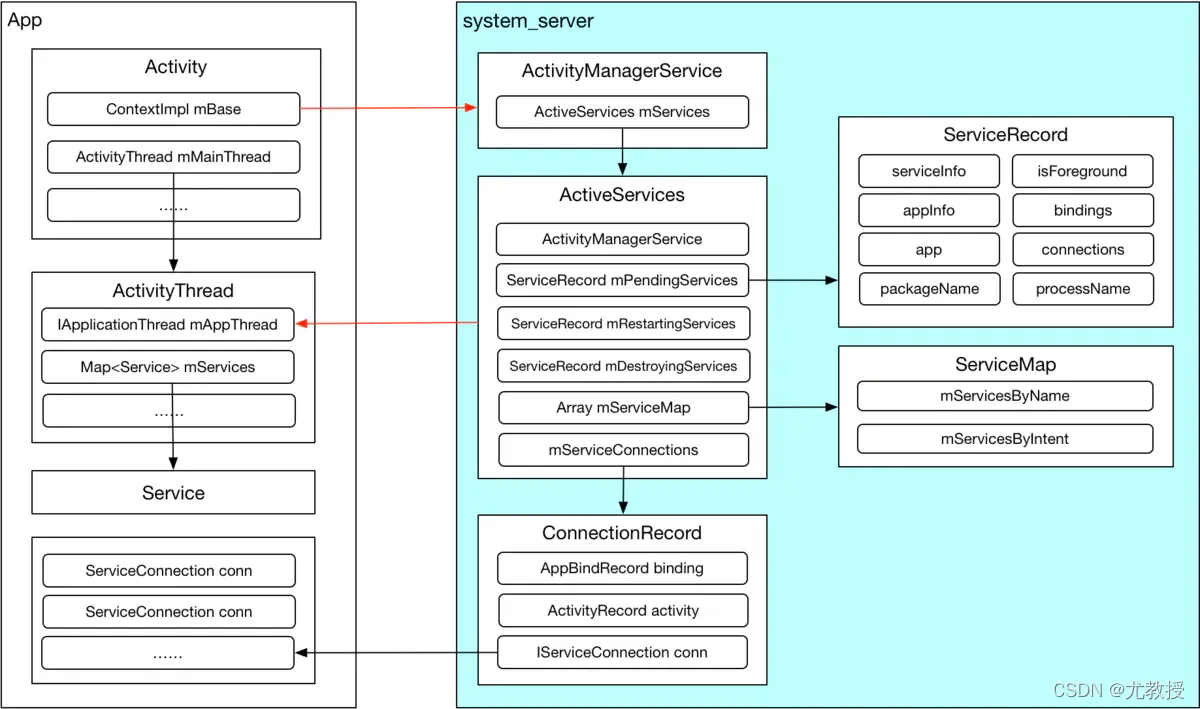
1.Service整体交互结构
Service作为Android四大组件之一,其生命周期是通过system_server进程中的ActivityManagerService(AMS)管理的,大致了解Service通信过程中涉及到的几个主要角色。
-
App端进程:
-
ContextImpl
Context抽象类所有api的实现,是Service、Activity和其他组件base Context。 -
ActivityThread
代表着App的主线程,是App的入口,Application、Activity、Service都在ActivityThread中创建,维护着该App所有运行中的Service实例。其中有一个IApplicationThread类型成员mAppThread,用于被AMS跨进程调用。 -
Service
具体提供服务的Service,被ActivityThread管理。 -
ServiceConnection
监听Service连接状态的接口,用于bindService。 -
AMS端:
-
ActivityManagerService
四大组件的大管家,是Framework中极为重要的一个类。 -
ActiveServices
AMS中管理Service的具体类。 -
ServiceRecord
Service结构的具体描述。 -
ServiceMap
描述了一个用户(App)的所有Service记录,主要用于检索。 -
ConnectionRecord
Client端与Service端绑定的抽象描述。
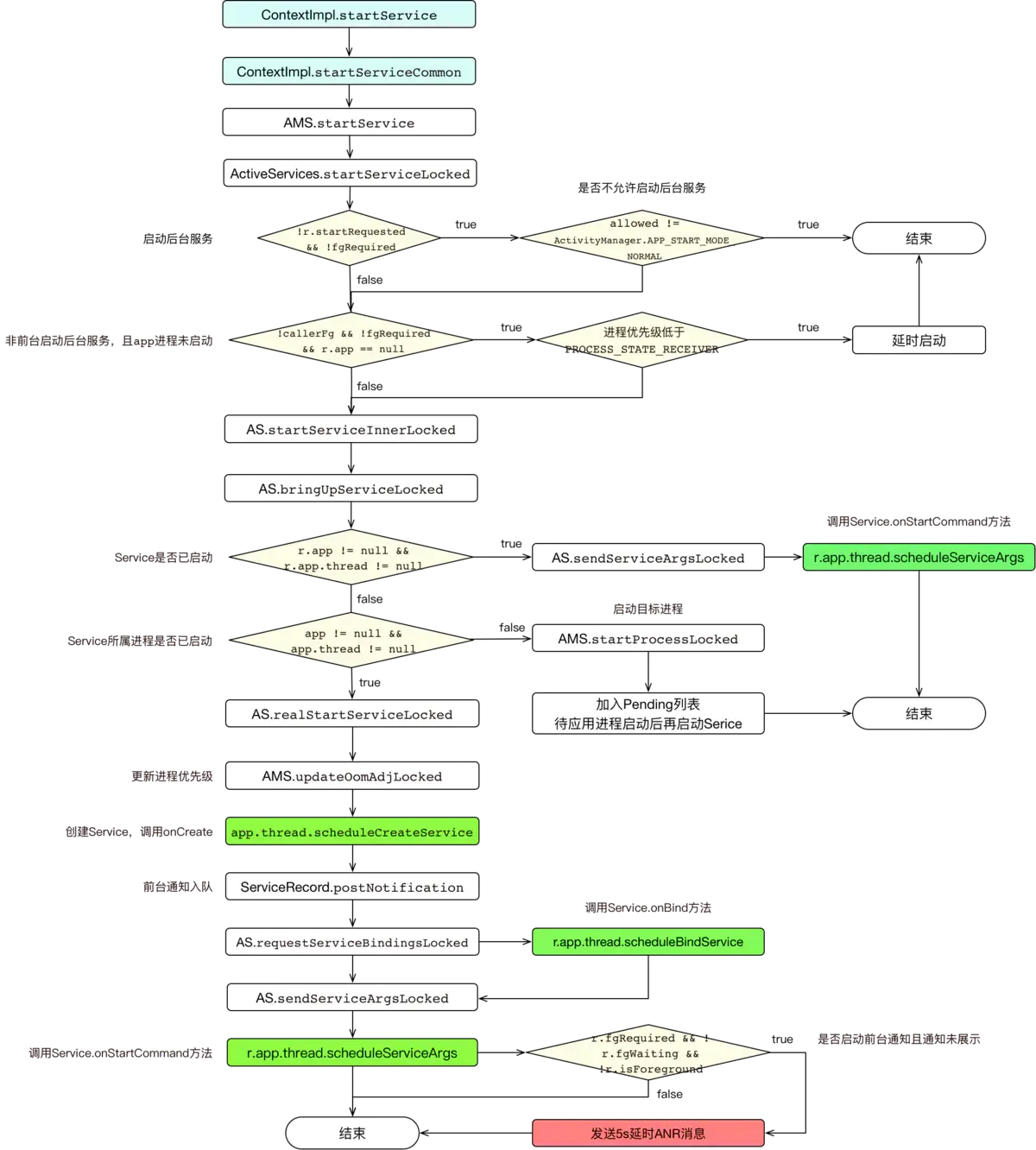
2. Service启动过程
2.1 startService
首先看入口:
ContextImpl.java
@Override
public ComponentName startService(Intent service) {
warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();
return startServiceCommon(service, false, mUser);
}
private ComponentName startServiceCommon(Intent service, boolean requireForeground, UserHandle user) {
validateServiceIntent(service);
service.prepareToLeaveProcess(this);
ComponentName cn = ActivityManager.getService().startService(mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), service, service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(getContentResolver()), requireForeground, getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier());
......
return cn;
}
ContextImpl中只做了validateServiceIntent校验(target 21之后限制隐式启动),然后调用了AMS的startService方法。再看AMS中的实现:
ActivityManagerService.java
@Override
public ComponentName startService(IApplicationThread caller, Intent service, String resolvedType, boolean requireForeground, String callingPackage, int userId)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
......
synchronized(this) {
final int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
final int callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid();
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
ComponentName res;
try {
res = mServices.startServiceLocked(caller, service, resolvedType, callingPid, callingUid, requireForeground, callingPackage, userId);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
return res;
}
}
直接调用了ActiveServices的startServiceLocked方法。
ActiveServices.java
ComponentName startServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller, Intent service, String resolvedType, int callingPid, int callingUid, boolean fgRequired, String callingPackage, final int userId)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
......
// 1. 从mServiceMap中查询SerivceRecord缓存,如果没有则创建一个
ServiceLookupResult res = retrieveServiceLocked(service, resolvedType, callingPackage, callingPid, callingUid, userId, true, callerFg, false);
......
ServiceRecord r = res.record;
......
// If this isn't a direct-to-foreground start, check our ability to kick off an arbitrary service
// fgRequired为false,即不是启动前台服务
if (!r.startRequested && !fgRequired) {
// 2. 检查是否允许启动方应用启动Service
final int allowed = mAm.getAppStartModeLocked(r.appInfo.uid, r.packageName, r.appInfo.targetSdkVersion, callingPid, false, false);
// app mode不为APP_START_MODE_NORMAL表示应用处于后台,而不在后台不受限的白名单中
if (allowed != ActivityManager.APP_START_MODE_NORMAL) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Background start not allowed: service " + service + " to " + r.name.flattenToShortString() + " from pid=" + callingPid + " uid=" + callingUid + " pkg=" + callingPackage);
// 不允许启动后台Service
return new ComponentName("?", "app is in background uid " + uidRec);
}
}
......
r.startRequested = true;
......
final ServiceMap smap = getServiceMapLocked(r.userId);
boolean addToStarting = false;
// 3. 非前台调用,且非启动前台服务,且app进程未启动
if (!callerFg && !fgRequired && r.app == null && mAm.mUserController.hasStartedUserState(r.userId)) {
ProcessRecord proc = mAm.getProcessRecordLocked(r.processName, r.appInfo.uid, false);
if (proc == null || proc.curProcState > ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_RECEIVER) {
// 如果调用方进程不在前台,而且正在启动的后台Service过多,该Service会被延时启动,避免在短时间内启动大量进程。
if (smap.mStartingBackground.size() >= mMaxStartingBackground) {
smap.mDelayedStartList.add(r);
r.delayed = true;
return r.name;
}
addToStarting = true;
}
......
}
......
ComponentName cmp = startServiceInnerLocked(smap, service, r, callerFg, addToStarting);
return cmp;
}
这个方法中做了几个检查操作:
- 从mServiceMap中查询SerivceRecord缓存,如果没有则创建一个;
- 如果不是启动前台服务,会检查启动方是否能启动Service,如果启动方应用不在前台,且未在允许后台启动Service的白名单中,将禁止启动。(白名单的逻辑在后面介绍)
- 如非前台调用,也非启动前台服务,且app进程未启动,且正在启动的后台Service过多,该Service会被延时启动,避免在短时间内启动大量进程。
- 通过了前面的检查,调用startServiceInnerLocked
ComponentName startServiceInnerLocked(ServiceMap smap, Intent service, ServiceRecord r, boolean callerFg, boolean addToStarting) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
......
// 调用bringUpServiceLocked启动Service
String error = bringUpServiceLocked(r, service.getFlags(), callerFg, false, false);
......
return r.name;
}
startServiceInnerLocked调用bringUpSrviceLocked启动Service。
private String bringUpServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, int intentFlags, boolean execInFg, boolean whileRestarting, boolean permissionsReviewRequired)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
// 1.如果此Service已经被启动,直接调用onStartCommand,app和app.thread在create时赋值,所以不为空表示service已经create
if (r.app != null && r.app.thread != null) {
sendServiceArgsLocked(r, execInFg, false);
return null;
}
......
if (!isolated) {
app = mAm.getProcessRecordLocked(procName, r.appInfo.uid, false);
// 2.Service所属进程已经启动
if (app != null && app.thread != null) {
try {
app.addPackage(r.appInfo.packageName, r.appInfo.versionCode, mAm.mProcessStats);
// 进入真正启动Service流程
realStartServiceLocked(r, app, execInFg);
return null;
} catch (TransactionTooLargeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception when starting service " + r.shortName, e);
}
}
}
// 3.如果Service所属进程尚未启动,则先启动进程
if (app == null && !permissionsReviewRequired) {
if ((app=mAm.startProcessLocked(procName, r.appInfo, true, intentFlags, hostingType, r.name, false, isolated, false)) == null) {
bringDownServiceLocked(r);
return msg;
}
}
// 加入Pengding列表
if (!mPendingServices.contains(r)) {
mPendingServices.add(r);
}
......
return null;
}
这个方法做了3件事情:
- 如果此Service已经被启动,直接调用onStartCommand;
- 如果此Service未启动,但所属进程已启动,则调用realStartServiceLocked进入真正启动Service的流程;
- 如果Service所属进程尚未启动,则先启动进程,如app进程启动失败则销毁此Service;如启动成功,则加入Pengding启动列表,待App进程启动结束后再启动Service。
下面看真正启动Service的方法realStartServiceLocked:
private final void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg) throws RemoteException {
.....
final boolean newService = app.services.add(r);
bumpServiceExecutingLocked(r, execInFg, "create");
mAm.updateLruProcessLocked(app, false, null);
updateServiceForegroundLocked(r.app, /* oomAdj= */ false);
// 1.调整应用进程优先级
mAm.updateOomAdjLocked();
boolean created = false;
try {
......
mAm.notifyPackageUse(r.serviceInfo.packageName, PackageManager.NOTIFY_PACKAGE_USE_SERVICE); app.forceProcessStateUpTo(ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_SERVICE);
// 2.通知ActivityThread创建Service,调用onCreate
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo, mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo), app.repProcState);
// 3.如果已经设置通知,创建前台通知
r.postNotification();
created = true;
}
......
// 通知ActivityThread调用Service的onBind方法
requestServiceBindingsLocked(r, execInFg);
updateServiceClientActivitiesLocked(app, null, true);
// 1.如启动前台服务,则发送一个5s的延时消息,如5s内未调用Service.startForeground,应用将ANR
// 2.通知ActivityThread调用Service的onStartCommand方法
sendServiceArgsLocked(r, execInFg, true);
......
}
- 通知AMS调整应用进程优先级
- 跨进程调用,通过Service所属进程的IApplicationThread,即ActivityThread创建Service实例,再调用其onCreate方法;
如果已经设置通知,则创建前台通知; - 如果Service已经被绑定,则调用onBind方法;
- 调用sendServiceArgsLocked
- 这个方法主要做了2个事情:
1)如启动前台服务,则发送一个5s的延时消息,如5s内未调用Service.startForeground,应用将ANR;
2)通知ActivityThread调用Service的onStartCommand方法;