Room的使用
Room 在 SQLite 上提供了一个抽象层,以便在充分利用 SQLite 的强大功能的同时,获享更强健的数据库访问机制。
如何配置
...
apply plugin: 'kotlin-kapt'
...
?
dependencies {
? ...
? ?kapt "androidx.room:room-compiler:$rootProject.roomVersion"
? ?implementation "androidx.room:room-runtime:$rootProject.roomVersion"
? ?implementation "androidx.room:room-ktx:$rootProject.roomVersion" ?//目前最新版本是2.3.0
? ?// 一些支持RxJava的配置可参考
? ?//implementation "androidx.room:room-rxjava2:$rootProject.roomVersion"
?
? ?// optional - RxJava3 support for Room
? ?//implementation "androidx.room:room-rxjava3:$rootProject.roomVersion"
?
? ...
}
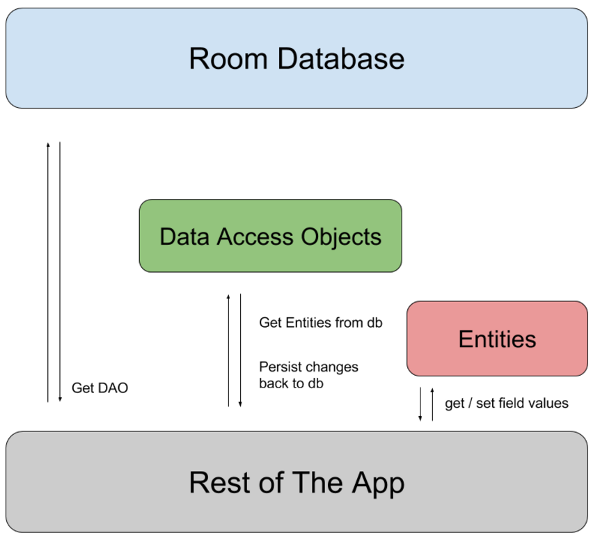
Room 包含 3 个主要组件:
-
数据库:包含数据库持有者,并作为应用已保留的持久关系型数据的底层连接的主要接入点。
使用
@Database注释的类应满足以下条件:- 是扩展
RoomDatabase的抽象类。 - 在注释中添加与数据库关联的实体列表。
- 包含具有 0 个参数且返回使用
@Dao注释的类的抽象方法。
在运行时,您可以通过调用
Room.databaseBuilder()或Room.inMemoryDatabaseBuilder()获取Database的实例。 - 是扩展
-
Entity:表示数据库中的表。
-
DAO:包含用于访问数据库的方法。
应用使用 Room 数据库来获取与该数据库关联的数据访问对象 (DAO)。然后,应用使用每个 DAO 从数据库中获取实体,然后再将对这些实体的所有更改保存回数据库中。 最后,应用使用实体来获取和设置与数据库中的表列相对应的值。
Room 不同组件之间的关系如图 1 所示:
下面以sunflower中的例子作为讲解:
数据库
/**
* The Room database for this app
* 一般来讲 RoomDatabase这个类都是一个单例类,因为实例化一个RoomDatabase的成本是很高的。除非是多进程的情况,不然我们一般讲RoomDatabase设置成单例。
* 在注解中添加与数据库关联的实体列表GardenPlanting和Plant
*/
@Database(entities = [GardenPlanting::class, Plant::class], version = 1, exportSchema = false)
@TypeConverters(Converters::class)
abstract class AppDatabase : RoomDatabase() {
abstract fun gardenPlantingDao(): GardenPlantingDao //这是一个Dao类,用于查询数据库中的表
abstract fun plantDao(): PlantDao //这是一个Dao类,用于查询数据库中的表
?
companion object {
?
// For Singleton instantiation
@Volatile private var instance: AppDatabase? = null
?
// 创建一个单例
fun getInstance(context: Context): AppDatabase {
return instance ?: synchronized(this) {
instance ?: buildDatabase(context).also { instance = it }
}
}
?
// Create and pre-populate the database. See this article for more details:
// https://medium.com/google-developers/7-pro-tips-for-room-fbadea4bfbd1#4785
private fun buildDatabase(context: Context): AppDatabase {
return Room.databaseBuilder(context, AppDatabase::class.java, DATABASE_NAME).build()
}
}
}
实例类
?
@Entity(
tableName = "garden_plantings",//这里是一个数据库的表名(注意:不区分大小写,所以建议用小写)
foreignKeys = [
ForeignKey(entity = Plant::class, parentColumns = ["id"], childColumns = ["plant_id"])
],//外键
indices = [Index("plant_id")] //用来指定索引列表
)
data class GardenPlanting(
// 这个列名在数据库中存储的时候为plant_id,我们使用的时候通过plantId来访问,列名也是不区分大小写的
@ColumnInfo(name = "plant_id") val plantId: String,
//val plantId: String,这个列名在数据库中存储的时候为plantid
?
/**
* Indicates when the [Plant] was planted. Used for showing notification when it's time
* to harvest the plant.
*/
@ColumnInfo(name = "plant_date") val plantDate: Calendar = Calendar.getInstance(),
?
/**
* Indicates when the [Plant] was last watered. Used for showing notification when it's
* time to water the plant.
*/
@ColumnInfo(name = "last_watering_date")
val lastWateringDate: Calendar = Calendar.getInstance()
) {
@PrimaryKey(autoGenerate = true)
@ColumnInfo(name = "id")
var gardenPlantingId: Long = 0
}
?
// 这是第二个实体类
@Entity(tableName = "plants")
data class Plant(
@PrimaryKey @ColumnInfo(name = "id") val plantId: String,
val name: String,
val description: String,
val growZoneNumber: Int,
val wateringInterval: Int = 7, // how often the plant should be watered, in days
val imageUrl: String = ""
) {
?
/**
* Determines if the plant should be watered. Returns true if [since]'s date > date of last
* watering + watering Interval; false otherwise.
*/
fun shouldBeWatered(since: Calendar, lastWateringDate: Calendar) =
since > lastWateringDate.apply { add(DAY_OF_YEAR, wateringInterval) }
?
override fun toString() = name
}
?
?
DAO类
@Dao
interface GardenPlantingDao {
@Query("SELECT * FROM garden_plantings")
fun getGardenPlantings(): Flow<List<GardenPlanting>>
?
// SQL语句引用传递的参数直接使用 :符号进行引用。
@Query("SELECT EXISTS(SELECT 1 FROM garden_plantings WHERE plant_id = :plantId LIMIT 1)")
fun isPlanted(plantId: String): Flow<Boolean>
?
/**
* This query will tell Room to query both the [Plant] and [GardenPlanting] tables and handle
* the object mapping.
*/
@Transaction
@Query("SELECT * FROM plants WHERE id IN (SELECT DISTINCT(plant_id) FROM garden_plantings)")
fun getPlantedGardens(): Flow<List<PlantAndGardenPlantings>>
?
//如果我们需要向表中插入一条数据,我们直接定义一个方法并用 @Insert注解标注就可以:
@Insert(onConflict = OnConflictStrategy.REPLACE)
suspend fun insertGardenPlanting(gardenPlanting: GardenPlanting): Long
?
//如果需要删除表的数据则使用 @Delete注解:使用主键来查找要删除的实体。
@Delete
suspend fun deleteGardenPlanting(gardenPlanting: GardenPlanting)
//还有update注解,这里就不一一列举了
}
?
/**
* The Data Access Object for the Plant class.
*/
@Dao
interface PlantDao {
@Query("SELECT * FROM plants ORDER BY name")
fun getPlants(): Flow<List<Plant>>
?
@Query("SELECT * FROM plants WHERE growZoneNumber = :growZoneNumber ORDER BY name")
fun getPlantsWithGrowZoneNumber(growZoneNumber: Int): Flow<List<Plant>>
?
@Query("SELECT * FROM plants WHERE id = :plantId")
fun getPlant(plantId: String): Flow<Plant>
?
@Insert(onConflict = OnConflictStrategy.REPLACE)
suspend fun insertAll(plants: List<Plant>)
}
以上就是整一个数据库的设计了。那么怎么使用呢?下面还是通过sunflow里面的例子来讲解一下。
??首先看一张MVVM的架构图,从架构图中可以看出,和Room直接交互的一层的Repository层。因为room是给应用提供数据的。而Repository层的功能,正是给应用提供数据。
@Singleton
class PlantRepository @Inject constructor(private val plantDao: PlantDao) {
?
fun getPlants() = plantDao.getPlants() //这里的getPlants()的返回值是Flow<List<Plant>>,也就是PlantDao里面getPlants的返回值
?
fun getPlant(plantId: String) = plantDao.getPlant(plantId)
?
fun getPlantsWithGrowZoneNumber(growZoneNumber: Int) =
plantDao.getPlantsWithGrowZoneNumber(growZoneNumber)
}
?
??首先这一段代码对于没有接触过Hilt依赖注入库的同学看起来有一点难理解。但是无关紧要,这里只需要知道,在这个PlantRepository中,通过plantDao去数据库中查找相关的数据,并且返回。 至于plantDao是怎么实例化来的,@Singleton是什么意思 @Inject是什么意思,通通不需要管。现在仓库层有了,那么接下来就是viewmodel去仓库拿东西了。所以接下来看一下viewmodel层是怎么实现的
/**
* The ViewModel for [PlantListFragment].
*/
@HiltViewModel
class PlantListViewModel @Inject internal constructor(
plantRepository: PlantRepository,
private val savedStateHandle: SavedStateHandle
) : ViewModel() {
...
private val growZone: MutableStateFlow<Int> = MutableStateFlow(
savedStateHandle.get(GROW_ZONE_SAVED_STATE_KEY) ?: NO_GROW_ZONE
)
?
val plants: LiveData<List<Plant>> = growZone.flatMapLatest { zone ->
if (zone == NO_GROW_ZONE) {
plantRepository.getPlants()
} else {
plantRepository.getPlantsWithGrowZoneNumber(zone)
}
}.asLiveData()
?
init {
viewModelScope.launch {
growZone.collect { newGrowZone ->
savedStateHandle.set(GROW_ZONE_SAVED_STATE_KEY, newGrowZone)
}
}
}
...
}
?
viewmodel里面的代码对于很多不熟悉jetpack同学来说看起来是很蒙圈的,但是无关紧要,我们只要简单分析plants这个方法就可以,知道他是用来做什么的。至于相关的flow或者其他的知识点,可以先忽略。
plants是一个LivaData数据类型的数据,LiveData数据最大的特点就是,如果数据源发生变化了,那么他会主动通知观察这个LiveData的观察者。 那么这个plants是用来做什么的?首先plantRepository.getPlants()和 plantRepository.getPlantsWithGrowZoneNumber(zone)都是PlantRepository里面的方法,而上面讲到,PlantRepository其实就是从数据库里面去拿数据。所以可以知道plants其实就是从数据库里面取出来的数据,只不过数据库取出来的是Flow<List<Plant>>,这里经过转换变成了LiveData<List<Plant>> 。那么现在就剩下UI层观察这个plants整一个链路就完整了。
@AndroidEntryPoint
class PlantListFragment : Fragment() {
...
? ?private val viewModel: PlantListViewModel by viewModels()
?
? ?override fun onCreateView(
? ? ? ?inflater: LayoutInflater,
? ? ? ?container: ViewGroup?,
? ? ? ?savedInstanceState: Bundle?
? ): View {
? ? ? ?subscribeUi(adapter)
?
? }
? ?
// 这里去观察viewModel.plants,当viewmodel的plants发生变化的时候会主动调用 adapter.submitList(plants)
? ?private fun subscribeUi(adapter: PlantAdapter) {
? ? ? ?viewModel.plants.observe(viewLifecycleOwner) { plants ->
? ? ? ? ? ?adapter.submitList(plants)
? ? ? }
? }
? ...
}
?
以上就是room在项目中的简单使用了。关于room的知识点还有块比较重要的就是数据库版本的升级,这一块知识点网上有一位老哥写的非常的不错。链接贴在下面了。如果在有关room方面有什么不懂的,欢迎留言探讨。
这一篇博客涉及到很多jetpack的知识点。之后我都会写一些博客专门讲解,欢迎大家的关注。谢谢。
关于数据库版本的升级请参考:https://juejin.cn/post/6844903889611800584#heading-5
sunflower的地址:https://github.com/android/sunflower