用户设计基础
UI设计相关概念
View
概念相关
可以理解为视图,占据屏幕上的一块矩形区域,用于提供主键绘制和事件处理的方法。
View通常以view类的形式出现,但是我们通常使用view类的子类(比如TextView)进行开发。
View类位于android.view包中,View类的子类一般都位于android.widget包中。
View类常用属性
android:id
用于为组件设置唯一标识
定义一个组件id为textView:
android:id="@+id/textView"
id的值分为两部分,前面的部分**@+id为固定写法,后面的textView**才是该组件的id值。
android:background
用于设置组件背景,属性值可以是图片资源,也可以是具体颜色值
使用图片资源:
android:background="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
**@mipmap/**为固定写法之一,ic_launcher为图片的名称,上面的值表示会到mipmap中找资源名为ic_launcher的图片。
直接写颜色:
android:background="#FF6600"
设置颜色没有固定部分,直接写颜色的值即可。
android:padding
用于设置组件上下左右的内边距
设置组件内边距为16dp:
android:padding="16dp"
也可以这么写:
android:padding="@dimen/activity_margin"
此时padding的值设置成一个尺寸资源内的变量(当然,首先得定义该资源)
如 果想单独设置某个方向上的内边距,可以使用这四个属性:android:paddingLeft(android:paddingStart)、android:paddingTop、android:paddingRight(android:paddingEnd)、android:paddingBottom。
ViewGroup
相关概念
容纳View以及其派生类的容器,本身也是继承自View类,是抽象类,开发通常使用它的子类来开发
VIewGroup控制其子组件分布时通常还依靠两个内部类:ViewGroup.LayoutParams,ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams
ViewGroup.LayoutParams
用于控制布局的位置、宽高
下面两个属性的值可以为具体的值,也可以是三个特定值:FILL_PARENT、MATCH_PARENT、WRAP_CONTENT,前面两个都表示于父容器相同,后面的属性表示由自身决定
android:layout_hieght
用于设置布局高度
android:layout_width
用于设置布局宽度
ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams
主要控制子组件的外边距
主要有以下属性:android:layout_marginTop、android:layout_marginBottom、android:layout_marginLeft(android:layout_marginStart)、android:layout_marginRight(android:layout_marginEnd)
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-NaaNJ6Vx-1628226902044)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210629213132890.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/3c710580183c465eb7d7d44622df8dee.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3NoaXlhbnNhbWE=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
值可以是具体值,也可以是引用资源文件的变量。
控制UI界面
控制UI界面有很多种方法,通常推荐使用XML的方式(其实和CSS的理念差不多)
使用XML布局文件控制UI界面
在Android应用的res/layout目录下编写XML布局文件
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-M3HHBV5B-1628226902045)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210629213949772.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/7c6e51e61df9461d8741578427868dba.png)
在Activity中使用Java代码显示XML文件中布局的内容
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
一个小实例
我们先在项目中新建一个module,命名为gamestarts,然后模板选择Empty Activity,其他的默认即可
先打开layout目录下的activity_main.xml布局文件,把整体布局改成帧布局FrameLayout
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
......
tools:context=".MainActivity">
......
</FrameLayout>
然后在TextView控件中设置该控件的text(文本内容)、layout_gravity(设置对齐)、textSize(文本大小)、textColor(文本颜色)四个属性,如下面这段代码所示:
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/start"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:textSize="18sp"
android:textColor="#115572"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
观察text的值,我们可以发现使用的是values目录下资源文件string.xml中的资源,在该文件中定义一下即可:
<string name="start">开始游戏</string>
选择该module运行,我们就可以看到结果了:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-ddZ4JAKB-1628226902046)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210803205506728.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/2b708823417f4da3a65b195174296ab1.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3NoaXlhbnNhbWE=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
在Java代码中控制UI界面
安卓支持像java Swing那样,完全通过代码控制UI界面(当然这种方式是很不聪明的,所以这里仅作了解)
先贴代码:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
// 设置布局管理器
FrameLayout frameLayout = new FrameLayout(this);
// frameLayout.setBackgroundResource(R.mipmap.bg); // 设置背景
setContentView(frameLayout);
//设置TextView相关属性
TextView textView = new TextView(this);
textView.setText("start");
textView.setTextSize(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_SP, 18);
textView.setTextColor(Color.rgb(17, 85, 114));
FrameLayout.LayoutParams params = new FrameLayout.LayoutParams(
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT,
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
params.gravity = Gravity.CENTER;
textView.setLayoutParams(params);
//设置点击事件
textView.setOnClickListener(v -> {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
new AlertDialog.Builder(MainActivity.this).setTitle("system prompt")
.setMessage("Clicking is risky, enter cautiously ")
.setPositiveButton("sure",
// 指定点击事件监听器
(dialog, which) -> Log.i("Desktop billiards", "enter the game"))
.setNegativeButton("quit",
(dialog, which) -> {
Log.i("Desktop billiards", "quit the game");
finish(); // 用于结束当前Activity
}).show(); // show显示对话框
}
});
//将控件添加刀布局上
frameLayout.addView(textView);
}
}
此时我们不再需要xml文件,所以将setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);去掉
最终的实现效果:

点击中间的textView控件之后:
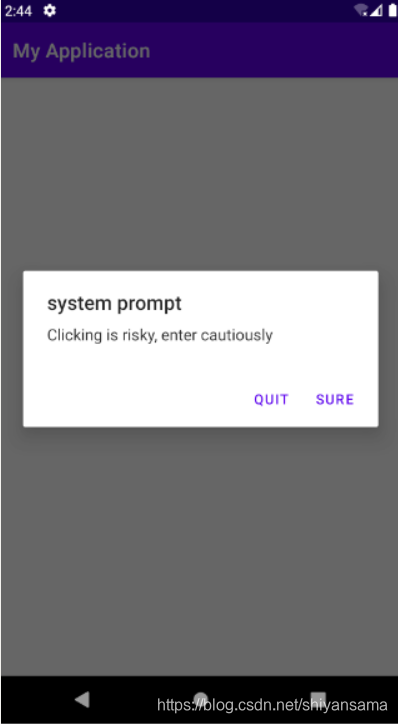
此时点击quit便能结束该程序,返回桌面。
需要注意的是,在代码中的textView.setOnClickListener部分,采用的是链式写法(安卓中较为常见)以及lambda表达式。
代码中分别设置了setPositiveButton和setNegativeButton,一般用于设置确认和取消按钮,他们的第二个参数传入一个监听器,用于设置点击之后应该做的事务。
其实跟java Swing的写法差不了多少,只不过这种写法跟Swing一样,都是旧时代的事物了(笑
使用XML和Java代码混合控制UI界面
按照学习惯例,毫无疑问,这种混合控制的方式要比上面那两个好。
现阶段如果使用java来开发安卓应用,推荐的还是通过xml和代码混合控制UI界面的方式:xml文件简单指明布局和控件的基础信息,java代码来负责处理复杂的渲染逻辑以及事物逻辑,
下面来一个小案例。
修改布局文件
首先我们对activity_main.xml文件进行修改,修改整体布局为GridLayout(网格布局),然后在GridLayout标签下指定id、orientation(指定布局内控件排列方式)、rowCount(网格布局最大行数)、columnCount(网格布局最大列数)四个属性,并删掉默认的TextView:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<GridLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/layout"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:rowCount="3"
android:columnCount="4"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
</GridLayout>
修改MainActivity
然后就是对MainActivity进行编写。
首先定义ImageView控件数组:
private ImageView[] imageViews = new ImageView[12];
然后定义照片地址数组,用于保存每张照片在资源文件的位置:
private int[] imagePath = new int[]{
R.mipmap.img01, R.mipmap.img02, R.mipmap.img03, R.mipmap.img04, R.mipmap.img05, R.mipmap.img06,
R.mipmap.img07,R.mipmap.img08,R.mipmap.img09, R.mipmap.img10,R.mipmap.img11,R.mipmap.img12,
};
把我们选择好的照片放入mipmap-hdpi目录中(一共12张):
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-9DvkONps-1628226902048)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210804144632337.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/64705da34631489d94ef4ecda194f9cd.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3NoaXlhbnNhbWE=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
注意放入的照片不要太大,否则模拟器加载的时候会很卡,尽可能整齐一些,不然效果不好(就像我这样)
接着编写主要逻辑:
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//获取GridLayout对象
GridLayout layout = findViewById(R.id.layout);
for (int i = 0; i < imagePath.length; i++) {
imageViews[i] = new ImageView(MainActivity.this); // 参数为上下文对象
imageViews[i].setImageResource(imagePath[i]); // 设置图片
imageViews[i].setPadding(2, 2, 2, 2); // 设置边距
/**
* LayoutParams: 告诉父控件,子控件要如何布局
* 这里对每个子控件设置长宽
*/
ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(250, 150); // 设置图片大小
imageViews[i].setLayoutParams(params);
layout.addView(imageViews[i]);
}
}
在ibCreate方法中,首先获取布局对象,接着对ImageView数组的每个成员进行一定程度的初始化,再将其放入布局中,达到动态渲染控件的目的。
运行上述代码,可以看到下面的结果:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-x4zPpVIa-1628226902049)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210804144515413.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/fc8db706605b4726b9a4bdbe264e37dd.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3NoaXlhbnNhbWE=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
开发自定义View
原生的View类时常不能满足我们的开发需求,所以通常我们除了使用View子类之外,还会自定义继承于View的子类
具体实现步骤为:在布局文件中定义好布局管理器,然后编写继承自View的子类,重写构造方法以及onDraw方法等,然后在MainActivity中实例化,添加到布局中。
一个小实例
下面通过一个小案例:跟随鼠标移动的兔子,来了解自定义View的流程
在项目中新建一个module,名字命名为selfView。
首先准备好两张图片,一张大一张小,大的为背景,小的随意:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-Qr6OCpWv-1628226902050)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210804150223363.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/0c3478377f9a4c51a2cbbc85c3451663.png)
然后放入mipmap目录下的xhdpi:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-1AnNMODC-1628226902051)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210804150354663.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e9d2f0aef3ae4cd8a4c300ba7e955bbf.png)
修改布局文件,布局管理器修改为FrameLayout,指定布局管理器的background、id,删除原来的TextView:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@mipmap/background"
android:id="@+id/mylayout"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
</FrameLayout>
在工作目录下新建RabbitView类,继承自View类,该子类定义两个私有变量,分别表示兔子的x、y坐标。重写onDraw方法,该方法里定义Paint类和Bitmap类的实例,重新绘制之后判断是否回收。
onDraw方法用于绘制View本身的内容
public class RabbitView extends View {
// 定义兔子坐标
private float bitmapX;
private float bitmapY;
public void setBitmapX(float bitmapX) {
this.bitmapX = bitmapX;
}
public void setBitmapY(float bitmapY) {
this.bitmapY = bitmapY;
}
public RabbitView(Context context) {
super(context);
bitmapX = 290;
bitmapY = 130;
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
Paint paint = new Paint(); // 画笔对象
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(this.getResources(), R.mipmap.rabbit);
canvas.drawBitmap(bitmap, bitmapX, bitmapY, paint);
if (bitmap.isRecycled()) {
bitmap.recycle();
}
}
}
Paint:画笔对象,制定了如何绘制文本和图形等
Bitmap:表示位图,本质是一张图片的内容在内存中的表达形式
Canvas:可以简单理解为画布, canvas.drawBitmap方法用于绘制Bitmap对象,
接下来是MainActivity类的编写,该类主要实例化RabbitView对象并将其加入到布局中,为RabbitView实例添加setOnTouchListener(触摸事件)监听,当触摸屏幕时会根据点击的坐标重新设置控件坐标,然后调用nvalidate()方法重绘控件:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
@SuppressLint("ClickableViewAccessibility")
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
FrameLayout frameLayout = findViewById(R.id.mylayout);
RabbitView rabbitView = new RabbitView(this);
rabbitView.setOnTouchListener((v, event) -> {
rabbitView.setBitmapX(event.getX());
rabbitView.setBitmapY(event.getY());
rabbitView.invalidate();
return true;
});
frameLayout.addView(rabbitView);
}
}
注意上面监听器内匿名方法的返回值,如果返回false,那么按下鼠标之后只能将RabbitView移动到点击的坐标,后续无法跟随跟下的鼠标进行移动,返回为true则可以。
具体请了解安卓关于事件分发以及事件优先级相关内容
运行结果:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-2x64MYJu-1628226902052)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210804192422562.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/96f33dca36c5412c82b4e07419194c2c.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3NoaXlhbnNhbWE=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
此时在屏幕下任意一处地方摁下鼠标,就可以发现兔子跟随鼠标移动而移动了。
布局管理器
布局管理器主要用于控制控件的布局
常用布局管理器
原生安卓提供的布局管理器主要为下面几种:
- RelativeLayout:相对布局管理器
- LinearLayout:线性布局管理器
- FrameLayout:帧布局管理器
- TableLayout:表格布局管理器
- Absolutel ayout:绝对布局管理器(由于其过于死板,所以现在一般使用其他布局管理器进行替代)
- GridLayout:网格布局管理器
- ConstraintLayout:约束布局管理器
- …
目前新建项目或者Module,一般默认为约束布局
相对布局(RelativeLayout)
相对布局讲究要有参考点,参考点可以是父容器、兄弟组件
新建一个Module,然后把布局改成RelativeLayout。
布局层面上的一些属性
注意,往后几种布局出现的属性不一定是私有,很多都是通用的
首先我们来认识布局层面中的一些基本的属性。
android:gravity
表示容器中各自组件的摆放方式,值有多个
比如设置其值为"cneter",那么子组件就会在父容器中上下居中显示:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-g9bjsxCQ-1628226902054)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210804202045743.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a051579dddbf45a79dc9a8a04c63cf12.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3NoaXlhbnNhbWE=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
android:ignoregravity
表明某个组件不受gravity影响,值为组件id。
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-SHMuvuu9-1628226902054)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210804201959223.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/974ef9f297a1435bb92cd04ad6ac4800.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3NoaXlhbnNhbWE=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
控件层面上的一些属性
为了更好地控制控件的相对位置,安卓还提供了一个用于控件的内部类RelativeLayout.LayoutParams,这个类提供了一些xml属性,通过这些属性我们可以更好地控制控件层面上的布局
主要四组属性
关于控件层面,我们主要了解四组属性。
关于组件之间的相对位置,值为id:
- android:layout_above:该组件位于另一个组件的上方
- android:layout_below:该组件位于另一个组件的下方
- android:layout_toLeftOf:该组件位于另一个组件的左侧
- android:layout_toRightOf;该组件位于另一个组件的右侧
以及关于组件和父容器之间的对齐方式,值为布尔类型:
- android:layout_alignParentBottom:组件与父容器底对齐
- android:layout_alignParentLeft:组件与父容器左对齐
- android:layout_alignParentRight:组件与父容器右对齐
- android:layout_alignParentTop:组件与父容器顶对齐
设置组件与另一个组件的某个边界对齐(注意与第一组区分,这里的对齐是某个水平线上的对齐)。值为id:
- ndroid:layout_alignBottom:控件下边缘与指定控件下边缘对齐
- ndroid:layout_alignLeft:控件左边缘与指定控件左边缘对齐
- ndroid:layout_alignRight:控件右边缘与指定控件右边缘对齐
- ndroid:layout_alignTop:控件上边缘与指定控件上边缘对齐
最后是设置组件在布局管理器中的位置:
- android:layout_centerInParent:表示组件位于布局的水平居中位置
- android:layout_centerHorizontal:表示组件位于布局的中央位置
- android:layout_centerVertical:表示组件位于布局的垂直居中位置
第一组属性的演示
复制几个TextView,分别给id赋值,改变text的值,去掉原本存在的app:layout_constraint部分属性
第一组属性:
首先贴上代码,一one为中心,其余四个分别设置layout_below、layout_above、layout_toLeftOf和layout_toRightOf属性:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textview"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="one"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textview2"
android:layout_below="@+id/textview"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="two"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textview3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_above="@+id/textview"
android:text="three" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textview4"
android:layout_toLeftOf="@+id/textview"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="four"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textview5"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/textview"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="five"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
此处为了显示方便,我为每个控件都添加了android:layout_centerInParent="true"属性,表示该控件位于布局管理器的中央
下面是演示效果:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-tEhygLoY-1628226902055)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210804205310620.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6da2977fcf6c440c812b5aa25b47bfde.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3NoaXlhbnNhbWE=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
可以看到,其余四个textView控件已经围绕在了one的四周
其余三组属性可自行百度其效果。
相对布局实例
下面我们就用相对布局整一个实例:软件更新提示界面
项目中新建一个Module,名字随意。这个实例只需要我们编写布局文件,所以较为简单。
随便找一张背景图片,放进mipmap目录下的xhdpi下:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-EJlgR6eD-1628226902056)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210805092328205.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/9a1f46a1bfb34c27a04c845ebcbb87c4.png)
然后把xml文件原本的约束布局改成RelativeLayout相对布局,增加背景,增加两个TextView控件,修改控件样式:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:background="@mipmap/bg"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textview"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="发现有新版本,你想现在安装吗?"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_below="@+id/textview"
android:layout_alignRight="@+id/textview"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="以后再说"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_below="@+id/textview"
android:layout_toLeftOf="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="现在更新"/>
</RelativeLayout>
运行效果入下:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-peH4Q52D-1628226902056)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210805092503268.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/2e0cdf2c31a34b5ab1829a38c6c7a107.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3NoaXlhbnNhbWE=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
线性布局(LinearLayout)
线性布局主要将放入的组件进行水平/垂直地排列
布局层面上的一些属性
android:orientation
线性布局的排列方式主要通过android:orientation属性来显示,该属性有两个值:horizontal(垂直)和vertical(水平)。
需要注意的是:
-
垂直线性布局每行只会放置一个控件,控件超出底部之后将不会显示
-
水平线性布局每列只能方式一个组件,控件超出水平边缘之后将不会显示
当然,对于水平线性布局,如果横屏状态下的控件足以让所有控件显示,那么属性状态下没显示的控件也会一并显示出来。垂直线性布局同理。
比如下面这部分xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="按钮"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="按钮"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="按钮"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="按钮"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button5"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="按钮"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button6"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="按钮"/>
</LinearLayout>
它的效果是这样的:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-zcWSjZOS-1628226902057)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210805101835840.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/f82a9feb0a4d4fe39c80f6acc71f018e.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3NoaXlhbnNhbWE=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-MhR1CzNq-1628226902057)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210805101936478.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a2e64314a7914c979f9cfbbac55ffabc.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3NoaXlhbnNhbWE=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
android:gravity
这个属性跟之前相对布局的用法差别不大,也是设置布局内组件的显示方式
修改一下上面的xml:
android:orientation="vertical"
android:gravity="center"
演示效果:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-jKHkhpJH-1628226902058)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210805102347843.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/1495a6b8140b452dba0d9aa1bf74f4ba.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3NoaXlhbnNhbWE=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
如果gravity使用多个属性,那么属性之间用 | 分隔:
比如下面这种写法,组件右下角显示:
android:gravity="bottom|right"
演示效果:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-mCxjmMj6-1628226902058)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210805102613663.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/93c6f9ae774649609f031d69722bd0ed.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3NoaXlhbnNhbWE=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
控件层面上的一些属性
在控件层面上有一个很重要的属性:android:layout_weight,它表示给标记的组件分配布局内的剩余空间。
如图所示:因为组件1和组件2的权重都是1,所以120的剩余控件被平均地分配给了两个组件,各自增加60。
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-HxPTfD5a-1628226902059)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210805103255600.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/09288053dbe44826b3b94c18e2c4c572.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3NoaXlhbnNhbWE=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
注意不要误认为是根据权重分配整体空间
线性布局实例
下面来写一个线性布局的实例,实现一个简单的登陆界面
创建一个新的Module,命名为login。
首先我们修改一下整体的主题,在AndroidManifest.xml文件中找到android:theme,然后修改值为@style/Theme.AppCompat.Light.DarkActionBar:
android:theme="@style/Theme.AppCompat.Light.DarkActionBar"
找到两张图片表示账号和密码,放在mipmap目录下的xxhdpi目录中:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-8YRcBoJQ-1628226902060)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210805104958276.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/7fd461f0bbb242d3a555c1439d9697c3.png)
当然,没有合适的图片自己写一个组件代替也可以
接着修改布局文件。先把整体布局改成LinearLayout,添加orientation属性,添加两个EditText组件、一个Button组件、一个TextView组件。
整体代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:paddingBottom="20dp"
android:hint="邮箱"
android:drawableLeft="@mipmap/zhanghao"
/>
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:paddingBottom="20dp"
android:hint="密码"
android:drawableLeft="@mipmap/zhanghao"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textColor="#FFFFFF"
android:background="#FF009688"
android:text="登陆"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="登陆遇到问题?"
android:paddingTop="20dp"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
/>
</LinearLayout>
下面是演示效果:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-ZpusenIE-1628226902061)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210805105557240.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e703e0c6af834668ae7617ed2a047105.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3NoaXlhbnNhbWE=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
帧布局(FrameLayout)
帧布局为每一个组件创建一个空白的区域,组件按照先后顺序层叠放置,后面的组件会覆盖前面的组件
帧布局由于其特殊性,所以一般用于实现层叠(比如手机时钟)、拖动比如上面自定义View小节中的实例)等效果(
布局层面上的一些属性
布局层面上的属性主要有两个:android:foreground和android:foregroundGravity。前者主要为布局设置前景图像,后者主要是为前景图像设置位置。
前景图像就是始终位于最上层的图像
下面来具体演示一下写法。
首先把布局改成FrameLayout,然后添加两个TextView控件,布局添加属性foreground以及foregroundGravity设置前景图像以及位置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:id="@+id/mylayout"
android:foreground="@mipmap/b"
android:foregroundGravity=""
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#FF0000"
android:text="第一层"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#FFFF00"
android:layout_marginLeft="20dp"
android:text="第二层"/>
</FrameLayout>
下面是演示效果:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-TTbXZ4lR-1628226902061)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210805211748392.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/ce50fe5f49784a5b8c2d5767f3a6c437.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3NoaXlhbnNhbWE=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
如果把前景图像去掉,那么将会是下面的结果:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-IN6I4912-1628226902062)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210805211910113.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/5be5bee4830e44779ea4b455022c3c92.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3NoaXlhbnNhbWE=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
一个小实例
下面来实现另一个小实例
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:id="@+id/mylayout"
android:foreground="@mipmap/g"
android:foregroundGravity="center"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:layout_width="280dp"
android:layout_height="280dp"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:background="#FF0000FF"
android:textColor="#FFFFFF"
android:text="蓝色背景"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="230dp"
android:layout_height="230dp"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:background="#FF0077FF"
android:textColor="#FFFFFF"
android:text="天蓝色背景"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="180dp"
android:layout_height="180dp"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:background="#FF00B4FF"
android:textColor="#FFFFFF"
android:text="水蓝色背景"/>
</FrameLayout>
下面是演示结果:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-1RHRPF1C-1628226902062)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210805212629655.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/4f08d80509d74c948dc367dac62dd390.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3NoaXlhbnNhbWE=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
表格布局(TableLayout)
表格布局管理器是以行列的形式来管理控件的
布局层面上的一些属性
表格布局主要使用TableRow标签来管理行,在该布局当中没有管理列的标签,列数主要由TableRow标签内控件的个数决定。
比如下面的写法:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TableRow>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Hello"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Hello"/>
</TableRow>
<TableRow>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Hello"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Hello"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Hello"/>
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>
得到的结果是这样的:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-EeYGKleG-1628226902063)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210805213445171.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b781ec356cc54c3bb2ba88366972c66f.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3NoaXlhbnNhbWE=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
当然,我们还可以设置某个列被隐藏、拉伸、收缩。
隐藏列使用android:collapseColumns属性来实现,该属性用于布局层面,多行使用逗号分隔。
下面的xml设置第1、2列被隐藏(从0开始):
android:collapseColumns="1,2"
结果:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-UcyblPjT-1628226902064)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210805213818322.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/f8b1a97e122545af8ee9c54f9a580f46.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3NoaXlhbnNhbWE=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
可以看到只剩下第0行了
下面的xml表示第1、2列被拉伸:
android:stretchColumns="1,2"
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-ZdfFRrLL-1628226902064)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210805214059235.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/aefe6a60cf654a7caec23f49ed725ebf.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3NoaXlhbnNhbWE=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
注意,这个属性是在空余空间层面上的拉伸
最后是列的收缩,收缩仅仅生效于某列被挤出屏幕的边缘。
假如有下面这部分xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TableRow>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Hello01111111111111111111111"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Hello1"/>
</TableRow>
<TableRow>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Hello0"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Hello1"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Hello2"/>
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>
它的效果应该是这样的:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-N0ODOEvd-1628226902065)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210805215309674.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/95c0a8478b6844068bbb4cb08af59fe5.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3NoaXlhbnNhbWE=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
可以看到第2列已经被挤出边缘。
这个时候我们添加下面的属性:
android:shrinkColumns="0"
这个时候第0行就被压缩了:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-eU5P8N8U-1628226902066)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210805215509133.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d5cae1aa24424881914a9a19b71c252f.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3NoaXlhbnNhbWE=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
一个小实例
下面通过表格布局实现一个登陆界面
创建一个新的Module,布局改成TableLayout,准备一张图片作为背景:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-kLg3d7O6-1628226902067)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210805222256126.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/0632bec75f1c47a08d036bd58e1628fd.png)
xml文件入下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@mipmap/biaoge"
android:theme="@style/Theme.AppCompat.Light.DarkActionBar"
android:stretchColumns="0,3"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TableRow android:paddingTop="320dp">
<TextView/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="账 号: "
android:textSize="18dp"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
/>
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="邮箱/手机号"
/>
<TextView/>
</TableRow>
<TableRow>
<TextView/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="密 码: "
android:textSize="18dp"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
/>
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="密码"
/>
<TextView/>
</TableRow>
<TableRow>
<TextView/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="注 册"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="登 陆"
/>
<TextView/>
</TableRow>
<TableRow
android:paddingTop="20dp">
<TextView/>
<TextView/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="忘记密码啊?"
android:textColor="#FF4500"
android:layout_gravity="right"
/>
<TextView/>
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>
效果如图:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-clVzZZ8c-1628226902067)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210805222409671.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c959c228ed344727aa7b342a1e311e59.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3NoaXlhbnNhbWE=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
这里的表格布局只包含了下面表单部分,上面的第三方登陆是背景图。
由于代码没有做动态适配,所以有些地方看起来有点丑
网格布局(GridLayout)
网格布局管理器跟表格不一样,网格布局总体更加灵活,允许控件跨行跨列显示,而表格只允许跨行,并且超出边缘的组件将会换行显示
布局层面上的一些属性
网格布局有三个主要属性。
- android:columnCount:用于指定网格最大列数
- android:orientation:当没有为放置在布局中的组件分配行和列时,这些组件的排列方式
- android:rowCount:指定网格最大行数
下面的代码指定最大行数为2,控件排列方式为vertical(竖直排列):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<GridLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:rowCount="2"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="按钮1"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="按钮2"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="按钮3"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="按钮4"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="按钮5"/>
</GridLayout>
效果为下图:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-3FZK6K6m-1628226902068)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210806100919472.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e2c588e90b1342208d4cd5bfc6fc46fe.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3NoaXlhbnNhbWE=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
控件层面上的一些属性
GridLayout.LayoutPatams提供了一些xml属性来管理各子组件的分布
主要有下面这几种属性:
- android:layout_column:指定某组件位于网格第几列
- android:layout_columnSpan:指定子组件横向跨几列
- android:layout_columnWeight:指定子组件水平方向上的权重(也就是水平剩余控件分配的比例)
- android:layout_gravity:设置子组件占据网格空间的方式(位置)
- android:layout_row:指定控件位于网格第几行
- android:layout_rowSpan:指定控件纵向跨行数
- android:layout_column:控件垂直方向上的权重
下面的代码设置了每个控件的行列数,其中第三个控件设置跨行数1,并且layout_gravity设置为fill(填充):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<GridLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_column="0"
android:layout_row="0"
android:text="按钮1"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_column="2"
android:layout_row="1"
android:text="按钮2"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_column="1"
android:layout_row="0"
android:layout_rowSpan="2"
android:layout_gravity="fill"
android:text="按钮3"/>
</GridLayout>
最终的效果如下图:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-kKuAMmLF-1628226902069)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210806102754438.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/292c50dae6c844cdb19fd41b78d21cfc.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3NoaXlhbnNhbWE=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
左边的图可能难以理解,看右边的图就知道了,按钮3被设置为占据两行,又因为layout_gravity设置为fill,所以它在横向与纵向上尽可能地占据了“全部空间”。
如果不设置layout_gravity为fill,那么按钮3还是只会占据第一行(根据其本身大小决定),除非把layout_height改成match_parent
一个小实例
创建一个新地Module。准备好一些图片,挡在mipmap的mdpi里:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-aiA6YIpw-1628226902070)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210806103705367.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e223f82c4c4a4c1e983ad80660ca4fc4.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3NoaXlhbnNhbWE=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
修改布局,增加8个ImageView控件,然后分别定义各自属性:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<GridLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:columnCount="6"
android:background="@mipmap/bg"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageview1"
android:src="@mipmap/a1"
android:layout_gravity="end"
android:layout_columnSpan="4"
android:layout_column="1"
android:layout_row="0"
android:layout_marginRight="5dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="20dp"
/>
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageview2"
android:src="@mipmap/ico2"
android:layout_column="5"
android:layout_row="0"
/>
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageview3"
android:src="@mipmap/ico1"
android:layout_column="0"
android:layout_row="1"
/>
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageview4"
android:src="@mipmap/b1"
android:layout_column="1"
android:layout_row="1"
android:layout_marginBottom="20dp"
/>
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageview5"
android:src="@mipmap/a2"
android:layout_gravity="end"
android:layout_columnSpan="4"
android:layout_column="1"
android:layout_row="2"
android:layout_marginRight="5dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="20dp"
/>
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageview6"
android:src="@mipmap/ico2"
android:layout_column="5"
android:layout_row="2"
/>
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageview7"
android:src="@mipmap/ico1"
android:layout_column="0"
android:layout_row="3"
/>
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageview8"
android:src="@mipmap/b2"
android:layout_column="1"
android:layout_row="3"
android:layout_marginBottom="20dp"
/>
</GridLayout>
下面是演示效果:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-caXPBVWY-1628226902070)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210806111117141.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/1c800508f2cc4a32af67ebc045fff8b8.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3NoaXlhbnNhbWE=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)
控件内的具体属性需要注意的有layout_gravity和layout_columnSpan的用法,以及考虑控件本身大小与这两个属性之间的关系。
约束布局
这个布局先不整,新建项目默认的就是这个布局
布局管理器的嵌套
实际开发中往往嵌套使用布局
嵌套原则
布局管理器嵌套主要有下面三个原则:
- 根布局管理器必须包含xmlns属性
- 一个布局文件中只能存在一个根布局管理器
- 不能嵌套过多,否则影响性能
嵌套实例
new一个Module,准备好几张图片。
xhdpi中:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-JnikSraS-1628226902070)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210806112547797.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e05b3d3da92444afb0dec20754a85290.png)
mdpi中:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-d4BzKnaF-1628226902071)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210806112608956.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e311678a4f2d4c0296c690e5aba25634.png)
整体布局采用线性布局管理,内部采用相对布局管理。
下面是xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingTop="16dp"
android:paddingBottom="16dp"
android:paddingLeft="16dp"
android:paddingRight="16dp"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="10dp">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/ico1"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:src="@mipmap/v_ico1"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/name1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="雪绒花"
android:textColor="#576B95"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/ico1"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/content1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/newyear"
android:minLines="3"
android:layout_marginTop="5dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="5dp"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/ico1"
android:layout_below="@+id/name1"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/time1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="昨天"
android:textColor="#9A9A9A"
android:layout_marginTop="3dp"
android:layout_below="@+id/content1"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/ico1"
/>
<ImageView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_below="@+id/content1"
android:src="@mipmap/comment"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
<ImageView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@mipmap/line"/>
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="10dp">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/ico2"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:src="@mipmap/v_ico2"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/name2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="李刚"
android:textColor="#576B95"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/ico2"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/content2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/fight"
android:minLines="3"
android:layout_marginTop="5dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="5dp"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/ico2"
android:layout_below="@+id/name2"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/time2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="前天"
android:textColor="#9A9A9A"
android:layout_marginTop="3dp"
android:layout_below="@+id/content2"
android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/ico2"
/>
<ImageView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_below="@+id/content2"
android:src="@mipmap/comment"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
<ImageView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@mipmap/line"/>
</LinearLayout>
实现的效果:
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-c9BB0syZ-1628226902072)(C:\Users\15998\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20210806121548256.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/205cc8f7b22b47378af25eaaa6bd329c.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3NoaXlhbnNhbWE=,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)