前言
在上一篇中,对Jetpack里面的Room进行了初步的使用,但每次操作数据后需要额外查询一次。在本篇中,将会对Room以及前面所学的进行一个整合。
话不多说,直接开始!
1、Room+ViewModel+LiveData
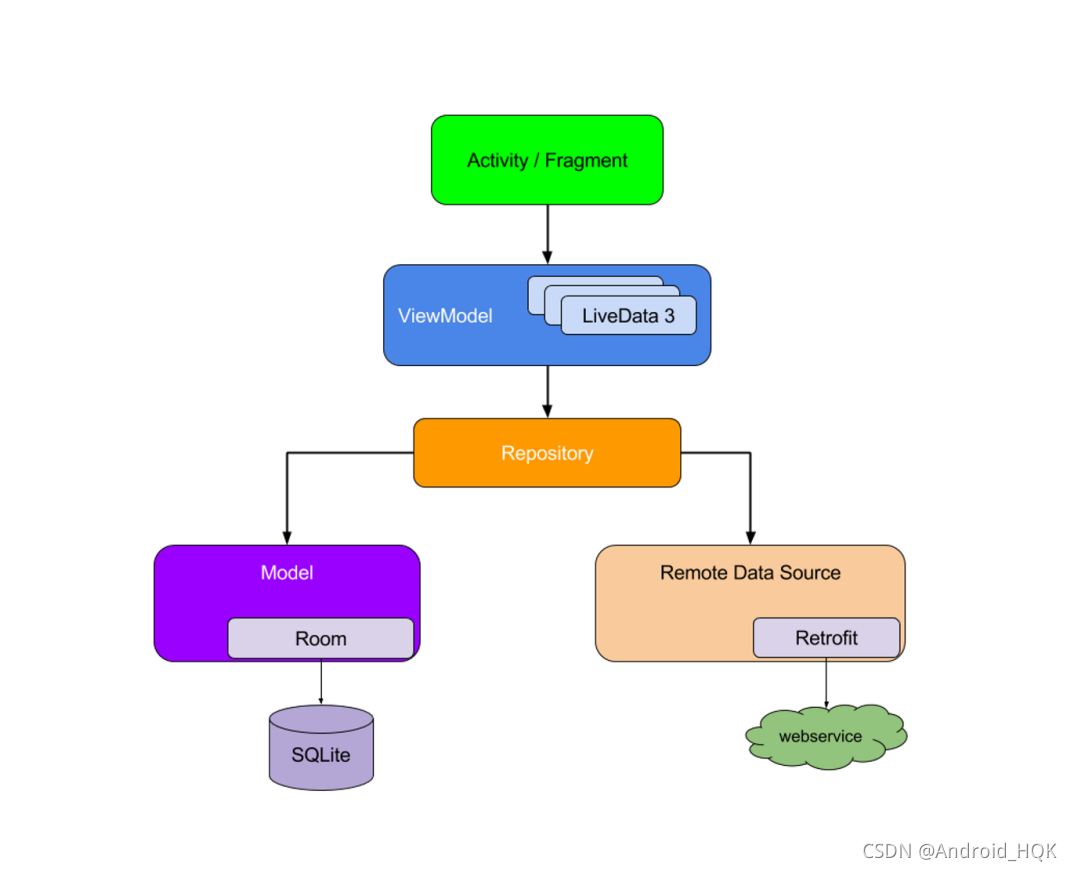
如图所示
这是官方推荐我们使用的架构,
- ViewModel和Repository交互
- Repository与对应的数据库、网络请求交互
在上一篇的基础上,对应Room数据库相关的暂且不动。
因为数据库和Repository相互关联,而Repository又与ViewModel相互关联,因此先来看看Repository究竟长啥样?
1.1 StudentRepository
class StudentRepository {
var studentDao: StudentDao? = null
constructor(context: Context) {
val database = MyDatabase.getInstance(context)
studentDao = database!!.getStudentDao()
}
fun insertStudent(vararg student: Student?) {
studentDao!!.insertStudent(*student)
}
fun deleteStudent(vararg student: Student) {
studentDao!!.deleteStudent(*student)
}
fun updateStudent(vararg student: Student) {
studentDao!!.updateStudent(*student)
}
fun deleteAllStudents() {
studentDao!!.deleteAllStudents()
}
fun getAllStudentsLive(): LiveData<List<Student>> {
return studentDao!!.getAllStudentsLive()
}
fun queryAll(): List<Student>? {
return studentDao!!.queryAll()
}
}
我们可以看到,之前关于Dao的所有操作都转移至Repository,也比较简单。
不过注意的是:getAllStudentsLive()方法返回的是LiveData<List<Student>>,LiveData集合!
接下来看看ViewModel?
1.2 StudentViewModel
class StudentViewModel(application: Application) : AndroidViewModel(application) {
//初始化对应的Repository对象
private val repository by lazy { StudentRepository(application) }
//定义对应得到LiveData集合
private var liveDataStudent: LiveData<List<Student>>? = null
init {
liveDataStudent = repository.getAllStudentsLive()
Log.d("StudentViewModel", "init liveDataStudent ${liveDataStudent?.value?.size}")
}
private fun insertStudent(vararg student: Student) {
viewModelScope.launch(Dispatchers.Default) {
repository.insertStudent(*student)
}
}
private fun deleteStudent(vararg student: Student) {
viewModelScope.launch(Dispatchers.Default) {
repository.deleteStudent(*student)
}
}
private fun updateStudent(vararg student: Student) {
viewModelScope.launch(Dispatchers.Default) {
repository.updateStudent(*student)
}
}
private fun deleteAllStudents() {
viewModelScope.launch(Dispatchers.Default) {
repository.deleteAllStudents()
}
}
fun getAllStudentsLive(): LiveData<List<Student>>? {
viewModelScope.launch(Dispatchers.Default) {
liveDataStudent = repository.getAllStudentsLive()
}
return liveDataStudent
}
//以下为DataBinding布局调用的方法-------------------
fun mInsert() {
val s1 = Student("hqk", 26)
val s2 = Student("Rose", 18)
insertStudent(s1, s2)
}
fun mClear() {
deleteAllStudents()
}
fun mDelete() {
var s1 = Student(3)
deleteStudent(s1)
}
fun mUpdate() {
val s1 = Student(2, "Jason", 21)
updateStudent(s1)
}
}
我们也能看到,这里的ViewModel与repository相互关联,而对应的布局通过DataBinding又与ViewModel相互绑定!
注意这里在ViewModel里面使用了viewModelScope,因此需要添加如下依赖
implementation "androidx.activity:activity-ktx:1.2.0"
implementation "androidx.fragment:fragment-ktx:1.3.0"
接下来看看如何使用:
1.3 mainActivity
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private var adapter: StudentRecyclerViewAdapter? = null
private var listStudent: ArrayList<Student> = ArrayList()
private var viewModel: StudentViewModel? = null
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
// setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
val binding =
DataBindingUtil.setContentView<ActivityMainBinding>(this, R.layout.activity_main)
viewModel = ViewModelProvider(this)[StudentViewModel::class.java]
binding.studentViewModel = viewModel
binding.lifecycleOwner = this
// val recycleView = findViewById<RecyclerView>(R.id.recycleView)
binding.recycleView.layoutManager = LinearLayoutManager(this)
adapter = StudentRecyclerViewAdapter(listStudent)
binding.recycleView.adapter = adapter
//监听对应的LiveData,当数据库发生数据改变时,将会主动回调通知!
viewModel!!.getAllStudentsLive()!!.observe(this, androidx.lifecycle.Observer {
Log.d("StudentViewModel", "main it ${it.size}")
adapter!!.students = it
adapter!!.notifyDataSetChanged()
})
}
}
这里很简单,就是通过ActivityMainBinding获取对应控件然后添加对应的逻辑,其次使用getAllStudentsLive方法获取到对应的LiveData,并通过observe监听LiveData集合。
Item对应的DataBinding为ItemBinding,相信经过第三篇DataBinding的讲解,读者应该轻易掌握了,这里就不贴对应代码了。
最后来看看运行效果吧

这里我们看到,每操作一次,数据自动加载,无需手动查询!
结束语
好了,本篇优化到这就结束了!在下一篇中,将会讲解Room对应的升级和预填充!