目录
6.18.1、通过 filter_path 来控制输出的的字段?
6.18.3、通过 _source 中的 includes 属性来控制输出字段
?6.18.4、通过 _source 中的 exclude属性排除指定字段输出(exclude后续版本已弃用)
6.18.5、设置 _source 为 false,这样不返回任何的 _source 信息:
8.1.2、avg示例:查询地址在?“广东省”用户的平均工资
8.1.6、cardinality示例:查询所有用户不同年龄的数量
8.1.7、stats示例:查出所有用户的年龄stats信息
8.1.8、extended_stats示例:查出所有用户的年龄extended_stats信息
8.1.9、percentile示例:查出所有用户的年龄占比
8.2.3、分桶group by示例:根据用户出生日期的年月分组分段聚合查询
8.2.4、group by 进阶示例:按照年龄聚合,并查询出每个年龄这些人的平均薪资
8.2.5、group by 进阶示例:查出所有年龄分布,并且这些年龄段中 性别为男 的平均薪资和 性别为女 的平均薪资以及这个年龄的用户信息
10.4、将test_index_v1 数据拷贝到 test_index_v2
1、Restfull
????????Elasticsearch默认走的是http协议,而http协议它是一种无状态的协议,无状态就是指服务端它不会记录客户端的所有信息和操作,客户端必须每次带上自己的状态去请求服务器。因此,如果客户端想要操作这个服务器,必须通过某些手段,才能让服务器发生状态转化。而这种转化是建立在表现层之上的,所以说这就表现层的状态转化。
转化手段:
- GET:用来获取资源
- POST:用来创建资源(也可以用来更新资源)
- PUT:用来更新资源
- DELETE:用来删除资源
我们对ES的所有操作,都被封装成了RestAPI,所以我们只要发送请求就行了。
2、查看ES的基本信息
2.1、查看集群信息
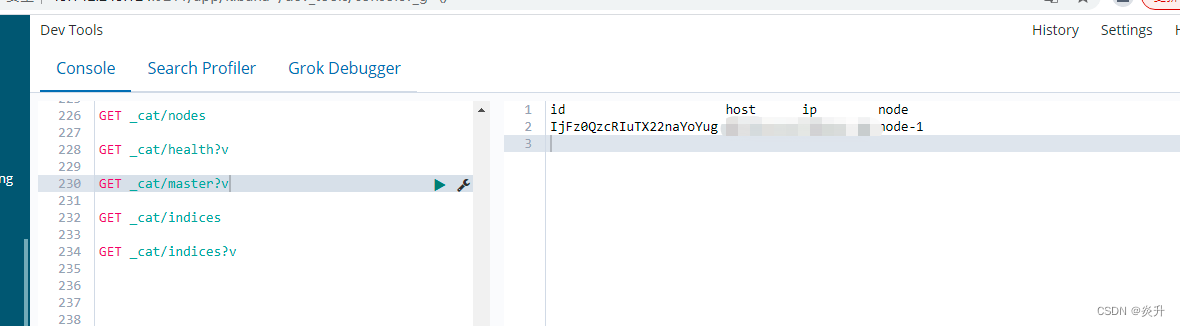
查看所有结点:GET _cat/nodes
查看ES健康状况:GET _cat/health
- Green:主分片与副本都正常分配
- Yellow:主分片全部正常分配,有副本分片未能正常分配
- Red:有主分片未能分配
查看主节点:GET _cat/master
查看所有索引:[类似于show databases] GET _cat/indices?

以上查询带上参数 ?v可以显示标题信息,如:
3、索引操作
3.1、创建并显示指定索引字段的类型
PUT user
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
},
"address": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
},
"remark": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
},
"age": {
"type": "long"
},
"salary": {
"type": "double"
},
"birthDate": {
"type": "date",
"format": "yyyy-MM-dd"
}
}
}
}
3.2、通过创建文档的方式自动映射字段的类型
? ? ? ? 创建文件时,当索引不存在的时候会自动创建并且字段类型自动根据值进行映射。
格式:PUT /索引名/类型名/文档id
6.x的写法是:{index}/{type}/{id},例如:user/_doc/1?
7.x的写法是:{index}/_doc/{id},例如:user/_doc/1
在6.x中一个index中type只能有一个,可以自定义;
在7.x中将type概念移除了,所以现在建议直接写成_doc,当然你硬要指定type类型也行,只是ES是给出一个警告。
创建文档,并自动生成index。示例如下:
PUT user/_doc/1
{
"name":"小白学es",
"age":3
}
如果索引原本中没有的字段,这是也会自动加上并且映射类型,比如之前是没有sex字段的。
PUT /user/_doc/1
{
"name":"小白学es",
"age":18,
"sex":"男"
}查看索引:GET user
查看索引字段类型:GET user/_mapping
删除索引:DELETE user
4、文档操作:
es使用版本:6.8.2
4.1、增加文档信息
未指定文档id时,创建文档,只能用POST(创建或更新)。
POST /user/_doc
{
"name": "张三",
"age": 29,
"salary": 100,
"address": "北京市",
"remark": "来自中国北京市的张先生",
"birthDate": "1990-01-10"
}
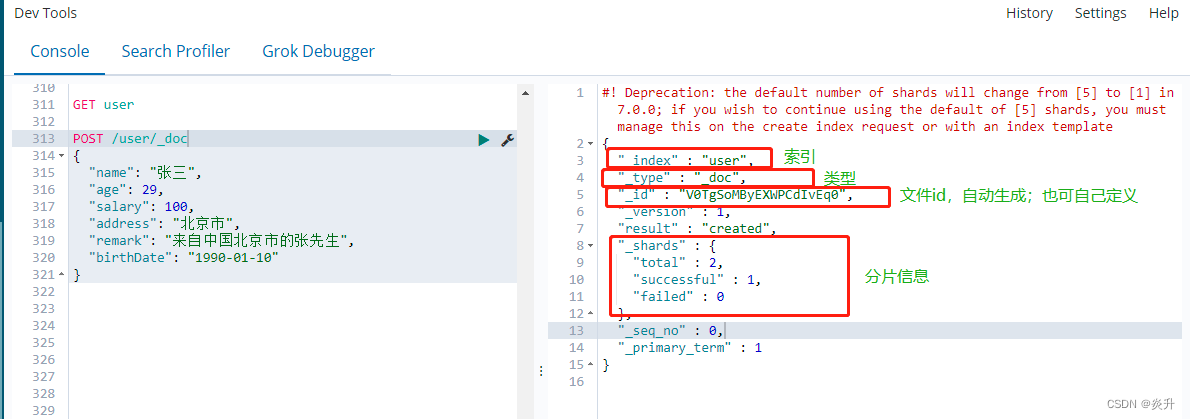
?说明:上面的红色报警信息,是指6.x版本中默认分片为5,从7.x开始,默认分片为1,如果要更改,需要自己创建索引,或使用索引模板。
增加文档时指定ID:该操作为更新操作,可以使用PUT(更新)、POST(创建或更新)
POST /user/_doc/1
{
"name": "张三",
"age": 29,
"salary": 100,
"address": "北京市",
"remark": "来自中国北京市的张先生",
"birthDate": "1990-01-10"
}4.2、更新文档信息
????????更新文档信息可以使用PUT和POST来请求。
????????PUT修改:全量字段更新。--?覆盖式修改
????????POST修改:指定字段更新(推荐使用)。
指定字段更新的命令:
????????
POST /user/_doc/1/_update { "doc": { "name": "王五" } }
使用PUT方式更新之前创建的 id=1 的文档信息。
PUT /user/_doc/1
{
"name": "李四"
}?可以发现这里只更新了name字段,没有更新其它的字段,所以其它字段默认会填充空值。

使用POST请求修改文档:
首先将没个字段的值都初始化
POST /user/_doc/1
{
"name": "张三",
"age": 29,
"salary": 100,
"address": "北京市",
"remark": "来自中国北京市的张先生",
"birthDate": "1990-01-10"
}然后再用POST请求执行修改文档操作:
POST方式第一种更新:
POST /user/_doc/1/_update
{
"doc": {
"name": "王五"
}
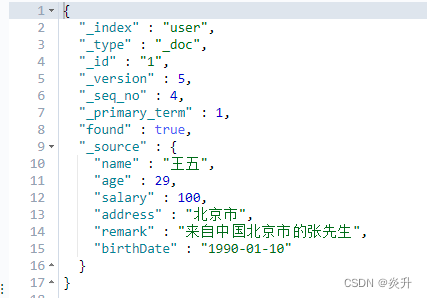
}第一次执行结果:

??第二次执行结果:
?????????使用这种更新操作进行重复更新时,若数据与原先一致,则不进行任何操作。返回的结果是:"result": "noop",而不是"result" : "updated"。
? 执行后的数据:
POST方式第二种更新:?
POST /user/_doc/1
{
"name":"赵六"
}
第一次执行结果:

?执行后的数据:

第二次执行结果:
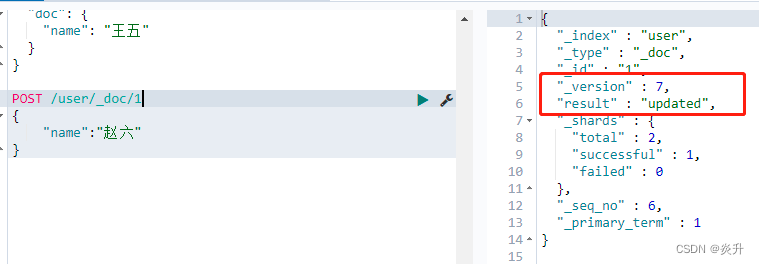
?????????使用第二种更新操作时[即不带_update],无论是否重复更新,数据是否一致,都会进行更新,version版本相应增加。因此若使用PUT方式,结果也一致。
4.3、获取文档信息
????????获取 user的索引 id=1 的文档信息。
GET /user/_doc/1
? ? ? ? 查询文档数量
GET user/_doc/_count 4.4、删除文档信息
????????删除之前创建的 id=1 的文档信息。
DELETE /user/_doc/1?????????根据查询语句删除:????????
# 根据查询语句删除
POST /my-index/_delete_by_query
{
"query": {
"match": {
"user.id": "elkbee"
}
}
}????????删除所有数据:
#删除所有数据
POST /my-index/_delete_by_query
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}5、批量操作?
????????有些情况下可以通过批量操作以减少网络请求。如:批量查询、批量插入数据等。
在Elasticsearch中,支持批量的插入、修改、删除操作,都是通过_bulk的api完成的。
_bulk分类:
| 行为 | 解释 |
| create | 当文档不存在时创建之 |
| index | 创建新文档或替换已有文档 |
| update | 局部更新文档 |
| delete | 删除一个文档 |
在索引、 创建、 更新或删除时必须指定文档的 _index 、 _type 、 _id 这些元数据(metadata)。
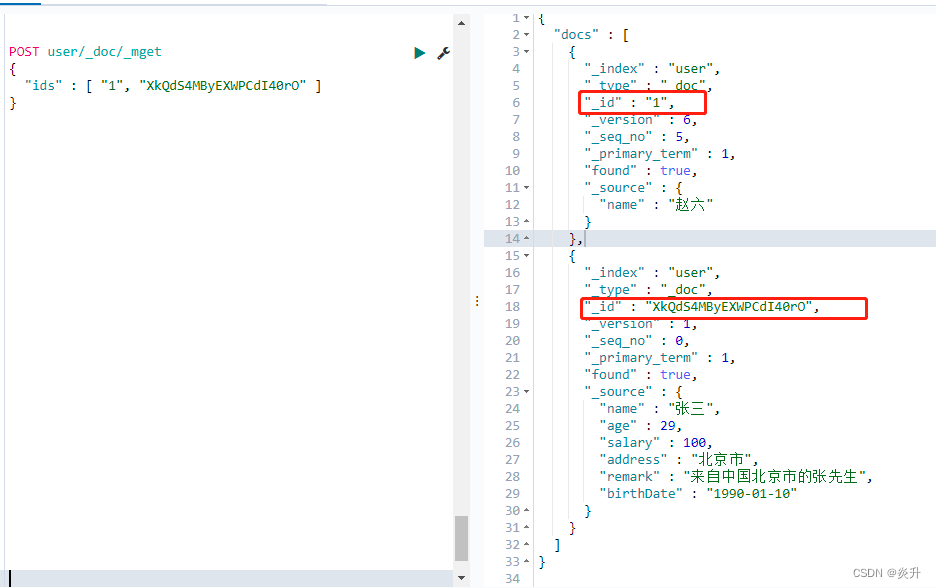
5.1、批量查询
POST user/_doc/_mget
{
"ids" : [ "1", "XkQdS4MByEXWPCdI40rO" ]
}
#批量查询还有如下写法:Ids 指定Id值查询
GET user/_search
{
"query": {
"ids": {
"values": [ "1", "XkQdS4MByEXWPCdI40rO"]
}
}
}
5.2、批量插入数据
??请求格式如下:
{ action: { metadata }}
{ request body }
{ action: { metadata }}
{ request body }
...????????需要注意的是,每一条数据都由两行构成(delete除外),其他的命令比如index和create都是由元信息行和数据行组成;update比较特殊它的数据行可能是doc也可能是upsert或者script。
????????注意,每一行都是通过回车符来判断结束,因此如果你自己定义了json,千万不要使用回车符。不然_bulk命令会报错的!
POST _bulk
{"create":{"_index":"user","_type":"_doc","_id":2001}}
{"name":"刘一","address":"广东省广州市花都区","remark":"公司底层码农员工","age":30,"salary":3000,"birthDate":"1989-11-11"}
{"create":{"_index":"user","_type":"_doc","_id":2002}}
{"name":"陈二","address":"广东省广州市花都区","remark":"公司底层码农员工","age":27,"salary":7900,"birthDate":"1992-01-25"}
{"create":{"_index":"user","_type":"_doc","_id":2003}}
{"name":"张三","address":"广东省广州市花都区","remark":"公司底层码农员工","age":28,"salary":8800,"birthDate":"1991-10-05"}
{"create":{"_index":"user","_type":"_doc","_id":2004}}
{"name":"李四","address":"广东省广州市花都区","remark":"公司底层码农员工","age":26,"salary":9000,"birthDate":"1993-08-18"}
{"create":{"_index":"user","_type":"_doc","_id":2005}}
{"name":"王五","address":"广东省广州市花都区","remark":"公司底层码农员工","age":31,"salary":4800,"birthDate":"1988-07-20"}5.3、批量删除:
_delete_by_query :通过查询删除,既先query出符合条件的内容再进行delete操作.
# 批量操作,同一批次中可以有 create、update、delete
POST _bulk
{"delete":{"_index":"user","_type":"_doc","_id":2001}}
{"delete":{"_index":"user","_type":"_doc","_id":2002}}
{"delete":{"_index":"user","_type":"_doc","_id":2003}}
# 根据查询结果批量删除
POST user/_doc/_delete_by_query
{
"query": {
"match": { "name": "程八"}
}
}
5.4、批量更新
可以通过ctx来获得_source、_index、_type、_id、_version、_parent、_timestamp、_ttl等字段信息。
update_by_query :顾名思义,通过查询更新,既先query出符合条件的内容再进行update操作,新增字段,修改字段值都可以满足
# 批量更新数据
POST user/_doc/_bulk
{"update": {"_id": "XkQdS4MByEXWPCdI40rO"}}
{"doc": {"name": "张三三"}}
{"update": {"_id": "8"}}
{"doc": {"name": "程巴巴"}}
# 将salary为4800的数据, remark修改为“薪资4800”:
POST user/_update_by_query
{
"script": {
"inline": "ctx._source.remark='薪资4800'"
},
"query": {
"term": {
"salary": {
"value": "4800"
}
}
}
}6、查询数据
在查询命令后拼上 ?pretty ,可以将返回结果进行格式化。
6.1、查询所有文档信息
GET user/_search6.2、根据关键字查询文档信息
????????注意:text类型可以根据字段分词搜索,keyword关键词不会处理分词器
#在所有字段中搜索字符串 “guide” 的基本匹配查询:
# 该命令暂时报错
GET /twitter/_search?q=guide
#指定字段查询
# 该命令暂时报错
GET /user/_search?q=name:张三
# 配合 from 来进行分页
GET /user/_search?size=2&from=26.3、全文匹配查询(match)
????????全文查询会分析查询条件,先将查询条件进行分词,然后查询,求并集。
?????????match是经过analyer的,也就是说,文档首先被分析器给处理了。根据不同的分析器,分析的结果也稍显不同,然后再根据分词结果进行匹配。???
match 查询语法汇总:
- match_all:查询全部。
- match:返回所有匹配的分词。
- match_phrase:短语查询,在match的基础上进一步查询词组,可以指定slop分词间隔。
- match_phrase_prefix:前缀查询,根据短语中最后一个词组做前缀匹配,可以应用于搜索提示,但注意和max_expanions搭配。其实默认是50.......
- multi_match:多字段查询,使用相当的灵活,可以完成match_phrase和match_phrase_prefix的工作。
Match中的模糊匹配与强制匹配 : ‘operator’
- or :匹配单个或多个字符 ,不区分大小写,不区分顺序。默认operator为OR。
- and :必须全匹配。
设置参数 minimum_should_match 来设置至少匹配的数量。
?6.3.1、单字段匹配查询
GET /user/_search
{
"query":{
"match_all":{
}
}
}
# 查看name字段有"张三"的数据
GET /user/_search
{
"query":{
"match": {
"name": "张三"
}
}
}
# 查看所有字段有"花都区" 的数据
GET /user/_search
{
"query":{
"multi_match": {
"query": "花都区"
}
}
}
# 查看address字段有"广州"or"市"的数据
GET /user/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"address": {
"query": "广州市",
"analyzer": "standard"
}
}
}
}
#如下至少要匹配“北”,“京”,“市”,“的” ,“z” ,"先"及 “生” 这7个中的5个字才可以
GET user/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"remark": {
"query": "北京市的z先生",
"operator": "or",
"minimum_should_match": 5
}
}
}
}
?6.3.2、多字段匹配查询:
# 查询 address 包含广东省 并且年龄在26-27的数据
GET user/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {"address": "广东省"}
},
{
"range": { "age": {"gte": 26,"lte": 37}}
}
]
}
}
}6.4、顺序匹配(Match_phrase)
????????match_phrase与match 类似,但是match 查询时不用分先后顺序的,match_phrase 严格按顺序匹配。
# 查询remark中包含“张先生北京市的” 分词后的信息 数据。
GET user/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"remark": {
"query": "张先生北京市的"
}
}
}
}
# 查询remark中包含“北京市的张先生” 分词后 顺序必须一致的 数据。
GET user/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"remark": {
"query": "北京市的张先生"
}
}
}
}6.5、多字段查询(multi_match)
?????????multi_match:不知道哪个字段含有?指定关键词,在这种情况下,我们可以使用 multi_match 来进行搜索。
# 查询 name or remark 含有 “北京市”的数据
GET /user/_search/
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "北京市",
"fields": [
"name",
"remark"
]
}
}
}
6.6、精确匹配(term)
关于查询过滤条件中term和match的区别
term是代表完全匹配,也就是精确查询,搜索前不会再对搜索词进行分词拆解。
match进行搜索的时候,会先进行分词拆分,拆完后,再来匹配。
# term 查询被用于精确值 匹配,
# 这些精确值可能是数字、时间、布尔或者那些未分词的字符串(keyword)
GET /user/_search/
{
"query":{
"term":{
"age":"26"
}
}
}
# term只能完整值匹配,这样就查询不出来
GET /user/_doc/_search/
{
"query":{
"term":{
"salary":"9000"
}
}
}
#对于未分词的字符串查找
GET /user/_search/
{
"query":{
"term":{
"name.keyword":"张三"
}
}
}
6.7、多词条精确匹配(terms)?
????????terms查询:terms 跟 term 有点类似,但 terms 允许指定多个匹配条件。 如果某个字段指定了多个值,那么文档需要一起去 做匹配。
????????terms里的[ ] 多个是or的关系,只要满足其中一个词就可以。
????????在这里我们使用了name.keyword。对于一些刚接触 Elasticsearch的人来说,这个可能比较陌生。正确的理解是 name在我们的 mapping 中是一个 multi-field 项。它既是 text 也是 keyword 类型。对于一个 keyword 类型的项来说,这个项里面的所有字符都被当做一个字符串。它们在建立文档时,不需要进行 index。keyword 字段用于精确搜索,聚合?和 排序(sorting)。keyword会使返回结果的_score 项为0。
#terms里的[ ] 多个是or的关系,只要满足其中一个词就可以
GET /user/_search
{
"query":{
"terms":{
"name.keyword":["张三","赵六1"]
}
}
}
#想要同时满足两个词的话,就得使用bool的must来做,如下
GET /user/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"term": {
"name.keyword": "张三"
}
},
{
"term": {
"address.keyword": "北京市"
}
}
]
}
}
}6.8、指定匹配数组内容(Terms_set)
测试数据如下:
PUT /job-candidates
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"programming_languages": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"required_matches": {
"type": "long"
}
}
}
}
PUT /job-candidates/_doc/1?refresh
{
"name": "Jane Smith",
"programming_languages": [ "c++", "java" ],
"required_matches": 2
}
PUT /job-candidates/_doc/2?refresh
{
"name": "Jason Response",
"programming_languages": [ "java", "php" ],
"required_matches": 2
}
????????refresh : 数据插入立即生效可以使更改可见以进行搜索的操作。通常会有一个 refresh timer 来定时完成这个操作。这个周期为1秒。这也是我们通常所说的 Elasticsearch 可以实现秒级的搜索。当然这个 timer 的周期也可以在索引的设置中进行配置。如果我们想让我们的结果马上可以对搜索可见,我们可以用refresh=true。
测试案例:
????????找出在 programming_languages 中同时含有 c++, java 以及 php 中至少有两项的文档。在这里,我们使用了一个在文档中定义的字段 required_matches 来定义最少满足要求的 term 个数,这里只数组中任意搭配,只要满足数量即可:
GET /job-candidates/_search
{
"query": {
"terms_set": {
"programming_languages": {
"terms": [ "c++", "java", "php" ],
"minimum_should_match_field": "required_matches"
}
}
}
}
terms : 指定要满足的数组。
minimum_should_match_field : 指定文档中条件的属性名。
required_matches 在文档的值为2,所以指定该值最后结果就是最少满足‘terms’属性中的至少2个。
如果没有一个专有的字段来定义满足条件的个数的话,可以再查询条件中自定义,示例如下:
GET /job-candidates/_search
{
"query": {
"terms_set": {
"programming_languages": {
"terms": [ "c++", "java", "php" ],
"minimum_should_match_script": {
"source": "2"
}
}
}
}
}
6.9、多条件复合查询
????????复合查询指把很多个 leaf 查询组合起来从而形成更为复杂的查询。
????????bool 查询由 下面的 must, must_not, should 及 filter 共同来组成的。你可以使用 minimum_should_match 参数指定返回的文档必须匹配的子句的数量或百分比。
示例:
POST _search
{
"query": {
"bool" : {
"must" : {
"match": {"address": "广东" }
},
"filter": {
"match" : { "address" : "广州市" }
},
"must_not" : {
"range" : {
"age" : { "gte" : 10, "lte" : 26 }
}
},
"should" : [
{ "term" : { "name" : "张三" } },
{ "term" : { "name" : "赵六" } }
]
}
}
}
# 只搜索指定索引
GET user/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"bool" : {
"must" : {
"match": {"address": "广东" }
},
"filter": {
"match" : { "address" : "广州市" }
},
"must_not" : {
"range" : {
"age" : { "gte" : 10, "lte" : 26 }
}
},
"should" : [
{ "term" : { "name" : "张三" } },
{ "term" : { "name" : "赵六" } }
]
}
}
}
说明:
"query": {?? ??? ?
?? ? ? "bool" : {
?? ? ? ? ?"must" : ? ? [],????????//与 AND 等价。? 单个条件使用{},多个条件使【】?.
?? ? ? ? ?"must_not" : ? [],? ?//与 NOT 等价 。?同上??
?? ? ? ? ?"should" : [],? ? ? ? ?//与 OR ?等价。???同上
?? ? ? ? ?"filter":? []? ? ? ? ? ? //与must相同结果,但不会参与评分。同上
? ? }
?}must : 必须满足的条件,按相关性降序排序显示。
must_not : 可以把一些满足条件的排出在外(not in )。
should : 它表述“或”的意思,也就是有就更好,没有就算了。如果条件满足,其相关性会更高,那么搜索得到的结果会排在前面。
filter : 与must相同表示满足条件,但不会参与评分。
查询类型对 hits(即:查询结果) 及 _score(即:评分、相关度) 的影响
| 查询类型 | 影响 hits | 影响 _score |
|---|---|---|
| must | Yes | Yes |
| must_not | Yes | No |
| should | No | Yes |
| filter | Yes | No |
????????should 只有在特殊的情况下才会影响 hits。在正常的情况下它不会影响搜索文档的个数。那么在哪些情况下会影响搜索的结果呢?这种情况就是针对只有 should 的搜索情况,也就是如果你在 bool query 里,不含有 must, must_not 及 filter 的情况下,一个或更多的 should 必须有一个匹配才会有结果。
filter与must的区别 :
- 同样是按条件匹配;
- filter不统计相关度,must统计相关度;
- must比filter计算更复杂,更耗时。
6.10、查询子句
????????返回与一个或多个包在一起的查询(称为查询子句或子句)匹配的文档。
????????如果返回的文档与多个查询子句匹配,则 dis_max 查询为该文档分配来自任何匹配子句的最高相关性得分,并为任何其他匹配子查询分配平局打破增量。
示例:
GET user/_search
{
"query": {
"dis_max": {
"queries": [
{ "term" : { "name.keyword": "张三" } },
{ "match" : { "address": "北京市" } }
],
"tie_breaker": 0.7
}
}
}dis_max参数 :
- queries :包含一个或者多个查询子句。返回的文档必须匹配其中的一个或者多个,如果文档匹配了多个,则返回最高得分。
- tie_breaker :一个介于0~1.0之间的Float数,用于当文档匹配了多个查询子句时提升相关度分数。默认为0.0
????????在上面的 dis_max 查询中,它将返回任何一个在 queries 中锁定的查询文档。每个匹配分数是按照如下的规则来进行计算的:
- 如果一个文档匹配其中的一个或多个查询,那么最终的得分将以其中最高的那个得分来进行计算。
- 在默认的情况下,tie_breaker 的值为0。它可以是 0 到 1.0 之间的数。
如果文档匹配多个子句,则 dis_max 查询将计算该文档的相关性得分,如下所示:
- 从具有最高分数的匹配子句中获取相关性分数。
- 将来自其他任何匹配子句的得分乘以 tie_breaker 值。
- 将最高分数加到相乘的分数上。
如果 tie_breaker 值大于0.0,则所有匹配子句均计数,但得分最高的子句计数最高。
6.11、SQL 查询
Elasticsearch?也对 SQL 有支持,示例如下:
GET _xpack/sql?pretty
{
"query": """
SELECT * FROM user
WHERE age > 25
"""
}返回结果:

可以通过如下的方法得到它对应的 DSL 语句(即es的查询语句):?
GET _xpack/sql/translate
{
"query": """
SELECT * FROM user
WHERE age > 25
"""
}返回结果如下:
{
"size" : 1000,
"query" : {
"range" : {
"age" : {
"from" : 25,
"to" : null,
"include_lower" : false,
"include_upper" : false,
"boost" : 1.0
}
}
},
"_source" : {
"includes" : [
"address",
"name",
"remark"
],
"excludes" : [ ]
},
"docvalue_fields" : [
{
"field" : "age",
"format" : "use_field_mapping"
},
{
"field" : "birthDate",
"format" : "epoch_millis"
},
{
"field" : "salary",
"format" : "use_field_mapping"
}
],
"sort" : [
{
"_doc" : {
"order" : "asc"
}
}
]
}
6.12、Range 范围查询与 Sort 排序
range : 查询范围
sort : 可以针对多个字段同时进行排序。下面首先以 age 进行降序排序。如果是 age 是一样的话,那么就按照salary来进行排序。
# 查看年龄大于26小于29的 数据,并根据 age、salary 排序
GET user/_search
{
"query": {
"range": {
"age": {
"gte": 26,
"lte": 29
}
},
"sort": [
{
"age": {
"order": "desc"
}
},
{
"salary": {
"order": "asc"
}
}
]
}
}6.13、通配符查询(Wildcard)
可以使用 wildcard 查询一个字符串里含有的字符:
- ? 匹配任何字符,
- * 匹配零个或多个字符
# 查询name为*三 的数据
GET user/_doc/_search
{
"query":{
"wildcard":{
"name":"*三"
}
}
}6.14、指定Id值查询(Ids)
# Ids 指定Id值查询
GET user/_search
{
"query": {
"ids": {
"values": [ "1", "XkQdS4MByEXWPCdI40rO"]
}
}
}
6.14、以特定前缀开头(Prefix)
# 查询 name 以“张” 开头的数据
GET user/_search
{
"query": {
"prefix": {
"name": {
"value": "张"
}
}
}
}
6.16、多查询一次提交(Msearch)
示例:
GET user/_msearch
{"index":"user"}
{"query":{"match_all":{}},"from":0,"size":1}
{"index":"user"}
{"query":{"bool":{"filter":{"term":{"name.keyword":"张三"}}}}, "size":1}
{"index":"user"}
{"query":{"match_all":{}}}????????会将多个查询一并提交,一并返回结果,一个查询报错不会影响另一个结果 。以上查询返回结果如下:
{
"responses" : [
{
"took" : 1,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 4,
"max_score" : 1.0,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "user",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2004",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"name" : "李四",
"address" : "广东省广州市花都区",
"remark" : "公司底层码农员工",
"age" : 26,
"salary" : 9000,
"birthDate" : "1993-08-18"
}
}
]
},
"status" : 200
},
{
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 1,
"max_score" : 0.0,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "user",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "XkQdS4MByEXWPCdI40rO",
"_score" : 0.0,
"_source" : {
"name" : "张三",
"age" : 29,
"salary" : 100,
"address" : "北京市",
"remark" : "来自中国北京市的张先生",
"birthDate" : "1990-01-10"
}
}
]
},
"status" : 200
},
{
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 4,
"max_score" : 1.0,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "user",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2004",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"name" : "李四",
"address" : "广东省广州市花都区",
"remark" : "公司底层码农员工",
"age" : 26,
"salary" : 9000,
"birthDate" : "1993-08-18"
}
},
{
"_index" : "user",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2005",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"name" : "王五",
"address" : "广东省广州市花都区",
"remark" : "公司底层码农员工",
"age" : 31,
"salary" : 4800,
"birthDate" : "1988-07-20"
}
},
{
"_index" : "user",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"name" : "赵六"
}
},
{
"_index" : "user",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "XkQdS4MByEXWPCdI40rO",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"name" : "张三",
"age" : 29,
"salary" : 100,
"address" : "北京市",
"remark" : "来自中国北京市的张先生",
"birthDate" : "1990-01-10"
}
}
]
},
"status" : 200
}
]
}
6.17、查询字段是否存在(Exists)
????????查询文档中包含address字段的所有文档信息。示例如下:
????????文档里只要address这个字段不为空,那么就会被返回。反之,如果一个文档里address这个字段是空的,那么就不会返回。
#?查询文档中包含address字段的所有文档
GET user/_search
{
"query": {
"exists": {
"field": "address"
}
}
}????????查询文档不含address 这个字段的所有的文档,可以这样查询 :
? ? ? ? 注:插入时指定字段值为null,那么exists也会过滤掉。
#?查询文档不含address 这个字段的所有的文档
GET user/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must_not": {
"exists": {
"field": "address"
}
}
}
}
}6.18、控制输出的的字段
正常的查询结果(不控制出参字段)如下:
{
"took" : 1,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 1,
"max_score" : 0.97997844,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "user",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2005",
"_score" : 0.97997844,
"_source" : {
"name" : "王五",
"address" : "广东省广州市花都区",
"remark" : "公司底层码农员工",
"age" : 31,
"salary" : 4800,
"birthDate" : "1988-07-20"
}
}
]
}
}
6.18.1、通过 filter_path 来控制输出的的字段?
#通过 filter_path 来控制输出的的字段
GET user/_search?filter_path=hits.hits._score,hits.hits._source.name返回结果如下:
{
"hits" : {
"hits" : [
{
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"name" : "李四"
}
},
{
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"name" : "王五"
}
},
{
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"name" : "赵六"
}
},
{
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"name" : "张三"
}
}
]
}
}
?6.18.2、通过 _source来控制输出字段
????????_source 设置为[] 或 {} 那么就是显示所有的字段
#通过 _source来控制输出的的字段
GET user/_doc/_search
{
"_source": ["age", "name","address"],
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {"address": "北京"}
}
]
}
}
}查询结果如下:
{
"took" : 1,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 1,
"max_score" : 0.5753642,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "user",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "XkQdS4MByEXWPCdI40rO",
"_score" : 0.5753642,
"_source" : {
"address" : "北京市",
"name" : "张三",
"age" : 29
}
}
]
}
}
6.18.3、通过 _source 中的 includes 属性来控制输出字段
#通过 _source 中的 includes 属性
GET user/_search
{
"_source": {
"includes": ["name", "address","birthDate"]
},
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {"address": "北京"}
}
]
}
}
}
查询结果如下:
{
"took" : 1,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 1,
"max_score" : 0.5753642,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "user",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "XkQdS4MByEXWPCdI40rO",
"_score" : 0.5753642,
"_source" : {
"address" : "北京市",
"name" : "张三",
"birthDate" : "1990-01-10"
}
}
]
}
}
?6.18.4、通过 _source 中的 exclude属性排除指定字段输出(exclude后续版本已弃用)
#通过 _source 中的 exclude属性排除指定字段输出
GET user/_search
{
"_source": {
"exclude": ["birthDate","age"]
},
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {"address": "北京"}
}
]
}
}
}
查询结果:
#! Deprecation: Deprecated field [exclude] used, expected [excludes] instead
{
"took" : 1,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 1,
"max_score" : 0.5753642,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "user",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "XkQdS4MByEXWPCdI40rO",
"_score" : 0.5753642,
"_source" : {
"address" : "北京市",
"name" : "张三",
"remark" : "来自中国北京市的张先生",
"salary" : 100
}
}
]
}
}
6.18.5、设置 _source 为 false,这样不返回任何的 _source 信息:
#设置 _source 为 false,这样不返回任何的 _source 信息
GET user/_doc/_search
{
"_source":false,
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {"address": "北京"}
}
]
}
}
}查询结果:
{
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 1,
"max_score" : 0.5753642,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "user",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "XkQdS4MByEXWPCdI40rO",
"_score" : 0.5753642
}
]
}
}
?6.19、分页查询
????????这里的分页查询和mysql中的分页查询操作本质上是没有区别的,是只要规定我们的起始点以及页的大小即可。
GET user/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all":{}
}
, "from": 0
, "size": 2
}查询结果:
????????总数据量是4条,但是这里我们查询出来只显示了前面的两条数据,显然分页查询已经执行成功。
{
"took" : 2,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 4,
"max_score" : 1.0,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "user",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2004",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"name" : "李四",
"address" : "广东省广州市花都区",
"remark" : "公司底层码农员工",
"age" : 26,
"salary" : 9000,
"birthDate" : "1993-08-18"
}
},
{
"_index" : "user",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2005",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"name" : "王五",
"address" : "广东省广州市花都区",
"remark" : "公司底层码农员工",
"age" : 31,
"salary" : 4800,
"birthDate" : "1988-07-20"
}
}
]
}
}
6.20、高亮查询
????????我们平时在使用百度的时候,输入关键字查询内容后,关键字一般都是高亮显示的。所以ES作为一个专业的搜索框架肯定也提供了这样的功能。
????????ES的默认高亮显示:。
如:
GET /user/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "李四"
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"name": {}
}
}
}
? ?查询结果:
{
"took" : 92,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 1,
"max_score" : 1.9616584,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "user",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2004",
"_score" : 1.9616584,
"_source" : {
"name" : "李四",
"address" : "广东省广州市花都区",
"remark" : "公司底层码农员工",
"age" : 26,
"salary" : 9000,
"birthDate" : "1993-08-18"
},
"highlight" : {
"name" : [
"<em>李</em><em>四</em>"
]
}
}
]
}
}
????????ES自定义高亮显示(在highlight中,pre_tags用来实现我们的自定义标签的前半部分,在这里,我们也可以为自定义的 标签添加属性和样式。post_tags实现标签的后半部分,组成一个完整的标签。至于标签中的内容,则还是交给fields来完成)
GET /user/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"remark": "中国"
}
},
"highlight": {
"pre_tags": "<b class='key' style='color:red'>",
"post_tags": "</b>",
"fields": {
"remark": {}
}
}
}
# 或者
GET /user/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"remark": "中国"
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"remark": {
"pre_tags": "<b class='key' style='color:red'>",
"post_tags": "</b>"
}
}
}
}查询结果如下:
{
"took" : 4,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 1,
"max_score" : 0.5753642,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "user",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "XkQdS4MByEXWPCdI40rO",
"_score" : 0.5753642,
"_source" : {
"name" : "张三三",
"age" : 29,
"salary" : 100,
"address" : "北京市",
"remark" : "来自中国北京市的张先生",
"birthDate" : "1990-01-10",
"id" : "1"
},
"highlight" : {
"remark" : [
"来自<b class='key' style='color:red'>中</b><b class='key' style='color:red'>国</b>北京市的张先生"
]
}
}
]
}
}
7、Profile 调试工具
????????会显示查询出结果的详细计算过程。
GET user/_search
{
"profile": "true",
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"remark": {
"query": "北京市的张先生"
}
}
}
}8、聚合查询
????????我们平时在使用Elasticsearch时,更多会用到聚合操作,它类似SQL中的group by操作。ES的聚合查询一定是先查出结果,然后对结果使用聚合函数做处理,常用的操作有:avg:求平均、max:最大值、min:最小值、sum:求和等。
在ES中聚合分为指标聚合和分桶聚合:
- 指标聚合:对一个数据集求最大、最小、和、平均值等。
- 分桶聚合:除了有聚合函数外,还可以对查询出的数据进行分组group by,再在组上进行游标聚合。
8.1、指标聚合分析(Metric?)
指标聚合:对一个数据集求最大、最小、和、平均值等.
- 单值分析,只输出一个分析结果——avg:求平均、max:最大值、min:最小值、sum:求和、cardinality:值去重计数。
- 多值分析,输出多个分析结果
- stats:统计了count 、max、 min、 avg、 sum? 5个值。
- extended_stats:比stats多很多更加高级的统计结果:如平方和、方差、标准差、平均值加/减两个标准差的区间等。
- percentile:占比百分位对应的值统计,默认返回【1,5,25,50,75,95,99】分位上的值
8.1.1、avg示例:查询所有用户的平均年龄
GET /user/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"aggs": {
"avg_age": {
"avg": {
"field": "age"
}
}
},
"_source": [
"name",
"age"
]
}?????????上例中,首先匹配查询所有的数据。在此基础上做查询平均值的操作,这里就用到了聚合函数,其语法被封装在aggs中,而avg_age则是为查询结果起个别名,封装了计算出的平均值。
上面示例查询结果如下:
{
"took" : 1,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 4,
"max_score" : 1.0,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "user",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "8",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"name" : "程巴巴"
}
},
{
"_index" : "user",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2005",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"name" : "王五",
"age" : 31
}
},
{
"_index" : "user",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2004",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"name" : "李四",
"age" : 26
}
},
{
"_index" : "user",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "XkQdS4MByEXWPCdI40rO",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"name" : "张三三",
"age" : 29
}
}
]
},
"aggregations" : {
"avg_age" : {
"value" : 28.666666666666668
}
}
}
如果只想看输出的值,而不关心输出的文档的话可以通过size=0来控制。
# 只想看输出的值,而不关心输出的文档的话可以通过size=0来控制
GET /user/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"aggs": {
"avg_age": {
"avg": {
"field": "age"
}
}
},
"size": 0,
"_source": [
"name",
"age"
]
}查询结果如下:
{
"took" : 5,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 4,
"max_score" : 0.0,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"avg_age" : {
"value" : 28.666666666666668
}
}
}
8.1.2、avg示例:查询地址在?“广东省”用户的平均工资
#avg示例:查询地址在?“广东省”用户的平均工资
GET /user/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"address": "广东省"
}
},
"aggs": {
"avg_salary": {
"avg": {
"field": "salary"
}
}
},
"size": 0
}
查询结果:
{
"took" : 3,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 2,
"max_score" : 0.0,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"avg_salary" : {
"value" : 6900.0
}
}
}
8.1.3、max示例:查询年龄的最大值
# max示例:查询年龄的最大值
GET /user/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"aggs": {
"max_age": {
"max": {
"field": "age"
}
}
},
"size": 0
}查询结果:
{
"took" : 4,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 4,
"max_score" : 0.0,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"max_age" : {
"value" : 31.0
}
}
}
8.1.4、min示例:查询年龄的最小值
#min示例:查询年龄的最小值
GET /user/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"aggs": {
"min_age": {
"min": {
"field": "age"
}
}
},
"size": 0
}查询结果:
{
"took" : 2,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 4,
"max_score" : 0.0,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"min_age" : {
"value" : 26.0
}
}
}
8.1.5、sum示例:查询符合条件的年龄之和
#sum示例:查询符合条件的年龄之和
GET /user/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"aggs": {
"sum_age": {
"sum": {
"field": "age"
}
}
},
"size": 0
}
查询结果:
{
"took" : 1,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 4,
"max_score" : 0.0,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"sum_age" : {
"value" : 86.0
}
}
}8.1.6、cardinality示例:查询所有用户不同年龄的数量
????????相同年龄的数据,count认为是1。
? ? ? ? 在执行该示例前,专门添加了一条年龄为29的数据(原数据中已存在年龄29的数据)。
示例:查询所有用户不同年龄的数量
GET /user/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"aggs": {
"count_age": {
"cardinality": {
"field": "age"
}
}
},
"size": 0
}
查询结果:
{
"took" : 2,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 5,
"max_score" : 0.0,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"count_age" : {
"value" : 3
}
}
}
8.1.7、stats示例:查出所有用户的年龄stats信息
# stats示例:查出所有用户的年龄统计信息
GET /user/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"aggs": {
"stats_age": {
"stats": {
"field": "age"
}
}
},
"size": 0
}查询结果:
{
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 5,
"max_score" : 0.0,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"stats_age" : {
"count" : 4,
"min" : 26.0,
"max" : 31.0,
"avg" : 28.75,
"sum" : 115.0
}
}
}
8.1.8、extended_stats示例:查出所有用户的年龄extended_stats信息
#查出所有用户的年龄extended_stats信息
GET /user/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"aggs": {
"extended_stats_age": {
"extended_stats": {
"field": "age"
}
}
},
"size": 0
}查询结果:
{
"took" : 1,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 5,
"max_score" : 0.0,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"extended_stats_age" : {
"count" : 4,
"min" : 26.0,
"max" : 31.0,
"avg" : 28.75,
"sum" : 115.0,
"sum_of_squares" : 3319.0,
"variance" : 3.1875,
"std_deviation" : 1.7853571071357126,
"std_deviation_bounds" : {
"upper" : 32.320714214271426,
"lower" : 25.179285785728574
}
}
}
}
8.1.9、percentile示例:查出所有用户的年龄占比
# 查出所有用户的年龄占比
POST /user/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"aggs": {
"pecent_age": {
"percentiles": {
"field": "age"
}
}
},
"size": 0
}
查询结果:
{
"took" : 3,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 5,
"max_score" : 0.0,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"pecent_age" : {
"values" : {
"1.0" : 26.0,
"5.0" : 26.0,
"25.0" : 27.5,
"50.0" : 29.0,
"75.0" : 30.0,
"95.0" : 31.0,
"99.0" : 31.0
}
}
}
}
8.2、Bucket 分桶聚合分析
????????分桶聚合:除了有聚合函数外,还可以对查询出的数据进行分组group by,再在组上进行游标聚合。
8.2.1、分桶group by示例:根据年龄聚合查询
# 根据年龄聚合查询
GET /user/_search
{
"size": 0,
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"aggs": {
"age_group": {
"terms": {
"field": "age"
}
}
}
}查询结果:
{
"took" : 6,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 5,
"max_score" : 0.0,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"age_group" : {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound" : 0,
"sum_other_doc_count" : 0,
"buckets" : [
{
"key" : 29,
"doc_count" : 2
},
{
"key" : 26,
"doc_count" : 1
},
{
"key" : 31,
"doc_count" : 1
}
]
}
}
}
8.2.2、分桶group by示例:根据年龄段聚合查询
#根据年龄段聚合查询
GET /user/_search
{
"size": 0,
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"aggs": {
"age_group": {
"range": {
"field": "age",
"ranges": [
{
"from": 20,
"to": 30
},
{
"from": 30,
"to": 40
}
]
}
}
}
}
查询结果:
{
"took" : 4,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 5,
"max_score" : 0.0,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"age_group" : {
"buckets" : [
{
"key" : "20.0-30.0",
"from" : 20.0,
"to" : 30.0,
"doc_count" : 3
},
{
"key" : "30.0-40.0",
"from" : 30.0,
"to" : 40.0,
"doc_count" : 1
}
]
}
}
}
8.2.3、分桶group by示例:根据用户出生日期的年月分组分段聚合查询
#根据用户出生日期的年月分组分段聚合查询
POST /user/_search
{
"size": 0,
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"aggs": {
"bithday_range": {
"date_range": {
"field": "birthDate",
"format": "yyyy-MM",
"ranges": [
{
"to": "1985-01"
},
{
"from": "1985-01",
"to": "1990-01"
},
{
"from": "1990-01",
"to": "1995-01"
},
{
"from": "1995-01"
}
]
}
}
}
}查询结果:
#! Deprecation: 'y' year should be replaced with 'u'. Use 'y' for year-of-era. Prefix your date format with '8' to use the new specifier.
{
"took" : 2,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 5,
"max_score" : 0.0,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"bithday_range" : {
"buckets" : [
{
"key" : "*-1985-01",
"to" : 4.733856E11,
"to_as_string" : "1985-01",
"doc_count" : 0
},
{
"key" : "1985-01-1990-01",
"from" : 4.733856E11,
"from_as_string" : "1985-01",
"to" : 6.31152E11,
"to_as_string" : "1990-01",
"doc_count" : 1
},
{
"key" : "1990-01-1995-01",
"from" : 6.31152E11,
"from_as_string" : "1990-01",
"to" : 7.889184E11,
"to_as_string" : "1995-01",
"doc_count" : 3
},
{
"key" : "1995-01-*",
"from" : 7.889184E11,
"from_as_string" : "1995-01",
"doc_count" : 0
}
]
}
}
}
8.2.4、group by 进阶示例:按照年龄聚合,并查询出每个年龄这些人的平均薪资
????????其实就是aggs里面又加了一个aggs,第二个aggs根据第一个aggs聚合后的结果在聚合。
GET /user/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"aggs": {
"ageAgg": {
"terms": {
"field": "age"
},
"aggs": {
"ageAvg": {
"avg": {
"field": "salary"
}
}
}
}
},
"size": 0
}查询结果:
{
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 5,
"max_score" : 0.0,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"ageAgg" : {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound" : 0,
"sum_other_doc_count" : 0,
"buckets" : [
{
"key" : 29,
"doc_count" : 2,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 4500.0
}
},
{
"key" : 26,
"doc_count" : 1,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 9000.0
}
},
{
"key" : 31,
"doc_count" : 1,
"ageAvg" : {
"value" : 4800.0
}
}
]
}
}
}
8.2.5、group by 进阶示例:查出所有年龄分布,并且这些年龄段中 性别为男 的平均薪资和 性别为女 的平均薪资以及这个年龄的用户信息
GET /user/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"age_agg": {
"terms": {
"field": "age",
"size": 1000
},
"aggs": {
"sex_agg": {
"terms": {
"field": "sex.keyword",
"size": 10
},
"aggs": {
"salary_avg": {
"avg": {
"field": "salary"
}
}
}
},
"salary_avg": {
"avg": {
"field": "salary"
}
}
}
}
}
}
查询结果:
{
"took" : 8,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 5,
"max_score" : 0.0,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"age_agg" : {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound" : 0,
"sum_other_doc_count" : 0,
"buckets" : [
{
"key" : 29,
"doc_count" : 2,
"sex_agg" : {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound" : 0,
"sum_other_doc_count" : 0,
"buckets" : [
{
"key" : "女",
"doc_count" : 1,
"salary_avg" : {
"value" : 3000.0
}
},
{
"key" : "男",
"doc_count" : 1,
"salary_avg" : {
"value" : 6000.0
}
}
]
},
"salary_avg" : {
"value" : 4500.0
}
},
{
"key" : 26,
"doc_count" : 1,
"sex_agg" : {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound" : 0,
"sum_other_doc_count" : 0,
"buckets" : [
{
"key" : "女",
"doc_count" : 1,
"salary_avg" : {
"value" : 9000.0
}
}
]
},
"salary_avg" : {
"value" : 9000.0
}
},
{
"key" : 31,
"doc_count" : 1,
"sex_agg" : {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound" : 0,
"sum_other_doc_count" : 0,
"buckets" : [
{
"key" : "男",
"doc_count" : 1,
"salary_avg" : {
"value" : 4800.0
}
}
]
},
"salary_avg" : {
"value" : 4800.0
}
}
]
}
}
}
9、queryString查询
????????会对查询条件进行分词, 然后将分词后的查询条件和词条进行等值匹配,默认取并集(OR),可以指定单个字段也可多个查询字段。
示例:
#查询1: 查询name 中包含指定 内容分词后的数据
POST /user/_search
{
"query": {
"query_string": {
"default_field": "name",
"query": "张三 OR 李四"
}
},
"size": 100
}
# 查询2:查询name、address 中包含指定 内容分词后的数据
GET /user/_search
{
"query": {
"query_string": {
"fields": ["name","address"],
"query": "张三三 or 国中人"
}
}
}查询结果:
#查询1:结果
{
"took" : 7,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 3,
"max_score" : 1.3862944,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "user",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2004",
"_score" : 1.3862944,
"_source" : {
"name" : "李四",
"address" : "广东省广州市花都区",
"remark" : "公司底层码农员工",
"age" : 26,
"salary" : 9000,
"birthDate" : "1993-08-18",
"sex" : "女"
}
},
{
"_index" : "user",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "XkQdS4MByEXWPCdI40rO",
"_score" : 0.68324494,
"_source" : {
"name" : "张三三",
"age" : 29,
"salary" : 3000,
"address" : "北京市",
"remark" : "来自中国北京市的张先生",
"birthDate" : "1990-09-10",
"sex" : "女"
}
},
{
"_index" : "user",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "13",
"_score" : 0.5753642,
"_source" : {
"name" : "张三",
"age" : 29,
"salary" : 6000,
"address" : "北京市",
"remark" : "来自中国北京市的张先生",
"birthDate" : "1990-09-10",
"sex" : "男"
}
}
]
}
}
# 查询2:结果
{
"took" : 1,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 5,
"successful" : 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 2,
"max_score" : 1.0788078,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "user",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "XkQdS4MByEXWPCdI40rO",
"_score" : 1.0788078,
"_source" : {
"name" : "张三三",
"age" : 29,
"salary" : 3000,
"address" : "北京市",
"remark" : "来自中国北京市的张先生",
"birthDate" : "1990-09-10",
"sex" : "女"
}
},
{
"_index" : "user",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "13",
"_score" : 0.8630463,
"_source" : {
"name" : "张三",
"age" : 29,
"salary" : 6000,
"address" : "北京市",
"remark" : "来自中国北京市的张先生",
"birthDate" : "1990-09-10",
"sex" : "男"
}
}
]
}
}10、重建索引
????????随着业务需求的变更,索引的结构可能发生改变。ElasticSearch的索引一旦创建,只允许添加字段,不允许改变字段。因为改变字段,需要重建倒排索引,影响内部缓存结构,性能太低。那么此时,就需要重建一个新的索引,并将原有索引的数据导入到新索引中。
- 原索引库 :test_index_v1
- 新索引库 :test_index_v2
10.1、创建test_index_v1索引、添加数据
? ? ? ? 创建test_index_v1索引,索引名称必须全部小写。
# 新建test_index_v1索引,索引名称必须全部小写
PUT test_index_v1
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"birthday":{
"type": "date"
}
}
}
}
# 查询索引
GET test_index_v1
# 添加数据
PUT test_index_v1/_doc/1
{
"birthday":"2020-11-11"
}
10.2、业务变更,字段类型需要变动
# 查询数据
GET test_index_v1/_search
# 随着业务的变更,换种数据类型进行添加数据,程序会直接报错
PUT test_index_v1/_doc/1
{
"birthday":"2020年11月11号"
}
10.3、?新建索引库 :test_index_v2
# 业务变更,需要改变birthday数据类型为text
# 1:创建新的索引 test_index_v2
# 2:将test_index_v1 数据拷贝到 test_index_v2
# 创建新的索引
PUT test_index_v2
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"birthday":{
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}10.4、将test_index_v1 数据拷贝到 test_index_v2
# 将test_index_v1 数据拷贝到 test_index_v2
POST _reindex
{
"source": {
"index": "test_index_v1"
},
"dest": {
"index": "test_index_v2"
}
}
# 查询新索引库数据
GET test_index_v2/_search
# 在新的索引库里面添加数据
PUT test_index_v2/_doc/2
{
"birthday":"2020年11月13号"
}
DELETE test_index_v111、别名的使用
11.1、查询别名
#获取指定索引的别名
GET /user/_alias
#获取ES中所有索引的别名
GET /_alias查询结果:
# 索引user的别名查询结果:
{
"user" : {
"aliases" : { }
}
}11.2、新增别名
# 给索引user 添加別名:user_alias_1.0
POST /_aliases
{
"actions": [
{
"add": {
"index": "user",
"alias": "user_alias_1.0"
}
}
]
}别名查询结果:
# 索引user的别名查询结果:
{
"user" : {
"aliases" : {
"user_alias_1.0" : { }
}
}
}
11.3、删除别名
# 删除别名
#方式一
POST /_aliases
{
"actions": [
{
"remove": {
"index": "user",
"alias": "user_alias_1.0"
}
}
]
}
#方式二
DELETE /user/_alias/user_alias_1.011.4、重命名别名
# 重命名别名
POST /_aliases
{
"actions": [
{
"remove": {
"index": "user",
"alias": "user_alias_1.0"
}
},
{
"add": {
"index": "user",
"alias": "user_alias_2.0"
}
}
]
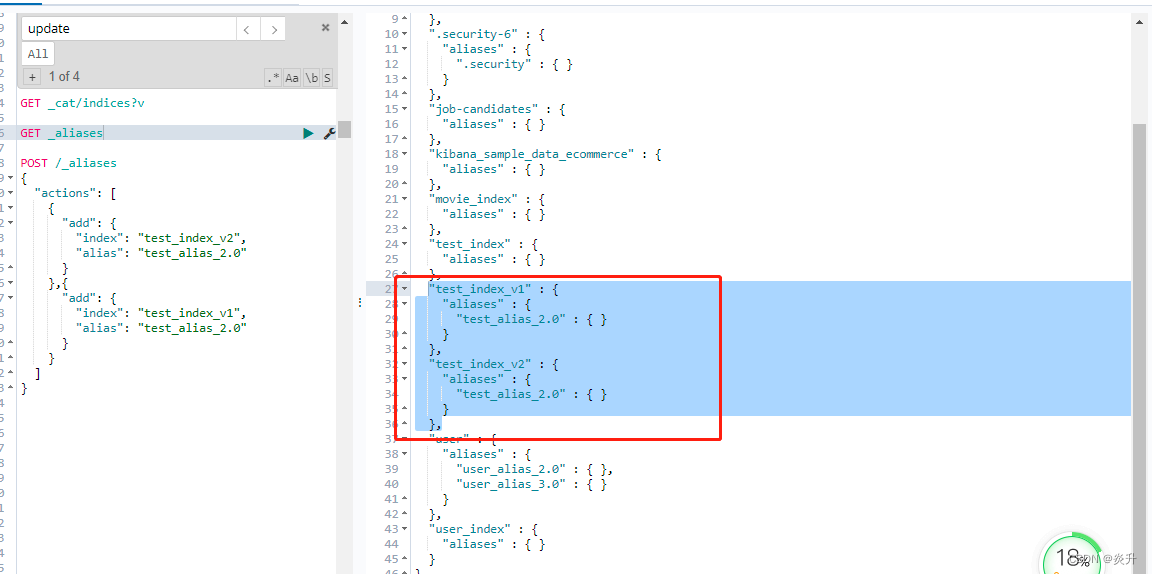
}11.5、为多个索引指定一个别名
# 为多个索引指定一个别名
POST /_aliases
{
"actions": [
{
"add": {
"index": "test_index_v2",
"alias": "test_alias_2.0"
}
},{
"add": {
"index": "test_index_v1",
"alias": "test_alias_2.0"
}
}
]
}查询所有别名:
11.6、为同个索引指定多个别名?
# 为同个索引指定多个别名?
POST /_aliases
{
"actions": [
{
"add": {
"index": "user",
"alias": "user_alias_2.0"
}
},{
"add": {
"index": "user",
"alias": "user_alias_3.0"
}
}
]
}11.7、通过别名读索引
GET user_alias_2.0/_doc/13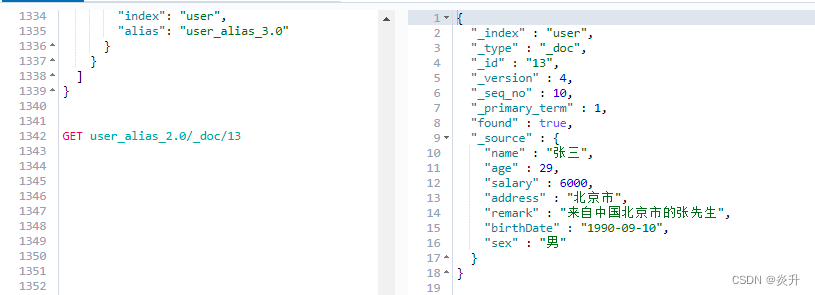
?11.8、通过别名写索引
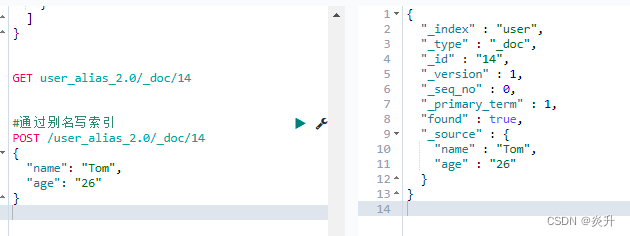
#通过别名写索引
POST /user_alias_2.0/_doc/14
{
"name": "Tom",
"age": "26"
}