在自定义View和雷达图两篇博客的基础上,进行了些许修改,这里总结一下我自己的学习心得。
自定义View有如下几种方式
| 类型 | 定义 |
|---|---|
| 自定义组合控件 | 多个控件组合成为一个新的控件,方便多处复用 |
| 继承系统View控件 | 继承自TextView等系统控件,在系统控件的基础功能上进行扩展 |
| 继承View | 不复用系统控件逻辑,继承View进行功能定义 |
| 继承系统ViewGroup | 继承自LinearLayout等系统控件,在系统控件的基础功能上进行扩展 |
| 继承ViewViewGroup | 不复用系统控件逻辑,继承ViewGroup进行功能定义 |
本文是通过继承于View来实现雷达图。
布局文件
在布局文件里加入雷达图控件,就能展示。控件程序在LeiDaMap类里,布局直接在layout文件夹里XML文件里添加:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<com.example.demo.radarMap.LeiDaMap
android:id="@+id/leiDaMap"
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_height="280dp"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal" />
</LinearLayout>
控件文件
完整的代码如下所示,下面详细介绍程序流程。
package com.example.demo.radarMap
import android.content.Context
import android.graphics.Canvas
import android.graphics.Color
import android.graphics.Paint
import android.graphics.Path
import android.util.AttributeSet
import android.view.View
import kotlin.math.cos
import kotlin.math.min
import kotlin.math.sin
/**
* @description: 雷达图
*/
class LeiDaMap(context: Context?, attrs: AttributeSet?, defStyleAttr: Int) :
View(context, attrs, defStyleAttr) {
/**
* 多边形点的个数
*/
private val count = 6
/**
* 雷达图层数
*/
private val num = 4
/**
* 多边形均等分角度,用弧度表示
*/
private val angle = (Math.PI * 2 / count).toFloat()
/**
* 网格最大半径
*/
private var radius = 0f
/**
* 中心x
*/
private var centerX = 0
/**
* 中心y
*/
private var centerY = 0
/**
* 数据最大值
*/
private var maxValue = 100f
/**
* 各维度分值
*/
private var data = doubleArrayOf(50.0, 60.0, 70.0, 80.0, 90.0, 100.0)
private var titles = arrayOf("一一", "二二", "三三", "四四", "五五", "六六")
/**
* 雷达区画笔
*/
private var mMainPaint: Paint? = null
/**
* 文本画笔
*/
private var mTextPaint: Paint? = null
/**
* 数据区画笔
*/
private var mValuePaint: Paint? = null
constructor(context: Context?) : this(context, null)
constructor(context: Context?, attrs: AttributeSet?) : this(context, attrs, 0)
private fun initPaint() {
mMainPaint = Paint()
mMainPaint?.isAntiAlias = true
mMainPaint?.strokeWidth = 3F
mMainPaint?.style = Paint.Style.STROKE
mMainPaint?.color = Color.BLACK
mTextPaint = Paint()
mTextPaint?.isAntiAlias = true
mTextPaint?.color = Color.BLUE
mTextPaint?.textSize = 60F
mValuePaint = Paint()
mValuePaint?.isAntiAlias = true
mValuePaint?.color = Color.RED
mValuePaint?.style = Paint.Style.FILL_AND_STROKE
}
override fun onSizeChanged(w: Int, h: Int, oldw: Int, oldh: Int) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh)
//网格最大半径
radius = min(h, w).toFloat() / 2 * 0.7f
centerX = w / 2
centerY = h / 2
postInvalidate()
}
override fun onDraw(canvas: Canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas)
//绘制正多边形
drawPolygon(canvas)
//绘制从中心到末端的直线
drawLines(canvas)
//绘制文本
drawText(canvas)
//绘制区域
drawRegion(canvas)
}
/**
* 绘制正多边形
*/
private fun drawPolygon(canvas: Canvas) {
val path = Path()
//蜘蛛丝之间的间距
val r = radius / num
for (i in 1..num) {
//当前半径
val curR = r * i
path.reset()
//多边形点的个数
for (j in 0 until count) {
if (j == 0) {
path.moveTo(centerX.toFloat(), centerY + curR)
} else {
//根据半径,计算出蜘蛛丝上每个点的坐标
val x = (centerX + curR * sin((angle * j).toDouble())).toFloat()
val y = (centerY + curR * cos((angle * j).toDouble())).toFloat()
path.lineTo(x, y)
}
}
//闭合路径
path.close()
mMainPaint?.let { canvas.drawPath(path, it) }
}
}
/**
* 绘制从中心到末端的直线
*/
private fun drawLines(canvas: Canvas) {
val path = Path()
for (i in 0 until count) {
path.reset()
path.moveTo(centerX.toFloat(), centerY.toFloat())
//计算最外侧蜘蛛丝上每个点的坐标
val x = (centerX + radius * sin((angle * i).toDouble())).toFloat()
val y = (centerY + radius * cos((angle * i).toDouble())).toFloat()
path.lineTo(x, y)
mMainPaint?.let { canvas.drawPath(path, it) }
}
}
/**
* 绘制文本
* 先计算出文本的长度,然后使起始绘制坐标向左偏移这个长度。
*/
private fun drawText(canvas: Canvas) {
val fontMetrics: Paint.FontMetrics = mTextPaint!!.fontMetrics
val fontHeight: Float = fontMetrics.descent - fontMetrics.ascent
for (i in 0 until count) {
//计算最外侧蜘蛛丝上每个点的坐标
val x =
(centerX + (radius + fontHeight / 2) * sin((angle * i).toDouble())).toFloat()
val y =
(centerY + (radius + fontHeight / 2) * cos((angle * i).toDouble())).toFloat()
// 文字长度,以文字长度为基准来移动文字
val dis: Float = mTextPaint!!.measureText(titles[i])
//一象限、二象限
if (i == 1 || i == 2) {
canvas.drawText(titles[i], x, y, mTextPaint!!)
}
// 三象限、四象限
else if (i == 4 || i == 5) {
canvas.drawText(titles[i], x - dis, y, mTextPaint!!)
}
// 坐标轴上的点
else if (i == 0) {
canvas.drawText(titles[i], x - dis / 2, y + dis / 3, mTextPaint!!)
}
else if (i == 3) {
canvas.drawText(titles[i], x - dis / 2, y, mTextPaint!!)
}
}
}
/**
* 绘制区域
*/
private fun drawRegion(canvas: Canvas) {
val path = Path()
mValuePaint?.alpha = 255
for (i in 0 until count) {
val percent = data[i] / maxValue
//计算最外侧蜘蛛丝上每个点的坐标
val x = (centerX + radius * sin((angle * i).toDouble()) * percent).toFloat()
val y = (centerY + radius * cos((angle * i).toDouble()) * percent).toFloat()
if (i == 0) {
path.moveTo(centerX.toFloat(), y)
} else {
path.lineTo(x, y)
}
//绘制小圆点
mValuePaint?.let { canvas.drawCircle(x, y, 20F, it) }
}
mValuePaint?.alpha = 127
//绘制填充区域
mValuePaint?.let { canvas.drawPath(path, it) }
}
/**
* @param titles
*/
fun setTitles(titles: Array<String>) {
this.titles = titles
}
/**
* 各维度分值
* @param data data
*/
fun setData(data: DoubleArray) {
this.data = data
}
/**
* 数据最大值
* @param maxValue maxValue
*/
fun setMaxValue(maxValue: Float) {
this.maxValue = maxValue
}
/**
* 设置蜘蛛网颜色
* @param color
*/
fun setMainPaintColor(color: Int) {
mMainPaint?.color = color
}
/**
* 设置标题颜色
* @param color
*/
fun setTextPaintColor(color: Int) {
mTextPaint?.color = color
}
/**
* @param color
*/
fun setValuePaintColor(color: Int) {
mValuePaint?.color = color
}
init {
initPaint()
}
}
运行后:
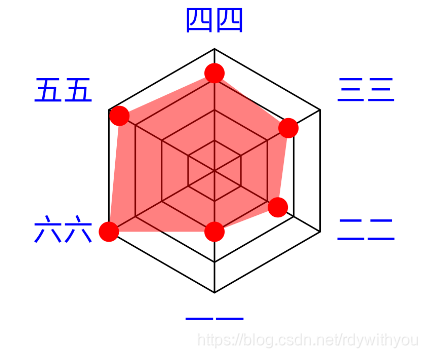
前面都是进行变量的初始化,绘图流程如下:
1、找到布局的中心
2、绘制多边形
3、绘制中心到角的连线
4、绘制文本(可能涉及到文字偏移)
5、绘制区域
1、找到布局的中心
重写onSizeChanged函数,找到中心点,以及雷达图的最大半径。为了给文本留有余地,需要乘以一个系数。
override fun onSizeChanged(w: Int, h: Int, oldw: Int, oldh: Int) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh)
//网格最大半径
radius = min(h, w).toFloat() / 2 * 0.7f
centerX = w / 2
centerY = h / 2
postInvalidate()
}
2、画多边形
private fun drawPolygon(canvas: Canvas) {
val path = Path()
//蜘蛛丝之间的间距
val r = radius / num
for (i in 1..num) {
//当前半径
val curR = r * i
path.reset()
//多边形点的个数
for (j in 0 until count) {
if (j == 0) {
path.moveTo(centerX.toFloat(), centerY + curR)
} else {
//根据半径,计算出蜘蛛丝上每个点的坐标
val x = (centerX + curR * sin((angle * j).toDouble())).toFloat()
val y = (centerY + curR * cos((angle * j).toDouble())).toFloat()
path.lineTo(x, y)
}
}
//闭合路径
path.close()
mMainPaint?.let { canvas.drawPath(path, it) }
}
}
3、绘制中心点到角的连线
private fun drawLines(canvas: Canvas) {
val path = Path()
for (i in 0 until count) {
path.reset()
path.moveTo(centerX.toFloat(), centerY.toFloat())
//计算最外侧蜘蛛丝上每个点的坐标
val x = (centerX + radius * sin((angle * i).toDouble())).toFloat()
val y = (centerY + radius * cos((angle * i).toDouble())).toFloat()
path.lineTo(x, y)
mMainPaint?.let { canvas.drawPath(path, it) }
}
}
4、绘制文本
可根据需要,在if选择语句里根据i的值或者根据象限进行判断。
private fun drawText(canvas: Canvas) {
val fontMetrics: Paint.FontMetrics = mTextPaint!!.fontMetrics
val fontHeight: Float = fontMetrics.descent - fontMetrics.ascent
for (i in 0 until count) {
//计算最外侧蜘蛛丝上每个点的坐标
val x =
(centerX + (radius + fontHeight / 2) * sin((angle * i).toDouble())).toFloat()
val y =
(centerY + (radius + fontHeight / 2) * cos((angle * i).toDouble())).toFloat()
// 文字长度,以文字长度为基准来移动文字
val dis: Float = mTextPaint!!.measureText(titles[i])
//一象限、二象限
if (i == 1 || i == 2) {
canvas.drawText(titles[i], x, y, mTextPaint!!)
}
// 三象限、四象限
else if (i == 4 || i == 5) {
canvas.drawText(titles[i], x - dis, y, mTextPaint!!)
}
// 坐标轴
else if (i == 0) {
canvas.drawText(titles[i], x - dis / 2, y + dis / 3, mTextPaint!!)
}
else if (i == 3) {
canvas.drawText(titles[i], x - dis / 2, y, mTextPaint!!)
}
}
}
5、绘制区域
private fun drawRegion(canvas: Canvas) {
val path = Path()
mValuePaint?.alpha = 255
for (i in 0 until count) {
val percent = data[i] / maxValue
//计算最外侧蜘蛛丝上每个点的坐标
val x = (centerX + radius * sin((angle * i).toDouble()) * percent).toFloat()
val y = (centerY + radius * cos((angle * i).toDouble()) * percent).toFloat()
if (i == 0) {
path.moveTo(centerX.toFloat(), y)
} else {
path.lineTo(x, y)
}
//绘制小圆点
mValuePaint?.let { canvas.drawCircle(x, y, 20F, it) }
}
mValuePaint?.alpha = 127
//绘制填充区域
mValuePaint?.let { canvas.drawPath(path, it) }
}