id,name,score,hobbid from info order by hobby,score desc;
#查询id,name,score,hobbid字段,先按照hobbid进行升序,如果出现相同的hobbid,就按照score进行降序排列
2.and和or判断
大型数据库中,有时查询数据需要数据符合某些特点,“abd"和"or"表示"且"和"或”
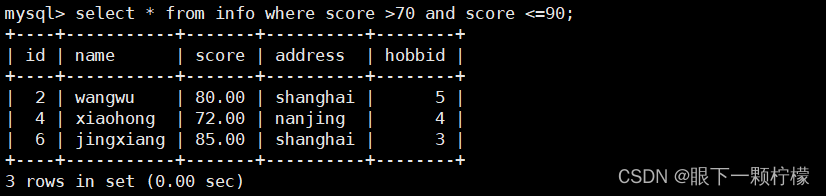
2.1and和or的使用
select * from info where score >70 and score <=90;
#查找score大于70和小于等于90的字段
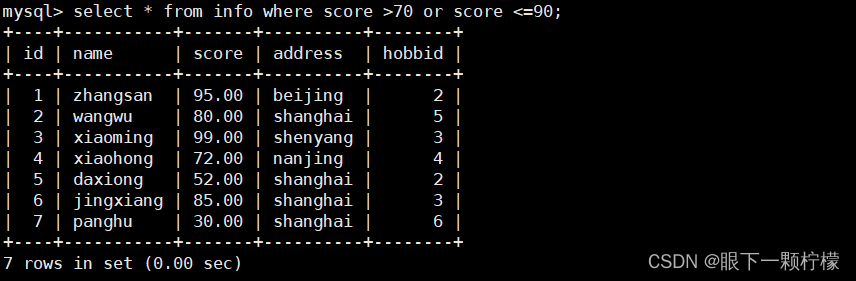
select * from info where score >70 or score <=90;
#查找score大于70或者小于等于90
2.2嵌套、多条件使用
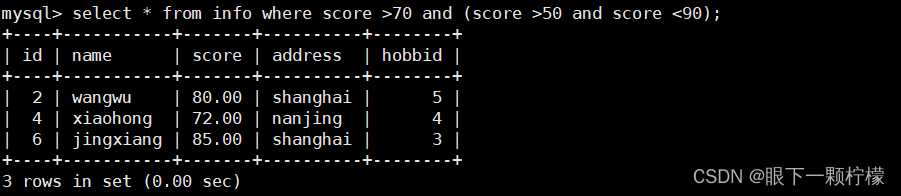
select * from info where score >70 and (score >50 and score <90);
#查找score大于70且在50和90之间的数据
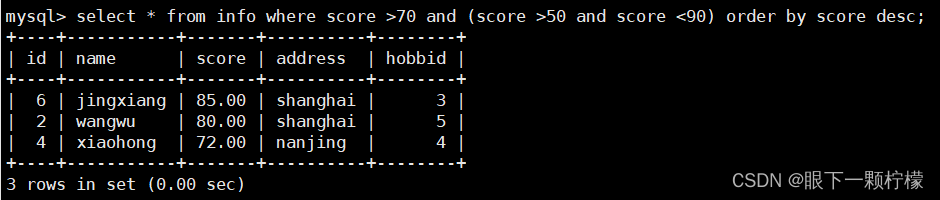
select * from info where score >70 and (score >50 and score <90) order by score desc;
#查找score大于70且在50和90之间的数据,并以score进行降序排序
3.distinct 查询不重复记录
语法:
select distinct 字段 from 表名;
#distinct必须放在最开头
#distinct只能使用需要去重的字段进行操作
#distinct去重多个字段时,含义是:几个字段同时重复时才能会过滤,会默认按左边第一个字段为依据
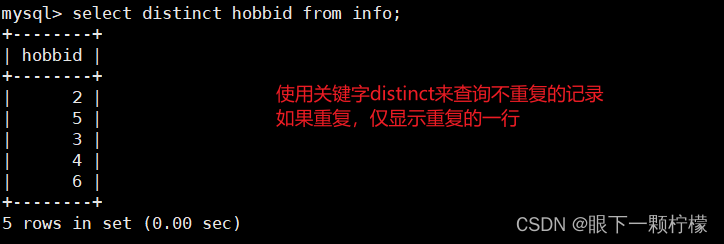
select distinct hobbid from info;
#使用distinct查询不重复记录(相当于去重)
4.group by 对结果进行分组
通过SQL查询出来的结果,还可以对其进行分组,使用group by 语句来实现,group by 通常都是结合聚合函数一起使用的
常用的聚合函数包括:计数(count)、求和(sum)、求平均数(avg)、最大值(max)、最小值(min),group by 分组的时候可以按一个或多个字段对结果进行分组处理。
- 对于group by 后面的字段的查询结果进行汇总分组,通常是结合聚合函数一起使用的
- group by 有一个原则,就是select后面的所有列中,没有聚合函数的列必须出现在group by后面
语法:
select 字段,聚合函数(字段) from 表名【where 字段 (匹配) 数值】group by 字段名;
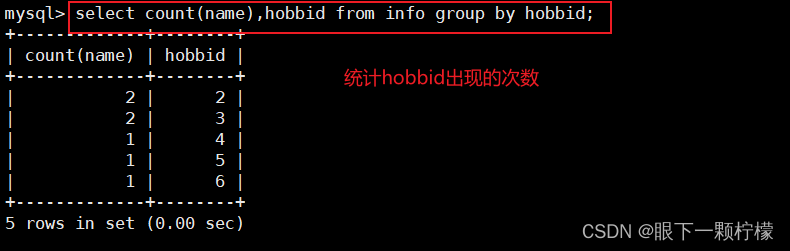
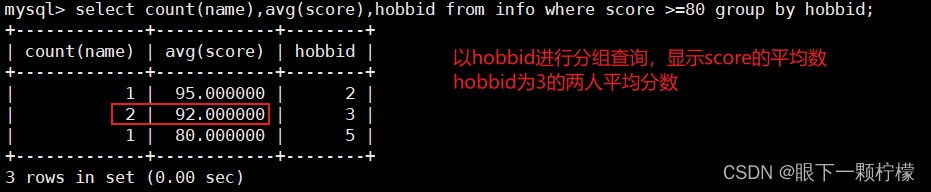
select count(name),hobbid from info group by hobbid;
#按hobbid相同的分株,基于name个数进行计数
select count(name),hobbid from info where score >=80 group by hobbid;
#筛选score大于80的分组,计算个数
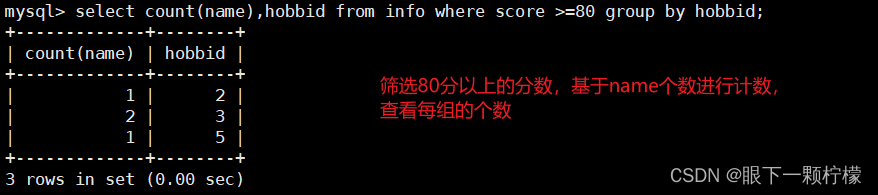
select count(name),avg(score),hobbid from info where score >=80 group by hobbid;
#以hobbid进行分组查询,显示score的平均数,hobbid为3的两人平均数
5.limit限制结果条目
limit限制输出的结果
在使用MySQL select 语句进行查询时,结果集返回的时所有匹配的记录(行)。有时候仅需要返回第一行或者前几行,这时候就需要用到limit子句
语法:
select column1,column2,... from table_name limit [offset] number
#limit的第一个参数是位置偏移量(可选参数),设置mysql从哪一行开始显示。
#如果不设定第一个参数,将会从表中的第一条记录开始显示。需要注意的是,第一条记录的位置偏移量是0,第二条是1
#offset:为索引下标
#number:为索引下标后的几位
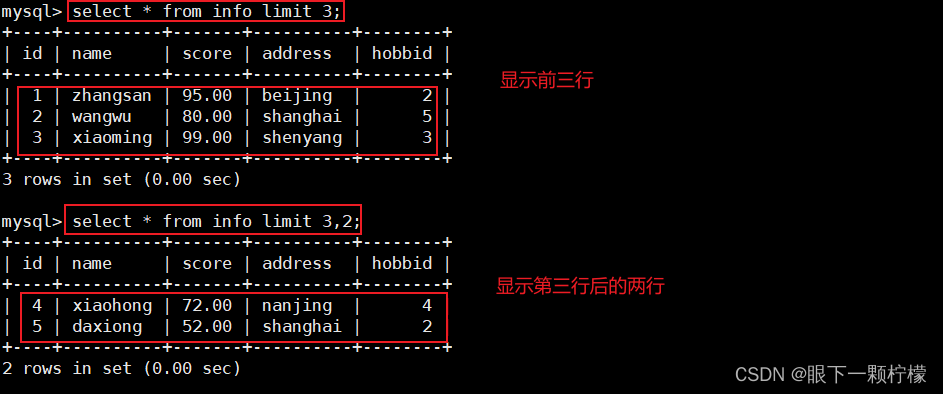
select * from info limit 3;
#显示前三行数据内容
select * from info limit 3,2;
#显示从第3行开始后面的2行内容(不包括第三行)
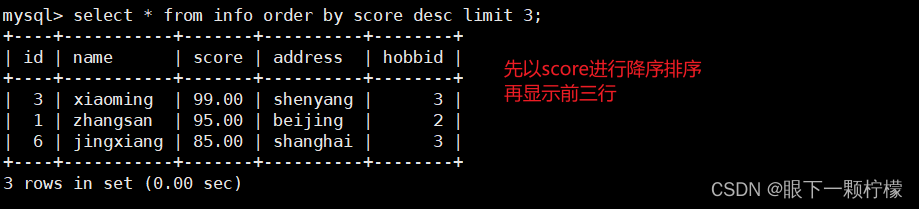
select * from info order by score desc limit 3;
#嫌疑score进行降序排序,再显示前三行
6.设置别名(alise -as)
再MySQL查询时,当表的名字比较长或者表内某些字段比较长时,为了方便书写或者多次使用相同的表,可以给字段列或表设置别名。使用的时候直接使用别名,方便操作,增强可读性
格式:
列的别名:select 字段 as 字段别名 表名;
表的别名:select 别名.字段 from 表名 as 别名;
as可以省略
使用场景
- 对复杂的表进行查询时,别名可以缩短查询语句的长度
- 多表相连查询的时候(通俗易懂,简短sql语句)
注意:在为表设置别名时,要保证别名不能与数据库中其他表的名称冲突
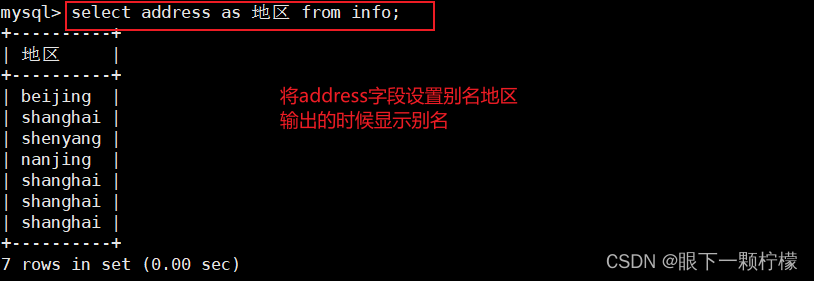
select address as 地区 from info;
#将address字段设置别名为"地区"显示
6.1查询表的记录数量,以别名显示
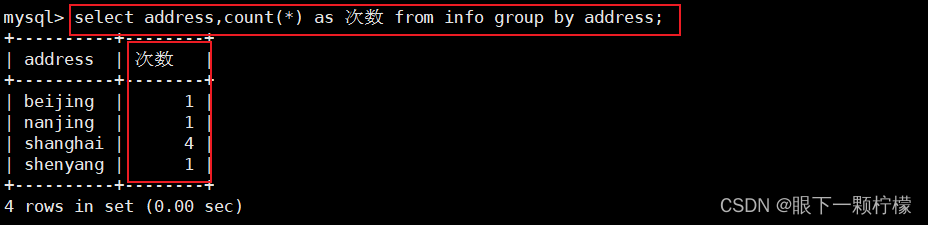
select address,count(*) as 次数 from info group by address;
#以address分组,查询表数据内容,以别名"次数"显示
6.2利用as,将查询的数据导入到另一个表内
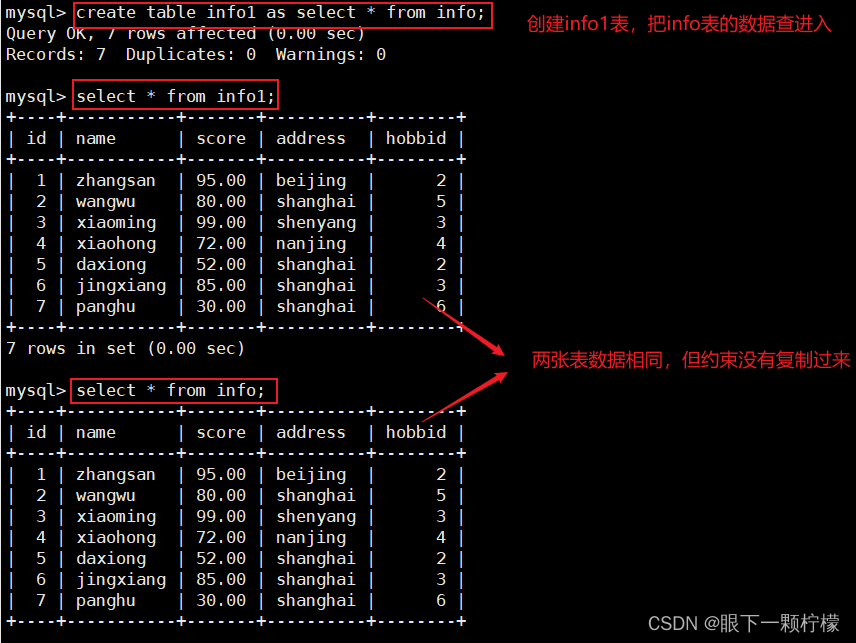
此处as起到的作用
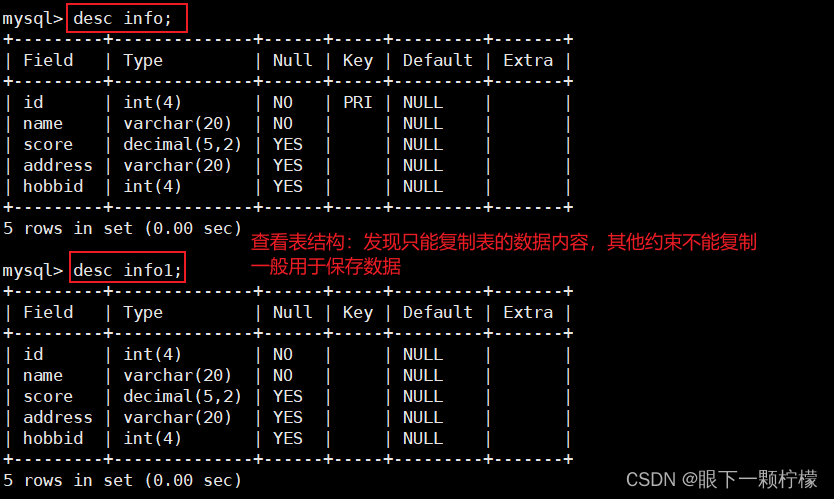
- 创建了一个新表,并定义表结构,插入表数据
- 但是"约束"没有完全复制过来,但是如果原表设置了主键,那么附表的:default字段会默认设置了一个0
create table info1 as select * from info;
#将表info的内容导入到info1中
select * from info;
select * from info1;
7.通配符
- 通配符主要用于替换字符串的部分字符,通过部分字符的匹配将相关结构查询出来
- 通常通配符都是跟like一起使用的,并协同where
- 子句共同来完成查询任务,常用的通配符有两个,分别是:“%“和”_”
%:百分号表hi0个、1个或多个字符
_:下划线表示单个字符
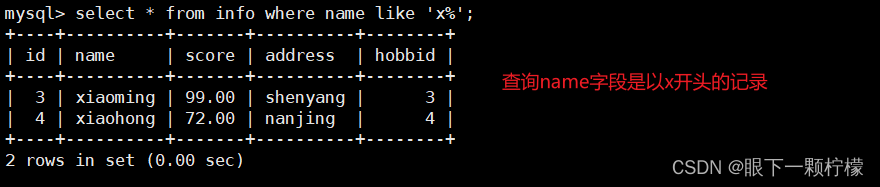
select * from info where name like 'x%';
#查询name以x开头的记录
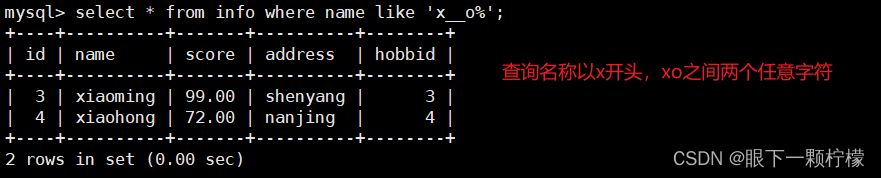
select * from info where name like 'x__o%';
#查询名称以x开头,xo之间两个任意字符,__代表两个字符
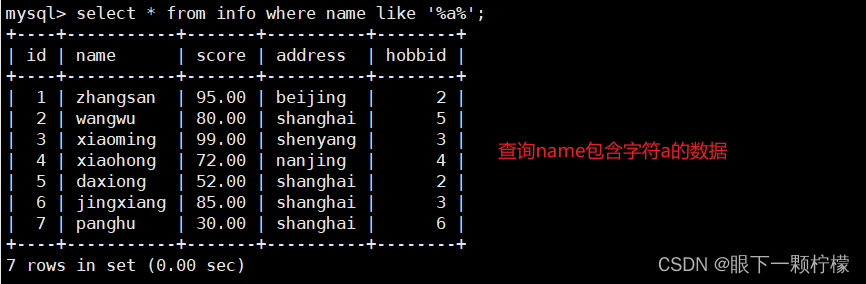
select * from info where name like '%a%';
#查询name包含字符a的数据
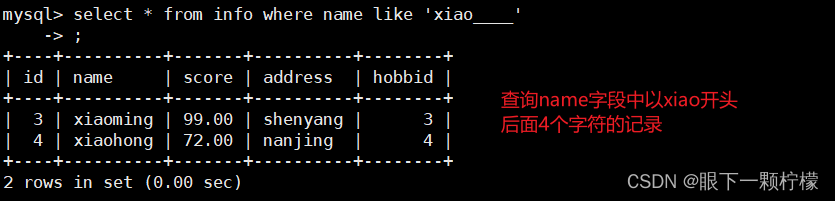
select * from info where name like 'xiao____';
#查询xiao后面带4个字符的名字记录
二、子查询
- 子查询也被称作内查询(内连)或嵌套查询,是指在一个查询语句里面还嵌套这另一个查询语句
- 子查询语句是先于著查询语句被执行,且结果作为外层的条件返回给主查询进行下一步的查询
- 在查询中可以与主语句相同的表,也可以是不同的表
1.select 查询
子语句可以与主语句所查询的表相同,也可以是不同的表
语法:
select 字段1,字段2 from 表名1 where 字段 in (select 字段 from 表名 where 条件);
#主语句:select 字段1,字段2 from 表名1 where 字段;
#in:将主表和子表关联/连接的语法
#子语句(集合):select 字段 from 表名 where 条件;
1.1相同表查询
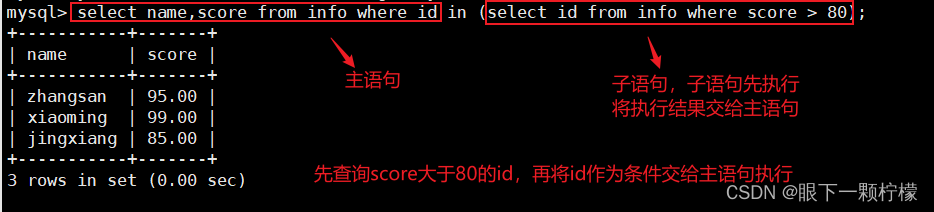
select name,score from info where id in (select id from where score > 80);
#先查询子语句中info表中的分数大于80的id,然后得出的id的集合作为主语句的条件
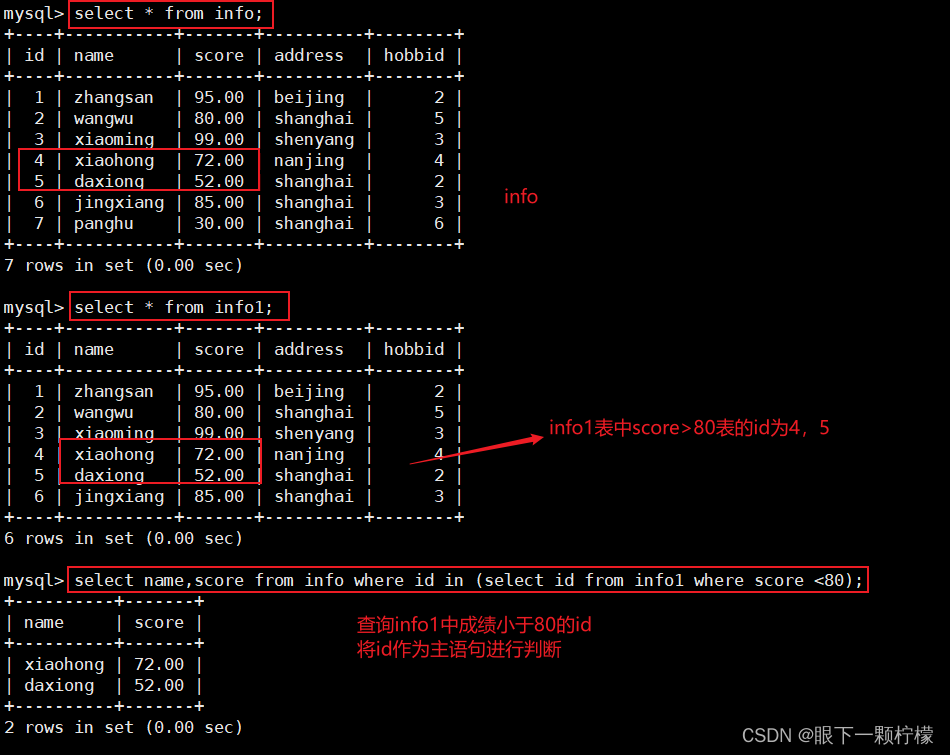
1.2多表查询
select name,score from info where id in (select id from info1 where score <80);
#查询info1表中分数低于80的id,然后得出的id的集合作为查询info表的查询条件
1.3not取反,将子查询的结果,进行取反操作
select name,score from info where id not in (select id from info1 where score <80);
#先查询info1表中分数低于80的id,根据取反后的id,查询info表中的name,score

1.4结合as别名进行子查询
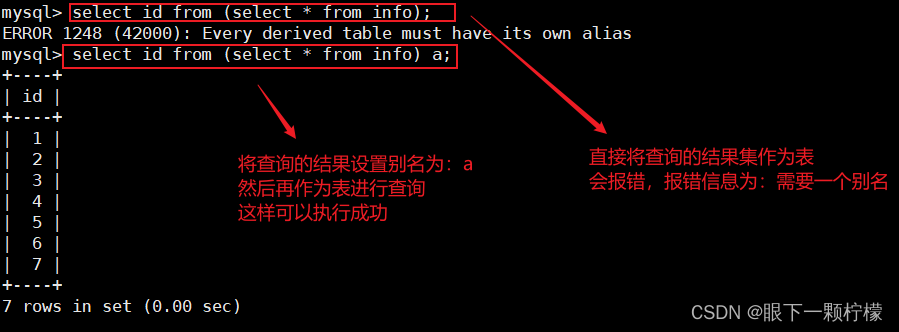
当我们将一个查询的结果集作为一个新表再进行查询时,直接使用会进行报错,我们需要是用到别名
- 如果直接使用select id from (select id,name from info);此时会报错,因为select * from表名,此格式为标准格式,而以上的查询的语句,"表名"的位置其实是一个完整结果集,mysql并不能直接识别,而此时给与结果集设置一个别名
- 所以可以使用select a.id from (select id,name from info) a;
select id from (select * from info);
#此条报错
select id from (select * from info) a;
#设置了别名,然后再作为表
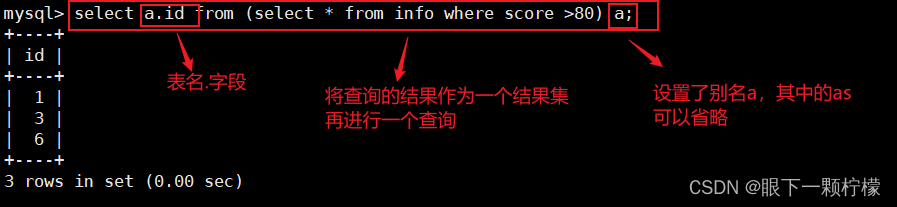
select a.id from (select * from info where score >80) a;
#将查询结果设置别名,然后将结果集作为表进行查询