对网络上热修复方案和原理的文章和三方框架进行了二次整理,让读者对热修复方案和原理有个整体的认知。总的来说热修复不是简单的一项技术,更贴切的说是一种解决方案,不仅涉及到APP端的补丁生成和生效技术,还涉及系统兼容性、开发过程代码管理、补丁管理系统等。除非有足够的人力物力支持,否则在生产环境中引入热修复还是推荐使用阿里、腾讯等大厂的现成方案,不推荐自己造轮子。
热修复框架
阿里系
| 框架 | 简介 | 官网 | 相关文章推荐 |
|---|---|---|---|
| HotFix | 阿里百川未开源免费、实时生效 | 官网 | 阿里百川HotFix快速集成 |
|
开源免费,基于native替换,实时生效,有兼容性问题,官方已不再维护
| github | ||
|
开源免费,劫持Java method实现AOP、插桩、热补丁、SDK hook 等功能,不支持art平台,官方已不再维护
| github | 阿里 Dexposed 热修复原理 | |
| Sophix |
阿里云未开源收费,实时生效/冷启动修复,图形界面一键打包、加密传输、签名校验和服务端控制发布与灰度功能,必须继承SophixApplication,但支持保留原Application
| 官网 | 阿里Sophix热修复接入指南 |
| Amigo |
饿了么出品,开源,冷启动修复,补丁管理平台已关闭
| github | - |
腾讯系
| 框架 | 简介 | 官网 | 相关文章推荐 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tinker | 微信部分开源收费,tinker出补丁包,burgly分发管理补丁 | github | wiki |
| QQ空间未开源,冷启动修复 | - | Qzone 超级补丁热修复方案原理 | |
| 手Q开源免费,冷启动修复,项目不再维护 | github | QFix探索之路——手Q热补丁轻量级方案 | |
| Shadow | 开源免费,无反射全动态 | github | wiki |
国内知名公司
| 框架 | 简介 | 官网 | 相关文章推荐 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Robust | 美团开源免费,实时修复 | github | wiki |
| 美丽说蘑菇街开源免费,实时修复,不再维护 | github | wiki | |
| 大众点评开源免费,冷启动修复,不再维护 | github | - |
其他组织或个人
| 框架 | 简介 | 官网 | 相关文章推荐 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 开源免费,不再维护 | github | - | |
| 开源免费,基于InstantRun,不再维护 | github | - |
核心技术
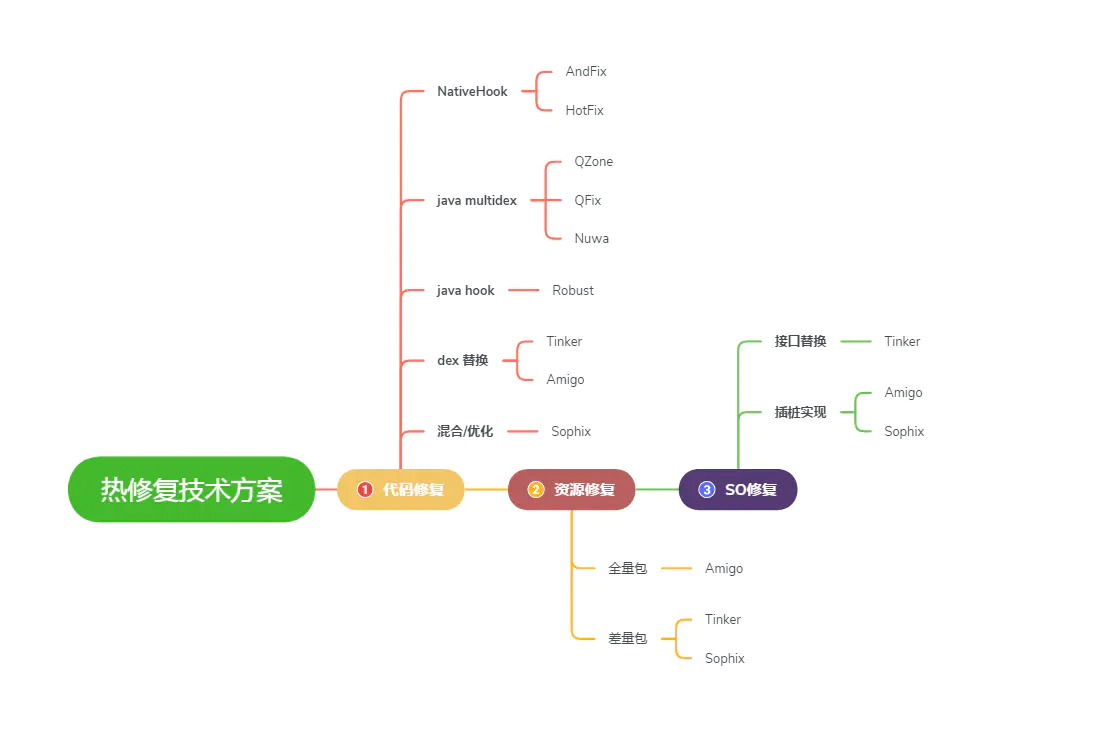
代码修复
multidex方案
由于Android不能直接执行class文件,而是执行的dex文件。所以加载dex就需要一些特殊的类加载器。Android中常见的类加载器有BootClassLoader、BaseDexClassLoader、PathClassLoader、DexClassLoader。
- BootClassLoader是加载Android系统源码,例如Activity,AMS等。
- PathClassLoader和DexClassLoader都是继承于BaseDexClassLoader,两者的区别在于构造方法参数不同。默认情况下,PathClassLoader是用于加载三方库,比如AppCompatActivity等这些代码。DexClassLoader是加载外部的dex文件,其实使用PathClassLoader去加载外部的dex文件也是没问题的。
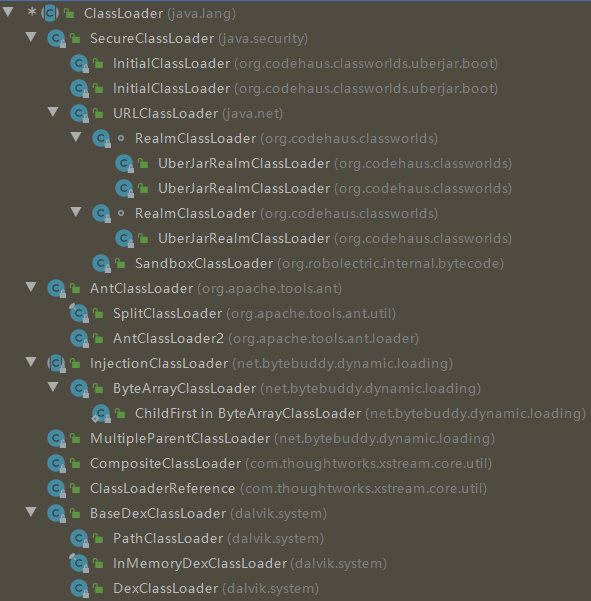
双亲委托机制
类加载过程可以描述为:先检查已加载的类,找不到则优先从父类加载器查找,否则从BootstrapClassLoader查找,还是没有则调用当前类加载器的findClass方法进行加载。
java.lang.ClassLoader#loadClass(java.lang.String, boolean)核心代码:
/**
* Loads the class with the specified <a href="#name">binary name</a>. The
* default implementation of this method searches for classes in the
* following order:
*
* <ol>
*
* <li><p> Invoke {@link #findLoadedClass(String)} to check if the class
* has already been loaded. </p></li>
*
* <li><p> Invoke the {@link #loadClass(String) <tt>loadClass</tt>} method
* on the parent class loader. If the parent is <tt>null</tt> the class
* loader built-in to the virtual machine is used, instead. </p></li>
*
* <li><p> Invoke the {@link #findClass(String)} method to find the
* class. </p></li>
*
* </ol>
*
* <p> If the class was found using the above steps, and the
* <tt>resolve</tt> flag is true, this method will then invoke the {@link
* #resolveClass(Class)} method on the resulting <tt>Class</tt> object.
*
* <p> Subclasses of <tt>ClassLoader</tt> are encouraged to override {@link
* #findClass(String)}, rather than this method. </p>
*
*
* @param name
* The <a href="#name">binary name</a> of the class
*
* @param resolve
* If <tt>true</tt> then resolve the class
*
* @return The resulting <tt>Class</tt> object
*
* @throws ClassNotFoundException
* If the class could not be found
*/
// Android-removed: Remove references to getClassLoadingLock
// Remove perf counters.
//
// <p> Unless overridden, this method synchronizes on the result of
// {@link #getClassLoadingLock <tt>getClassLoadingLock</tt>} method
// during the entire class loading process.
protected Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve)
throws ClassNotFoundException
{
// First, check if the class has already been loaded
Class<?> c = findLoadedClass(name);
if (c == null) {
try {
if (parent != null) {
c = parent.loadClass(name, false);
} else {
c = findBootstrapClassOrNull(name);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// ClassNotFoundException thrown if class not found
// from the non-null parent class loader
}
if (c == null) {
// If still not found, then invoke findClass in order
// to find the class.
c = findClass(name);
}
}
return c;
}
Android类加载机制
ClassLoader#findClass是抽象方法,Android的BaseDexClassLoader实现了此方法:
public class BaseDexClassLoader extends ClassLoader {
private final DexPathList pathList;
@Override
protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
List<Throwable> suppressedExceptions = new ArrayList<Throwable>();
Class c = pathList.findClass(name, suppressedExceptions);
if (c == null) {
ClassNotFoundException cnfe = new ClassNotFoundException(
"Didn't find class \"" + name + "\" on path: " + pathList);
for (Throwable t : suppressedExceptions) {
cnfe.addSuppressed(t);
}
throw cnfe;
}
return c;
}
}
下面的代码均不能在AS中查看,介绍两个可以在线看framework源码的网站:
Class通过DexPathList#findClass(String, List<Throwable>)来查找:
// 加载名字为name的class对象
public Class findClass(String name, List<Throwable> suppressed) {
// 遍历从dexPath查询到的dex和资源Element
for (Element element : dexElements) {
DexFile dex = element.dexFile;
// 如果当前的Element是dex文件元素
if (dex != null) {
// 使用DexFile.loadClassBinaryName加载类
Class clazz = dex.loadClassBinaryName(name, definingContext, suppressed);
if (clazz != null) {
return clazz;
}
}
}
if (dexElementsSuppressedExceptions != null) {
suppressed.addAll(Arrays.asList(dexElementsSuppressedExceptions));
}
return null;
}
/**
* See {@link #loadClass(String, ClassLoader)}.
*
* This takes a "binary" class name to better match ClassLoader semantics.
*
* @hide
*/
public Class loadClassBinaryName(String name, ClassLoader loader, List<Throwable> suppressed) {
return defineClass(name, loader, mCookie, this, suppressed);
}
private static Class defineClass(String name, ClassLoader loader, Object cookie,
DexFile dexFile, List<Throwable> suppressed) {
Class result = null;
try {
result = defineClassNative(name, loader, cookie, dexFile);
} catch (NoClassDefFoundError e) {
if (suppressed != null) {
suppressed.add(e);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
if (suppressed != null) {
suppressed.add(e);
}
}
return result;
}
private static native Class defineClassNative(String name, ClassLoader loader, Object cookie, DexFile dexFile) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoClassDefFoundError;
dex文件转换成dexFile对象,存入Element[]数组,findclass顺序遍历Element数组获取DexFile,然后执行DexFile的loadClassBinaryName。Android这种类加载机制的目的是防止类的重复加载和实现就近加载原则,而这也为我们实现类的动态加载和替换提供了可能。
核心代码
通过上面类加载过程的分析,我们只需要hook ClassLoader.pathList.dexElements[],将补丁的dex插入到数组的首位即可实现Class替换。
以下是Nuwa的关键实现源码:
public static void injectDexAtFirst(String dexPath, String defaultDexOptPath) throws NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException {
//新建一个ClassLoader加载补丁Dex
DexClassLoader dexClassLoader = new DexClassLoader(dexPath, defaultDexOptPath, dexPath, getPathClassLoader());
//反射获取旧DexElements数组
Object baseDexElements = getDexElements(getPathList(getPathClassLoader()));
//反射获取补丁DexElements数组
Object newDexElements = getDexElements(getPathList(dexClassLoader));
//合并,将新数组的Element插入到最前面
Object allDexElements = combineArray(newDexElements, baseDexElements);
Object pathList = getPathList(getPathClassLoader());
//更新旧ClassLoader中的Element数组
ReflectionUtils.setField(pathList, pathList.getClass(), "dexElements", allDexElements);
}
private static PathClassLoader getPathClassLoader() {
PathClassLoader pathClassLoader = (PathClassLoader) DexUtils.class.getClassLoader();
return pathClassLoader;
}
private static Object getDexElements(Object paramObject)
throws IllegalArgumentException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
return ReflectionUtils.getField(paramObject, paramObject.getClass(), "dexElements");
}
private static Object getPathList(Object baseDexClassLoader)
throws IllegalArgumentException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException {
return ReflectionUtils.getField(baseDexClassLoader, Class.forName("dalvik.system.BaseDexClassLoader"), "pathList");
}
private static Object combineArray(Object firstArray, Object secondArray) {
Class<?> localClass = firstArray.getClass().getComponentType();
int firstArrayLength = Array.getLength(firstArray);
int allLength = firstArrayLength + Array.getLength(secondArray);
Object result = Array.newInstance(localClass, allLength);
for (int k = 0; k < allLength; ++k) {
if (k < firstArrayLength) {
Array.set(result, k, Array.get(firstArray, k));
} else {
Array.set(result, k, Array.get(secondArray, k - firstArrayLength));
}
}
return result;
}
patch.dex生成
1. 补丁class生成全量patch.dex
通过技术手段筛选出需要替换的类生成的class文件,将这些class文件生成一个单独patch.dex。
这种方式比较直观,但是容易遭遇CLASS_ISPREVERIFIED标志问题:例如MainAcivity和Utils类存在于同一个dex中,这个时候MainActivity会被打上CLASS_ISPREVERIFIED标志,大概意思就是当MainActivity使用Utils类的时候,会直接从该dex中加载,而不会从其他dex中加载,补丁失效。
《安卓App热补丁动态修复技术介绍》给出了一种解决方案,采取对抗策略:为了避免类被加上CLASS_ISPREVERIFIED,使用插桩,单独放一个帮助类在独立的dex中让其他类调用。
2. 差量patch.dex合并替换主dex
为了避免dex插桩带来的性能损耗,dex替换采取另外的方式:使用diff工具生成patch.dex差量包,在运行时使用patch工具将patch.dex与应用的classes.dex合并成一个完整的dex,插入到ClassLoader.pathList.dexElements[]头部。
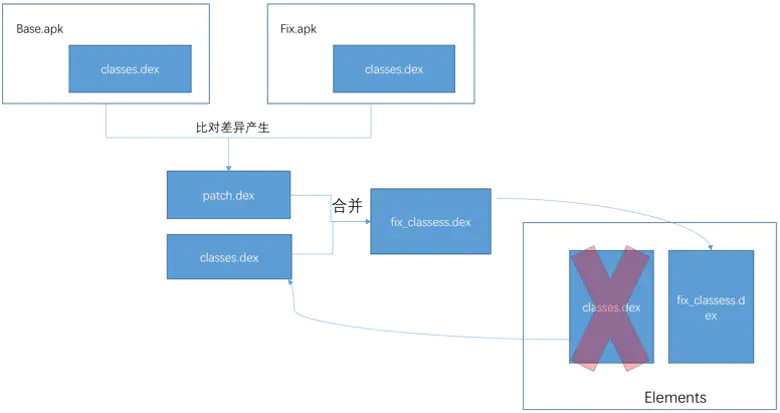
这也是微信Tinker采用的方案,并且Tinker自研了DexDiff/DexMerge算法。这个方案具有补丁小,兼容性好的优点,但是无法做到实时生效,需要在下次启动才能生效,并且Dex合并内存消耗大,容易OOM导致合并失败,应该要另起一个进程做这个事情。
特点总结
| 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|
|
|
Java Hook方案
在打基础包时插桩,在每个方法前插入一段补丁发现和应用代码,实现有补丁时补丁生效,没补丁时执行原来的代码。
核心代码
以美团的Robust为例,打基础包时插桩,在每个方法前插入一段类型为 ChangeQuickRedirect 静态变量的逻辑:
public static ChangeQuickRedirect u;
protected void onCreate(Bundle bundle) {
//为每个方法自动插入修复逻辑代码,如果ChangeQuickRedirect为空则不执行
if (u != null) {
if (PatchProxy.isSupport(new Object[]{bundle}, this, u, false, 78)) {
PatchProxy.accessDispatchVoid(new Object[]{bundle}, this, u, false, 78);
return;
}
}
super.onCreate(bundle);
...
}
然后是补丁发现和加载的方法:
public class PatchExecutor extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
...
applyPatchList(patches);
...
}
/**
* 应用补丁列表
*/
protected void applyPatchList(List<Patch> patches) {
...
for (Patch p : patches) {
...
currentPatchResult = patch(context, p);
...
}
}
/**
* 核心修复源码
*/
protected boolean patch(Context context, Patch patch) {
...
//新建ClassLoader
DexClassLoader loader
= new DexClassLoader(patch.getTempPath(), context.getCacheDir().getAbsolutePath(),
null, PatchExecutor.class.getClassLoader());
patch.delete(patch.getTempPath());
...
try {
patchsInfoClass = classLoader.loadClass(patch.getPatchesInfoImplClassFullName());
patchesInfo = (PatchesInfo) patchsInfoClass.newInstance();
} catch (Throwable t) {
...
}
...
//通过遍历其中的类信息进而反射修改其中 ChangeQuickRedirect 对象的值
for (PatchedClassInfo patchedClassInfo : patchedClasses) {
...
try {
oldClass = classLoader.loadClass(patchedClassName.trim());
Field[] fields = oldClass.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
if (TextUtils.equals(field.getType().getCanonicalName(), ChangeQuickRedirect.class.getCanonicalName()) && TextUtils.equals(field.getDeclaringClass().getCanonicalName(), oldClass.getCanonicalName())) {
changeQuickRedirectField = field;
break;
}
}
...
try {
patchClass = classLoader.loadClass(patchClassName);
Object patchObject = patchClass.newInstance();
changeQuickRedirectField.setAccessible(true);
changeQuickRedirectField.set(null, patchObject);
} catch (Throwable t) {
...
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
...
}
}
return true;
}
}
特点总结
| 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|
|
|
InstantRun方案
native替换方案
每一个Java方法在art中都对应一个ArtMethod,ArtMethod记录了这个Java方法的所有信息,包括访问权限及代码执行地址等。通过env->FromReflectedMethod得到方法对应的ArtMethod的真正开始地址,然后强转为ArtMethod指针,从而对其所有成员进行修改。这样以后调用这个方法时就会直接走到新方法的实现中,达到热修复的效果。
核心代码
示例:AndFix安卓6.0 ArtMethod替换代码片段
void replace_6_0(JNIEnv* env, jobject src, jobject dest) {
// 通过Method对象得到底层Java函数对应ArtMethod的真实地址
art::mirror::ArtMethod* smeth =
(art::mirror::ArtMethod*) env->FromReflectedMethod(src);
art::mirror::ArtMethod* dmeth =
(art::mirror::ArtMethod*) env->FromReflectedMethod(dest);
reinterpret_cast<art::mirror::Class*>(dmeth->declaring_class_)->class_loader_ =
reinterpret_cast<art::mirror::Class*>(smeth->declaring_class_)->class_loader_; //for plugin classloader
reinterpret_cast<art::mirror::Class*>(dmeth->declaring_class_)->clinit_thread_id_ =
reinterpret_cast<art::mirror::Class*>(smeth->declaring_class_)->clinit_thread_id_;
reinterpret_cast<art::mirror::Class*>(dmeth->declaring_class_)->status_ = reinterpret_cast<art::mirror::Class*>(smeth->declaring_class_)->status_-1;
//for reflection invoke
reinterpret_cast<art::mirror::Class*>(dmeth->declaring_class_)->super_class_ = 0;
//把旧函数的所有成员变量都替换为新函数的
smeth->declaring_class_ = dmeth->declaring_class_;
smeth->dex_cache_resolved_methods_ = dmeth->dex_cache_resolved_methods_;
smeth->dex_cache_resolved_types_ = dmeth->dex_cache_resolved_types_;
smeth->access_flags_ = dmeth->access_flags_ | 0x0001;
smeth->dex_code_item_offset_ = dmeth->dex_code_item_offset_;
smeth->dex_method_index_ = dmeth->dex_method_index_;
smeth->method_index_ = dmeth->method_index_;
smeth->ptr_sized_fields_.entry_point_from_interpreter_ =
dmeth->ptr_sized_fields_.entry_point_from_interpreter_;
smeth->ptr_sized_fields_.entry_point_from_jni_ =
dmeth->ptr_sized_fields_.entry_point_from_jni_;
smeth->ptr_sized_fields_.entry_point_from_quick_compiled_code_ =
dmeth->ptr_sized_fields_.entry_point_from_quick_compiled_code_;
LOGD("replace_6_0: %d , %d",
smeth->ptr_sized_fields_.entry_point_from_quick_compiled_code_,
dmeth->ptr_sized_fields_.entry_point_from_quick_compiled_code_);
}
void setFieldFlag_6_0(JNIEnv* env, jobject field) {
art::mirror::ArtField* artField =
(art::mirror::ArtField*) env->FromReflectedField(field);
artField->access_flags_ = artField->access_flags_ & (~0x0002) | 0x0001;
LOGD("setFieldFlag_6_0: %d ", artField->access_flags_);
}
特点总结
| 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|
|
|
资源替换
原理概述:
- 构建一个新的AssetManager,并通过反射调用addAssertPath,把这个完整的新资源包加入到AssetManager中,这样就得到一个含有所有新资源的AssetManager;
- 找到所有值钱引用到原有AssetManager的地方,通过反射,把引用处替换为AssetManager;
核心代码
public static void monkeyPatchExistingResources(Context context, String externalResourceFile, Collection activities) {
if (externalResourceFile == null) {
return;
}
try {
//反射一个新的 AssetManager
AssetManager newAssetManager = (AssetManager) AssetManager.class
.getConstructor(new Class[0]).newInstance(new Object[0]);
//反射 addAssetPath 添加新的资源包
Method mAddAssetPath = AssetManager.class.getDeclaredMethod("addAssetPath", new Class[]{String.class});
mAddAssetPath.setAccessible(true);
if (((Integer) mAddAssetPath.invoke(newAssetManager,
new Object[]{externalResourceFile})).intValue() == 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Could not create new AssetManager");
}
Method mEnsureStringBlocks = AssetManager.class.getDeclaredMethod("ensureStringBlocks", new Class[0]);
mEnsureStringBlocks.setAccessible(true);
mEnsureStringBlocks.invoke(newAssetManager, new Object[0]);
//反射得到Activity中AssetManager的引用处,全部换成刚新构建的AssetManager对象
if (activities != null) {
for (Activity activity : activities) {
Resources resources = activity.getResources();
try {
Field mAssets = Resources.class.getDeclaredField("mAssets");
mAssets.setAccessible(true);
mAssets.set(resources, newAssetManager);
} catch (Throwable ignore) {
Field mResourcesImpl = Resources.class.getDeclaredField("mResourcesImpl");
mResourcesImpl.setAccessible(true);
Object resourceImpl = mResourcesImpl.get(resources);
Field implAssets = resourceImpl.getClass().getDeclaredField("mAssets");
implAssets.setAccessible(true);
implAssets.set(resourceImpl, newAssetManager);
}
Resources.Theme theme = activity.getTheme();
try {
try {
Field ma = Resources.Theme.class.getDeclaredField("mAssets");
ma.setAccessible(true);
ma.set(theme, newAssetManager);
} catch (NoSuchFieldException ignore) {
Field themeField = Resources.Theme.class.getDeclaredField("mThemeImpl");
themeField.setAccessible(true);
Object impl = themeField.get(theme);
Field ma = impl.getClass().getDeclaredField("mAssets");
ma.setAccessible(true);
ma.set(impl, newAssetManager);
}
Field mt = ContextThemeWrapper.class.getDeclaredField("mTheme");
mt.setAccessible(true);
mt.set(activity, null);
Method mtm = ContextThemeWrapper.class.getDeclaredMethod("initializeTheme", new Class[0]);
mtm.setAccessible(true);
mtm.invoke(activity, new Object[0]);
Method mCreateTheme = AssetManager.class.getDeclaredMethod("createTheme", new Class[0]);
mCreateTheme.setAccessible(true);
Object internalTheme = mCreateTheme.invoke(newAssetManager, new Object[0]);
Field mTheme = Resources.Theme.class.getDeclaredField("mTheme");
mTheme.setAccessible(true);
mTheme.set(theme, internalTheme);
} catch (Throwable e) {
Log.e("InstantRun",
"Failed to update existing theme for activity "
+ activity, e);
}
pruneResourceCaches(resources);
}
}
Collection references;
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 19) {
Class resourcesManagerClass = Class.forName("android.app.ResourcesManager");
Method mGetInstance = resourcesManagerClass.getDeclaredMethod("getInstance", new Class[0]);
mGetInstance.setAccessible(true);
Object resourcesManager = mGetInstance.invoke(null, new Object[0]);
try {
Field fMActiveResources = resourcesManagerClass.getDeclaredField("mActiveResources");
fMActiveResources.setAccessible(true);
ArrayMap arrayMap = (ArrayMap) fMActiveResources.get(resourcesManager);
references = arrayMap.values();
} catch (NoSuchFieldException ignore) {
Field mResourceReferences = resourcesManagerClass.getDeclaredField("mResourceReferences");
mResourceReferences.setAccessible(true);
references = (Collection) mResourceReferences.get(resourcesManager);
}
} else {
Class activityThread = Class.forName("android.app.ActivityThread");
Field fMActiveResources = activityThread.getDeclaredField("mActiveResources");
fMActiveResources.setAccessible(true);
Object thread = getActivityThread(context, activityThread);
HashMap map = (HashMap) fMActiveResources.get(thread);
references = map.values();
}
for (WeakReference wr : references) {
Resources resources = (Resources) wr.get();
if (resources != null) {
try {
Field mAssets = Resources.class.getDeclaredField("mAssets");
mAssets.setAccessible(true);
mAssets.set(resources, newAssetManager);
} catch (Throwable ignore) {
Field mResourcesImpl = Resources.class.getDeclaredField("mResourcesImpl");
mResourcesImpl.setAccessible(true);
Object resourceImpl = mResourcesImpl.get(resources);
Field implAssets = resourceImpl.getClass().getDeclaredField("mAssets");
implAssets.setAccessible(true);
implAssets.set(resourceImpl, newAssetManager);
}
resources.updateConfiguration(resources.getConfiguration(), resources.getDisplayMetrics());
}
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new IllegalStateException(e);
}
}
动态链接库修复
so加载入口替换
APP中所有加载so文件的地方统一调用sdk提供的方法:
SOPatchManger.loadLibrary(String libName)
替换
System.loadLibrary(String libName)
SOPatchManger.loadLibrary接口加载so库的时候优先尝试去加载sdk指定目录下补丁的so。若不存在,则再去加载安装apk目录下的so库。
特点总结
| 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|
|
|
反射注入
采取类似类修复反射注入方式,把补丁so库的路径插入到nativeLibraryDirectories数组的最前面,就能够达到加载so库的时候是补丁so库而不是原来so库的目录,从而达到修复。
public String findLibrary(String libraryName) {
String fileName = System.mapLibraryName(libraryName);
for (NativeLibraryElement element : nativeLibraryPathElements) {
String path = element.findNativeLibrary(fileName);
if (path != null) {
return path;
}
}
return null;
}
特点总结
| 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|
|
|