安卓开发过程中的五种存储方式
安卓存储的概念
 安卓存储分为内部存储和外部存储
安卓存储分为内部存储和外部存储
- 内部存储
这种方式用来存储一些复杂的数据结构。因为是内部存储方式,所以其他程序无法访问。这样可以保证数据的安全性。当你的程序卸载以后,这些内部存储数据也会被清除掉。
这类数据一般包括像一些对象,或者本地需要一些类似文件系统访问模式的数据。

- 外部存储
这种存储方式用来存储一些文件对象。这些文件可以被其他程序来访问。要使用外部存储,需要申请特别的写权限WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE。如果其他程序需要访问这些外部存储数据的话,也需要申请读权限READ_EXTERNAL_STORAGE。
从安卓4.4开始,用户可以把自己的数据写入一个私有的外部存储文件夹中,如果这样的话,用户就不需要申请写权限WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE。当用户卸载程序的时候,这个文件夹也会被清除。
从安卓7.0开始,
安卓程序可以申请访问特定的文件目录,而不是申请访问整个外部存储空间。这样可以保证数据的安全性,防止误操作。用户只可以访问图片目录,或者文档目录。
SharedPreferences轻量数据存储
在安卓开发过程中,通常用它来存储一些简单设置上的信息,使用的数据结构类型为Map数据结构,以key-value的形式存储,键必须是字符串类型的,值可以是布尔型的,浮点型的,整型的,长整型的,或者字符串类型的采用了XML格式将数据存储到设备中。例如:是否是第一次打开,是否允许推送,登录用户名和密码等等,通常不会用它存储很长或者很复杂的数据。
存储数据的xml文件的存储路径为(data文件夹应该需要真机root之后才能看见)
在实际开发中我们可以使用SharedPreferences类对数据进行存储,SharedPreferences.Editor类进行数据的读取。
下方为一个小例子:(因为几种存储方式是在同一个项目里演示的所以代码可能会不全,以及中间有一些讲解注释)
public class SharedPreferences extends AppCompatActivity {
private EditText et1;
private Button bt1,bt2;
private TextView tv1;
private android.content.SharedPreferences sp;
private android.content.SharedPreferences.Editor spEditor;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_shared_preferences);
et1 = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.et_name);
bt1 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_save);
bt2 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_show);
tv1 = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv_show);
sp = getSharedPreferences("data",MODE_PRIVATE);//这个方法的返回值就是SharedPreferences类对象
//MODE_PRIVATE即只有本应用可以进行读写
//MODE_WORLD_READABLE 其他应用是否可以读
//MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE 其他应用是否可以写
//MODE_APPEND 在文件末尾追加而不是覆盖文件
//MODE_WORLD_READABLE ,MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE存在安全性问题,可以用,但官方已经将其废弃,可以用contentProvider
spEditor = sp.edit();
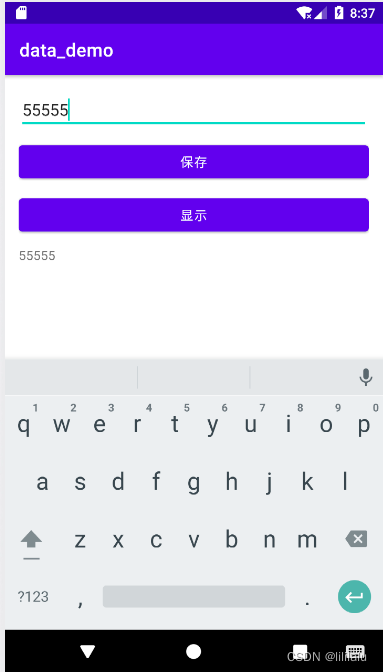
bt1.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
spEditor.putString("name",et1.getText().toString());
spEditor.apply();
//commit方法是一个同步存储的过程,需等待同步完成后才继续其他工作
//apply方法是一个异步过程,内存上是即时生效的,推荐使用
}
});
bt2.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
tv1.setText(sp.getString("name",""));
}
});
}
}
然后这里是xml文件的代码
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:padding="15dp">
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_name"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="input name"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_save"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:text="保存"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_show"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:text="显示"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_show"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"/>
</LinearLayout>
file存储数据
该储存方式是比较常用的方法,分为内部存储和外部存储。在Android中读取/写入文件的方法,与java中实现I/O程序是一样的,通过I/O流的形式把数据直接存储到文档中。可以存储大数据,如文本、图片、音频等。
- 内部存储
内部存储是指将应用程序中的数据以文件方式存储到设备的内部(该文件默认位于data/data//files/目录下,该路径挂载再手机自身储存目录),内部存储方式储存的文件被其所创建的应用程序所私有,如果其他应用程序要操作本应用程序中的文件,需要设置权限。当创建的应用程序被卸载时,其内部存储文件也随之删除。
Android提供了FileOutputStream和FileInputStream两个类对内部存储进行操作。因为我用的一套交互模板所以演示效果都是一样的就不多次贴图了。
bt1.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
save(et1.getText().toString());
}
});
bt2.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
tv1.setText(read());
}
});
}
//save方法用于存储信息
private void save(String content){
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
fileOutputStream = openFileOutput("test.txt",MODE_PRIVATE);
fileOutputStream.write(content.getBytes());
//fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(fileOutputStream != null){
try {
fileOutputStream.close();//如果fileOutputStream为空的话会抛出空指针异常因此需要判断一下
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
//read方法用来读取数据
private String read(){
try {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = openFileInput("test.txt");
byte[] buff = new byte[1024];
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("");
int len = 8;
while((len = fileInputStream.read(buff)) > 0){
sb.append(new String(buff,0,len));
}
return sb.toString();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
- 外部存储
外部存储是指将文件储存到一些外部设备上,例如SD卡或者设备内嵌的存储卡,属于永久性的储存方式(该文件通常位于mnt/scard目录下)。Android的API6.0之后,根目录文件储存是需要用户授权的,即使再AndroidManifest.xml中配合了储存权限,也是需要用户动态授权的,如果用户不授权也无法使用。
外部存储和内部存储的操作原理基本一致,只是存储路径不同,此处演示在公共文件夹新建文件夹,并加入文件。
记得需要加上这个语句
 以及如果sdk版本在23以上需要考虑安卓6.0的权限的问题,需要动态申请权限
以及如果sdk版本在23以上需要考虑安卓6.0的权限的问题,需要动态申请权限
ActivityCompat.requestPermissions(this,new String[](Manifest.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE),1);
private void save(String content){
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
//fileOutputStream = openFileOutput("test.txt",MODE_PRIVATE);
File dir = new File(Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory(),"lbr")
if (!dir.exists()){
dir.mkdir();
}
File file = new File(dir,"hhhh");
if(!file.exists()){
file.createNewFile();
}
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
fileOutputStream.write(content.getBytes());
//fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(fileOutputStream != null){
try {
fileOutputStream.close();//如果fileOutputStream为空的话会抛出空指针异常因此需要判断一下
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
//read方法用来读取数据
private String read(){
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
try {
//FileInputStream fileInputStream = openFileInput("test.txt");
File file = new File(Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory().getAbsolutePath()+File.separator+"lbr","lbr");
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
byte[] buff = new byte[1024];
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("");
int len = 8;
while((len = fileInputStream.read(buff)) > 0){
sb.append(new String(buff,0,len));
}
return sb.toString();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
SQLite数据库存储数据
SQLite是一款轻量级的数据库,提供了操控数据库的封装类,CRUD(添加(Create)、查询(Retrieve)、更新(Update)、删除(Delete))
- 创建一个数据库
需要新建一个数据库操作类例如DatabaseHelper去继承SQLiteOpenHelper
public class DatabaseHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
/**
*
* @ context 上下文
* @ name 数据库名
* @ factory 游标工厂(类似指针的概念,一个可以游动的指针)
* @ version 版本号
*/
public DatabaseHelper(Context context) {
super(context, Constants.DATABASE_NAME, null,Constants.VERSION_CODE);
}
@Override
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase sqLiteDatabase) {
Log.d(TAG,"创建数据库...");
String sql = "create table "+Constants.TABLE_NAME+"(_id,name varhar,age integer,salary integer)";
}
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase sqLiteDatabase, int i, int i1) {
Log.d(TAG,"升级数据库...");
}
}
然后使用这两个语句就可以创建一个新的数据库,数据库里有一个名字叫employee的表(定义了一个常量TABLE_NAME = “employee”)其中_id为主键
DatabaseHelper helper = new DatabaseHelper(this);
helper.getWritableDatabase();
关于onUpgrade()方法,它可以更改数据库的列,每次更改后需要将版本号+1才会运行,比如现在表已经建好了,但是我想再往表里追加一列phone,那么我就需要在该方法里操作并将版本号+1。数据库只能升级不能降级
- 数据库的增删改查
- 可以用sql语句执行,如下
public void insert(){
SQLiteDatabase db = helper.getWritableDatabase();
String sql = "insert into " + Constants.TABLE_NAME + "(_id,name,age,salary) values(?,?,?,?)";
db.execSQL(sql,new Object[]{1,"LBR",53,100});
db.close();
}
public void delete(){
SQLiteDatabase db = helper.getWritableDatabase();
String sql = "delete from " + Constants.TABLE_NAME + " where id = 1";
db.execSQL(sql);
db.close();
}
public void update(){
SQLiteDatabase db = helper.getWritableDatabase();
String sql = "update " + Constants.TABLE_NAME + " set salary = 200 where id = 1";
db.execSQL(sql);
db.close();
}
public void query(){
SQLiteDatabase db = helper.getWritableDatabase();
String sql = "select * from " + Constants.TABLE_NAME;
Cursor cursor = db.rawQuery(sql,null);
while (cursor.moveToNext()){
int index = cursor.getColumnIndex("name");
String name = cursor.getString(index);
Log(TAG,"name == "+name);
}
db.close();
}
也可以用AndroidStudio提供的api接口写,如下:
public void insert(){
SQLiteDatabase db = helper.getWritableDatabase();
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put("_id",2);
values.put("name","lll");
values.put("age",15);
values.put("salary",50);
db.insert(Constants.TABLE_NAME,null,values);
db.close();
}
public void delete(){
SQLiteDatabase db = helper.getWritableDatabase();
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
db.delete(Constants.TABLE_NAME,null,null);
db.close();
}
public void update(){
SQLiteDatabase db = helper.getWritableDatabase();
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put("salary",600);
db.update(Constants.TABLE_NAME,values,null,null);
db.close();
}
public void query(){
SQLiteDatabase db = helper.getWritableDatabase();
Cursor cursor = db.query(Constants.TABLE_NAME,null,null,null,null,null,null);
while(cursor.moveToNext()){
int id = cursor.getInt(0);
String name = cursor.getString(1);
Log.d(TAG,"id =="+id+"name == "+name);
}
db.close();
}
其他
除了以上的存储方式外,还有使用ContentProvider存储数据和网络存储数据两种方法。
作者:刘冰茹
引用:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_35507234/article/details/88367564
