okHttp基本用法
关于okHttp基本的用法,这里简单提一下吧。
okHttp可以使用同步请求和异步请求两种方式,当然同步请求不能在UI线程里面做,这样会导致app崩溃。
同步请求
//构造OkHttpClient
final OkHttpClient client=new OkHttpClient.Builder().build();
//构造请求体
final Request request=new Request.Builder().url("www.baidu.com").build();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
//请求得到响应
Response response=client.newCall(request).execute();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
异步请求
//构造OkHttpClient
final OkHttpClient client=new OkHttpClient.Builder().build();
//构造请求体
final Request request=new Request.Builder().url("www.baidu.com").build();
//异步请求
client.newCall(request).enqueue(new Callback() {
@Override
public void onFailure(Call call, IOException e) {
//请求失败响应
}
@Override
public void onResponse(Call call, Response response) throws IOException {
//请求成功响应
}
});
okHttp的基本工作流程
okHttp有三个队列:
/** Ready async calls in the order they'll be run. */
//等待队列,存放所有待执行请求的任务
private final Deque<AsyncCall> readyAsyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>();
/** Running asynchronous calls. Includes canceled calls that haven't finished yet. */
//正在执行的异步请求队列,存放所有正在执行异步请求任务
private final Deque<AsyncCall> runningAsyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>();
/** Running synchronous calls. Includes canceled calls that haven't finished yet. */
//正在执行的同步请求队列,存放所有正在执行同步请求任务
private final Deque<RealCall> runningSyncCalls = new ArrayDeque<>();
enqueue方法
该方法传入一个AsyncCall对象,每个AsyncCall对象都封装了一个请求所需要的所有信息。同时,将当前请求加入到待执行队列里
void enqueue(AsyncCall call) {
synchronized (this) {
//加入等待队列中
readyAsyncCalls.add(call);
}
promoteAndExecute();
}
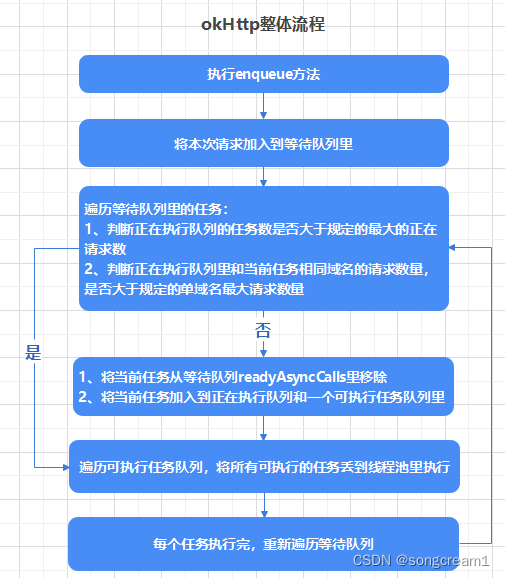
promoteAndExecute方法
1、遍历待执行任务队列
2、判断如果正在执行的任务数量超过规定的最大请求数量,则跳出
3、判断如果当前域名的请求数超过规定的最大单域名请求数量,则当前请求不做处理
4、从待执行列表里移除当前请求,将它添加到正在执行队列和可执行列表里
5、遍历可执行列表,将刚才的待执行任务,全部丢到线程池里去执行
private boolean promoteAndExecute() {
assert (!Thread.holdsLock(this));
List<AsyncCall> executableCalls = new ArrayList<>();
boolean isRunning;
synchronized (this) {
//遍历待执行任务队列
for (Iterator<AsyncCall> i = readyAsyncCalls.iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) {
AsyncCall asyncCall = i.next();
//判断如果正在执行的任务数量超过规定的最大请求数量,则跳出
if (runningAsyncCalls.size() >= maxRequests) break;
//判断如果当前域名的请求数超过规定的最大单域名请求数量,则当前请求不做处理
if (runningCallsForHost(asyncCall) >= maxRequestsPerHost) continue;
//从待执行列表里移除当前请求,将它添加到正在执行队列和可执行列表里
i.remove();
executableCalls.add(asyncCall);
runningAsyncCalls.add(asyncCall);
}
isRunning = runningCallsCount() > 0;
}
//遍历可执行列表,将刚才的待执行任务,全部丢到线程池里去执行
for (int i = 0, size = executableCalls.size(); i < size; i++) {
AsyncCall asyncCall = executableCalls.get(i);
asyncCall.executeOn(executorService());
}
return isRunning;
}
丢到线程池后,会执行每个请求AsyncCall的execute方法
execute()方法主要的两个功能:
1、调用getResponseWithInterceptorChain方法,构造拦截器链,对请求进行处理
2、任务结束时调用dispatcher.finish方法,将当前请求移出正在执行队列,重新遍历待执行队列间,将待执行任务推到线程池中执行
protected void execute() {
.....
try {
//构造拦截器链,执行各种拦截器后得到响应
Response response = getResponseWithInterceptorChain();
signalledCallback = true;
responseCallback.onResponse(RealCall.this, response);
} catch (IOException e) {
...
} catch (Throwable t) {
...
} finally {
//任务结束,调用finished方法
client.dispatcher().finished(this);
}
}
}
我们先看finished方法,getResponseWithInterceptorChain后面分析。
finished方法又去调用了promoteAndExecute()方法,还记得这个方法的功能吗,就是去遍历待执行队列,将待执行的任务丢到线程池里执行,因为本次请求执行完毕了,线程池就空闲出来了,如果之前还有待执行的请求,那么这时就又去重新调用执行一遍
private <T> void finished(Deque<T> calls, T call) {
Runnable idleCallback;
synchronized (this) {
//将当前任务从正在执行队列里移除
if (!calls.remove(call)) throw new AssertionError("Call wasn't in-flight!");
idleCallback = this.idleCallback;
}
//主要是这里,又去调用了promoteAndExecute()方法
boolean isRunning = promoteAndExecute();
if (!isRunning && idleCallback != null) {
idleCallback.run();
}
}
到这里,我们就了解了okHttp是怎么去推请求,下面看,具体每个请求任务在线程池里都做了些什么,先上图
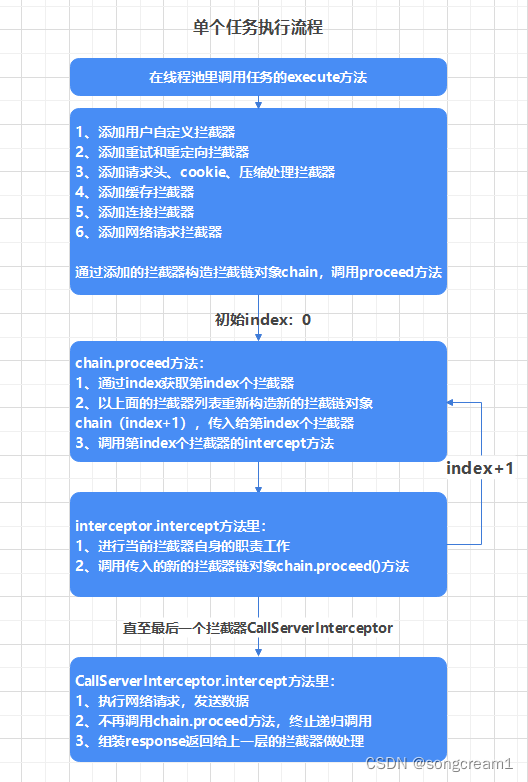
线程池会执行每个请求任务的execute()方法,
execute里调用getResponseWithInterceptorChain去构造了拦截器链,对请求进行处理
protected void execute() {
.....
try {
//构造拦截器链,执行各种拦截器后得到响应
Response response = getResponseWithInterceptorChain();
signalledCallback = true;
responseCallback.onResponse(RealCall.this, response);
} catch (IOException e) {
...
} catch (Throwable t) {
...
} finally {
//任务结束,调用finished方法
client.dispatcher().finished(this);
}
}
}
getResponseWithInterceptorChain()方法
这个方法主要构造一个拦截器链对象,并调用它的proceed方法
Response getResponseWithInterceptorChain() throws IOException {
List<Interceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<>();
//添加用户自定义的拦截器
interceptors.addAll(client.interceptors());
//添加重连和重定向拦截器
interceptors.add(retryAndFollowUpInterceptor);
//添加请求头、cookie、压缩处理拦截器
interceptors.add(new BridgeInterceptor(client.cookieJar()));
//添加缓存处理拦截器
interceptors.add(new CacheInterceptor(client.internalCache()));
//添加连接拦截器
interceptors.add(new ConnectInterceptor(client));
if (!forWebSocket) {
interceptors.addAll(client.networkInterceptors());
}
//添加发送请求拦截器
interceptors.add(new CallServerInterceptor(forWebSocket));
//构造拦截器链对象,index传入0
Interceptor.Chain chain = new RealInterceptorChain(interceptors, null, null, null, 0,
originalRequest, this, eventListener, client.connectTimeoutMillis(),
client.readTimeoutMillis(), client.writeTimeoutMillis());
//调用链对象的proceed方法
Response response = chain.proceed(originalRequest);
if (retryAndFollowUpInterceptor.isCanceled()) {
closeQuietly(response);
throw new IOException("Canceled");
}
return response;
}
chain.proceed方法
public Response proceed(Request request, StreamAllocation streamAllocation, HttpCodec httpCodec,
RealConnection connection) throws IOException {
.....
//使用原有的拦截器列表构造新的拦截链对象,index+1
RealInterceptorChain next = new RealInterceptorChain(interceptors, streamAllocation, httpCodec,
connection, index + 1, request, call, eventListener, connectTimeout, readTimeout,
writeTimeout);
//获取当前index的拦截器
Interceptor interceptor = interceptors.get(index);
//调用当前拦截器的intercept方法,并且传入新的拦截链对象(index已经+1的)
Response response = interceptor.intercept(next);
.....
return response;
}
interceptor.intercept方法
除了CallServerInterceptor外,其他所有的interceptor.intercept方法,都会调用chain.proceed()方法,
public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
.....
1、做自身拦截器的职责
2、调用chain.proceed()方法,由于传入的chain为新构造的,index加了1,于是重新执行上面的chain.proceed方法时,
获取的拦截器就是下一个的,并且又会构造index+2的新的拦截链对象,传入index+1的拦截器中
}
直到最后一个拦截器CallServerInterceptor就不会调用chain.proceed()方法,而是请求网络,构造返回Response对象,后面会单独将每个拦截器的代码