?什么是协程,谈谈你对协程的认识
协程是一段可执行的任务,可挂起/恢复执行,概念上语言无关,通常实现是用户态的协作式调度,从具体实现上来说,可以分为两大类:有栈协程和无栈协程
协程关注点:Task Hierarchy、异常取消机制、三种常用的CoroutineContext、Task 状态
- 有栈协程:协程切换会保存完成上下文,可以在其任意嵌套函数中被挂起
- 无栈协程:通过状态机维护代码运行状态,协程切换的本质是指令指针寄存器的改变
Coroutine Scope
- CoroutineScope
public interface CoroutineScope {
/**
* The context of this scope.
* Context is encapsulated by the scope and used for implementation of coroutine builders that are extensions on the scope.
* Accessing this property in general code is not recommended for any purposes except accessing the [Job] instance for advanced usages.
*
* By convention, should contain an instance of a [job][Job] to enforce structured concurrency.
*/
public val coroutineContext: CoroutineContext
}- MainScope
@Suppress("FunctionName")
public fun MainScope(): CoroutineScope = ContextScope(SupervisorJob() + Dispatchers.Main)- GlobalScope
不绑定任何 Job,用于启动在整个应用程序生命周期内运行且不会过早取消的顶级协程
/** There are limited circumstances under which `GlobalScope` can be
* legitimately and safely used, such as top-level background
* processes that must stay active for the whole duration of the
* application's lifetime. Because of that, any use of `GlobalScope` requires
* an explicit opt-in with `@OptIn(DelicateCoroutinesApi::class)`, like this:
*/
// A global coroutine to log statistics every second, must be always active
val globalScopeReporter = GlobalScope.launch {
while (true) {
delay(1000)
logStatistics()
}
}
@ExperimentalCoroutinesApi
public actual fun CoroutineScope.newCoroutineContext(context: CoroutineContext): CoroutineContext {
val combined = coroutineContext + context
val debug = if (DEBUG) combined + CoroutineId(COROUTINE_ID.incrementAndGet()) else combined
return if (combined !== Dispatchers.Default && combined[ContinuationInterceptor] == null)
debug + Dispatchers.Default else debug
}CoroutineContext
Parent context = Defaults + inherited CoroutineContext + arguments
- Some elements have default values: Dispatchers.Default is the default of CoroutineDispatcher and “coroutine” the default of CoroutineName.
- The inherited CoroutineContext is the CoroutineContext of the CoroutineScope or coroutine that created it.
- Arguments passed in the coroutine builder will take precedence over those elements in the inherited context.
协程总是在 CoroutineContext 中执行,CoroutineContext 是一组元素,用于定义线程执行策略、异常逻辑处理、生命周期维护
- Job
- Parent-child hierarchies
- SupervisorJob vs?Job
With a SupervisorJob, the failure of a child doesn’t affect other children. A SupervisorJob won’t cancel itself or the rest of its children. Moreover, SupervisorJob won’t propagate the exception either, and will let the child coroutine handle it.
- CoroutineDispatcher(ContinuationInterceptor)
- Dispatchers.Default
- Dispatchers.IO
- Dispatchers.Main
- Dispatchers.Unconfined : The coroutine executes in the current thread first and lets the coroutine resume in whatever thread that is used by the corresponding suspending function.
- CoroutineExceptionHandler : Normally, uncaught exceptions can only result from coroutines created using the launch builder. A coroutine that was created using async always catches all its exceptions and represents them in the resulting Deferred object.
Job 状态
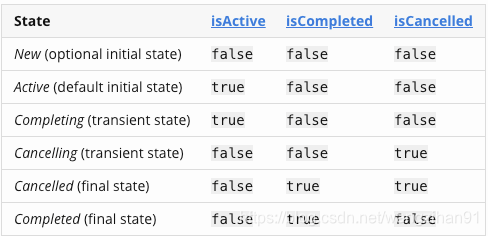
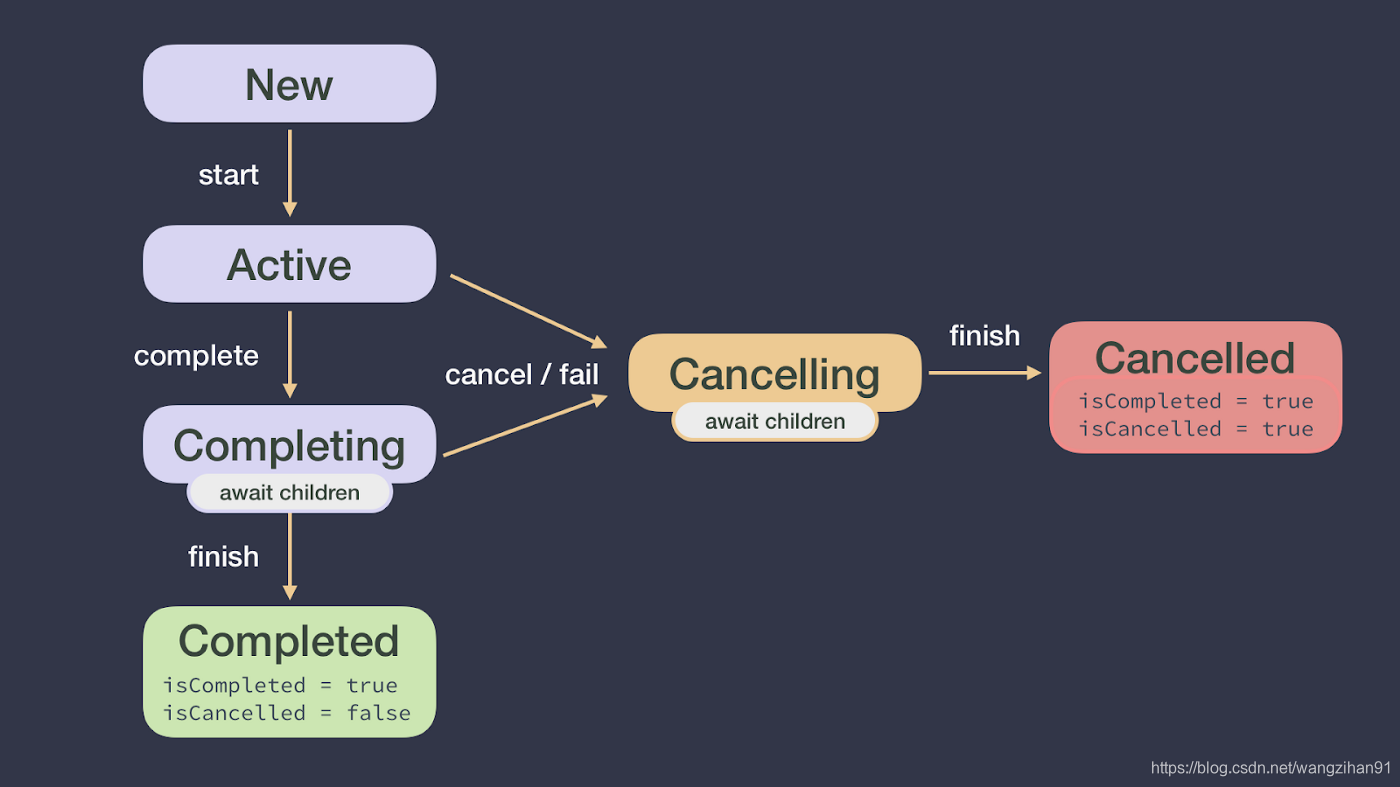
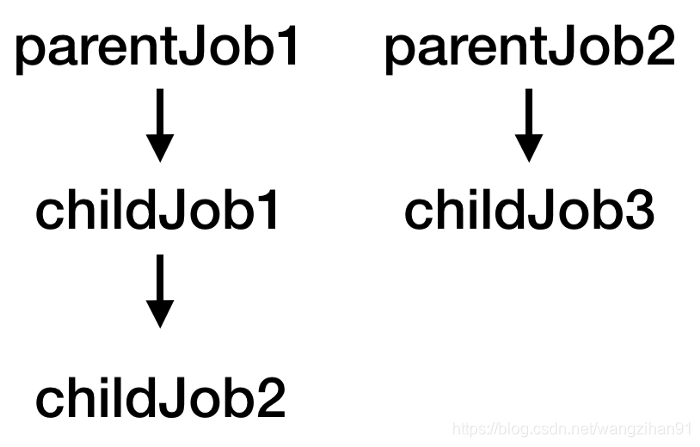
Job 层级关系
val parentJob1 = Job()
val parentJob2 = Job()
val childJob1 = CoroutineScope(parentJob1).launch {
val childJob2 = launch { ... }
val childJob3 = launch(parentJob2) { ... }
}
?协程作用域
- 顶级作用域:通过 CoroutineScope.launch 启动的协程
- 协同作用域:协程内直接调用 launch 或协程内通过 coroutineScope 启动的协程
- 主从作用域:通过 supervisorScope 或通过传入 SupervisorJob 创建的协程,主从作用域只和直接子协程是主从关系(孙子协程如果发生异常,还是会 cancel 掉同级的协程)
异常和取消处理
- cancel 父协程会同时 cancel 所有子协程
- cancelChildren 用于取消所有的子协程,而不取消自己
- cancel 子协程不会影响兄弟协程和父协程
-
public override fun cancel(cause: CancellationException?) { cancelInternal(cause ?: defaultCancellationException()) } - 顶级作用域:发生异常时可以通过自身的 CoroutineExceptionHandler 捕获,如果没有捕获异常,异常会传给线程处理,导致崩溃
- 协同作用域:子协程无法单独处理异常,即使设置了 CoroutineExceptionHandler,异常也会向上传递,并且异常会 cancel 父协程和其他同级的协程
- 主从作用域:异常可以由子协程的 CoroutineExceptionHandler 处理,如果子协程没有处理异常,则异常向上传递,但不会 cancel 父协程和其他同级的协程
- 协程通过特殊的异常(CancellationException)取消当前协程,该异常不遵循异常传递模型(不会向上传递,不会被 CoroutineExceptionHandler 捕获)
Exceptions will be caught if these requirements are met:
- When ?: The exception is thrown by a coroutine that automatically throws exceptions (works with launch, not with async).
- Where 🌍: If it’s in the CoroutineContext of a CoroutineScope or a root coroutine (direct child of CoroutineScope or a supervisorScope).
协同作用域内无法捕获 await 抛出的异常,而是在 async 中直接向上抛
supervisorScope {
val deferred = async {
codeThatCanThrowExceptions()
}
try {
deferred.await()
} catch(e: Exception) {
// Handle exception thrown in async
}
}
coroutineScope {
try {
val deferred = async {
codeThatCanThrowExceptions()
}
deferred.await()
} catch(e: Exception) {
// Exception thrown in async WILL NOT be caught here
// but propagated up to the scope
}
}外层的 Try / Catch 无法捕获协程的异常
try {
CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Main).launch {
doSomething()
}
} catch (e: IOException) {
// Cannot catch IOException() here.
Log.d("demo", "try-catch: $e")
}
private suspend fun doSomething() {
delay(1_000)
throw IOException()
}Job.invokeOnCompletion 可以获取异常信息
val job = CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Main).launch {
doSomething()
}
job.invokeOnCompletion {
val error = it ?: return@invokeOnCompletion
// Prints "invokeOnCompletion: java.util.concurrent.CancellationException".
Log.d("demo", "invokeOnCompletion: $error")
}
}
private suspend fun doSomething() {
delay(1_000)
throw CancellationException()
}Coroutine builder
- launch 没有返回值,用来启动一个无需结果的耗时任务(如批量文件删除、创建),可以抛出异常
- async 有返回值(如网络请求、数据库读写、文件读写),通过await函数获取返回值,对于顶级作用域或主从作用域启动的 async,异常只会在 await 时抛出
- 如果 cancel 掉 launch 返回的 Job,再次调用 Job.join,不会抛出异常,而是等待 Job 正常结束
- 如果 cancel 掉 async 返回的 Deferred,再次调用 Deferred.await,则会抛出CancellationException异常
suspend fun main() {
val deferred = GlobalScope.async<Int> {
throw ArithmeticException()
}
try {
val value = deferred.await()
log("1. $value")
} catch (e: Exception) {
log("2. $e")
}
}
// 13:25:14:693 [main] 2. java.lang.ArithmeticException
suspend fun main() {
val deferred = GlobalScope.async<Int> {
throw ArithmeticException()
}
try {
deferred.join()
log(1)
} catch (e: Exception) {
log("2. $e")
}
}
// 13:26:15:034 [main] 1Suspend Function
挂起函数会阻塞协程体,直到挂起函数执行结束。Kotlin 内置的挂起函数会响应 cancel 请求(检查 Job 状态,如果Job是cancelled状态会立即回收资源并抛出CancellationException),我们在实现 withContext、suspendCancellableCoroutine 等挂起函数时需要事实检查Job状态并手动清理资源,如果我们没有抛出CancellationException,在挂起函数返回时系统会自动抛出 CancellationException
- Checking job.isActive or ensureActive
- Let other work happen using yield
如果协程体内不存在挂起函数,则需要自己在一定时机来判断 Job 状态,并抛出 CancellationException
- delay
- withContext 可以切换 Dispatcher,无法设置自身的 ExceptionHandler(类似协同作用域)
- coroutineScope 协同作用域
- supervisorScope
- suspendCancellableCoroutine
suspend fun work() {
return suspendCancellableCoroutine { continuation ->
continuation.invokeOnCancellation {
// do cleanup
}
// rest of the implementation
}To be able to call suspend functions when a coroutine is cancelled, we will need to switch the cleanup work we need to do in a NonCancellable CoroutineContext. This will allow the code to suspend and will keep the coroutine in the Cancelling state until the work is done
val job = launch {
try {
work()
} catch (e: CancellationException){
println(“Work cancelled!”)
} finally {
withContext(NonCancellable){
delay(1000L) // or some other suspend fun
println(“Cleanup done!”)
}
}
}
delay(1000L)
println(“Cancel!”)
job.cancel()
println(“Done!”)协程启动模式
- CoroutineStart.DEFAULT:直接调度并执行协程体
- CoroutineStart.LAZY:只在需要的时候开始调度执行(Job.start、Job.join)
- CoroutineStart.ATOMIC:只能在挂起点(start、await、join)取消
- CoroutineStart.UNDISPATCHED:立即执行,直到运行到第一个挂起点切换线程
拦截器/调度器
suspend fun main() {
GlobalScope.launch(MyContinuationInterceptor()) {
log(1)
val job = async {
log(2)
delay(1000)
log(3)
"hello"
}
log(4)
val result = job.await()
log("5. $result")
}.join()
log(6)
}
//[main] <MyContinuation> Success(kotlin.Unit)
//[main] 1
//[main] <MyContinuation> Success(kotlin.Unit)
//[main] 2
//[main] 4
//[kotlinx.coroutines.DefaultExecutor] <MyContinuation> Success(kotlin.Unit)
//[kotlinx.coroutines.DefaultExecutor] 3
//[kotlinx.coroutines.DefaultExecutor] <MyContinuation> Success(Hello)
//[kotlinx.coroutines.DefaultExecutor] 5. Hello
//[kotlinx.coroutines.DefaultExecutor] 6
/*
所有协程启动的时候,都会有一次?Continuation.resumeWith?的操作,这一次操作对于调度器来说就是一次调度的机会
其次,delay 是挂起点,在 JVM 上?delay?实际上是在一个?ScheduledExcecutor?里面添加了一个延时任务,因此会发生线程切换
*/Dispatchers.IO、Dispatchers.Default、Dispatchers.Main
suspend fun main() {
val myDispatcher =
Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor { r ->
Thread(r, "MyThread")
}.asCoroutineDispatcher() // 线程池转调度器
GlobalScope.launch(myDispatcher) {
log(1)
}.join()
log(2)
}
myDispatcher.close() // 需要关闭Kotlin 协程具体原理
协程体内的代码都是通过Continuation.resumeWith调用,调用resumeWith时会通过CoroutineInterceptor完成线程切换,每调用一次label加1,每一个挂起点对应于一个case分支,挂起函数在返回COROUTINE_SUSPENDED时才会挂起
通过该方法配合Continuation状态转移以及CoroutineInterceptor即可完成协程奇妙的功能
// 状态转移
suspend fun returnSuspend() = suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn<String> {
continuation ->
thread {
Thread.sleep(1000)
continuation.resume("Return suspended")
}
COROUTINE_SUSPENDED
}
suspend fun returnImmediately() = suspendCoroutineUninterceptedOrReturn<String> {
"Return immediately"
}
// Continuation代表一个回调,编译器会通过switch策略控制执行,每当遇到挂起点状态值加一,并把当前的Continuation传给挂起点
// suspend方法会自动添加一个Continuation参数
// 协程体内的代码都是通过Continuation.resumeWith调用;
// 每次调用label加1,每个挂起点对应于一个case分支;
// 挂起函数在返回COROUTINE_SUSPENDED时才会挂起;runBlocking
运行一个新的协程并**阻塞**当前线程直到它完成。不应在协程中使用此函数,它旨在将常规同步代码桥接到以挂起风格编写的库,以用于“main”函数和测试。
Runs a new coroutine and **blocks** the current thread _interruptibly_ until its completion. This function should not be used from a coroutine. It is designed to bridge regular blocking code?to libraries that are written in suspending style, to be used in `main` functions and in tests.