View的绘制流程
View 的绘制流程是从 ViewRootImpl 的 performTraversals() 方法开始的,经过测量(measure)、布局(layout)和绘制(draw)三个过程才能把一个 View 绘制出来,measure方法用于测量 View 的宽高,layout用于确定 View 在父容器中的放置位置,draw负责做具体的绘制操作。
ViewRootImpl 的 performTraversal() 方法会依次调用 performMeasure,performLayout和 performDraw三个方法,这三个方法分别完成 DecorView 的测量、布局和绘制三大流程。
测量过程
对于 ViewGroup,除了要完成自己的测量,还要遍历调用子元素的 measure() 方法,而 View 只需通过 measure() 方法就能确定测量规格。
其中,MeasureSpec 在很大程度上决定了一个 View 的尺寸规格,MeasureSpec由两部分组成,一部分是测量模式,另一部分是测量的尺寸大小。
测量模式分为三类:
- EXACTLY:对应match_parent和具体数值这两种,检测到View所需要的精确大小
- AT_MOST :对应wrap_content,View的大小不能大于父容器的大小
- UNSPECIFIED:不对View进行任何限制,要多大给多大,一般用于系统内部,如ListView,ScrollView等
View 的 measure() 方法会调用 onMeasure() 方法,我们重写此方法,此方法的参数widthMeasureSpec 和 heightMeasureSpec 是从父 View 传过来的宽高测量规格,可以以此来获取默认宽高。
布局过程
layout() 方法的作用是 ViewGroup 用于确定子元素的位置,当 ViewGroup 的位置确定后,会在 onLayout() 方法中遍历所有子 View 并调用子 View 的 layout() 方法,确定子View 自己的位置。
View 的 layout() 方法首先会通过 setFrame() 方法设定 View 的边框,也就是 mLeft、mRight、mTop 和 mBottom 四个顶点的值,这时 View 在父 View 中的位置就确定了,设定了四个顶点后,layout() 方法就会调用onLayout() 方法确定子 View 的位置。
绘制过程
绘制过程的 draw() 方法中主要的 4 个绘制步骤为:绘制背景、绘制 View 内容、绘制子 View 内容以及绘制装饰(比如 foreground 和 scrollbar)。
getWidth()和getMeasuredWidth()的区别
getMeasuredWidth()必须在onMeasure之后使用才有效,getMeasuredWidth() 的取值最终来源于setMeasuredDimension() 方法调用时传递的参数, getWidth()返回的是,mRight - mLeft,mRight、mLeft分别表示 View 相对父容器的左右边缘位置,getWidth()必须在layout执行之后才有效。
view.post {
val width: Int = view.width
val measuredWidth: Int = view.measuredWidth
Log.i(TAG, "width: $width")
Log.i(TAG, "measuredWidth: $measuredWidth")
}
invalidate,postInvalidate和requestLayout区别
invalidate()方法在 UI 线程中调用,重绘当前 UI。postInvalidate() 方法在非 UI 线程中调用,通过Handler通知 UI 线程重绘,requestLayout()也可以达到重绘view的目的,但是与前两者不同,它会先调用onLayout()重新排版,再调用onDraw方法。
自定义View实现方式
- 继承系统View控件:继承自TextView等系统控件,在此基础上进行扩展;
- 继承系统ViewGroup:继承自LinearLayout等系统控件,在此基础上进行扩展;
- 继承View:不复用系统控件逻辑,继承View进行功能定义;
- 继承ViewGroup:不复用系统控件逻辑,继承ViewGroup进行功能定义;
- 自定义组合控件:多个控件组合成为一个新的控件,方便复用。
坐标系
以屏幕左上角作为原点,原点向右是X轴的正轴,向下是Y轴正轴。
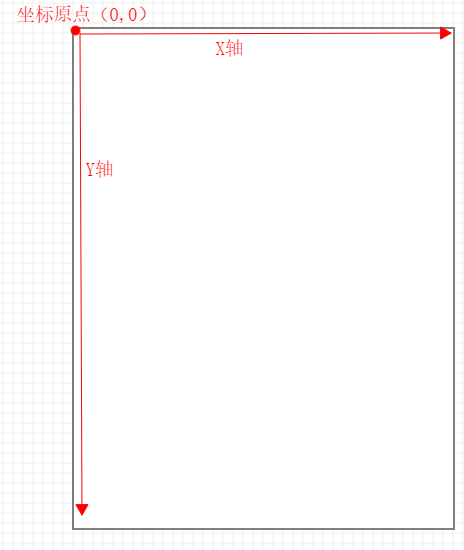
View的坐标系
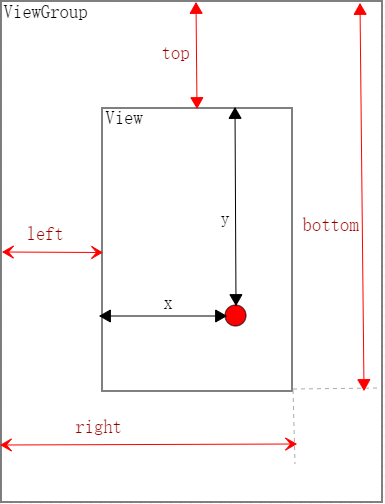
View的宽高计算:
val width = right - left
val height = bottom - top
View也提供了 width 和 height 来获取View的宽高,我们可以直接调用。
构造函数
class MyView : View {
//创建对象的时候用到
constructor(context: Context?) : super(context) {}
//在xml布局文件中使用时自动调用
constructor(context: Context?, attrs: AttributeSet?) : super(context, attrs) {}
//不会自动调用,如果有默认style时,在第二个构造函数中调用
constructor(context: Context?, attrs: AttributeSet?, defStyleAttr: Int) : super(
context,
attrs,
defStyleAttr
) {
}
//API>21时才会用到,不会自动调用,如果有默认style时,在第二个构造函数中调用
@RequiresApi(api = Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP)
constructor(
context: Context?,
attrs: AttributeSet?,
defStyleAttr: Int,
defStyleRes: Int
) : super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes) {
}
}
自定义属性
<declare-styleable name="MyView">
<attr name="viewAttr1" format="string" />
<attr name="viewAttr2" format="string" />
</declare-styleable>
class MyView(context: Context?, attrs: AttributeSet?) : View(context, attrs) {
init {
val typeArray = context?.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.MyView)
val viewAttr1 = typeArray?.getString(R.styleable.MyView_viewAttr1)
val viewAttr2 = typeArray?.getString(R.styleable.MyView_viewAttr2)
typeArray?.recycle()
}
}
<com.example.openglapp.MyView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
app:viewAttr1="hello"
app:viewAttr2="world" />
继承系统View控件
这种方式会复用系统的逻辑,大多数情况下希望复用系统的onMeasure和onLayout流程,所以我们只需要重写onDraw方法。
下面,我们继承AppCompatTextView系统控件,给其绘制背景
class MyView(context: Context, attrs: AttributeSet?) : AppCompatTextView(context, attrs) {
private val paint: Paint = Paint()
override fun onDraw(canvas: Canvas?) {
super.onDraw(canvas)
paint.color = context.getColor(R.color.blue)
val rect = Rect(0, 0, width, height)
//绘制背景
canvas?.drawRect(rect, paint)
}
}
继承系统ViewGroup
这里简单继承了LinearLayout,往里面加入Button和TextView
class CusLinearLayout(context: Context) : LinearLayout(context) {
private val button: Button = Button(context)
private val textView = TextView(context)
init {
orientation = VERTICAL
val layoutParam =
LayoutParams(DensityUtils.dp2px(context, 300f), DensityUtils.dp2px(context, 300f))
button.layoutParams = layoutParam
textView.layoutParams = layoutParam
textView.text = "welcome to pay attention to me"
button.text = "button"
button.setOnClickListener {
Toast.makeText(context, "click", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
addView(button)
addView(textView)
}
}
继承View
这种方式因为不复用系统控件的逻辑,所以onDraw和onMeasure方法都要重写。
在View的源码中并没有对AT_MOST和EXACTLY两个模式做出区分,也就是说,View在 wrap_content 和 match_parent 两个模式下是完全相同的,都是 match_parent,这显然与我们平时用的View不同,所以我们要重写onMeasure方法。
class MyView(context: Context, attrs: AttributeSet?) : View(context, attrs) {
private val paint: Paint = Paint()
override fun onDraw(canvas: Canvas?) {
super.onDraw(canvas)
paint.color = Color.RED
val viewWidth = width - paddingStart - paddingEnd
val viewHeight = height - paddingTop - paddingBottom
canvas?.drawRect(
paddingStart.toFloat(),
paddingTop.toFloat(), (viewWidth - paddingStart).toFloat(),
(viewHeight + paddingTop).toFloat(), paint
)
}
override fun onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec: Int, heightMeasureSpec: Int) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec)
val widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec)
val widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec)
val heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec)
val heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec)
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST && heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
//该方法用来设置View的宽高
setMeasuredDimension(
DensityUtils.dp2px(context, 300f),
DensityUtils.dp2px(context, 300f)
)
} else if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
setMeasuredDimension(DensityUtils.dp2px(context, 300f), heightSize)
} else if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
setMeasuredDimension(widthSize, DensityUtils.dp2px(context, 300f))
}
}
}
同时贴上dp和px的互转工具类
class DensityUtils {
companion object {
fun px2dp(context: Context, pxValue: Float): Int {
val scale = context.resources.displayMetrics.density
return (pxValue / scale + 0.5f).toInt()
}
fun dp2px(context: Context, dpValue: Float): Int {
val scale = context.resources.displayMetrics.density
return (dpValue * scale + 0.5f).toInt()
}
}
}
继承ViewGroup
这里简单实现一个流式布局FlowLayout
class FlowLayout : ViewGroup {
constructor(context: Context?) : super(context) {}
constructor(context: Context?, attrs: AttributeSet?) : super(context, attrs) {}
override fun onLayout(changed: Boolean, l: Int, t: Int, r: Int, b: Int) {
for (i in 0 until childCount) {
val child = getChildAt(i)
val rect = child.tag as Rect
child.layout(rect.left, rect.top, rect.right, rect.bottom)
}
}
override fun onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec: Int, heightMeasureSpec: Int) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec)
//遍历去调用所有子元素的measure方法,这样child.measuredHeight才有值
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec)
var measuredWidth = 0
var measureHeight = 0
val widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec)
val widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec)
val heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec)
val heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec)
//由于计算子view所占宽度,先减去PaddingRight,PaddingLeft在计算子元素位置时加上
val compute = compute(widthSize - paddingRight)
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
measuredWidth = widthSize
} else if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
measuredWidth = compute["allWidth"]!!
}
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
measureHeight = heightSize
} else if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
measureHeight = compute["allHeight"]!!
}
setMeasuredDimension(measuredWidth, measureHeight)
}
private fun compute(flowWidth: Int): Map<String, Int> {
var aRow = true
var rowsWidth = paddingLeft //当前行已占宽度
var columnHeight = paddingTop //当前行已占高度
var rowsMaxHeight = 0 //当前行所有子元素的最大高度
for (i in 0 until childCount) {
val child = getChildAt(i)
//获取元素测量高度和宽度
val measureWidth = child.measuredWidth
val measureHeight = child.measuredHeight
//获取元素边距
val marginParams: MarginLayoutParams = child.layoutParams as MarginLayoutParams
//子元素所占宽度
val childWidth = marginParams.leftMargin + marginParams.rightMargin + measureWidth
val childHeight = marginParams.topMargin + marginParams.bottomMargin + measureHeight
rowsMaxHeight = rowsMaxHeight.coerceAtLeast(childHeight)
//判断是否换行:该行已占大小+该元素大小>父容器宽度,则换行
if (rowsWidth + childWidth > flowWidth) {
rowsWidth = paddingLeft
columnHeight += rowsMaxHeight
rowsMaxHeight = childHeight
aRow = false
}
rowsWidth += childWidth
//给View设置tag,在onLayout给子元素设置位置遍历取出
child.tag = Rect(
rowsWidth - childWidth + marginParams.leftMargin,
columnHeight + marginParams.topMargin,
rowsWidth - marginParams.rightMargin,
columnHeight + childHeight - marginParams.bottomMargin
)
}
val flowMap = HashMap<String, Int>()
flowMap["allWidth"] = if (aRow) rowsWidth else flowWidth
//FlowLayout测量高度 = 当前行顶部已占高度 + 当前行内子元素最大高度 + FlowLayout的PaddingBottom
flowMap["allHeight"] = columnHeight + rowsMaxHeight + paddingBottom
return flowMap
}
}
使用方式
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<com.xzj.normalapp.FlowLayout
android:id="@+id/flowLayout"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="5dp" />
</LinearLayout>
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private var flowLayout: FlowLayout? = null
private var list: MutableList<String> = ArrayList()
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
initFlow()
}
private fun initFlow() {
val dp5 = DensityUtils.dp2px(this, 5f)
val dp15 = DensityUtils.dp2px(this, 15f)
flowLayout = findViewById(R.id.flowLayout)
for (i in 0 until 10) { //加入的测试数据
list.add("my")
list.add("name")
list.add("is")
list.add("Uncle Xing")
}
//往容器内添加文本
val layoutParams = LinearLayout.LayoutParams(
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT,
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT
)
layoutParams.setMargins(dp15, dp5, dp15, dp5)
if (flowLayout != null) {
flowLayout?.removeAllViews()
}
for (i in 0 until list.size) {
val tv = TextView(this)
tv.setPadding(dp15, dp5, dp15, dp5)
tv.text = list[i]
tv.setSingleLine()
tv.layoutParams = layoutParams
flowLayout?.addView(tv, layoutParams)
}
}
}
自定义组合控件
这方面,最常见的就是自定义标题栏,那下面就以此为例吧
自定义属性
<declare-styleable name="MyToolbar">
<attr name="left_button_visible" format="boolean" />
<attr name="right_button_visible" format="boolean" />
<attr name="title_text" format="string" />
<attr name="right_button_text" format="string" />
<attr name="left_button_text" format="string" />
</declare-styleable>
标题栏的布局如下
<merge xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<Button
android:id="@+id/toolbar_left"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentStart="true"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:layout_marginStart="7dp"
android:minWidth="45dp"
android:minHeight="45dp"
android:textSize="14sp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/toolbar_title"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:singleLine="true"
android:textSize="17sp" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/toolbar_right"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentEnd="true"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:layout_marginEnd="7dp"
android:minWidth="45dp"
android:minHeight="45dp"
android:textSize="14sp" />
</merge>
自定义标题栏
class MyToolbar(context: Context?, attrs: AttributeSet?) : RelativeLayout(context, attrs) {
private var leftBtn: Button? = null
private var rightBtn: Button? = null
private var title: TextView? = null
init {
inflate(context, R.layout.toolbar, this)
leftBtn = findViewById(R.id.toolbar_left)
rightBtn = findViewById(R.id.toolbar_right)
title = findViewById(R.id.toolbar_title)
val attributes = context?.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.MyToolbar)
attributes?.let {
//设置左边按钮是否显示
val leftVisible = it.getBoolean(R.styleable.MyToolbar_left_button_visible, true)
leftBtn?.visibility = if (leftVisible) View.VISIBLE else View.GONE
//设置左边按钮的文字
val leftText = it.getString(R.styleable.MyToolbar_left_button_text)
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(leftText)) {
leftBtn?.text = leftText
}
//设置标题
val titleText = it.getString(R.styleable.MyToolbar_title_text)
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(titleText)) {
title?.text = titleText
}
//设置右边按钮是否显示
val rightVisible = it.getBoolean(R.styleable.MyToolbar_right_button_visible, true)
rightBtn?.visibility = if (rightVisible) View.VISIBLE else View.GONE
//设置右边按钮文字
val rightText = it.getString(R.styleable.MyToolbar_right_button_text)
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(rightText)) {
rightBtn?.text = rightText
}
}
}
}
使用
<com.xzj.normalapp.MyToolbar
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="45dp"
app:left_button_text="left"
app:left_button_visible="true"
app:right_button_text="right"
app:right_button_visible="true"
app:title_text="标题" />