1 前言
大部分OpenGL示例代码,要么播放个视频,要么画个三角形,有点简单了,就无法理解游戏中那么复杂的人物,是怎么渲染出来的。
所以这里写一片文章,来讲讲openGL怎么加载一个复杂的3D模型。
先上一个效果,吸引一下大家的注意力:

有关3D模型文件的介绍,请见:
OBJ 模型文件与MTL材质文件 介绍
制作3D模型的软件有很多,例如3D max, Blender, Maya等。于是就有很多模型文件格式。这么多格式,怎么解析呢?答案就是开源的Assimp(Open Asset Import Library缩写,中文名有点别扭,叫开放的资产导入库)。
它可以解析大部分3D模型文件格式,转换成统一格式的数据结构。开发者只需要关心转换后的数据结构即可。
一个 3D模型一般是由很多小模型组成,小模型也称为网格,即Mesh。
网格是独立的渲染单元,Mesh 对象本身包含渲染所需的所有相关数据,比如顶点位置、法向量、纹理坐标以及物体的材质。
渲染一个网格,就是一次DrawCall。渲染一帧完整的图像,就会有多次的DrawCall。
Assimp也是按上面的规则来解析数据。最后生成的是多个Mesh对象,方便开发者使用,甚至修改某个网格。
2 Assimp介绍
Assimp是开源的,代码和编译方式见Assimp in Github。
Assimp导入一个模型,生成一个场景(Scene)对象,它会包含导入的模型的所有数据。此外还加了一个链表,用于表示网格Mesh之间的关系。
Assimp数据结构的(简化)模型如下:
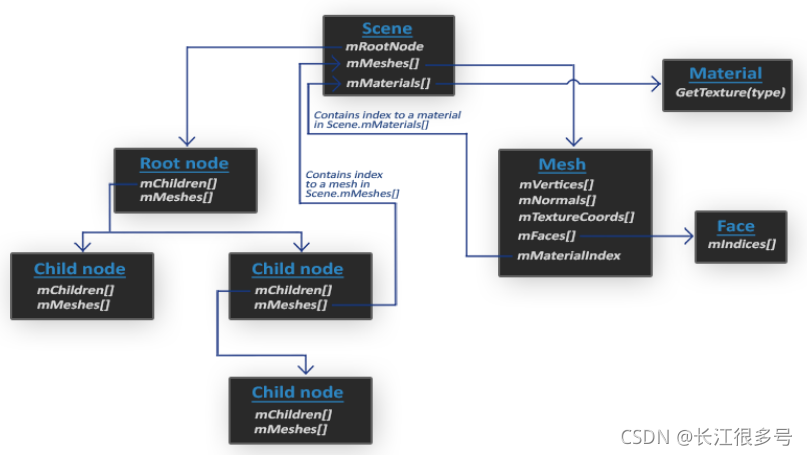
在这篇文章中,OBJ 模型文件与MTL材质文件 介绍,我们知道obj文件声明了网格的所有几何信息,如顶点&纹理坐标,法向量,以及使用哪些材质等,而mtl文件声明了材质的详细信息,如光照参数,纹理图片的路径等。
这和Assimp的数据结构有点匹配。
例如,Scene的变量:
mMeshes是网格数组, 每个单元,都存了相应的几何信息。还有指向材质数组的索引。
mMaterials是材质数组,每个单元,都存了相应的材质信息。
而Node节点的mMeshes是int数组,是存指向Scene对象的mMeshes数组的索引。
我们打开assimp的几个头文件scene.h, mesh.h, material.h,来一窥关键的数据结构。基本上,都是ai开头,如aiScene,aiMesh。
1.1 全局类 aiScene
struct aiScene {
aiNode* mRootNode;//链表
aiMesh** mMeshes;//网格指针的数组,也可以写成aiMesh* mMeshes[]
aiMaterial** mMaterials;//材质指针的数组
aiAnimation** mAnimations;//动效数组,注意obj格式不支持动效
aiTexture** mTextures;//纹理指针的数组
}
1.2 节点类aiNode
struct aiNode{
aiNode* mParent;//父节点
aiNode** mChildren;//子节点数组,也就是可能有多个子节点
unsigned int* mMeshes;//aiScene的网格列表的索引
}
1.3 网格类aiMesh
struct aiMesh {
aiVector3D* mVertices;//顶点数组
aiVector3D* mNormals;//法向量数组
aiVector3D* mTextureCoords[8];//纹理坐标数组,为啥是8个?因为一个顶点可以有多个纹理,例如diffuse纹理,specular纹理。当然了,大部分情况就一个
aiFace* mFaces;//面的索引数组,也就是三角形。比如4个顶点,组成2个三角形
}
1.4 材质类aiMaterial
struct aiMaterial {
/** List of all material properties loaded. */
aiMaterialProperty** mProperties;
aiReturn GetTexture(aiTextureType type...);
}
接下来,我们讨论如何使用assimp加载数据,并用OpenGL渲染出来。
3 使用assimp渲染
本文参考了openGL ES3.0教程的代码,来讨论如何渲染assimp的数据。
3.1 数据准备
首先,要定义一些类,来把assimp的数据都读取出来,做一些预处理。例如,把纹理图片解码,加载到GPU,生成纹理Id。
3.1.1 顶点的定义
定义一个类,来存所有的顶点信息:
struct Vertex {
// position 顶点
glm::vec3 Position;
// normal 法向量
glm::vec3 Normal;
// texCoords 纹理坐标
glm::vec2 TexCoords;
// tangent 切线坐标
glm::vec3 Tangent;
};
3.1.2 纹理的定义
定义一个类,来加载材质所包含的纹理,生成纹理id。
struct Texture {
unsigned int id;//纹理id,OpenGL环境下生成,不是assimp给的
string type;//类型,如diffuse纹理或者specular纹理
string path;//纹理的路径
};
3.1.3 网格的定义
定义一个类,来网格的所有数据。包络几何信息和纹理信息。
同时,实现一个方法,可以绘制网格Mesh。如前面所说,网格是最小的绘制单位。
class Mesh {
public:
/* Mesh Data */
vector<Vertex> vertices;
vector<unsigned int> indices;
vector<Texture> textures;
unsigned int VAO;
/* Functions */
// 构造函数,主要是初始化mesh
Mesh(vector<Vertex> vertices, vector<unsigned int> indices, vector<Texture> textures)
{
this->vertices = vertices;
this->indices = indices;
this->textures = textures;
// now that we have all the required data, set the vertex buffers and its attribute pointers.
setupMesh();
}
// 渲染函数
void Draw(Shader shader);
void Destroy();
private:
/* Render data */
unsigned int VBO, EBO;
/* Functions */
// initializes all the buffer objects/arrays
void setupMesh();
};
3.1.4 全局管理类定义
定义一个类,用于加载assimp数据,实现Draw函数,绘制所有的网格。
2个关键的函数:
- loadModel加载assimp数据,生成渲染所需要的数据;
- Draw 绘制一帧画面
class Model
{
public:
Model(GLchar* path)
{
loadModel(path);
}
//渲染模型,即依次渲染各个网格
void Draw(Shader shader);
//销毁模型的所有网格
void Destroy();
private:
//模型所包含的网格
vector<Mesh> meshes;
//模型文件所在目录
string directory;
//加载模型
void loadModel(string path);
//处理 aiScene 对象包含的节点和子节点
void processNode(aiNode* node, const aiScene* scene);
//生成网格
Mesh processMesh(aiMesh* mesh, const aiScene* scene);
//创建纹理并加载图像数据
vector<Texture> loadMaterialTextures(aiMaterial* mat, aiTextureType type, string typeName);
};
3.2 模型加载loadModel
类定义好了,现在就是具体的实现了。
模型加载就是3.1.4节说的loadModule的具体实现
简单的说以下过程:
- Assimp::Importer根据模型路径,加载生成aiScene。
- processNode遍历aiScene的Node节点,从而获得所有的aiMesh。
- processMesh处理aiMesh,把顶点/纹理坐标,以及纹理图片全部解析出来
- loadMaterialTextures 加载纹理,生成纹理id
上面过程的函数实现如下:
void loadModel(string const &path)
{
// 读取路径path的一个模型文件
Assimp::Importer importer;
const aiScene* scene = importer.ReadFile(path, aiProcess_Triangulate | aiProcess_FlipUVs | aiProcess_CalcTangentSpace);
// 出错则返回
if(!scene || scene->mFlags & AI_SCENE_FLAGS_INCOMPLETE || !scene->mRootNode) // if is Not Zero
{
return;
}
//遍历节点
processNode(scene->mRootNode, scene);
}
//处理节点的Mesh数据
void processNode(aiNode *node, const aiScene *scene)
{
// 遍历当前node的mesh数组
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < node->mNumMeshes; i++)
{
//根据数组存的index,从scene拿到原始的aiMesh
aiMesh* mesh = scene->mMeshes[node->mMeshes[i]];
if(mesh != nullptr)
meshes.push_back(processMesh(mesh, scene));//处理mesh数据,具体见下一个函数
}
// 遍历子节点
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < node->mNumChildren; i++)
{
processNode(node->mChildren[i], scene);
}
}
//处理一个mesh数据
Mesh processMesh(aiMesh *mesh, const aiScene *scene)
{
// data to fill
vector<Vertex> vertices;
vector<unsigned int> indices;
vector<Texture> textures;
// Walk through each of the mesh's vertices
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < mesh->mNumVertices; i++)
{
Vertex vertex;
glm::vec3 vector; //把assimp的坐标格式转换为glm::vec3,方便openGL读取
// 顶点坐标
vector.x = mesh->mVertices[i].x;
vector.y = mesh->mVertices[i].y;
vector.z = mesh->mVertices[i].z;
vertex.Position = vector;
updateMaxMinXyz(vector);
// 法线坐标
vector.x = mesh->mNormals[i].x;
vector.y = mesh->mNormals[i].y;
vector.z = mesh->mNormals[i].z;
vertex.Normal = vector;
// 纹理坐标
if(mesh->mTextureCoords[0]) // does the mesh contain texture coordinates?
{
glm::vec2 vec;
// 顶点最多可以指向8个纹理坐标,但一般只有一个
vec.x = mesh->mTextureCoords[0][i].x;
vec.y = mesh->mTextureCoords[0][i].y;
vertex.TexCoords = vec;
}
else
vertex.TexCoords = glm::vec2(0.0f, 0.0f);
// 切线
vector.x = mesh->mTangents[i].x;
vector.y = mesh->mTangents[i].y;
vector.z = mesh->mTangents[i].z;
vertex.Tangent = vector;
// 双切线
vector.x = mesh->mBitangents[i].x;
vector.y = mesh->mBitangents[i].y;
vector.z = mesh->mBitangents[i].z;
vertex.Bitangent = vector;
vertices.push_back(vertex);
}
// 遍历所有的面,即三角形
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < mesh->mNumFaces; i++)
{
aiFace face = mesh->mFaces[i];
// 检索一个面的顶点索引,并存到indices变量
for(unsigned int j = 0; j < face.mNumIndices; j++)
indices.push_back(face.mIndices[j]);
}
// 开始处理网格锁使用的材质
aiMaterial* material = scene->mMaterials[mesh->mMaterialIndex];
//遍历各种类型的纹理,根据不同的类型,耶规范纹理名称,后面的shader会使用这种纹理名称
// 例如所有漫反射纹理,在shader中的名字为'texture_diffuseN', N 从1 到 MAX_SAMPLER_NUMBER.
// 其他的类型耶类似
// diffuse: texture_diffuseN
// specular: texture_specularN
// normal: texture_normalN
// 1. diffuse maps
vector<Texture> diffuseMaps = loadMaterialTextures(material, aiTextureType_DIFFUSE, "texture_diffuse");
textures.insert(textures.end(), diffuseMaps.begin(), diffuseMaps.end());
// 2. specular maps
vector<Texture> specularMaps = loadMaterialTextures(material, aiTextureType_SPECULAR, "texture_specular");
textures.insert(textures.end(), specularMaps.begin(), specularMaps.end());
// 3. normal maps
std::vector<Texture> normalMaps = loadMaterialTextures(material, aiTextureType_HEIGHT, "texture_normal");
textures.insert(textures.end(), normalMaps.begin(), normalMaps.end());
// 4. height maps
std::vector<Texture> heightMaps = loadMaterialTextures(material, aiTextureType_AMBIENT, "texture_height");
textures.insert(textures.end(), heightMaps.begin(), heightMaps.end());
// 最后生成了一个纹理,包含了坐标和纹理数据
return Mesh(vertices, indices, textures);
}
纹理的加载:
vector<Texture> loadMaterialTextures(aiMaterial *mat, aiTextureType type, string typeName)
{
DEBUG_LOGCATE();
vector<Texture> textures;
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < mat->GetTextureCount(type); i++)
{
Texture texture;
texture.id = TextureFromFile(str.C_Str(), this->directory);//生成纹理id
texture.type = typeName;
texture.path = str.C_Str();
textures.push_back(texture);
textures_loaded.push_back(texture);
}
return textures;
}
unsigned int TextureFromFile(const char *path, const string &directory, bool gamma = false)
{
string filename = string(path);
filename = directory + '/' + filename;
unsigned int textureID;
glGenTextures(1, &textureID);//生成纹理id
int width, height, nrComponents;
unsigned char *data = nullptr;
// 使用OpenCV加载纹理
cv::Mat textureImage = cv::imread(filename);
if (!textureImage.empty())
{
hasTexture = true;
// opencv reads textures in BGR format, change to RGB for GL
cv::cvtColor(textureImage, textureImage, CV_BGR2RGB);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureID);
glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGB, textureImage.cols,
textureImage.rows, 0, GL_RGB, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE,
textureImage.data);//把数据拷贝到纹理单元中
glGenerateMipmap(GL_TEXTURE_2D);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_REPEAT);//设置纹理使用方式
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_REPEAT);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR_MIPMAP_LINEAR);
glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
GO_CHECK_GL_ERROR();
}
return textureID;
}
3.3 着色器shader
怎么个渲染法,就要靠着色器了。
3.3.1 顶点着色器
顶点着色器代码如下,已写了详细的注释。
#version 300 es
precision mediump float;
layout (location = 0) in vec3 a_position;//顶点
layout (location = 1) in vec3 a_normal;//法线
layout (location = 2) in vec2 a_texCoord;//纹理
out vec2 v_texCoord;
uniform mat4 u_MVPMatrix;//MVP矩阵
uniform mat4 u_ModelMatrix;//模型矩阵
uniform vec3 lightPos;//光照位置
uniform vec3 lightColor;//光照颜色
uniform vec3 viewPos;//人眼的位置,在计算
//冯氏光照模型(Phong Lighting Model)
//由三种元素光组成,分别是环境光(Ambient Lighting)、散射光(Diffuse Lighting)及镜面光(Specular Lighting)
out vec3 ambient;
out vec3 diffuse;
out vec3 specular;
void main()
{
v_texCoord = a_texCoord;
vec4 position = vec4(a_position, 1.0);
gl_Position = u_MVPMatrix * position;//得到顶点在裁减空间下的坐标,后面那些不做的话,也没事,就是没有光照效果而已
vec3 fragPos = vec3(u_ModelMatrix * position);//得到顶点在世界空间下的坐标
// Ambient 环境光
float ambientStrength = 0.25;
ambient = ambientStrength * lightColor;
// Diffuse 散射光
float diffuseStrength = 0.5;
vec3 unitNormal = normalize(vec3(u_ModelMatrix * vec4(a_normal, 1.0)));
vec3 lightDir = normalize(lightPos - fragPos);//光照的方向
float diff = max(dot(unitNormal, lightDir), 0.0);
diffuse = diffuseStrength * diff * lightColor;
// Specular 镜面光
float specularStrength = 0.3;
vec3 viewDir = normalize(viewPos - fragPos);
vec3 reflectDir = reflect(-lightDir, unitNormal);
float spec = pow(max(dot(unitNormal, reflectDir), 0.0), 16.0);
specular = specularStrength * spec * lightColor;
};
3.3.2 片元着色器
片元着色器代码如下,已写了详细的注释。
#version 300 es
precision mediump float;
out vec4 outColor;
in vec2 v_texCoord;
//3个光照颜色
in vec3 ambient;
in vec3 diffuse;
in vec3 specular;
uniform sampler2D texture_diffuse1;//为简单说明,暂时只支持1个纹理
void main()
{
vec4 objectColor = texture(texture_diffuse1, v_texCoord);
//光照色乘于纹理颜色,等于最终的效果颜色
vec3 finalColor = (ambient + diffuse + specular) * vec3(objectColor);//
outColor = vec4(finalColor, 1.0);
};
3.4 渲染
好了,数据准备好了,着色器也准备好了。接下来就是开始渲染了。开始实现3.1.4节的Draw函数。
代码和说明如下:
void Draw(int screenW, int screenH)
{
//1. 根据用户手势,得到MVP矩阵
UpdateMVPMatrix(m_MVPMatrix, m_AngleX, m_AngleY, (float)screenW / screenH);
//2. 把各种参数传给着色器shader
m_pShader->use();
m_pShader->setMat4("u_MVPMatrix", m_MVPMatrix);
m_pShader->setMat4("u_ModelMatrix", m_ModelMatrix);
m_pShader->setVec3("lightPos", glm::vec3(0, 0, m_pModel->GetMaxViewDistance()));
m_pShader->setVec3("lightColor", glm::vec3(1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f));
m_pShader->setVec3("viewPos", glm::vec3(0, 0, m_pModel->GetMaxViewDistance()));
//3. 挨个Mesh渲染
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < meshes.size(); i++)
meshes[i].Draw(shader);
}
Mesh的绘制方法如下:
void Draw(Shader shader)
{
// bind appropriate textures
unsigned int diffuseNr = 1;
unsigned int specularNr = 1;
unsigned int normalNr = 1;
unsigned int heightNr = 1;
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < textures.size(); i++)
{
//激活第N个纹理单元,最大值是31 #define GL_TEXTURE31 0x84DF
glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0 + i); // active proper texture unit before binding
// retrieve texture number (the N in diffuse_textureN)
string number;
string name = textures[i].type;//判断纹理类型
if(name == "texture_diffuse")//一般都是这个类型
number = std::to_string(diffuseNr++);
else if(name == "texture_specular")//少见
number = std::to_string(specularNr++);
else if(name == "texture_normal")//少见
number = std::to_string(normalNr++);
else if(name == "texture_height")//少见
number = std::to_string(heightNr++);
//glUniform1i设置shader中的纹理采样器(uniform sampler2D texture_diffuse1)使用第几个纹理单元
//glGetUniformLocation 返回统一变量的位置,例如"sampler2D texture_diffuse1"的问值
glUniform1i(glGetUniformLocation(shader.ID, (name + number).c_str()), i);
// 绑定纹理
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, textures[i].id);
}
// 绑定顶点缓冲数据
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
//终于可以提交DrawCall了
glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLES, indices.size(), GL_UNSIGNED_INT, 0);
glBindVertexArray(0);
//解绑定
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < textures.size(); i++) {
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D + i, 0);//解绑
}
}
好了,整体完成了。完整源码,请参考:
https://github.com/githubhaohao/NDK_OpenGLES_3_0
参考
Learn OpenGL ---- Assimp
NDK OpenGL ES 3.0 开发(二十一):3D 模型加载和渲染