因为工作涉及到Android Camera系统的问题,本文整理了在Android P上讲解OpenCamera比较详细的文章,结合Andriod P源码,以架构图、UML顺序图、UML类图和关键代码走读的方式,从App层、Framework层、Hal层详细分析了OpenCamera的流程。如有分析的不对的地方,欢迎大家指正~
注意:Camera系统架构采用Camera2+Hal3。
参考博客:
Android Camera2+HAL3架构_既不是天才,便做那疯子!-CSDN博客
[Android O] HAL3 之 Open Camera2 流程(零)—— 概览_小石不识月,呼作白玉盘。-CSDN博客
Android P之Camera HAL3流程分析(0)_Vincentywj的博客-CSDN博客
AndroidO Treble架构(二):CameraProvider 及其守护进程_QGov的博客-CSDN博客
1 Camera2+Hal3整体架构
先看下Camera2+Hal3的整体架构:

?图1-1 Android Camera2+Hal3整体架构图
上图归纳的关键信息是2个接口和3个层次。
2个接口是指aidl接口和hidl接口。aidl接口包含ICameraDeviceUser,ICameraDeviceCallbacks,ICameraService和ICameraServiceListener。其中ICameraDeviceCallbacks和ICameraServiceListener是回调接口。hidl接口包含ICameraDeviceSession,ICameraDevice和ICameraProvider。
3个层次从上到下依次是app层,framework层和hal层。app层的进程是app(camera client)进程。framework层的进程是camera server进程。hal层的进程是hal(camera provider)进程。其中app(camera client)和camera server通信使用 AIDL(Android Interface Definition Language) ,camera server和hal(camera provider)进程通信使用HIDL(HAL interface definition language) 。
2 分层分析
本节按照如下顺序进行详细分析:
2.1 camera server进程和hal(camera provider)进程的启动
2.2 app(camera client)进程<-->camera server进程
2.3 camera server进程<-->hal(camera provider)进程
2.4 camera hal分析
2.1 camera server进程和hal(camera provider)进程的启动
我们知道app(camera client)进程是在用户打开相机时启动的,而camera server进程和hal(camera provider)进程是在Android系统开机时就准备好了。
下图总结了一下camera server进程与hal(camera provider)进程启动并初始化的关键逻辑:

?图2-1-1 camera server进程与hal(camera provider)进程启动架构图
图中两点关键信息:
1 hal(camera provider)进程启动,实例化CameraProvider,并注册服务到HwServiceManager;
实例化CameraProvider时会实例化CameraModule,CameraModule用来与Camera HAL进行交互。
2 camera server进程启动,初始化,并从ICameraProvider和HwServiceManager中获取camera provider服务;
CameraService类通过CameraProviderManager类来管理对CameraProvider的操作。
2.1.1 camera provider进程的启动
camera provider进程的主要工作是注册CameraProvider服务,以便camera server启动时能找到它。下图是camera provider进程的启动UML顺序图,后面按照此图分析关键代码:

?图2-1-2?camera provider进程的启动UML顺序图
Step1 provider.rc?
启动脚本
文件:"hardware/interfaces/camera/provider/2.4/default/android.hardware.camera.provider@2.4-service_64.rc"
service vendor.camera-provider-2-4 /vendor/bin/hw/android.hardware.camera.provider@2.4-service_64
class hal
user cameraserver
group audio camera input drmrpc
ioprio rt 4
capabilities SYS_NICE
writepid /dev/cpuset/camera-daemon/tasks /dev/stune/top-app/taskscamera provider守护进程由init进程启动。
Step2 main?
文件:"hardware/interfaces/camera/provider/2.4/default/service.cpp"
int main()
{
ALOGI("Camera provider Service is starting.");
// The camera HAL may communicate to other vendor components via
// /dev/vndbinder
// Step 3
android::ProcessState::initWithDriver("/dev/vndbinder");
// Step 4
return defaultPassthroughServiceImplementation<ICameraProvider>("legacy/0", /*maxThreads*/ 6);
}先与"/dev/vndbinder"进行某种关联,表明Camera provider Service会通过它与其它 vendor 组件进行通信。然后创建默认为直通模式(passthrough)的 CameraProvider服务。
Step3 initWithDriver
文件:"frameworks/native/libs/binder/ProcessState.cpp"
sp<ProcessState> ProcessState::initWithDriver(const char* driver)
{
Mutex::Autolock _l(gProcessMutex);
if (gProcess != NULL) {
// Allow for initWithDriver to be called repeatedly with the same
// driver.
if (!strcmp(gProcess->getDriverName().c_str(), driver)) {
return gProcess;
}
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("ProcessState was already initialized.");
}
if (access(driver, R_OK) == -1) {
ALOGE("Binder driver %s is unavailable. Using /dev/binder instead.", driver);
driver = "/dev/binder";
}
// 3.1
gProcess = new ProcessState(driver);
return gProcess;
}initWithDriver是ProcessState的static函数,这里以driver的名字("/dev/vndbinder")实例化android::ProcessState。
3.1 new ProcessState
文件:"frameworks/native/libs/binder/ProcessState.cpp"
ProcessState::ProcessState(const char *driver)
: mDriverName(String8(driver))
, mDriverFD(open_driver(driver))
...
{
if (mDriverFD >= 0) {
// mmap the binder, providing a chunk of virtual address space to receive transactions.
mVMStart = mmap(0, BINDER_VM_SIZE, PROT_READ, MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_NORESERVE, mDriverFD, 0);
if (mVMStart == MAP_FAILED) {
// *sigh*
ALOGE("Using %s failed: unable to mmap transaction memory.\n", mDriverName.c_str());
close(mDriverFD);
mDriverFD = -1;
mDriverName.clear();
}
}
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(mDriverFD < 0, "Binder driver could not be opened. Terminating.");
}实例化ProcessState时,主要工作是打开文件"dev/vndbinder"并mmap映射内存,将内核虚拟内存空间映射到用户空间。
注意,这里的ProcessState类的命名空间是andriod::ProcessState。
Step4 defaultPassthroughServiceImplementation
文件:"system/libhidl/transport/include/hidl/LegacySupport.h"
/**
* Creates default passthrough service implementation. This method never returns.
*
* Return value is exit status.
*/
template<class Interface>
__attribute__((warn_unused_result))
status_t defaultPassthroughServiceImplementation(std::string name,
size_t maxThreads = 1) {
// Step 5
configureRpcThreadpool(maxThreads, true);
// Step 6
status_t result = registerPassthroughServiceImplementation<Interface>(name);
if (result != OK) {
return result;
}
// Step 7
joinRpcThreadpool();
return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}注意:此时函数的命名空间是android::hardware::defaultPassthroughServiceImplementation。
配置RPC线程池并将Interface(ICameraProvider)以入参"legacy/0"为名注册到相应的管理服务中。
Step5 configureRpcThreadpool
文件:"system/libhidl/transport/HidlTransportSupport.cpp"
void configureRpcThreadpool(size_t maxThreads, bool callerWillJoin) {
// TODO(b/32756130) this should be transport-dependent
// 5.1
configureBinderRpcThreadpool(maxThreads, callerWillJoin);
}5.1 configureBinderRpcThreadpool
文件:"system/libhidl/transport/HidlBinderSupport.cpp"
void configureBinderRpcThreadpool(size_t maxThreads, bool callerWillJoin) {
// 5.2, 5.3
ProcessState::self()->setThreadPoolConfiguration(maxThreads, callerWillJoin /*callerJoinsPool*/);
}注意,这里ProcessState类的命名空间是andriod::hardware::ProcessState。
5.2 ProcessState::self()
文件:"system/libhwbinder/ProcessState.cpp"
ProcessState::self()这个函数最后会open("/dev/hwbinder")。
sp<ProcessState> ProcessState::self()
{
Mutex::Autolock _l(gProcessMutex);
if (gProcess != NULL) {
return gProcess;
}
gProcess = new ProcessState(DEFAULT_BINDER_VM_SIZE);
return gProcess;
}
ProcessState::ProcessState(size_t mmap_size)
: mDriverFD(open_driver())
, mVMStart(MAP_FAILED)
...
{
if (mDriverFD >= 0) {
// mmap the binder, providing a chunk of virtual address space to receive transactions.
mVMStart = mmap(0, mMmapSize, PROT_READ, MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_NORESERVE, mDriverFD, 0);
if (mVMStart == MAP_FAILED) {
// *sigh*
ALOGE("Using /dev/hwbinder failed: unable to mmap transaction memory.\n");
close(mDriverFD);
mDriverFD = -1;
}
}
else {
ALOGE("Binder driver could not be opened. Terminating.");
}
}
static int open_driver()
{
int fd = open("/dev/hwbinder", O_RDWR | O_CLOEXEC);
if (fd >= 0) {
int vers = 0;
status_t result = ioctl(fd, BINDER_VERSION, &vers);
if (result == -1) {
ALOGE("Binder ioctl to obtain version failed: %s", strerror(errno));
close(fd);
fd = -1;
}
...
} else {
ALOGW("Opening '/dev/hwbinder' failed: %s\n", strerror(errno));
}
return fd;
}5.3 setThreadPoolConfiguration
文件:"system/libhwbinder/ProcessState.cpp"
status_t ProcessState::setThreadPoolConfiguration(size_t maxThreads, bool callerJoinsPool) {
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(maxThreads < 1, "Binder threadpool must have a minimum of one thread.");
status_t result = NO_ERROR;
// the BINDER_SET_MAX_THREADS ioctl really tells the kernel how many threads
// it's allowed to spawn, *in addition* to any threads we may have already
// spawned locally. If 'callerJoinsPool' is true, it means that the caller
// will join the threadpool, and so the kernel needs to create one less thread.
// If 'callerJoinsPool' is false, we will still spawn a thread locally, and we should
// also tell the kernel to create one less thread than what was requested here.
size_t kernelMaxThreads = maxThreads - 1;
if (ioctl(mDriverFD, BINDER_SET_MAX_THREADS, &kernelMaxThreads) != -1) {
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
mMaxThreads = maxThreads;
mSpawnThreadOnStart = !callerJoinsPool;
} else {
result = -errno;
ALOGE("Binder ioctl to set max threads failed: %s", strerror(-result));
}
return result;
}这里的mDriverFD是指/dev/hwbinder,ioctl下发BINDER_SET_MAX_THREADS命令给"dev/hwbinder"的驱动。
Step6 registerPassthroughServiceImplementation
文件:"system/libhidl/transport/include/hidl/LegacySupport.h"
/**
* Registers passthrough service implementation.
*/
template<class Interface>
__attribute__((warn_unused_result))
status_t registerPassthroughServiceImplementation(
std::string name = "default") {
// 6.1
sp<Interface> service = Interface::getService(name, true /* getStub */);
if (service == nullptr) {
ALOGE("Could not get passthrough implementation for %s/%s.",
Interface::descriptor, name.c_str());
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
LOG_FATAL_IF(service->isRemote(), "Implementation of %s/%s is remote!",
Interface::descriptor, name.c_str());
// 6.2
status_t status = service->registerAsService(name);
if (status == OK) {
ALOGI("Registration complete for %s/%s.",
Interface::descriptor, name.c_str());
} else {
ALOGE("Could not register service %s/%s (%d).",
Interface::descriptor, name.c_str(), status);
}
return status;
}入参name为"legacy/0",模板类参数Interface为ICameraProvider。
这个函数做了两件事:
1 实例化CameraProvider对象?
2 注册CameraProvider服务到HwServiceManager
getService()和registerAsService()是CameraProviderAll.cpp里的函数,CameraProviderAll.cpp是hidl机制通过ICameraProvider.hal编译生成的。
ICameraProvider.hal:hardware/interfaces/camera/provider/2.4/ICameraProvider.hal
6.1 ICameraProvider::getService
当getStub=ture时,getService是以passthrough模式打开 HAL 实现,得到的是CameraProvider的实例化对象(BnHwCameraProvider)。当getStub=false时,得到的是binder代理对象(BpHwCameraProvider),后面camera server进程会用到。
详细分析请参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/wzoxylwzoxyl/article/details/82227506
最后会调用到HIDL_FETCH_ICameraProvider函数。
6.1.1 HIDL_FETCH_ICameraProvider
文件:"./hardware/interfaces/camera/provider/2.4/default/CameraProvider.cpp"
ICameraProvider* HIDL_FETCH_ICameraProvider(const char* name) {
if (strcmp(name, kLegacyProviderName) == 0) {
// 6.1.2
CameraProvider* provider = new CameraProvider();
if (provider == nullptr) {
ALOGE("%s: cannot allocate camera provider!", __FUNCTION__);
return nullptr;
}
if (provider->isInitFailed()) {
ALOGE("%s: camera provider init failed!", __FUNCTION__);
delete provider;
return nullptr;
}
return provider;
} else if (strcmp(name, kExternalProviderName) == 0) {
ExternalCameraProvider* provider = new ExternalCameraProvider();
return provider;
}
ALOGE("%s: unknown instance name: %s", __FUNCTION__, name);
return nullptr;
}
CameraProvider::CameraProvider() :
camera_module_callbacks_t({sCameraDeviceStatusChange,
sTorchModeStatusChange}) {
// 6.1.3
mInitFailed = initialize();
}
bool CameraProvider::initialize() {
camera_module_t *rawModule;
// 6.1.4 "hardware/libhardware/hardware.c"
int err = hw_get_module(CAMERA_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
(const hw_module_t **)&rawModule);
if (err < 0) {
ALOGE("Could not load camera HAL module: %d (%s)", err, strerror(-err));
return true;
}
// 6.1.5 "hardware/interfaces/camera/common/1.0/default/CameraModule.cpp"
mModule = new CameraModule(rawModule);
// 6.1.6
err = mModule->init();
if (err != OK) {
ALOGE("Could not initialize camera HAL module: %d (%s)", err, strerror(-err));
mModule.clear();
return true;
}
ALOGI("Loaded \"%s\" camera module", mModule->getModuleName());
...
}6.1.2:创建一个 CameraProvider 实例
6.1.4:通过 hw_get_module 函数获取到rawModule的实例(从相应的 Camera HAL 动态库中加载得到,hw_get_module->hw_get_module_by_class->load->dlopen)。rawModule是连接到 HAL 层的关键结构,通过它就可以调用到 HAL 中的一些函数。CAMERA_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID为字符串"camera"。
6.1.5:基于 rawModule 创建 CameraModule 实例并初始化。之后都是通过 mModule 来对 HAL 进行操作的。CameraModule 是对于 camera_module_t 的一层封装,诸如 init、open 这样的操作,实际上都是通过调用 camera_module_t 结构中函数指针来完成的。
6.2 registerAsService
文件:out/.../CameraProviderAll.cpp
::android::status_t ICameraProvider::registerAsService(const std::string &serviceName) {
::android::hardware::details::onRegistration("android.hardware.camera.provider@2.4", "ICameraProvider", serviceName);
// 得到 BpHwServiceManager 对象,就是HwServiceManager对象的binder代理
const ::android::sp<::android::hidl::manager::V1_0::IServiceManager> sm
= ::android::hardware::defaultServiceManager();
// 调用 BpHwServiceManager::add() 注册服务
// 6.2.1
::android::hardware::Return<bool> ret = sm->add(serviceName.c_str(), this);
return ret.isOk() && ret ? ::android::OK : ::android::UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}将CameraProvider注册为一个服务,其他进程需要使用camera hal时通过binder得到CameraProvider代理类(BpHwCameraProvider)即可操作camera hal 。注意,是将CameraProvider服务注册到HwServiceManager中,不是ServiceManager。
Step7 joinRpcThreadpool
文件:"system/libhidl/transport/HidlTransportSupport.cpp"
void joinRpcThreadpool() {
// TODO(b/32756130) this should be transport-dependent
// 7.1
joinBinderRpcThreadpool();
}CameraProvider服务进入循环,等待binder请求并处理。这里的joinRpcThreadpool()是把主线程也放入线程池中等待请求,防止这个进程退出。
7.1 joinBinderRpcThreadpool
文件:"system/libhidl/transport/HidlBinderSupport.cpp"
void joinBinderRpcThreadpool() {
// 7.2
IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool();
}7.2 joinThreadPool
文件:"system/libhwbinder/IPCThreadState.cpp"
void IPCThreadState::joinThreadPool(bool isMain)
{
LOG_THREADPOOL("**** THREAD %p (PID %d) IS JOINING THE THREAD POOL\n", (void*)pthread_self(), getpid());
mOut.writeInt32(isMain ? BC_ENTER_LOOPER : BC_REGISTER_LOOPER);
status_t result;
// 循环处理请求
do {
processPendingDerefs();
// now get the next command to be processed, waiting if necessary
result = getAndExecuteCommand();
if (result < NO_ERROR && result != TIMED_OUT && result != -ECONNREFUSED && result != -EBADF) {
ALOGE("getAndExecuteCommand(fd=%d) returned unexpected error %d, aborting",
mProcess->mDriverFD, result);
abort();
}
// Let this thread exit the thread pool if it is no longer
// needed and it is not the main process thread.
if(result == TIMED_OUT && !isMain) {
break;
}
} while (result != -ECONNREFUSED && result != -EBADF);
LOG_THREADPOOL("**** THREAD %p (PID %d) IS LEAVING THE THREAD POOL err=%d\n",
(void*)pthread_self(), getpid(), result);
// 如果走到这表明出现了一些错误,需要告诉驱动这个线程不再处理消息了,即退出LOOPER
mOut.writeInt32(BC_EXIT_LOOPER);
talkWithDriver(false);
}getAndExecuteCommand()会处理command,必要时阻塞线程。
分析完camera provider进程的启动,我们再来看camera server进程的启动。
2.1.2 camera server进程的启动
camera provider进程先启动,然后camera server进程再启动。camera server进程启动后会去 "连接" CameraProvider服务,从HwServiceManager里获取CameraProvider服务。
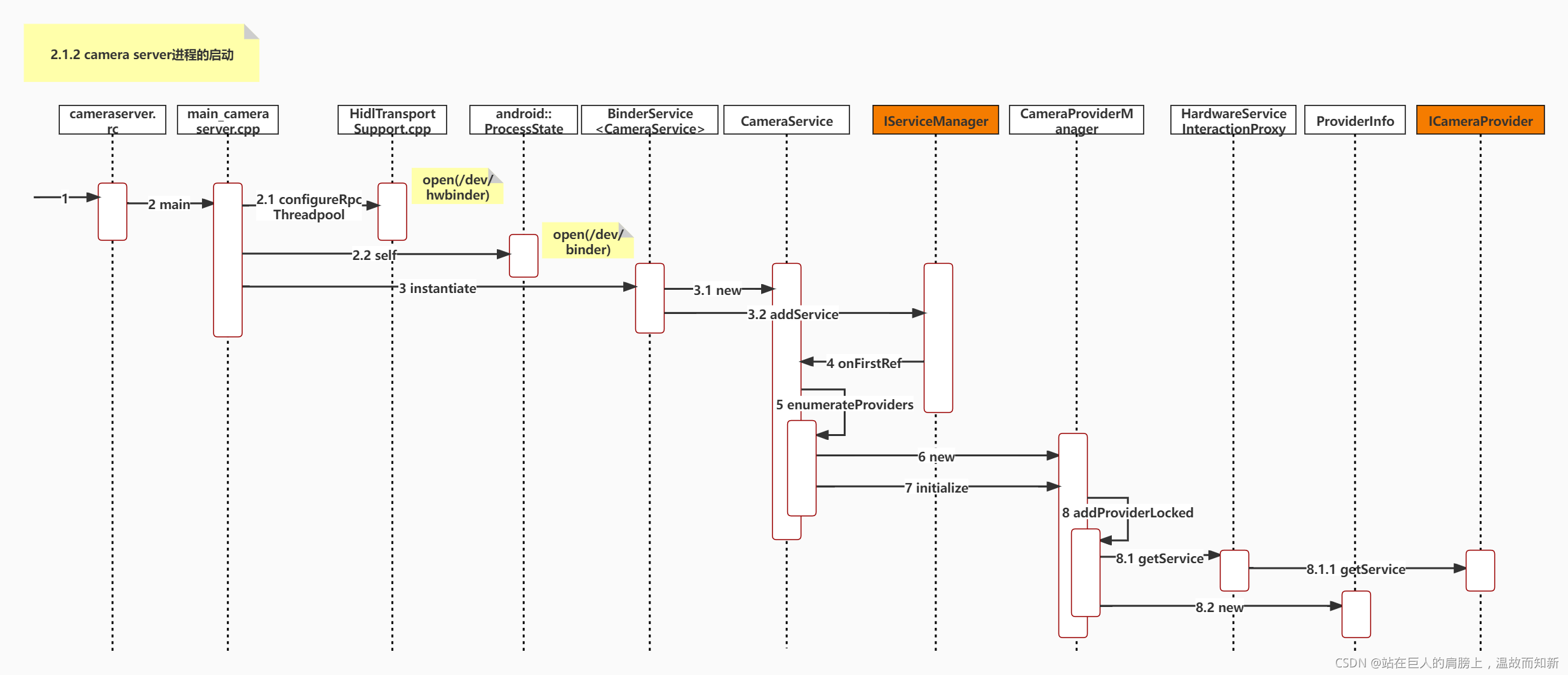
?图2-1-3 camera server进程的启动UML顺序图
Step1 cameraserver.rc
启动脚本
文件:"frameworks/av/camera/cameraserver/cameraserver.rc"
service cameraserver /system/bin/cameraserver
class main
user cameraserver
group audio camera input drmrpc
ioprio rt 4
writepid /dev/cpuset/camera-daemon/tasks /dev/stune/top-app/taskscamera server进程由init进程启动。
Step2 main?
文件:"frameworks/av/camera/cameraserver/main_cameraserver.cpp"
using namespace android;
int main(int argc __unused, char** argv __unused)
{
signal(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN);
// Set 3 threads for HIDL calls
// open(/dev/hwbinder),用于和BnHwServiceManager通信
// 2.1
hardware::configureRpcThreadpool(3, /*willjoin*/ false);
// open(/dev/binder),用于和BnServiceManager通信
// 2.2
sp<ProcessState> proc(ProcessState::self());
// 获得ServiceManager的代理类BpServiceManager, 注意不是HwServiceManager的代理类
sp<IServiceManager> sm = defaultServiceManager();
ALOGI("ServiceManager: %p", sm.get());
// 做了两件事 (1)得到CameraService实例化对象 (2)注册CameraService服务
// Step 3
CameraService::instantiate();
ProcessState::self()->startThreadPool();
IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool();
}注意,命名空间是android。
todo signal信号干嘛用的?
注意,defaultServiceManager()获得的是ServiceManager不是HwServiceManager,即CameraService服务是注册在ServiceManager里的。
defaultServiceManager的实现容易混淆,系统中有两个实现,在调用时需要注意方法所在的域:
android:defaultServiceManager可以获的BpServiceManager,
android:hardware:defaultServiceManager可以获的BpHwServiceManager。
Step3 instantiate
文件:"frameworks/native/libs/binder/include/binder/BinderService.h"
static void instantiate() { publish(); }
static status_t publish(bool allowIsolated = false,
int dumpFlags = IServiceManager::DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_DEFAULT) {
sp<IServiceManager> sm(defaultServiceManager());
// 3.1,3.2
return sm->addService(String16(SERVICE::getServiceName()), new SERVICE(), allowIsolated,
dumpFlags);
}这个 instantiate() 接口并不是定义在 CameraService 类中的,而是定义在 BinderService 类里(CameraService 继承了它)。在此处,它的作用是创建一个 CameraService实例,并将其注册到 ServiceManager 中。
3.1 new CameraService
SERVICE为CameraService。
3.2 addService
文件:"frameworks/native/libs/binder/IServiceManager.cpp"
virtual status_t addService(const String16& name, const sp<IBinder>& service,
bool allowIsolated, int dumpsysPriority) {
Parcel data, reply;
data.writeInterfaceToken(IServiceManager::getInterfaceDescriptor());
data.writeString16(name);
data.writeStrongBinder(service);
data.writeInt32(allowIsolated ? 1 : 0);
data.writeInt32(dumpsysPriority);
status_t err = remote()->transact(ADD_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, &reply);
return err == NO_ERROR ? reply.readExceptionCode() : err;
}注意,在这一过程中CameraService被sp强指针引用了。通过UML类图可以看出CameraService实际是IBinder的子类。
ICameraService.aidl:./frameworks/av/camera/aidl/android/hardware/ICameraService.aidl
ICameraService.aidl会通过aidl编译生成ICameraService.h。
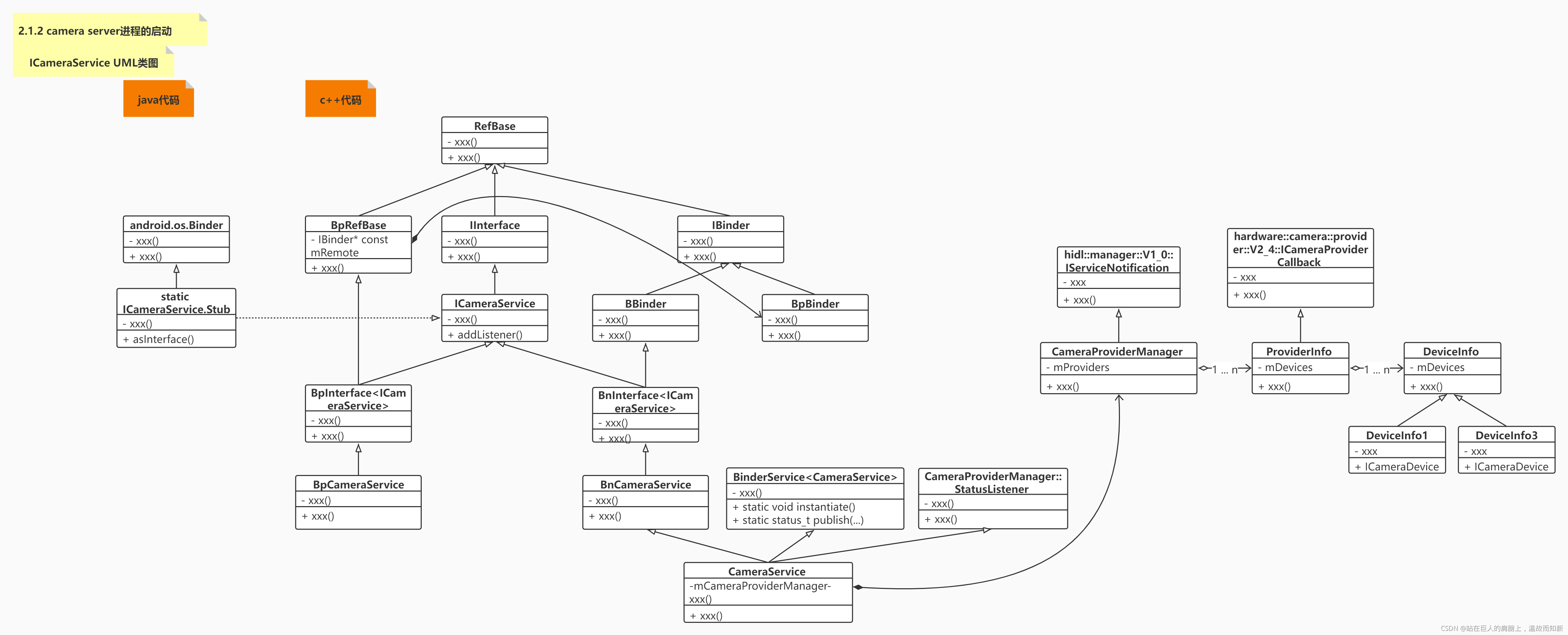
?图2-1-4 ICameraService UML类图
Step4 onFirstRef
文件:"frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/CameraService.cpp"
首次被sp强指针引用时,就会调用 onFirstRef() 函数。
void CameraService::onFirstRef()
{
ALOGI("CameraService process starting");
BnCameraService::onFirstRef();
// Update battery life tracking if service is restarting
BatteryNotifier& notifier(BatteryNotifier::getInstance());
notifier.noteResetCamera();
notifier.noteResetFlashlight();
status_t res = INVALID_OPERATION;
// Step 5
res = enumerateProviders();
if (res == OK) {
mInitialized = true;
}
CameraService::pingCameraServiceProxy();
mUidPolicy = new UidPolicy(this);
mUidPolicy->registerSelf();
}枚举Providers。
Step5 enumerateProviders
文件:"frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/CameraService.cpp"
status_t CameraService::enumerateProviders() {
status_t res;
std::vector<std::string> deviceIds;
{
Mutex::Autolock l(mServiceLock);
if (nullptr == mCameraProviderManager.get()) {
// Step 6
mCameraProviderManager = new CameraProviderManager();
// Step 7
res = mCameraProviderManager->initialize(this);
if (res != OK) {
ALOGE("%s: Unable to initialize camera provider manager: %s (%d)",
__FUNCTION__, strerror(-res), res);
return res;
}
}
...
deviceIds = mCameraProviderManager->getCameraDeviceIds();
}
for (auto& cameraId : deviceIds) {
String8 id8 = String8(cameraId.c_str());
onDeviceStatusChanged(id8, CameraDeviceStatus::PRESENT);
}
return OK;
}将 CameraProviderManager 实例化,然后调用 initialize() 接口初始化,传入的参数是 this 指针,指向当前CameraService实例的地址。
Step6 new CameraProviderManager()
文件:"frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/common/CameraProviderManager.cpp"
Step7 initialize
文件:"frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/common/CameraProviderManager.h"
先看下函数声明:
/**
* Initialize the manager and give it a status listener; optionally accepts a service
* interaction proxy.
*
* The default proxy communicates via the hardware service manager; alternate proxies can be
* used for testing. The lifetime of the proxy must exceed the lifetime of the manager.
*/
status_t initialize(wp<StatusListener> listener,
ServiceInteractionProxy *proxy = &sHardwareServiceInteractionProxy);wp<StatusListener> listener是CameraService 实例。采用的是默认代理。默认代理有什么作用?(Step 9)
文件:"frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/common/CameraProviderManager.cpp"
status_t CameraProviderManager::initialize(wp<CameraProviderManager::StatusListener> listener,
ServiceInteractionProxy* proxy) {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mInterfaceMutex);
if (proxy == nullptr) {
ALOGE("%s: No valid service interaction proxy provided", __FUNCTION__);
return BAD_VALUE;
}
// listener是CameraService 对象
mListener = listener;
// proxy是sHardwareServiceInteractionProxy
mServiceProxy = proxy;
// Registering will trigger notifications for all already-known providers
bool success = mServiceProxy->registerForNotifications(
/* instance name, empty means no filter */ "",
this);
if (!success) {
ALOGE("%s: Unable to register with hardware service manager for notifications "
"about camera providers", __FUNCTION__);
return INVALID_OPERATION;
}
// See if there's a passthrough HAL, but let's not complain if there's not
// Step 8
addProviderLocked(kLegacyProviderName, /*expected*/ false);
addProviderLocked(kExternalProviderName, /*expected*/ false);
return OK;
}通过服务代理作出一个注册动作。根据注释,注册会触发一个给所有已知 Provider 进行通知的动作。传入的参数 kLegacyProviderName,为字符串"legacy/0"。
Step8 addProviderLocked
文件:"frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/common/CameraProviderManager.cpp"
status_t CameraProviderManager::addProviderLocked(const std::string& newProvider, bool expected) {
for (const auto& providerInfo : mProviders) {
if (providerInfo->mProviderName == newProvider) {
ALOGW("%s: Camera provider HAL with name '%s' already registered", __FUNCTION__,
newProvider.c_str());
return ALREADY_EXISTS;
}
}
sp<provider::V2_4::ICameraProvider> interface;
// 上面分析过mServiceProxy=sHardwareServiceInteractionProxy,这里getService(newProvider)其实就是得到CameraProvider的代理类(BpHwCameraProvider)
// 8.1
interface = mServiceProxy->getService(newProvider);
if (interface == nullptr) {
if (expected) {
ALOGE("%s: Camera provider HAL '%s' is not actually available", __FUNCTION__,
newProvider.c_str());
return BAD_VALUE;
} else {
return OK;
}
}
// 8.2
sp<ProviderInfo> providerInfo = new ProviderInfo(newProvider, interface, this);
status_t res = providerInfo->initialize();
if (res != OK) {
return res;
}
mProviders.push_back(providerInfo);
return OK;
}检查已知的 Provider 中是否已有名为 legacy/0 的。
根据 legacy/0 从服务代理处获取 CameraProvider 接口,这里getService(newProvider)其实就是得到CameraProvider的代理类(BpHwCameraProvider)。采用的是默认代理即sHardwareServiceInteractionProxy。
通过ProviderInfo来保存当前 Provider相关信息。
8.1 getService
文件:"frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/common/CameraProviderManager.h"
// Standard use case - call into the normal generated static methods which invoke
// the real hardware service manager
struct HardwareServiceInteractionProxy : public ServiceInteractionProxy {
...
virtual sp<hardware::camera::provider::V2_4::ICameraProvider> getService(
const std::string &serviceName) override {
// getStub的默认值为flase,之前分析过getStub = flase 会得到 CameraProvider 的代理类(BpHwCameraProvider)
// 8.1.1
return hardware::camera::provider::V2_4::ICameraProvider::getService(serviceName);
}
};getService的实现在hidl编译生成的CameraProviderAll.cpp里。
小结:framework的上层通过ServiceManager(/dev/binder)得到CameraService服务,而CameraService通过HwServiceManager(/dev/hwbinder)得到 CameraProvider 服务,而CameraProvider可以访问Camera HAL。这样上层 framework 就能够访问 Camera HAL 了。
2.1.3 总结流程
1 camera provider进程启动,实例化CameraProvider,并将CameraProvider服务注册到HwServiceManager;
在CameraProvider初始化过程中,从动态库中加载了HAL层的关键结构(camera_module_t),并将其封装到CameraModule中。
2 camera server进程启动,实例化CameraService,并将CameraService服务注册到ServiceManager。
3 由于强指针首次引用,CameraService::onFirstRef()被调用,进行初始化;在CameraService初始化过程中,通过CameraProviderManager来获取HwServiceManager中已注册的CameraProvider服务,获取BpHwCameraProvider实例。
这样,framework的上层通过ServiceManager(/dev/binder)得到CameraService服务,而CameraService通过HwServiceManager(/dev/hwbinder)得到 CameraProvider 服务,而CameraProvider可以访问Camera HAL。这样上层 framework 就能够访问 Camera HAL 了。
2.2 app(camera client)进程<-->camera server进程
打开相机的流程就是打通 APP 到相机设备之间的连路的过程,按照Android架构从上到下依次打通下行控制路线,并通过设置回调来构建上行的状态、数据路线。
下图是OpenCamera总体架构图。黑色虚线是下行路线,红色虚线是上行路线:

图2-2-1 OpenCamera总体架构图
上图包含了三层的内容:
1 app(camera client)进程
2 camera server进程
3 hal(camera provider)进程
2.1节中我们已经分析了camera provider进程和camera server进程的启动和初始化过程,下面我们按照如下三个内容继续分析:
1 app(camera client)进程<-->camera server进程(2.2节)
2 camera server进程<-->hal(camera provider)进程(2.3节)
3 camera hal(2.4节)
本节(2.2节)详细分析app(camera client)进程<-->camera server进程这个过程。这一部分主要的函数调用逻辑如下图所示。

?图2-2-2 app(camera client)进程<-->camera server进程架构图
下图是app(camera client)进程<-->camera server进程 UML顺序图,根据UML顺序图分析源码:
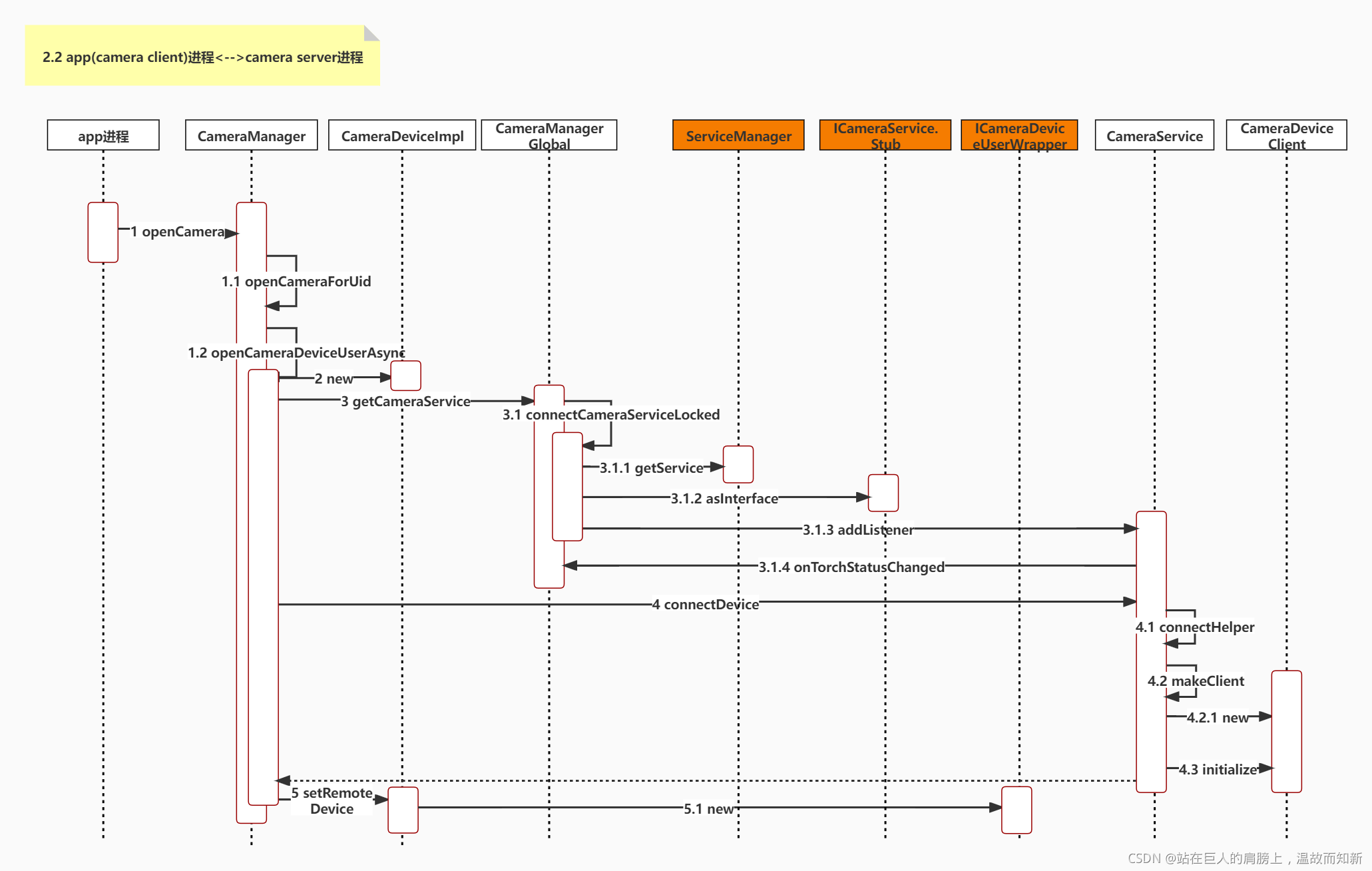
?图2-2-3 app(camera client)进程<-->camera server进程 UML顺序图
Step1 ?openCamera
文件:"./frameworks/base/core/java/android/hardware/camera2/CameraManager.java"
@RequiresPermission(android.Manifest.permission.CAMERA)
public void openCamera(@NonNull String cameraId,
@NonNull final CameraDevice.StateCallback callback, @Nullable Handler handler)
throws CameraAccessException {
// 1.1
openCameraForUid(cameraId, callback, CameraDeviceImpl.checkAndWrapHandler(handler),
USE_CALLING_UID);
}
public void openCameraForUid(@NonNull String cameraId,
@NonNull final CameraDevice.StateCallback callback, @NonNull Executor executor,
int clientUid)
throws CameraAccessException {
...
// 1.2
openCameraDeviceUserAsync(cameraId, callback, executor, clientUid);
}app进程里打开相机:mCameraManager.openCamera,最后调用openCameraDeviceUserAsync。
1.2 openCameraDeviceUserAsync
文件:"./frameworks/base/core/java/android/hardware/camera2/CameraManager.java"
private CameraDevice openCameraDeviceUserAsync(String cameraId,
CameraDevice.StateCallback callback, Executor executor, final int uid)
throws CameraAccessException {
CameraCharacteristics characteristics = getCameraCharacteristics(cameraId);
CameraDevice device = null;
synchronized (mLock) {
ICameraDeviceUser cameraUser = null;
// 应用端的相机对象类
// Step2
android.hardware.camera2.impl.CameraDeviceImpl deviceImpl =
new android.hardware.camera2.impl.CameraDeviceImpl(
cameraId,
callback,
executor,
characteristics,
mContext.getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion);
// 应用端的回调函数
ICameraDeviceCallbacks callbacks = deviceImpl.getCallbacks();
try {
if (supportsCamera2ApiLocked(cameraId)) {
// Use cameraservice's cameradeviceclient implementation for HAL3.2+ devices
// Step3
ICameraService cameraService = CameraManagerGlobal.get().getCameraService();
if (cameraService == null) {
throw new ServiceSpecificException(
ICameraService.ERROR_DISCONNECTED,
"Camera service is currently unavailable");
}
// 通过cameraService跨进程获得BpCameraDeviceUser对象
// Step4
cameraUser = cameraService.connectDevice(callbacks, cameraId,
mContext.getOpPackageName(), uid);
} else {
...
}
} catch (ServiceSpecificException e) {
...
}
// TODO: factor out callback to be non-nested, then move setter to constructor
// For now, calling setRemoteDevice will fire initial
// onOpened/onUnconfigured callbacks.
// This function call may post onDisconnected and throw CAMERA_DISCONNECTED if
// cameraUser dies during setup.
// 保存CameraDeviceClient对象到CameraDeviceImpl,触发应用的回调函数
// Step5
deviceImpl.setRemoteDevice(cameraUser);
device = deviceImpl;
}
return device;
}Step2,首先实例化一个android.hardware.camera2.impl.CameraDeviceImpl对象。值得注意的是,构造时传入了 CameraDevice.StateCallback 以及 Handler。注意,CameraDeviceImpl类是CameraDevice类的子类,这两个类是app层用来管理camera设备的。
Step3,通过CameraManagerGlobal获取CameraService的本地接口(BpCameraService)。(即图2-1-4 ICameraService UML类图BpCameraService)。
todo ICameraService.Stub与BpCameraService是如何通过aidl联系上的?
Step4,通过BpCameraService远端调用connectDevice 法连接到相机设备,注意返回的cameraUser实际上指向的是远端CameraDeviceClient的本地接口(BpCameraDeviceUser)。ICameraDeviceUser UML类图如下:
frameworks/av/camera/aidl/android/hardware/camera2/ICameraDeviceUser.aidl

图2-2-4 ICameraDeviceUser UML类图
Step5,最后将CameraDeviceClient对象保存到CameraDeviceImpl中进行管理。
Step2 new android.hardware.camera2.impl.CameraDeviceImpl
文件:"frameworks/base/core/java/android/hardware/camera2/impl/CameraDeviceImpl.java"
将输入参数保存到该类的成员变量。
Step3 getCameraService
文件: "frameworks/base/core/java/android/hardware/camera2/CameraManager.java"
注意这个CameraManagerGlobal类,是个static单例类,用来保存对CameraService的连接。
/**
* A per-process global camera manager instance, to retain a connection to the camera service,
* and to distribute camera availability notices to API-registered callbacks
*/
private static final class CameraManagerGlobal extends ICameraServiceListener.Stub
implements IBinder.DeathRecipient
{
private static final String TAG = "CameraManagerGlobal";
...
// Singleton instance
private static final CameraManagerGlobal gCameraManager =
new CameraManagerGlobal();
...
// Singleton, don't allow construction
private CameraManagerGlobal() {
}
public static CameraManagerGlobal get() {
return gCameraManager;
}
/**
* Return a best-effort ICameraService.
*
* <p>This will be null if the camera service is not currently available. If the camera
* service has died since the last use of the camera service, will try to reconnect to the
* service.</p>
*/
public ICameraService getCameraService() {
synchronized(mLock) {
//3.1
connectCameraServiceLocked();
if (mCameraService == null && !sCameraServiceDisabled) {
Log.e(TAG, "Camera service is unavailable");
}
return mCameraService;
}
}
}ICameraServiceListener.aidl:./frameworks/av/camera/aidl/android/hardware/ICameraServiceListener.aidl
3.1 connectCameraServiceLocked
/**
* Connect to the camera service if it's available, and set up listeners.
* If the service is already connected, do nothing.
*
* <p>Sets mCameraService to a valid pointer or null if the connection does not succeed.</p>
*/
private void connectCameraServiceLocked() {
// Only reconnect if necessary
if (mCameraService != null || sCameraServiceDisabled) return;
Log.i(TAG, "Connecting to camera service");
// 3.1.1
IBinder cameraServiceBinder = ServiceManager.getService(CAMERA_SERVICE_BINDER_NAME);
...
// 3.1.2
ICameraService cameraService = ICameraService.Stub.asInterface(cameraServiceBinder);
try {
// 注册回调监听,CameraService(下层)可以通知CameraManagerGlobal(上层)状态变化
// 3.1.3
CameraStatus[] cameraStatuses = cameraService.addListener(this);
for (CameraStatus c : cameraStatuses) {
onStatusChangedLocked(c.status, c.cameraId);
}
mCameraService = cameraService;
}
}首先从ServiceManager里查找CameraService服务,CAMERA_SERVICE_BINDER_NAME为字符串"media.camera"。找到CameraService后,将CameraManagerGlobal类的this指针设置为CameraService的回调监听。
3.1.3 addListener
文件:frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/CameraService.cpp
来看下整体架构图中的ICameraServiceListener.aidl回调接口怎么注册的:
// 注册回调
private void connectCameraServiceLocked() {
...
// 3.1.3
CameraStatus[] cameraStatuses = cameraService.addListener(this);
for (CameraStatus c : cameraStatuses) {
onStatusChangedLocked(c.status, c.cameraId);
}
}
// 调用服务
Status CameraService::addListener(const sp<ICameraServiceListener>& listener,
std::vector<hardware::CameraStatus> *cameraStatuses) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < mTorchStatusMap.size(); i++ ) {
String16 id = String16(mTorchStatusMap.keyAt(i).string());
// 跨进程回调监听函数
// 3.1.4
listener->onTorchStatusChanged(mapToInterface(mTorchStatusMap.valueAt(i)), id);
}
}通过以上注册回调和调用服务的流程,实现将java服务作为监听对象注册到C++层服务,C++层服务跨进程回调java层服务。下图是ICameraServiceListener UML类图:

图2-2-5 ICameraServiceListener UML类图
Step4 connectDevice
文件:"./frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/CameraService.cpp"
Status CameraService::connectDevice(
const sp<hardware::camera2::ICameraDeviceCallbacks>& cameraCb,
const String16& cameraId,
const String16& clientPackageName,
int clientUid,
/*out*/
sp<hardware::camera2::ICameraDeviceUser>* device) {
ATRACE_CALL();
Status ret = Status::ok();
String8 id = String8(cameraId);
sp<CameraDeviceClient> client = nullptr;
// 4.1
ret = connectHelper<hardware::camera2::ICameraDeviceCallbacks,CameraDeviceClient>(cameraCb, id,
/*api1CameraId*/-1,
CAMERA_HAL_API_VERSION_UNSPECIFIED, clientPackageName,
clientUid, USE_CALLING_PID, API_2,
/*legacyMode*/ false, /*shimUpdateOnly*/ false,
/*out*/client);
if(!ret.isOk()) {
logRejected(id, getCallingPid(), String8(clientPackageName),
ret.toString8());
return ret;
}
*device = client;
return ret;
}这个方法实现在CameraService类中。client是最终返回的CameraDeviceClient对象。
template<class CALLBACK, class CLIENT>
Status CameraService::connectHelper(const sp<CALLBACK>& cameraCb, const String8& cameraId,
int halVersion, const String16& clientPackageName, int clientUid, int clientPid,
apiLevel effectiveApiLevel, bool legacyMode, bool shimUpdateOnly,
/*out*/sp<CLIENT>& device) {
binder::Status ret = binder::Status::ok();
String8 clientName8(clientPackageName);
...
sp<BasicClient> tmp = nullptr;
// 4.2
if(!(ret = makeClient(this, cameraCb, clientPackageName, cameraId, facing, clientPid,
clientUid, getpid(), legacyMode, halVersion, deviceVersion, effectiveApiLevel,
/*out*/&tmp)).isOk()) {
return ret;
}
client = static_cast<CLIENT*>(tmp.get());
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(client.get() == nullptr, "%s: CameraService in invalid state",
__FUNCTION__);
// 4.3
err = client->initialize(mCameraProviderManager);
...
// Important: release the mutex here so the client can call back into the service from its
// destructor (can be at the end of the call)
device = client;
return ret;
}CALLBACK为ICameraDeviceCallbacks,CLIENT为CameraDeviceClient。先通过makeClient生成client(CameraDeviceClient对象),再调用CameraDeviceClient的initialize函数。
4.2 makeClient
Status CameraService::makeClient(const sp<CameraService>& cameraService,
const sp<IInterface>& cameraCb, const String16& packageName, const String8& cameraId,
int api1CameraId, int facing, int clientPid, uid_t clientUid, int servicePid,
bool legacyMode, int halVersion, int deviceVersion, apiLevel effectiveApiLevel,
/*out*/sp<BasicClient>* client) {
if (halVersion < 0 || halVersion == deviceVersion) {
switch(deviceVersion) {
...
case CAMERA_DEVICE_API_VERSION_3_4:
if (effectiveApiLevel == API_1) { // Camera1 API route
sp<ICameraClient> tmp = static_cast<ICameraClient*>(cameraCb.get());
*client = new Camera2Client(cameraService, tmp, packageName,
cameraId, api1CameraId,
facing, clientPid, clientUid,
servicePid, legacyMode);
} else { // Camera2 API route
sp<hardware::camera2::ICameraDeviceCallbacks> tmp =
static_cast<hardware::camera2::ICameraDeviceCallbacks*>(cameraCb.get());
//4.2.1
*client = new CameraDeviceClient(cameraService, tmp, packageName, cameraId,
facing, clientPid, clientUid, servicePid);
}
break;
default:
// Should not be reachable
ALOGE("Unknown camera device HAL version: %d", deviceVersion);
return STATUS_ERROR_FMT(ERROR_INVALID_OPERATION,
"Camera device \"%s\" has unknown HAL version %d",
cameraId.string(), deviceVersion);
}
} else {
...
}
...
}makeClient主要是根据 API 版本以及 HAL 版本来实例化CameraDeviceClient。最后在Step5,这一client返回到openCameraDeviceUserAsync中保存起来。
Step5 setRemoteDevice
文件:"./frameworks/base/core/java/android/hardware/camera2/impl/CameraDeviceImpl.java"
/**
* Set remote device, which triggers initial onOpened/onUnconfigured callbacks
*
* <p>This function may post onDisconnected and throw CAMERA_DISCONNECTED if remoteDevice dies
* during setup.</p>
*
*/
public void setRemoteDevice(ICameraDeviceUser remoteDevice) throws CameraAccessException {
synchronized(mInterfaceLock) {
// TODO: Move from decorator to direct binder-mediated exceptions
// If setRemoteFailure already called, do nothing
if (mInError) return;
// 5.1
mRemoteDevice = new ICameraDeviceUserWrapper(remoteDevice);
IBinder remoteDeviceBinder = remoteDevice.asBinder();
// For legacy camera device, remoteDevice is in the same process, and
// asBinder returns NULL.
if (remoteDeviceBinder != null) {
try {
remoteDeviceBinder.linkToDeath(this, /*flag*/ 0);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
CameraDeviceImpl.this.mDeviceExecutor.execute(mCallOnDisconnected);
throw new CameraAccessException(CameraAccessException.CAMERA_DISCONNECTED,
"The camera device has encountered a serious error");
}
}
mDeviceExecutor.execute(mCallOnOpened);
mDeviceExecutor.execute(mCallOnUnconfigured);
}
}将打开Camera获取的ICameraDeviceUser对象(即Framework层的CameraDeviceClient对象)封装到一个ICameraDeviceUserWrapper类的实例中,并保存为mRemoteDevice。注意,此处触发onOpened与onUnconfigured这两个回调,每个回调都是通过mDeviceHandler启用一个新线程来调用的。
小结:
通过以上流程,相机应用获得了CameraDeviceImpl对象,而CameraDeviceImpl保存了ICameraDeviceUserWrapper对象,ICameraDeviceUserWrapper保存BpCameraDeviceUser对象,BpCameraDeviceUser具有aidl跨进程的能力,这样应用就可以和CameraService端的CameraDeviceClient进行通信了。
Java层要想与C++层的CameraService层进行通信,是通过aidl进行的,主要包括ICameraService.aidl以及ICameraDeviceUser.aidl两个接口来实现,其会在Java层维护一个CameraDeviceImpl类(即BpCameraDeviceUser类)。
2.3 camera server进程<-->hal(camera provider)进程
camera server进程与camera provider进程,它们之间通过HIDL进行通信。CameraService会寻找现存的ProviderService,将其加入到内部的 CameraProviderManager中进行管理,相关操作都是通过远端调用进行的;而CameraProvider,它在初始化时(initialize)就已经连接到libhardware的Camera HAL实现层,并用CameraModule来进行管理。(图2-1-1 camera server进程与hal(camera provider)进程启动架构图)
这一部分的主要调用逻辑如下图:
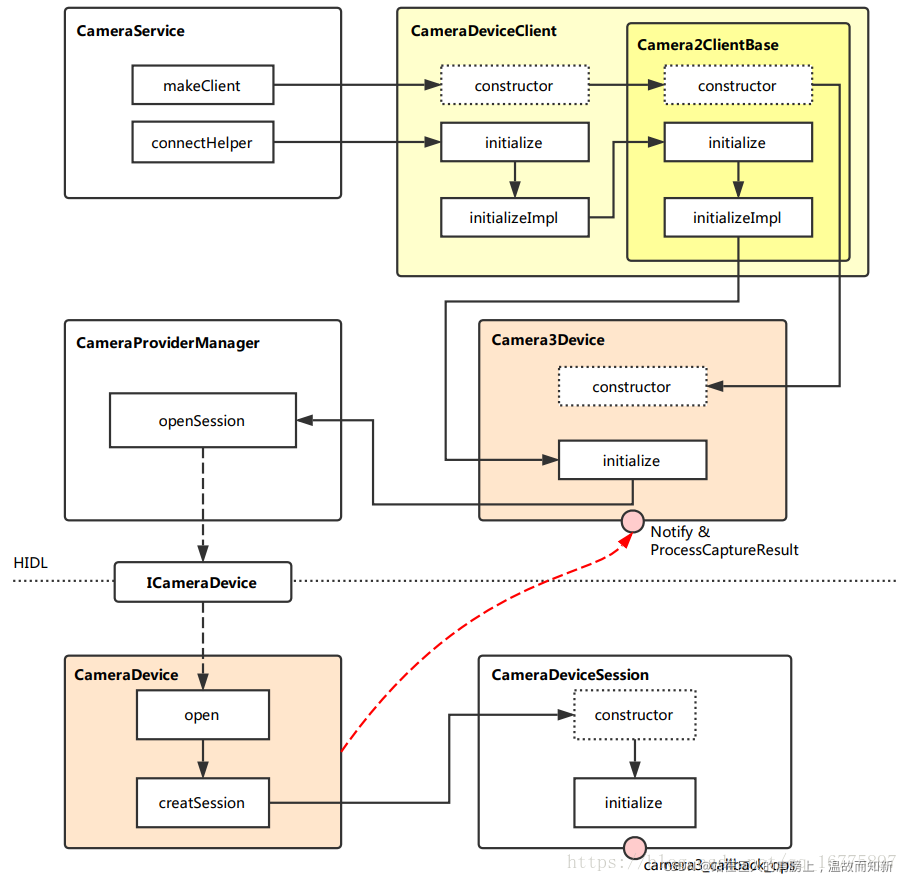
?图2-3-1 camera server进程<-->hal(camera provider)进程架构图
下图是camera server进程<-->hal(camera provider)进程 UML顺序图:
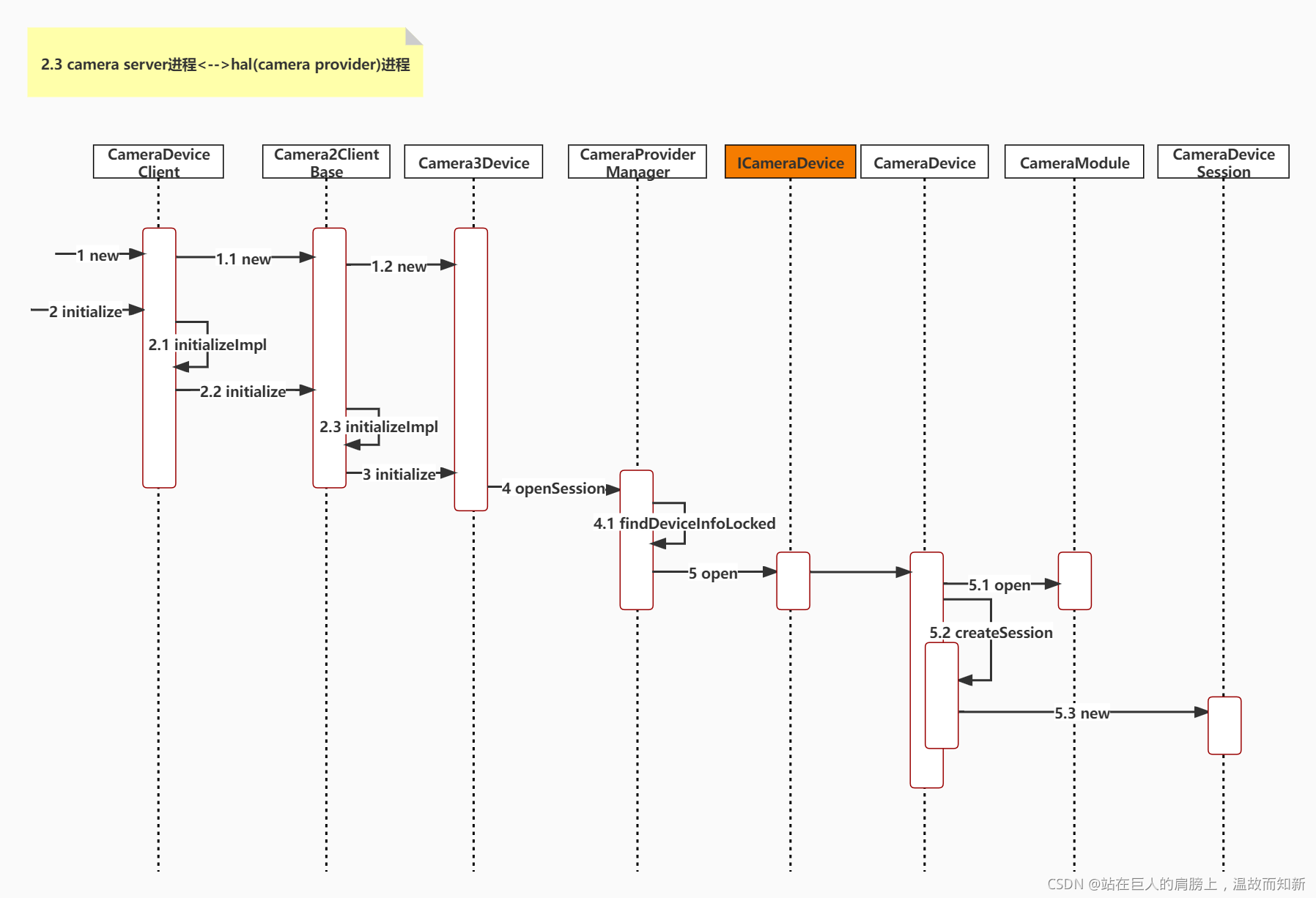
图2-3-2 camera server进程<-->hal(camera provider)进程 UML顺序图
2.2节(4.2.1)讲到实例化了一个CameraDeviceClient对象,我们从它的构造函数开始分析:
Step1 new CameraDeviceClient(2.2节(4.2.1))
文件:"./frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/api2/CameraDeviceClient.cpp"
CameraDeviceClient::CameraDeviceClient(const sp<CameraService>& cameraService,
const sp<hardware::camera2::ICameraDeviceCallbacks>& remoteCallback,
const String16& clientPackageName,
const String8& cameraId,
int cameraFacing,
int clientPid,
uid_t clientUid,
int servicePid) :
// 1.1
Camera2ClientBase(cameraService, remoteCallback, clientPackageName,
cameraId, /*API1 camera ID*/ -1,
cameraFacing, clientPid, clientUid, servicePid),
mInputStream(),
mStreamingRequestId(REQUEST_ID_NONE),
mRequestIdCounter(0) {
ATRACE_CALL();
ALOGI("CameraDeviceClient %s: Opened", cameraId.string());
}1.1 Camera2ClientBase
文件:"frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/common/Camera2ClientBase.cpp"
template <typename TClientBase>
Camera2ClientBase<TClientBase>::Camera2ClientBase(
const sp<CameraService>& cameraService,
const sp<TCamCallbacks>& remoteCallback,
const String16& clientPackageName,
const String8& cameraId,
int api1CameraId,
int cameraFacing,
int clientPid,
uid_t clientUid,
int servicePid):
TClientBase(cameraService, remoteCallback, clientPackageName,
cameraId, api1CameraId, cameraFacing, clientPid, clientUid, servicePid),
mSharedCameraCallbacks(remoteCallback),
mDeviceVersion(cameraService->getDeviceVersion(TClientBase::mCameraIdStr)),
mDeviceActive(false), mApi1CameraId(api1CameraId)
{
ALOGI("Camera %s: Opened. Client: %s (PID %d, UID %d)", cameraId.string(),
String8(clientPackageName).string(), clientPid, clientUid);
mInitialClientPid = clientPid;
// 1.2
mDevice = new Camera3Device(cameraId);
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL_IF(mDevice == 0, "Device should never be NULL here.");
}TClientBase是CameraDeviceClientBase类,从ICameraDeviceUser UML类图中CameraDeviceClient的继承关系可以看出。TCamCallbacks是ICameraDeviceCallbacks类。创建Camera3Device实例。
1.2 new Camera3Device
文件:"frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/device3/Camera3Device.cpp"
Camera3Device::Camera3Device(const String8 &id):
mId(id),
mOperatingMode(NO_MODE),
mIsConstrainedHighSpeedConfiguration(false),
mStatus(STATUS_UNINITIALIZED),
mStatusWaiters(0),
mUsePartialResult(false),
mNumPartialResults(1),
mTimestampOffset(0),
mNextResultFrameNumber(0),
mNextReprocessResultFrameNumber(0),
mNextShutterFrameNumber(0),
mNextReprocessShutterFrameNumber(0),
mListener(NULL),
mVendorTagId(CAMERA_METADATA_INVALID_VENDOR_ID),
mLastTemplateId(-1)
{
ATRACE_CALL();
camera3_callback_ops::notify = &sNotify;
camera3_callback_ops::process_capture_result = &sProcessCaptureResult;
ALOGV("%s: Created device for camera %s", __FUNCTION__, mId.string());
}设置两个回调。
Step2 initialize(2.2节(4.3))
文件:"./frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/api2/CameraDeviceClient.cpp"
status_t CameraDeviceClient::initialize(sp<CameraProviderManager> manager,
const String8& monitorTags) {
// 2.1
return initializeImpl(manager, monitorTags);
}
template<typename TProviderPtr>
status_t CameraDeviceClient::initializeImpl(TProviderPtr providerPtr, const String8& monitorTags) {
ATRACE_CALL();
status_t res;
// 2.2
res = Camera2ClientBase::initialize(providerPtr, monitorTags);
if (res != OK) {
return res;
}
...
return OK;
}TProviderPtr是指CameraProviderManager类。调用父类初始化接口。
2.2 Camera2ClientBase::initialize
文件:"frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/common/Camera2ClientBase.cpp"
template <typename TClientBase>
status_t Camera2ClientBase<TClientBase>::initialize(sp<CameraProviderManager> manager,
const String8& monitorTags) {
// 2.3
return initializeImpl(manager, monitorTags);
}
template <typename TClientBase>
template <typename TProviderPtr>
status_t Camera2ClientBase<TClientBase>::initializeImpl(TProviderPtr providerPtr,
const String8& monitorTags) {
ATRACE_CALL();
ALOGV("%s: Initializing client for camera %s", __FUNCTION__,
TClientBase::mCameraIdStr.string());
status_t res;
// Verify ops permissions
res = TClientBase::startCameraOps();
if (res != OK) {
return res;
}
if (mDevice == NULL) {
ALOGE("%s: Camera %s: No device connected",
__FUNCTION__, TClientBase::mCameraIdStr.string());
return NO_INIT;
}
// Step 3
res = mDevice->initialize(providerPtr, monitorTags);
if (res != OK) {
ALOGE("%s: Camera %s: unable to initialize device: %s (%d)",
__FUNCTION__, TClientBase::mCameraIdStr.string(), strerror(-res), res);
return res;
}
wp<CameraDeviceBase::NotificationListener> weakThis(this);
res = mDevice->setNotifyCallback(weakThis);
return OK;
}注意此处,TClientBase 对应 CameraDeviceClientBase,而 TProviderPtr 对应的是 CameraProviderManager。mDevice是Camera3Device对象。
调用TClientBase(CameraDeviceClientBase)的 startCameraOps 方法,检查 ops 的权限;初始化Camera3Device;为Camera3Device设置Notify回调。
Step3 mDevice->initialize
文件:"frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/device3/Camera3Device.cpp"
status_t Camera3Device::initialize(sp<CameraProviderManager> manager, const String8& monitorTags) {
ATRACE_CALL();
Mutex::Autolock il(mInterfaceLock);
Mutex::Autolock l(mLock);
ALOGV("%s: Initializing HIDL device for camera %s", __FUNCTION__, mId.string());
if (mStatus != STATUS_UNINITIALIZED) {
CLOGE("Already initialized!");
return INVALID_OPERATION;
}
if (manager == nullptr) return INVALID_OPERATION;
sp<ICameraDeviceSession> session;
ATRACE_BEGIN("CameraHal::openSession");
// Step 4
status_t res = manager->openSession(mId.string(), this,
/*out*/ &session);
ATRACE_END();
if (res != OK) {
SET_ERR_L("Could not open camera session: %s (%d)", strerror(-res), res);
return res;
}
...
mInterface = new HalInterface(session, queue);
std::string providerType;
mVendorTagId = manager->getProviderTagIdLocked(mId.string());
mTagMonitor.initialize(mVendorTagId);
if (!monitorTags.isEmpty()) {
mTagMonitor.parseTagsToMonitor(String8(monitorTags));
}
return initializeCommonLocked();
}调用了CameraProviderManager的openSession方法,打开了一个远端的Session。
Step4 openSession
文件:"frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/common/CameraProviderManager.cpp"
status_t CameraProviderManager::openSession(const std::string &id,
const sp<hardware::camera::device::V3_2::ICameraDeviceCallback>& callback,
/*out*/
sp<hardware::camera::device::V3_2::ICameraDeviceSession> *session) {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mInterfaceMutex);
// 根据id和version找到对应的CameraDevice3
// 4.1
auto deviceInfo = findDeviceInfoLocked(id,
/*minVersion*/ {3,0}, /*maxVersion*/ {4,0});
if (deviceInfo == nullptr) return NAME_NOT_FOUND;
auto *deviceInfo3 = static_cast<ProviderInfo::DeviceInfo3*>(deviceInfo);
Status status;
hardware::Return<void> ret;
// 其中mInterface是指Hal层的CameraDevice类, cameraSession等于CameraDevice3SessionImpl
// Step 5
ret = deviceInfo3->mInterface->open(callback, [&status, &session]
(Status s, const sp<device::V3_2::ICameraDeviceSession>& cameraSession) {
status = s;
if (status == Status::OK) {
*session = cameraSession;
}
});
if (!ret.isOk()) {
ALOGE("%s: Transaction error opening a session for camera device %s: %s",
__FUNCTION__, id.c_str(), ret.description().c_str());
return DEAD_OBJECT;
}
return mapToStatusT(status);
}首先调用 findDeviceInfoLocked,获取 HAL3 相关的 DeviceInfo3,这个信息在CameraService服务启动与初始化的时候就已经创建出来并保存下来了。
然后通过hidl远端调用CameraDevice的open 方法(todo hidl远端调用具体怎么进程间通信的?),创建CameraDeviceSession实例并通过session返回。DeviceInfo3这个类的mInterface成员类型是ICameraDevice,通过它可以调用远端(Hal层)CameraDevice中的方法。
文件:"frameworks/av/services/camera/libcameraservice/common/CameraProviderManager.h"
// HALv3-specific camera fields, including the actual device interface
struct DeviceInfo3 : public DeviceInfo {
typedef hardware::camera::device::V3_2::ICameraDevice InterfaceT;
const sp<InterfaceT> mInterface;
virtual status_t setTorchMode(bool enabled) override;
virtual status_t getCameraInfo(hardware::CameraInfo *info) const override;
virtual bool isAPI1Compatible() const override;
virtual status_t dumpState(int fd) const override;
virtual status_t getCameraCharacteristics(
CameraMetadata *characteristics) const override;
DeviceInfo3(const std::string& name, const metadata_vendor_id_t tagId,
const std::string &id, uint16_t minorVersion,
const hardware::camera::common::V1_0::CameraResourceCost& resourceCost,
sp<InterfaceT> interface);
virtual ~DeviceInfo3();
private:
CameraMetadata mCameraCharacteristics;
};Step5?open
文件:"./hardware/interfaces/camera/device/3.2/default/CameraDevice.cpp"
Return<void> CameraDevice::open(const sp<ICameraDeviceCallback>& callback, open_cb _hidl_cb) {
Status status = initStatus();
sp<CameraDeviceSession> session = nullptr;
...
/** Open HAL device */
status_t res;
camera3_device_t *device;
ATRACE_BEGIN("camera3->open");
// 5.1
res = mModule->open(mCameraId.c_str(),
reinterpret_cast<hw_device_t**>(&device));
ATRACE_END();
...
struct camera_info info;
res = mModule->getCameraInfo(mCameraIdInt, &info);
if (res != OK) {
ALOGE("%s: Could not open camera: getCameraInfo failed", __FUNCTION__);
device->common.close(&device->common);
mLock.unlock();
_hidl_cb(Status::ILLEGAL_ARGUMENT, nullptr);
return Void();
}
// 5.2
session = createSession(
device, info.static_camera_characteristics, callback);
if (session == nullptr) {
ALOGE("%s: camera device session allocation failed", __FUNCTION__);
mLock.unlock();
_hidl_cb(Status::INTERNAL_ERROR, nullptr);
return Void();
}
...
mSession = session;
...
return Void();
}
sp<CameraDeviceSession> CameraDevice::createSession(camera3_device_t* device,
const camera_metadata_t* deviceInfo,
const sp<ICameraDeviceCallback>& callback) {
// 5.3
return new CameraDeviceSession(device, deviceInfo, callback);
}CameraDevice的实例是在初始化CameraProvider时初始化的(todo)。这个函数主要做两件事,一件事是通过mModule调用Camera HAL接口的open接口,mModule(CameraModule)是对Camera HAL的一层封装;另一件事是创建session并让mSession保存创建的session。
creatSession中直接创建了一个 CameraDeviceSession实例。
ICameraDevice.hal:./hardware/interfaces/camera/device/3.2/ICameraDevice.hal
ICameraDevice UML类图如下:
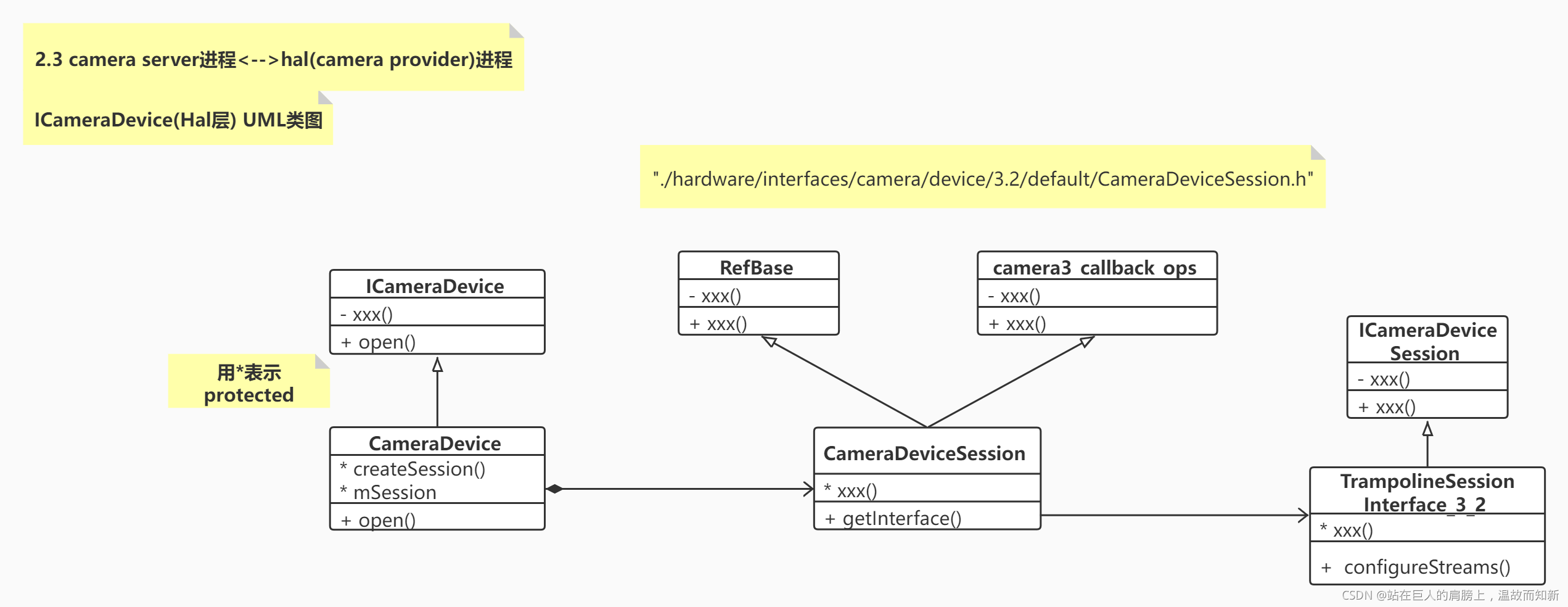
图2-3-3 ICameraDevice UML类图
2.4 camera hal分析
在 HAL3 中,Camera HAL的接口转化层以及流解析层由QCamera3HardwareInterface负责,而接口层与实现层是在mm_camera_interface.c与mm_camera.c 中。下图展示了Camera HAL初始化的主要调用流程:?
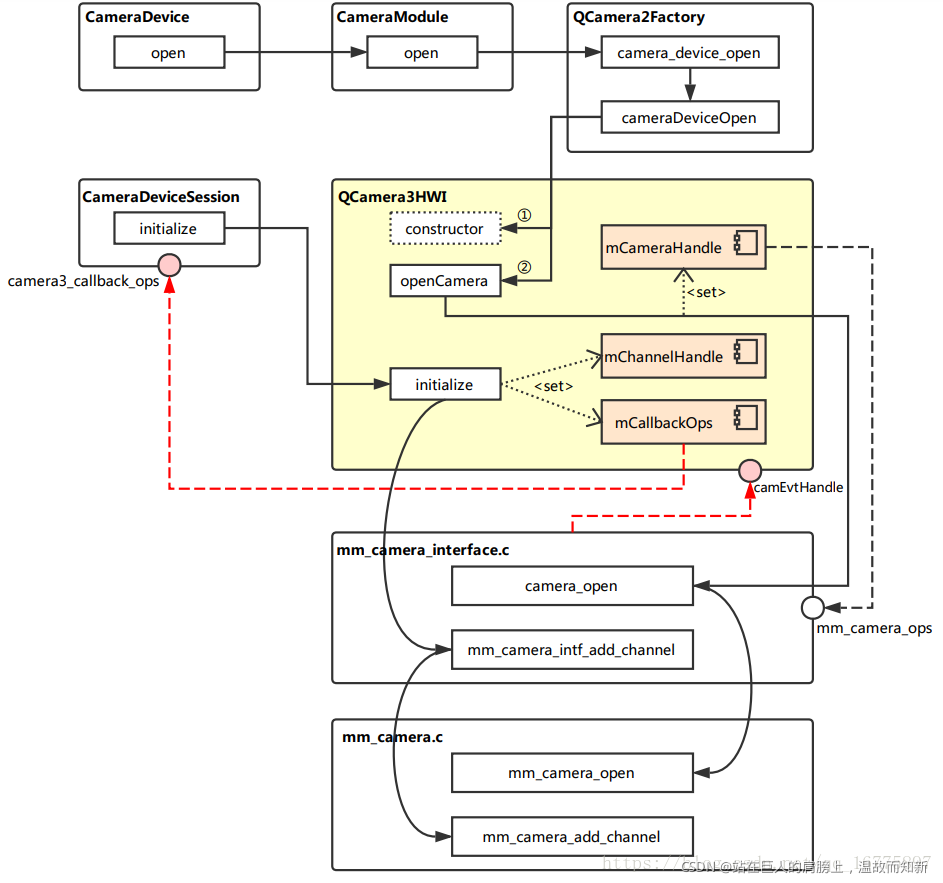
?图2-4-1 camera hal分析架构图
下图是camera hal分析UML顺序图:

?图2-4-2 camera hal分析UML顺序图
Step1 open(2.3节(5.1))
文件:"./hardware/interfaces/camera/common/1.0/default/CameraModule.cpp"
2.3节(5.1)讲到调用了mModule->open,即CameraModule::open(),接着往下看:
int CameraModule::open(const char* id, struct hw_device_t** device) {
int res;
ATRACE_BEGIN("camera_module->open");
// Step 2
res = filterOpenErrorCode(mModule->common.methods->open(&mModule->common, id, device));
ATRACE_END();
return res;
}注意,mModule是camera_module类型,mModule是在构造函数里赋值的,而CameraModule实例化是在CameraProvider实例化时(见2.1.1节(6.1.5))。
open 是一个函数指针,它指向的是QCamera2Factory的camera_device_open方法,分析如下:
先看下这些struct类型定义(camera_module, hw_module_t, hw_module_methods_t):
文件:"hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/camera_common.h"
typedef struct camera_module {
/**
* Common methods of the camera module. This *must* be the first member of
* camera_module as users of this structure will cast a hw_module_t to
* camera_module pointer in contexts where it's known the hw_module_t
* references a camera_module.
*
* The return values for common.methods->open for camera_module are:
*
* 0: On a successful open of the camera device.
*
* -ENODEV: The camera device cannot be opened due to an internal
* error.
*
* -EINVAL: The input arguments are invalid, i.e. the id is invalid,
* and/or the module is invalid.
*
* -EBUSY: The camera device was already opened for this camera id
* (by using this method or open_legacy),
* regardless of the device HAL version it was opened as.
*
* -EUSERS: The maximal number of camera devices that can be
* opened concurrently were opened already, either by
* this method or the open_legacy method.
*
* All other return values from common.methods->open will be treated as
* -ENODEV.
*/
hw_module_t common;
...
}文件:"hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/hardware.h"
typedef struct hw_module_t {
/** tag must be initialized to HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG */
uint32_t tag;
...
/** Identifier of module */
const char *id;
/** Name of this module */
const char *name;
/** Author/owner/implementor of the module */
const char *author;
/** Modules methods */
struct hw_module_methods_t* methods;
...
}
typedef struct hw_module_methods_t {
/** Open a specific device */
int (*open)(const struct hw_module_t* module, const char* id,
struct hw_device_t** device);
} hw_module_methods_t;hw_module_t中的成员是在QCamera2Hal.cpp赋值的,每个厂商不一样,以qcom msm8998为例:
文件:"hardware/qcom/camera/msm8998/QCamera2/QCamera2Hal.cpp"
static hw_module_t camera_common = {
.tag = HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG,
.module_api_version = CAMERA_MODULE_API_VERSION_2_4,
.hal_api_version = HARDWARE_HAL_API_VERSION,
.id = CAMERA_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
.name = "QCamera Module",
.author = "Qualcomm Innovation Center Inc",
.methods = &qcamera::QCamera2Factory::mModuleMethods,
.dso = NULL,
.reserved = {0}
};文件:"./hardware/qcom/camera/msm8998/QCamera2/QCamera2Factory.cpp"
struct hw_module_methods_t QCamera2Factory::mModuleMethods = {
.open = QCamera2Factory::camera_device_open,
};注意,mModuleMethods是个static类成员变量。
可以得出结论:open指向的是 QCamera2Factory的camera_device_open方法。
Step2 camera_device_open
文件:"./hardware/qcom/camera/msm8998/QCamera2/QCamera2Factory.cpp"
/*===========================================================================
* FUNCTION : camera_device_open
*
* DESCRIPTION: static function to open a camera device by its ID
*
* PARAMETERS :
* @camera_id : camera ID
* @hw_device : ptr to struct storing camera hardware device info
*
* RETURN : int32_t type of status
* NO_ERROR -- success
* none-zero failure code
*==========================================================================*/
int QCamera2Factory::camera_device_open(
const struct hw_module_t *module, const char *id,
struct hw_device_t **hw_device)
{
int rc = NO_ERROR;
if (module != &HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM.common) {
LOGE("Invalid module. Trying to open %p, expect %p",
module, &HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM.common);
return INVALID_OPERATION;
}
if (!id) {
LOGE("Invalid camera id");
return BAD_VALUE;
}
#ifdef QCAMERA_HAL1_SUPPORT
if(gQCameraMuxer)
rc = gQCameraMuxer->camera_device_open(module, id, hw_device);
else
#endif
// 2.1
rc = gQCamera2Factory->cameraDeviceOpen(atoi(id), hw_device);
return rc;
}
/*===========================================================================
* FUNCTION : cameraDeviceOpen
*
* DESCRIPTION: open a camera device with its ID
*
* PARAMETERS :
* @camera_id : camera ID
* @hw_device : ptr to struct storing camera hardware device info
*
* RETURN : int32_t type of status
* NO_ERROR -- success
* none-zero failure code
*==========================================================================*/
int QCamera2Factory::cameraDeviceOpen(int camera_id,
struct hw_device_t **hw_device)
{
int rc = NO_ERROR;
if (camera_id < 0 || camera_id >= mNumOfCameras)
return -ENODEV;
if ( NULL == mHalDescriptors ) {
LOGE("Hal descriptor table is not initialized!");
return NO_INIT;
}
LOGI("Open camera id %d API version %d",
camera_id, mHalDescriptors[camera_id].device_version);
if ( mHalDescriptors[camera_id].device_version == CAMERA_DEVICE_API_VERSION_3_0 ) {
CAMSCOPE_INIT(CAMSCOPE_SECTION_HAL);
// 2.2
QCamera3HardwareInterface *hw = new QCamera3HardwareInterface(mHalDescriptors[camera_id].cameraId,
mCallbacks);
if (!hw) {
LOGE("Allocation of hardware interface failed");
return NO_MEMORY;
}
// Step3
rc = hw->openCamera(hw_device);
if (rc != 0) {
delete hw;
}
}
...
}HAL3调用cameraDeviceOpen函数。创建QCamera3HardwareInterface实例,调用openCamera接口。
Step3 openCamera
文件:"hardware/qcom/camera/msm8998/QCamera2/HAL3/QCamera3HWI.cpp"
/*===========================================================================
* FUNCTION : openCamera
*
* DESCRIPTION: open camera
*
* PARAMETERS :
* @hw_device : double ptr for camera device struct
*
* RETURN : int32_t type of status
* NO_ERROR -- success
* none-zero failure code
*==========================================================================*/
int QCamera3HardwareInterface::openCamera(struct hw_device_t **hw_device)
{
int rc = 0;
if (mState != CLOSED) {
*hw_device = NULL;
return PERMISSION_DENIED;
}
...
// 3.1
rc = openCamera();
if (rc == 0) {
*hw_device = &mCameraDevice.common;
} else {
*hw_device = NULL;
...
}
...
}
/*===========================================================================
* FUNCTION : openCamera
*
* DESCRIPTION: open camera
*
* PARAMETERS : none
*
* RETURN : int32_t type of status
* NO_ERROR -- success
* none-zero failure code
*==========================================================================*/
int QCamera3HardwareInterface::openCamera()
{
int rc = 0;
char value[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
// Step 4
rc = camera_open((uint8_t)mCameraId, &mCameraHandle);
if (rc) {
LOGE("camera_open failed. rc = %d, mCameraHandle = %p", rc, mCameraHandle);
return rc;
}
if (!mCameraHandle) {
LOGE("camera_open failed. mCameraHandle = %p", mCameraHandle);
return -ENODEV;
}
rc = mCameraHandle->ops->register_event_notify(mCameraHandle->camera_handle,
camEvtHandle, (void *)this);
...
}openCamera的工作是从接口转化层进入到接口层。openCamera成功后,将mCameraDevice.common通过双重指针 hw_device 返回。接口层是调用camera_open接口,并通过mCameraHandle注册notify回调。
Step4 camera_open
文件:"./hardware/qcom/camera/msm8998/QCamera2/stack/mm-camera-interface/src/mm_camera_interface.c"
/*===========================================================================
* FUNCTION : camera_open
*
* DESCRIPTION: open a camera by camera index
*
* PARAMETERS :
* @camera_idx : camera index. should within range of 0 to num_of_cameras
* @camera_vtbl : ptr to a virtual table containing camera handle and operation table.
*
* RETURN : int32_t type of status
* 0 -- success
* non-zero error code -- failure
*==========================================================================*/
int32_t camera_open(uint8_t camera_idx, mm_camera_vtbl_t **camera_vtbl)
{
int32_t rc = 0;
mm_camera_obj_t *cam_obj = NULL;
uint32_t cam_idx = camera_idx;
uint32_t aux_idx = 0;
uint8_t is_multi_camera = 0;
...
// Step 5
rc = mm_camera_open(cam_obj);
if (rc != 0) {
LOGE("mm_camera_open err = %d", rc);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&cam_obj->cam_lock);
pthread_mutex_lock(&g_intf_lock);
g_cam_ctrl.cam_obj[cam_idx] = NULL;
free(cam_obj);
cam_obj = NULL;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&g_intf_lock);
*camera_vtbl = NULL;
return rc;
}
...
}进入接口层,调用mm_camera_open。
Step5 mm_camera_open
文件:"hardware/qcom/camera/msm8998/QCamera2/stack/mm-camera-interface/src/mm_camera.c"
/*===========================================================================
* FUNCTION : mm_camera_open
*
* DESCRIPTION: open a camera
*
* PARAMETERS :
* @my_obj : ptr to a camera object
*
* RETURN : int32_t type of status
* 0 -- success
* -1 -- failure
*==========================================================================*/
int32_t mm_camera_open(mm_camera_obj_t *my_obj)
{
char dev_name[MM_CAMERA_DEV_NAME_LEN];
int32_t rc = 0;
int8_t n_try=MM_CAMERA_DEV_OPEN_TRIES;
uint8_t sleep_msec=MM_CAMERA_DEV_OPEN_RETRY_SLEEP;
int cam_idx = 0;
const char *dev_name_value = NULL;
int l_errno = 0;
LOGD("begin\n");
if (NULL == my_obj) {
goto on_error;
}
dev_name_value = mm_camera_util_get_dev_name_by_num(my_obj->my_num,
my_obj->my_hdl);
if (NULL == dev_name_value) {
goto on_error;
}
snprintf(dev_name, sizeof(dev_name), "/dev/%s",
dev_name_value);
sscanf(dev_name, "/dev/video%d", &cam_idx);
LOGD("dev name = %s, cam_idx = %d", dev_name, cam_idx);
do{
n_try--;
errno = 0;
my_obj->ctrl_fd = open(dev_name, O_RDWR | O_NONBLOCK);
l_errno = errno;
LOGD("ctrl_fd = %d, errno == %d", my_obj->ctrl_fd, l_errno);
if((my_obj->ctrl_fd >= 0) || (errno != EIO && errno != ETIMEDOUT) || (n_try <= 0 )) {
break;
}
LOGE("Failed with %s error, retrying after %d milli-seconds",
strerror(errno), sleep_msec);
usleep(sleep_msec * 1000U);
}while (n_try > 0);
...
LOGD("Launch evt Thread in Cam Open");
snprintf(my_obj->evt_thread.threadName, THREAD_NAME_SIZE, "CAM_Dispatch");
mm_camera_cmd_thread_launch(&my_obj->evt_thread,
mm_camera_dispatch_app_event,
(void *)my_obj);
/* launch event poll thread
* we will add evt fd into event poll thread upon user first register for evt */
LOGD("Launch evt Poll Thread in Cam Open");
snprintf(my_obj->evt_poll_thread.threadName, THREAD_NAME_SIZE, "CAM_evntPoll");
mm_camera_poll_thread_launch(&my_obj->evt_poll_thread,
MM_CAMERA_POLL_TYPE_EVT);
mm_camera_evt_sub(my_obj, TRUE);
...
}打开camera设备文件open("/dev/video%d",...),并起事件线程。
Step6 new CameraDeviceSession((2.3节(5.3)))
文件:"./hardware/interfaces/camera/device/3.2/default/CameraDeviceSession.cpp"
2.3节分析过,调用CameraModule的open接口后会创建CameraDeviceSession实例,继续往下看,这里会调用QCamera3HWI的初始化方法 initialize。
CameraDeviceSession::CameraDeviceSession(
camera3_device_t* device,
const camera_metadata_t* deviceInfo,
const sp<ICameraDeviceCallback>& callback) :
camera3_callback_ops({&sProcessCaptureResult, &sNotify}),
mDevice(device),
mDeviceVersion(device->common.version),
mIsAELockAvailable(false),
mDerivePostRawSensKey(false),
mNumPartialResults(1),
mResultBatcher(callback) {
mDeviceInfo = deviceInfo;
camera_metadata_entry partialResultsCount =
mDeviceInfo.find(ANDROID_REQUEST_PARTIAL_RESULT_COUNT);
if (partialResultsCount.count > 0) {
mNumPartialResults = partialResultsCount.data.i32[0];
}
mResultBatcher.setNumPartialResults(mNumPartialResults);
camera_metadata_entry aeLockAvailableEntry = mDeviceInfo.find(
ANDROID_CONTROL_AE_LOCK_AVAILABLE);
...
// 6.1
mInitFail = initialize();
}
bool CameraDeviceSession::initialize() {
/** Initialize device with callback functions */
ATRACE_BEGIN("camera3->initialize");
// Step7
status_t res = mDevice->ops->initialize(mDevice, this);
ATRACE_END();
if (res != OK) {
ALOGE("%s: Unable to initialize HAL device: %s (%d)",
__FUNCTION__, strerror(-res), res);
mDevice->common.close(&mDevice->common);
mClosed = true;
return true;
}
...
}文件:"hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/camera3.h"
/**********************************************************************
*
* Camera device definition
*
*/
typedef struct camera3_device {
/**
* common.version must equal CAMERA_DEVICE_API_VERSION_3_0 to identify this
* device as implementing version 3.0 of the camera device HAL.
*
* Performance requirements:
*
* Camera open (common.module->common.methods->open) should return in 200ms, and must return
* in 500ms.
* Camera close (common.close) should return in 200ms, and must return in 500ms.
*
*/
hw_device_t common;
camera3_device_ops_t *ops;
void *priv;
} camera3_device_t;
/**********************************************************************
*
* Camera device operations
*
*/
typedef struct camera3_device_ops {
/**
* initialize:
*
* One-time initialization to pass framework callback function pointers to
* the HAL. Will be called once after a successful open() call, before any
* other functions are called on the camera3_device_ops structure.
*
* Performance requirements:
*
* This should be a non-blocking call. The HAL should return from this call
* in 5ms, and must return from this call in 10ms.
*
* Return values:
*
* 0: On successful initialization
*
* -ENODEV: If initialization fails. Only close() can be called successfully
* by the framework after this.
*/
int (*initialize)(const struct camera3_device *,
const camera3_callback_ops_t *callback_ops);
...
} camera3_device_ops_t;可以看出mDevice是camera3_device_t*类型,ops是camera3_device_ops_t*类型。initialize是在哪里赋值的呢?
文件:"./device/google/marlin/camera/QCamera2/HAL3/QCamera3HWI.cpp"
camera3_device_ops_t QCamera3HardwareInterface::mCameraOps = {
.initialize = QCamera3HardwareInterface::initialize,
.configure_streams = QCamera3HardwareInterface::configure_streams,
.register_stream_buffers = NULL,
.construct_default_request_settings = QCamera3HardwareInterface::construct_default_request_settings,
.process_capture_request = QCamera3HardwareInterface::process_capture_request,
.get_metadata_vendor_tag_ops = NULL,
.dump = QCamera3HardwareInterface::dump,
.flush = QCamera3HardwareInterface::flush,
.reserved = {0},
};所以最后调用到了QCamera3HardwareInterface::initialize这个静态函数。
Step7 initialize
文件:"./device/google/marlin/camera/QCamera2/HAL3/QCamera3HWI.cpp"
/*===========================================================================
* FUNCTION : initialize
*
* DESCRIPTION: Pass framework callback pointers to HAL
*
* PARAMETERS :
*
*
* RETURN : Success : 0
* Failure: -ENODEV
*==========================================================================*/
int QCamera3HardwareInterface::initialize(const struct camera3_device *device,
const camera3_callback_ops_t *callback_ops)
{
LOGD("E");
QCamera3HardwareInterface *hw =
reinterpret_cast<QCamera3HardwareInterface *>(device->priv);
if (!hw) {
LOGE("NULL camera device");
return -ENODEV;
}
// 7.1
int rc = hw->initialize(callback_ops);
LOGD("X");
return rc;
}
/*===========================================================================
* FUNCTION : initialize
*
* DESCRIPTION: Initialize frameworks callback functions
*
* PARAMETERS :
* @callback_ops : callback function to frameworks
*
* RETURN :
*
*==========================================================================*/
int QCamera3HardwareInterface::initialize(
const struct camera3_callback_ops *callback_ops)
{
ATRACE_CALL();
int rc;
LOGI("E :mCameraId = %d mState = %d", mCameraId, mState);
pthread_mutex_lock(&mMutex);
// Validate current state
switch (mState) {
case OPENED:
/* valid state */
break;
default:
LOGE("Invalid state %d", mState);
rc = -ENODEV;
goto err1;
}
rc = initParameters();
if (rc < 0) {
LOGE("initParamters failed %d", rc);
goto err1;
}
mCallbackOps = callback_ops;
// Step8
mChannelHandle = mCameraHandle->ops->add_channel(
mCameraHandle->camera_handle, NULL, NULL, this);
if (mChannelHandle == 0) {
LOGE("add_channel failed");
rc = -ENOMEM;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mMutex);
return rc;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mMutex);
mCameraInitialized = true;
mState = INITIALIZED;
LOGI("X");
return 0;
err1:
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mMutex);
return rc;
}进入接口转化层QCamera3HardwareInterface。注意,callback_ops回调指针是指CameraDeviceSession实例地址,用mCallbackOps保存回调指针。通过mCameraHandle->ops->add_channel进入接口层mm_camera_interface。调用的方法实际是 mm_camera_interface.c 中的mm_camera_intf_add_channel。
文件:"hardware/qcom/camera/msm8998/QCamera2/stack/common/mm_camera_interface.h"
/** mm_camera_vtbl_t: virtual table for camera operations
* @camera_handle : camera handler which uniquely identifies a
* camera object
* @ops : API call table
**/
typedef struct {
uint32_t camera_handle;
mm_camera_ops_t *ops;
} mm_camera_vtbl_t;
typedef struct {
...
/** add_channel: fucntion definition for adding a channel
* @camera_handle : camer handler
* @ch_id : channel handler
* @attr : pointer to channel attribute structure
* @channel_cb : callbak to handle bundled super buffer
* @userdata : user data pointer
* Return value: channel id, zero is invalid ch_id
* Note: attr, channel_cb, and userdata can be NULL if no
* superbufCB is needed
**/
uint32_t (*add_channel) (uint32_t camera_handle,
mm_camera_channel_attr_t *attr,
mm_camera_buf_notify_t channel_cb,
void *userdata);
...
} mm_camera_ops_t;可以看到mCameraHandle的类型为mm_camera_vtbl_t *,mCameraHandle->ops的类型为mm_camera_ops_t*。
文件:"hardware/qcom/camera/msm8998/QCamera2/stack/mm-camera-interface/src/mm_camera_interface.c"
/* camera ops v-table */
static mm_camera_ops_t mm_camera_ops = {
.query_capability = mm_camera_intf_query_capability,
.register_event_notify = mm_camera_intf_register_event_notify,
.close_camera = mm_camera_intf_close,
.set_parms = mm_camera_intf_set_parms,
.get_parms = mm_camera_intf_get_parms,
.do_auto_focus = mm_camera_intf_do_auto_focus,
.cancel_auto_focus = mm_camera_intf_cancel_auto_focus,
.prepare_snapshot = mm_camera_intf_prepare_snapshot,
.start_zsl_snapshot = mm_camera_intf_start_zsl_snapshot,
.stop_zsl_snapshot = mm_camera_intf_stop_zsl_snapshot,
.map_buf = mm_camera_intf_map_buf,
.map_bufs = mm_camera_intf_map_bufs,
.unmap_buf = mm_camera_intf_unmap_buf,
.add_channel = mm_camera_intf_add_channel,
...
}可以看到,最后调用到mm_camera_interface.c文件的mm_camera_intf_add_channel接口。
Step8 add_channel
文件:"hardware/qcom/camera/msm8998/QCamera2/stack/mm-camera-interface/src/mm_camera_interface.c"
/*===========================================================================
* FUNCTION : mm_camera_intf_add_channel
*
* DESCRIPTION: add a channel
*
* PARAMETERS :
* @camera_handle: camera handle
* @attr : bundle attribute of the channel if needed
* @channel_cb : callback function for bundle data notify
* @userdata : user data ptr
*
* RETURN : uint32_t type of channel handle
* 0 -- invalid channel handle, meaning the op failed
* >0 -- successfully added a channel with a valid handle
* NOTE : if no bundle data notify is needed, meaning each stream in the
* channel will have its own stream data notify callback, then
* attr, channel_cb, and userdata can be NULL. In this case,
* no matching logic will be performed in channel for the bundling.
*==========================================================================*/
static uint32_t mm_camera_intf_add_channel(uint32_t camera_handle,
mm_camera_channel_attr_t *attr,
mm_camera_buf_notify_t channel_cb,
void *userdata)
{
uint32_t ch_id = 0, aux_ch_id = 0;
mm_camera_obj_t * my_obj = NULL;
uint32_t handle = get_main_camera_handle(camera_handle);
uint32_t aux_handle = get_aux_camera_handle(camera_handle);
LOGD("E camera_handler = %d", camera_handle);
if (handle) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&g_intf_lock);
my_obj = mm_camera_util_get_camera_by_handler(handle);
if(my_obj) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&my_obj->cam_lock);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&g_intf_lock);
// Step9
ch_id = mm_camera_add_channel(my_obj, attr, channel_cb, userdata);
} else {
pthread_mutex_unlock(&g_intf_lock);
}
}
...
LOGH("camera_handle = %u ch_id = %u X", camera_handle, ch_id);
return ch_id;
}通过调用实现层的 mm_camera_add_channel 来获取一个 ch_id。
Step9 mm_camera_add_channel
文件:"hardware/qcom/camera/msm8998/QCamera2/stack/mm-camera-interface/src/mm_camera.c"
/*===========================================================================
* FUNCTION : mm_camera_add_channel
*
* DESCRIPTION: add a channel
*
* PARAMETERS :
* @my_obj : camera object
* @attr : bundle attribute of the channel if needed
* @channel_cb : callback function for bundle data notify
* @userdata : user data ptr
*
* RETURN : uint32_t type of channel handle
* 0 -- invalid channel handle, meaning the op failed
* >0 -- successfully added a channel with a valid handle
* NOTE : if no bundle data notify is needed, meaning each stream in the
* channel will have its own stream data notify callback, then
* attr, channel_cb, and userdata can be NULL. In this case,
* no matching logic will be performed in channel for the bundling.
*==========================================================================*/
uint32_t mm_camera_add_channel(mm_camera_obj_t *my_obj,
mm_camera_channel_attr_t *attr,
mm_camera_buf_notify_t channel_cb,
void *userdata)
{
mm_channel_t *ch_obj = NULL;
uint8_t ch_idx = 0;
uint32_t ch_hdl = 0;
for(ch_idx = 0; ch_idx < MM_CAMERA_CHANNEL_MAX; ch_idx++) {
if (MM_CHANNEL_STATE_NOTUSED == my_obj->ch[ch_idx].state) {
ch_obj = &my_obj->ch[ch_idx];
break;
}
}
if (NULL != ch_obj) {
/* initialize channel obj */
memset(ch_obj, 0, sizeof(mm_channel_t));
ch_hdl = mm_camera_util_generate_handler_by_num(my_obj->my_num, ch_idx);
ch_obj->my_hdl = ch_hdl;
ch_obj->state = MM_CHANNEL_STATE_STOPPED;
ch_obj->cam_obj = my_obj;
pthread_mutex_init(&ch_obj->ch_lock, NULL);
ch_obj->sessionid = my_obj->sessionid;
// 9.1
mm_channel_init(ch_obj, attr, channel_cb, userdata);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&my_obj->cam_lock);
return ch_hdl;
}先找出状态为NOTUSED的通道channel,再进行通道channel初始化。
文件:"hardware/qcom/camera/msm8998/QCamera2/stack/mm-camera-interface/src/mm_camera_channel.c"
/*===========================================================================
* FUNCTION : mm_channel_init
*
* DESCRIPTION: initialize a channel
*
* PARAMETERS :
* @my_obj : channel object be to initialized
* @attr : bundle attribute of the channel if needed
* @channel_cb : callback function for bundle data notify
* @userdata : user data ptr
*
* RETURN : int32_t type of status
* 0 -- success
* -1 -- failure
* NOTE : if no bundle data notify is needed, meaning each stream in the
* channel will have its own stream data notify callback, then
* attr, channel_cb, and userdata can be NULL. In this case,
* no matching logic will be performed in channel for the bundling.
*==========================================================================*/
int32_t mm_channel_init(mm_channel_t *my_obj,
mm_camera_channel_attr_t *attr,
mm_camera_buf_notify_t channel_cb,
void *userdata)
{
int32_t rc = 0;
my_obj->bundle.super_buf_notify_cb = channel_cb;
my_obj->bundle.user_data = userdata;
if (NULL != attr) {
my_obj->bundle.superbuf_queue.attr = *attr;
}
my_obj->num_s_cnt = 0;
memset(&my_obj->frame_sync, 0, sizeof(my_obj->frame_sync));
pthread_mutex_init(&my_obj->frame_sync.sync_lock, NULL);
mm_muxer_frame_sync_queue_init(&my_obj->frame_sync.superbuf_queue);
my_obj->bundle.is_cb_active = 1;
LOGD("Launch data poll thread in channel open");
snprintf(my_obj->poll_thread[0].threadName, THREAD_NAME_SIZE, "CAM_dataPoll");
mm_camera_poll_thread_launch(&my_obj->poll_thread[0],
MM_CAMERA_POLL_TYPE_DATA);
/* change state to stopped state */
my_obj->state = MM_CHANNEL_STATE_STOPPED;
return rc;
}