第一章 界面设计
1.1控制UI界面
1.1.1 使用XML布局控制UI界面
1.在res/layout目录下编写main.xml布局文件
2.在mainActivity.java文件中使用
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
显示布局效果
main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<!--文字提示-->
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/title"
style="@style/text"
/>
<!--按钮-->
<Button
android:id="@+id/startButton"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical|center_horizontal"
android:text="@string/start"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
style="@style/text"
/>
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
res/values/strings.xml 用于定义应用中字符串常量
<resources>
<string name="title">使用XML布局文件控制UI界面</string>
<string name="start">单击进入Android...</string>
</resources>
res/values/styles.xml 用于定义组件的样式
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<style name="text">
<item name="android:textSize">24px</item>
<item name="android:textColor">#111111</item>
</style>
</resources>
1.1.2 在代码中控制UI界面(不建议耦合性太高)
1.创建布局管理器
2.创建具体的组件
3.将创建的集体组件添加到布局管理器中
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
public TextView text2;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
//创建布局管理器
FrameLayout frameLayout=new FrameLayout(this);
//设置背景
frameLayout.setBackgroundDrawable(this.getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.ic_launcher_background));
//设置在Activity中显示framelayout
setContentView(frameLayout);
TextView text1=new TextView(this);
text1.setText("在代码中控制UI界面");//文字
text1.setTextSize(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_PX,24);//文字大小单位像素
text1.setTextColor(Color.rgb(1,1,1));//文字颜色
frameLayout.addView(text1);//添加到布局管理中
text2=new TextView(this);
text2.setText("单击进入Android...");//文字
text2.setTextSize(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_PX,24);//文字大小单位像素
text2.setTextColor(Color.rgb(1,1,1));//文字颜色
FrameLayout.LayoutParams params=new FrameLayout.LayoutParams(
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT,
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT//创建保存布局参数的对象
);
params.gravity= Gravity.CENTER_HORIZONTAL|Gravity.CENTER_VERTICAL;//居中显示
text2.setLayoutParams(params);//设置布局参数
//按钮的事件监听器
text2.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//对话框标题
new AlertDialog.Builder(MainActivity.this).setTitle("系统提示")
.setMessage("确定进入吗?")//对话框显示内容
.setPositiveButton("确定",//确定按钮对应的事件
new DialogInterface.OnClickListener(){
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog,int which){
Log.i("Android","进入");//输出消息日志
}
}).setNegativeButton("退出",//退出按钮对应的事件
new DialogInterface.OnClickListener(){
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog,int which){
Log.i("Android","退出");//输出消息日志
finish();
}
}).show();
}
});
frameLayout.addView(text2);//text2添加到布局管理器中
}
}
1.1.3 使用XML和Java代码混合控制UI界面
原则把变化小、行为比较固定的组件放在XML布局文件中,把变化比较多香味控制比较复杂的组件交给Java代码来管理。
layout/activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:id="@+id/layout"
/>
MainActivity.java
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private ImageView[] img=new ImageView[12];//声明一个保存ImageView组件
private int[] imagePath=new int[]{
R.drawable.img01,R.drawable.img02,R.drawable.img03,R.drawable.img04
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
LinearLayout layout=(LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.layout);//获取XML文件中定义的线性布局
for (int i=0;i<imagePath.length;i++){
img[i]=new ImageView(this);//创建ImageView组件
img[i].setImageResource(imagePath[i]);//为组件指定图片
img[i].setPadding(5,5,5,5);//组件的内边距
LinearLayout.LayoutParams params=new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(253,148);//设置图片的宽度和高度
img[i].setLayoutParams(params);//设置组建的布局参数
layout.addView(img[i]);//把ImageView组件添加到布局管理器中
}
}
}
1.1.4 开发自定义的View
Android中所有的UI界面都是由View类和ViewGroup类及其子类组合而成。View类是所有UI类的基类
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-HhNgPzaP-1647238680230)(C:\Users\机械师\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\1646879573783.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/320957e159c545768a42d095c90e73b3.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBA5Yid57qn54K85Li55biIWWlreS0tMTIyOQ==,size_14,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
一般情况下,开发Android应用程序的UI界面都不直接使用View和ViewGroup类,而是使用这两个类的子类。开发者可以根据需要,通过继承View类来开发自己的组件。
自定义View组件
1.创建一个继承android.view.View类的View类,并重写构造方法
2.根据需要重写相应的方法。
3.在项目的活动中,创建并实例化自定义View类,并将其添加到布局管理器中
layout/main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:id="@+id/mylayout"
/>
KiteView.java
public class KiteView extends View {
public float bitmapX;//风筝的X轴坐标
public float bitmapY;//风筝的Y轴坐标
public KiteView(Context context){
super(context);
bitmapX=750;//默认显示的X轴坐标
bitmapY=500;//默认显示的Y轴坐标
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas){
super.onDraw(canvas);
Paint paint=new Paint();//创建并实例化paint对象
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(this.getResources(), R.drawable.kite);//根据图片生成位图
canvas.drawBitmap(bitmap,bitmapX,bitmapY,paint);//生成风筝
if (bitmap.isRecycled()){//判断是否被强制回收
bitmap.recycle();//强制回收
}
}
}
MainActivity.java
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
FrameLayout frameLayout = (FrameLayout) findViewById(R.id.mylayout);//获取帧布局管理器
final KiteView kite = new KiteView(MainActivity.this);//创建并实例化kite类
//添加事件监听器
kite.setOnTouchListener(new View.OnTouchListener() {
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
kite.bitmapX=event.getX();//设置X坐标
kite.bitmapY=event.getY();//设置Y坐标
kite.invalidate();//重新绘制图形
return true;
}
});
frameLayout.addView(kite);//添加到布局管理器中
}
}
1.2 布局管理器
1.2.1线性布局
在线性布局中,每一行(针对垂直排列)或每一列(针对水平排列)中只能放一个组件,Android的线性布局不会换行,当组件排列到窗体边缘后,后面的组件不会被显示出来。
排列方式由android:orientation控制
对齐方式由android:gravity控制
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-urWPC08G-1647238547036)(C:\Users\机械师\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\1646899935270.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c0c7b5321e324659b3e75ec8ed4ce518.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBA5Yid57qn54K85Li55biIWWlreS0tMTIyOQ==,size_20,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-rl435TWo-1647238547037)(C:\Users\机械师\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\1646900112099.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c6efa71f44e445b49b6d7938052c5d5f.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBA5Yid57qn54K85Li55biIWWlreS0tMTIyOQ==,size_20,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
线性布局实现4个按钮
layout/main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:id="@+id/layout"
tools:context=".MainActivity"
>
<Button
android:text="按钮1"
android:id="@+id/bt1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<Button
android:text="按钮2"
android:id="@+id/bt2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<Button
android:text="按钮3"
android:id="@+id/bt3"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<Button
android:text="按钮4"
android:id="@+id/bt4"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</LinearLayout>
1.2.2表格布局
表格布局以行、列的形式来管理放入其中的UI组件。表格布局使用使用标记定义,在表格布局中,可以添加多个标记,每个 标记占用一行。由于标记也是容器,所以还可在该标记中添加其他组件,每添加一个组件,表格就会增加一列。在表格布局中,列可以被隐藏,也可以被设置为伸展的,从而填充可利用的屏幕空间,还可以设置为强制收缩,直到表格匹配屏幕大小。
如果在表格布局中, 直接向中添加 UI组件,那么该组件将独占一行。
TableLayout继承了LinerLayout,所以它支持后者的全部XML属性
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-wILHzTfQ-1647238547038)(C:\Users\机械师\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\1646902135057.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e5c26d2d66a742bda3882033c2e143c1.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBA5Yid57qn54K85Li55biIWWlreS0tMTIyOQ==,size_20,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/tablelayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:gravity="center_vertical"
android:stretchColumns="0,3"
>
<TableRow
android:id="@+id/tableRow01"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
>
<TextView/>
<TextView
android:text="用户名"
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:textSize="24px"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editText1"
android:textSize="24px"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:minWidth="200px"
/>
<TextView/>
</TableRow>
<TableRow
android:id="@+id/tableRow02"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
>
<TextView/>
<TextView
android:text="密码"
android:id="@+id/textView2"
android:textSize="24px"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editText2"
android:textSize="24px"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:inputType="textPassword"
/>
<TextView/>
</TableRow>
<TableRow
android:id="@+id/tableRow03"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
>
<TextView/>
<Button
android:text="登录"
android:id="@+id/btn02"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
/>
<Button
android:text="退出"
android:id="@+id/btn01"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
/>
<TextView/>
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>
1.2.3 帧布局
在帧布局管理器中,每加入一个组件,都将创建一个空白的去与,通常称为一帧,这些帧都会根据gravity属性执行自动对齐。默认情况下,帧布局从屏幕的左上角坐标点开始布局,多个人组件层叠排序,后面的组件覆盖前面的组件。
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-O8RcG8g1-1647238547039)(C:\Users\机械师\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\1646905096094.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/2fedc25a5ada4120a81c401a969abb87.png)
main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/framelayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:foregroundGravity="bottom|right"
>
<TextView
android:text="红色背景的TextView"
android:id="@+id/textView01"
android:background="#FFF00000"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_width="400px"
android:layout_height="400px"/>
<TextView
android:text="橙色背景的TextView"
android:id="@+id/textView02"
android:background="#FFFF6600"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_width="300px"
android:layout_height="300px"/>
<TextView
android:text="黄色背景的TextView"
android:id="@+id/textView03"
android:background="#FFFFEE00"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_width="200px"
android:layout_height="200px"/>
</FrameLayout>
1.2.4 相对布局
相对布局是指按照组件之间的相对位置来进行布局,如某个组件在另一个组件的左边、右边、上方或下方等。在Android中,可以在XML布局文件中定义相对布局管理器,也可以使用Java代码来创建。推荐使用前者。在XML布局文件中定义相对布局管理器可以使用标记
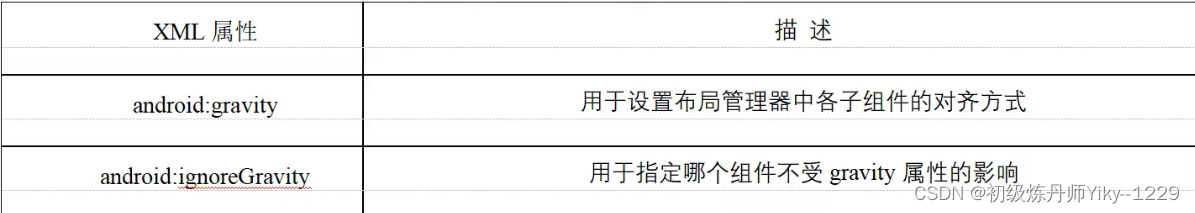
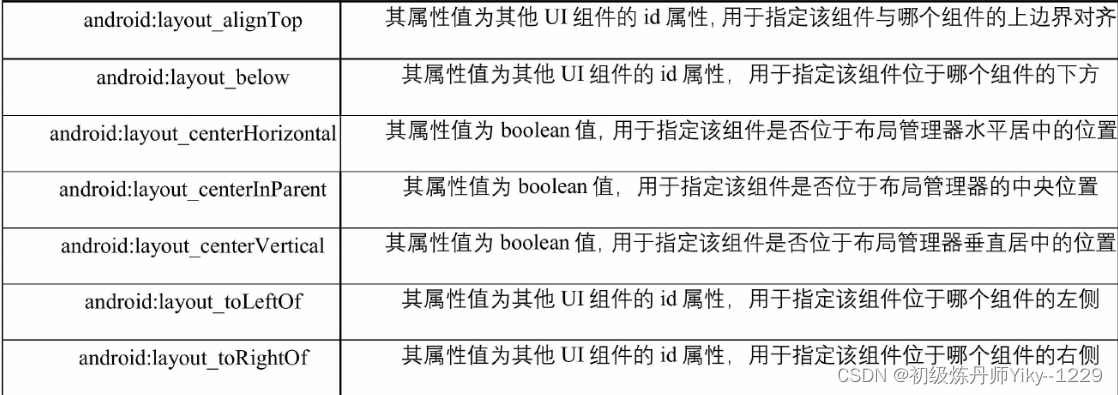
在相对布局管理器中,只有上面介绍的两个属性是不够的,为了更好地控制该布局管理器中各子组件的布局分布,RelativeLayout提供了一个内部类RelativeLayout.LayoutParams,通过该类提供的大量XML属性,可以很好地控制相对布局管理器中各组件的分布方式。
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-oqHRfzzR-1647238547042)(C:\Users\机械师\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\1646906559924.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/91228cbf6e4d40a9856de08d1e31f177.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBA5Yid57qn54K85Li55biIWWlreS0tMTIyOQ==,size_20,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/relativelayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:foregroundGravity="bottom|right"
>
<!--一个居中显示的文本视图textView1-->
<TextView
android:text="发现新版本,您想现在就进行安装吗?"
android:id="@+id/textView01"
android:textSize="24px"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"/>
<!--一个在button2左侧显示的按钮button1-->
<Button
android:text="立即更新"
android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/textView01"
android:layout_toLeftOf="@+id/btn2"
/>
<Button
android:text="稍后再说"
android:id="@+id/btn2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignRight="@+id/textView01"
android:layout_below="@+id/textView01"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
1.2.5 【案例】使用表格布局和线性布局实现分类工具栏
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/tablelayout01"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="10px"
>
<!--第一行-->
<TableRow
android:id="@+id/tableRow01"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="@drawable/bgblock"
>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/linearlayout01"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView01"
android:text="@string/time"
android:gravity="center"
style="@style/text"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"/>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/linearlayout02"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="@drawable/bgblock"
android:padding="40px">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView01"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:src="@drawable/dingdan" />
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView02"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_marginLeft="50px"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:src="@drawable/daishouhuo" />
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView03"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_marginLeft="50px"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:src="@drawable/gouwuche" />
</LinearLayout>
</TableRow>
<!--第二行-->
<TableRow
android:id="@+id/tableRow02"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/linearlayout03"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="@drawable/bgblock"
android:padding="40px">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView04"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:src="@drawable/dingdan" />
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView05"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_marginLeft="40px"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:src="@drawable/daishouhuo" />
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView06"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_marginLeft="40px"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:src="@drawable/gouwuche" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/linearlayout04"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="@drawable/bgblock"
android:padding="40px">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView07"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="40px"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:src="@drawable/daishouhuo" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView02"
android:text="订单待确认"
android:gravity="center_vertical"
style="@style/text"
android:layout_weight="3"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"/>
</LinearLayout>
</TableRow>
<!--第三行-->
<TableRow
android:id="@+id/tableRow03"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/linearlayout05"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_marginLeft="20px"
>
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView08"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="20px"
android:src="@drawable/gouwuche" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView03"
android:text="购物车"
android:gravity="center_vertical"
android:layout_marginLeft="20px"
style="@style/text"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</LinearLayout>
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-7mEyF3LT-1647238547044)(C:\Users\机械师\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\1647065349880.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/3e0fa8c4b57747a6b9cbefc7acc5df3c.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBA5Yid57qn54K85Li55biIWWlreS0tMTIyOQ==,size_7,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
1.3 基本组件
1.3.1 文本框与编辑框
1.文本框
在Android中,文本框使用TextView表示,用于在屏幕上显示文本。与Java中的文本框组件不同,Text View相当于Java中的标签,也就是JLable。需要说明的是,Android 中的文本框组件可以显示单行文本,也可以显示多行文本,还可以显示带图像的文本。在Android中,可以使用两种方法向屏幕中添加文本框: -种是通过在XML布局文件中使用标记添加;另一种是在Java文件中,通过new关键字创建。推荐采用第一种方法, 也就是通过标记在XML布局文件中添加文本框
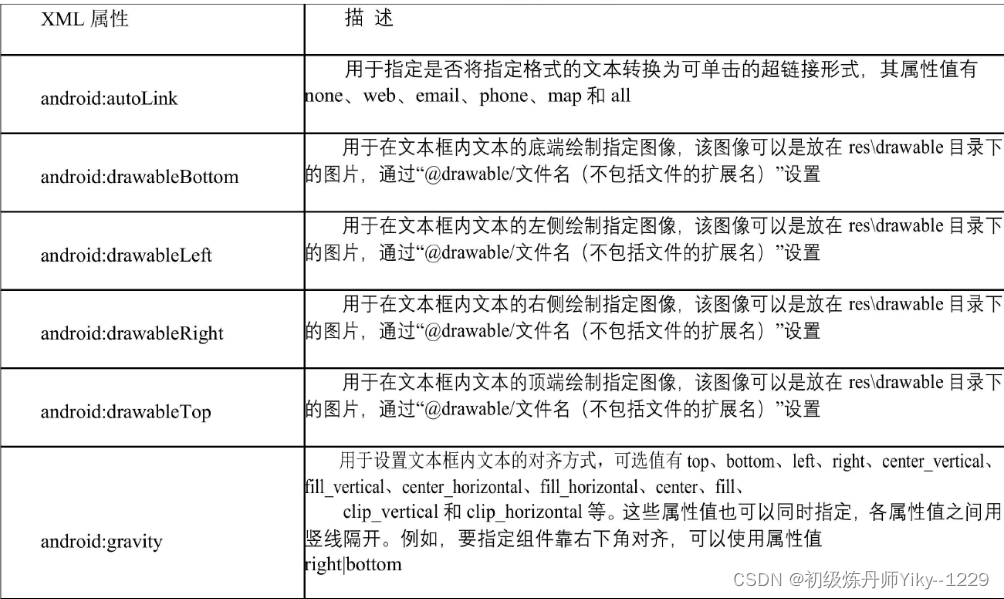
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-ktNdsqKD-1647238547047)(C:\Users\机械师\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\1647067347578.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e0f924334f554e189309e50e3fc4bc98.png)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Hello World"
android:autoLink="email"
android:height="50px"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView01"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="带图片的TextView"
android:drawableTop="@drawable/icon"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView02"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:width="300px"
android:text="多行文本:在很久很久以前,有一位老人他带给我们一个苹果,在很久很久以前,有一位老人他带给我们一个苹果,在很久很久以前,有一位老人他带给我们一个苹果"
android:textSize="20px"
android:textColor="#0f0"
/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView03"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textColor="#f00"
android:width="300px"
android:text="多行文本:在很久很久以前,有一位老人他带给我们一个苹果,在很久很久以前,有一位老人他带给我们一个苹果,在很久很久以前,有一位老人他带给我们一个苹果"
android:textSize="20px"
android:singleLine="true"
/>
</LinearLayout>
2.编辑框
在Android中,编辑框使用EditText表示,用于在屏幕上显示文本输入框,这与Java中的文本框组件功能类似。
需要说明的是,Android 中的编辑框组件可以输入单行文本,也可以输入多行文本,还可以输入指定格式的文本(如
密码、电话号码、E-mail 地址等)。
在Android中,可以使用两种方法向屏幕中添加编辑框: - -种是通过在XML布局文件中使用标记添
加;另一种是在Java文件中,通过new关键字创建。推荐采用第一种方法,也就是通过标记在XML布局
文件中添加编辑框。
由于EditText类是TextView的子类,所以对于表3.5中列出的XML属性,同样适用于EditText 组件。需要特别
注意的是,在EditText组件中,android:inputType 属性可以帮助输入框显示合适的类型。例如,要添加一个密码框,
可以将android:inputType属性设置为textPassword。
在屏幕中添加编辑框后,还需要获取编辑框中输入的内容,这可以通过编辑框组件提供的getText()方法实现。使
用该方法时,先要获取到编辑框组件,然后再调用getText()方法。例如,要获取布局文件中添加的id属性为login 的
编辑框的内容,可以通过以下代码实现:
EditText login= (EditText)findViewById(R. id.1ogin);
String loginText= login. getText().toString();
注册案例
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/tablelayout01"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
>
<TableRow
android:id="@+id/tableRow01"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:inputType="textPersonName"
android:text="会员昵称:"
android:height="50px"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/nickname"
android:hint="请输入会员昵称"
android:layout_width="400px"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:singleLine="true"
/>
</TableRow>
<TableRow
android:id="@+id/tableRow02"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="输入密码:"
android:height="50px"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/pwd"
android:layout_width="400px"
android:inputType="textPassword"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
</TableRow>
<TableRow
android:id="@+id/tableRow03"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="确认密码:"
android:height="50px"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/apwd"
android:layout_width="400px"
android:inputType="textPassword"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
</TableRow>
<TableRow
android:id="@+id/tableRow04"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="E-mail:"
android:height="50px"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/email"
android:layout_width="400px"
android:inputType="textEmailAddress"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
</TableRow>
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:text="注册"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn2"
android:text="重置"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</LinearLayout>
</TableLayout>
java
package com.jingyi.register;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Button button = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn1);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
EditText nicknameText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.nickname);//获取昵称编辑框组件
String nickname = nicknameText.getText().toString();//获取输入的昵称内容
EditText pwdText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.pwd);//获取密码编辑框的组件
String password= pwdText.getText().toString();//获取输入的密码
EditText apwdText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.apwd);//获取再次密码编辑框的组件
String apassword= apwdText.getText().toString();//获取第二次输入的密码
EditText emailText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.email);//获取E-mail编辑狂组件
String email = emailText.getText().toString();//获取输入的E-mail地址
Log.i("编辑框","会员昵称:"+nickname);
Log.i("编辑框","E-mail地址:"+email);
if (password.equals(apassword)){
Log.i("编辑框","密码:"+password);
}else{
Log.i("提示","前后两次输入的密码不一致!");
}
}
});
}
}
1.3.2 按钮
Android中提供了普通按钮和图片按钮两种按钮组件。这两种按钮组件都用于在UI界面上生成一-个可以单击的按
钮。当用户单击按钮时,将会触发-一个onClick事件,可以通过为按钮添加单击事件监听器指定所要触发的动作。
1.普通按钮
按钮监听事件
在屏幕上添加按钮后,还需要为按钮添加单击事件监听器,才能让按钮发挥其特有的用途。Android 提供了两种为按钮添加单击事件监听器的方法,-种是在Java代码中完成,例如,在Activity的onCreate()方法中完成,具体的代码如下:
import android.view.View.OnClickListener ;
import android.widget.Button;
Button login= (Button)findViewById(R. id.login);
login.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//编写要执行的动作代码
}
});
另一种是在Activity中编写-个包含View类型参数的方法,并且将要触发的动作代码放在该方法中,然后在布局文件中,通过android:onClick属性指定对应的方法名实现。例如,在Activity中编写一个名为myClick0的方法,关键代码如下:
public void myClick(View view){
//编写要执行的动作代码
}
2.图片按钮
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="登录"
android:id="@+id/login"
/>
<ImageButton
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/login1"
android:src="@drawable/login"
android:onClick="myClick"
android:background="#000"
/>
</LinearLayout>
java
package com.jingyi.btn;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
Button button = (Button) findViewById(R.id.login);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "您点击了普通按钮", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
}
public void myClick(View view){
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "您点击了图片按钮", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
1.3.3 单选按钮和复选框
1.单选按钮
在默认情况下,单选按钮显示为一个圆形图标,并且在该图标旁边放置一些说明性文字。在程序中,一般将多个单选按钮放置在按钮组中,使这些单选按钮表现出某种功能,当用户选中某个单选按钮后,按钮组中的其他按钮将被自动取消选中状态。在Android中,单选按钮使用RadioButton表示,而RadioButton类又是Button的子类,所以单选按钮可以直接使用Button支持的各种属性。
事件监听
在改变单选按钮组的值时获取选中项的值时,首先需要获取单选按钮组,然后为其添加OnCheckedChangeListener,并在其onCheckedChanged)方法中根据参数checkedId获取被选中的单选按钮,并通过其getText()方法获取该单选按钮对应的值。例如,要获取id属性为radioGroupl的单选按钮组的值,可以通过下面的代码实现。
RadioGroup sex= ( RadioGroup)findViewById(R.id.radioGroup1);
sex. setOnCheckedChangeListener (new OnCheckedChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onCheckedChanged(RadioGroup grouRe1 int, checkedId) {
RadioButton r= ( RadioButton)findViewById(checkedId);
r.getText();//获取被选中的单选按钮的值
});
[V]单击其他按钮时获取
单击其他按钮时获取选中项的值时,首先需要在该按钮的单击事件监听器的onClick(方法中,通过for循环语句遍历当前单选按钮组,并根据被遍历到的单选按钮的isChecked)方法判断该按钮是否被选中,当被选中时,通过单选按钮getText()方法获取对应的值。例如,要在单击‘提交’按钮时,获取id属性为radioGroupl 的单选按钮组的值,可以通过下面的代码实现。
final RadioGroup sex=(RadioGroup )findViewById(R. id. radioGroup1);
Button button=( Button )findViewById(R. id. button1);
//获取一个提交按钮
button. setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
for(int i=0;i<sex. getChildCount();i++){
RadioButton r= ( RadioButton)sex . getChildAt(i); // 根据索引值获取单选按钮
if(r. isChecked()){ // 判断单选按钮是否被选中
r.getText(); // 获取被选中的单选按钮的值
break; //跳出 for循环
});
}
}
}
案例
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="性别:"
android:height="50px"
/>
<RadioGroup
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/radioGroup1"
android:orientation="horizontal"
>
<!--radiobutton通常在radiogroup中使用-->
<RadioButton
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/radio1"
android:text="男"
android:checked="true"/> <!--默认选中-->
<RadioButton
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/radio2"
android:text="女" />
</RadioGroup>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:text="提交"
></Button>
</LinearLayout>
java
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
final RadioGroup sex = (RadioGroup) findViewById(R.id.radioGroup1);//获取按钮组
sex.setOnCheckedChangeListener(new RadioGroup.OnCheckedChangeListener() {//为单选按钮组添加事件监听器
@Override
public void onCheckedChanged(RadioGroup group, int checkedId) {
RadioButton r = (RadioButton) findViewById(checkedId);//获取被选择单选按钮
Log.i("单选按钮","您的选择是"+r.getText());
}
});
//通过提交按钮获取单选按钮选项
Button btn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn1);
btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
for (int i=0;i<sex.getChildCount();i++) {
RadioButton r=(RadioButton)sex.getChildAt(i);//通过索引获取每个单选按钮对象
if(r.isChecked()){
Log.i("单选按钮","性别:"+r.getText());
break;
}
}
}
});
}
}
2.复选框
在默认情况下,复选框显示为一个方块图标,并且在该图标旁边放置一些说 明性文字。与单选按钮唯一不同的是,复选框可以进行多选设置,每一个复 选框都提供“选中”和“不选中”两种状态。在Android 中,复选框使用CheckBox表示,而CheckBox类又是Button的子类,所以可以直接使用Button支持的各种属性。
监听事件
由于使用复选框可以选中多项,所以为了确定用户是否选择了某-项,还需要为每-一个选项添加事件监听器。例如,要为id为likel的复选框添加状态改变事件监听器,可以使用下面的代码:
final CheckBox like1=(CheckBox )findViewById(R. id.like1);//根据id属性获取复选框
like1. setOnCheckedChangeListener (new OnCheckedChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onCheckedChanged ( CompoundButton buttonView, boolean isChecked) {
if(like1. isChecked()){ //判断该 复选框是否被选中
like1. getText(); // 获取选中项的值
}
}
});
案例
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:width="100px"
android:height="50px"
android:gravity="right"
android:text="爱好:"
/>
<CheckBox
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="体育"
android:id="@+id/item1"
/>
<CheckBox
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="音乐"
android:id="@+id/item2"
/>
<CheckBox
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="美术"
android:id="@+id/item3"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:text="提交"
></Button>
</LinearLayout>
java
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
//重写监听方法
private CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener checkbox_listener= new CompoundButton.OnCheckedChangeListener(){
@Override
public void onCheckedChanged(CompoundButton buttonView, boolean isChecked) {
if (isChecked){
Log.i("复选框","选择了["+buttonView.getText().toString()+"]");
}
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
CheckBox it1 = (CheckBox) findViewById(R.id.item1);
CheckBox it2 = (CheckBox) findViewById(R.id.item2);
CheckBox it3 = (CheckBox) findViewById(R.id.item3);
it1.setOnCheckedChangeListener(checkbox_listener);
it2.setOnCheckedChangeListener(checkbox_listener);
it3.setOnCheckedChangeListener(checkbox_listener);
Button button = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn1);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
String items=new String();
if (it1.isChecked()){
items+=it1.getText().toString()+",";
}if (it2.isChecked()){
items+=it2.getText().toString()+",";
}if (it3.isChecked()){
items+=it3.getText().toString()+",";
}
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, items, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
}
}
1.3.4 图像视图
图像视图(ImageView) ,用于在屏幕中显示任何Drawable对象,通常用来显示图片。
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
>
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imgeView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="5px"
android:src="@drawable/spring" />
<ImageView
android:maxHeight="180px"
android:maxWidth="180px"
android:adjustViewBounds="true"
android:id="@+id/imgeView2"
android:layout_margin="5px"
android:src="@drawable/spring"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
/>
<ImageView
android:layout_width="180px"
android:layout_height="180px"
android:scaleType="fitEnd"
android:id="@+id/imgeView3"
android:layout_margin="5px"
android:src="@drawable/spring"
/>
<ImageView
android:layout_width="180px"
android:layout_height="180px"
android:id="@+id/imageView4"
android:src="@drawable/spring"
app:tint="#77ff0000" />
</LinearLayout>
1.3.5 列表选择框
Android中提供的列表选择框(Spinner) 相当于在网页中常见的下拉列表框,通常用于提供一系列可选择的列表项供用户进行选择,从而方便用户。
<Spinner
android:prompt= "@string/info"
android :entries="@array/数组名称"
android:layout_ height= "wrap_ content'
android:layout_ _width= "wrap_ content
android:id="@+id/ID号">
其中,android:entries 为可选属性,用于指定列表项,如果在布局文件中不指定该属性,可以在Java代码中通过为其指定适配器的方式指定; android:prompt 属性也是可选属性,用于指定列表选择框的标题。
直接在布局文件中显示列表项
main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
>
<Spinner
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/spinner1"
android:entries="@array/province"
/>
</LinearLayout>
valus/arrays.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<string-array name="province">
<item>辽宁省</item>
<item>河北省</item>
<item>吉林省</item>
<item>黑龙江省</item>
<item>山东省</item>
</string-array>
</resources>
事件监听器
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Spinner spinner = (Spinner) findViewById(R.id.spinner1);
spinner.getSelectedItem();//获取下拉框中的所有选择项
spinner.setOnItemSelectedListener(new AdapterView.OnItemSelectedListener() {
@Override
public void onItemSelected(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position, long id) {
String itempos = parent.getItemAtPosition(position).toString();//被选中项
Log.i("Spinner被选中",itempos);
}
@Override
public void onNothingSelected(AdapterView<?> parent) {
}
});
}
}
在代码中实现要显示的列表项
通过数组资源文件创建
ArrayAdapter<CharSequence> adapter = ArrayAdapter.createFromResource(
this,R.array.province, android.R.layout.simple_dropdown_item_1line
);
adapter.setDropDownViewResource(android.R.layout.simple_dropdown_item_1line);
spinner.setAdapter(adapter);//将适配器与选择列表关联
通过在Java文件中使用字符串数组创建
String[] province = {"辽宁省", "黑龙江省", "吉林省"};
ArrayAdapter<String> adapter = new ArrayAdapter<String>(this,android.R.layout.simple_spinner_dropdown_item,province);
//为适配器设置列表框下拉时的选项样式
adapter.setDropDownViewResource(android.R.layout.simple_spinner_dropdown_item);
//将适配器与选择列表关联
spinner.setAdapter(adapter);
1.3.6 列表视图
列表视图(ListView)是Android中最常用的一种视图组件,它以垂直列表的形式列出需要显示的列表项。例如,
显示系统设置项或功能内容列表等。
1.使用ListView组件创建
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-0I16mKAJ-1647238547050)(C:\Users\机械师\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\1647162711146.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/14f1d833100f4fe395066547e14a3c0c.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBA5Yid57qn54K85Li55biIWWlreS0tMTIyOQ==,size_15,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
在使用列表视图时,重要的是如何设置选项内容。同Spinner列表选择框一样,如果没有在布局文件中为ListView指定要显示的列表项,也可以通过为其设置Adapter来指定需要显示的列表项。通过Adapter来为ListView指定要
显示的列表项,可以分为以下两个步骤。
(1)创建Adapter对象。对于纯文字的列表项,通常使用ArrayAdapter对象。创建ArayAdapter对象通常可以有两种方式:一种是通过数组资源文件创建:另-种是通过在Java文件中使用字符串数组创建。这与1.3.5 节Spinner列表选择框中介绍的创建ArrayAdapter对象基本相同,所不同的就是在创建该对象时,指定列表项的外观
形式。为ListView指定的外观形式通常有以下几个。
simple_ list item_ 1:每个列表项都是一个普通的文本。
simple_ list item 2: 每个列表项都是一-个普通的文本(字体略大)。
simple list item. checked: 每个列表项都有-个已选中的列表项。
simple list item_ multiple_ choice:每个列表项都是带复选框的文本。
simple_ list item. single choice: 每个列表项都是带单选按钮的文本。
(2)将创建的适配器对象与ListView 相关联,可以通过ListView对象的setAdapter()方法实现,具体代码如下:
listView. setAdapter (adapter); //将适配器 与ListView关联
适配器指定列表创建ListView
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical"
>
<ListView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/listView1"
android:footerDividersEnabled="false"
android:headerDividersEnabled="false"
android:dividerHeight="3px"
/>
</LinearLayout>
java
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
final ListView listView = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.listView1);
ArrayAdapter<CharSequence> adapter = ArrayAdapter.createFromResource(
this,R.array.song, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_checked
);//创建适配器
listView.setAdapter(adapter);
listView.setOnItemClickListener(new AdapterView.OnItemClickListener() {
@Override
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position, long id) {
String pos = parent.getItemAtPosition(position).toString();
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, pos, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
}
}
2.使用Activity继承ListActivity实现
如果程序的窗口仅仅需要显示一个列表,则可以直接让Activity继承ListActivity来实现。继承了ListActivity的类中无须调用setContentView0方法来显示页面,而是可以直接为其设置适配器,从而显示一 个列表。
public class MainActivity extends ListActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
String[] songs = {"歌曲名:Normal No More (Explicit),歌手名:Tysm", "歌曲名:Not A Love Song,歌手名:Bülow", "歌曲名:Old Town Road,歌手名:Lil Nas X"};
ArrayAdapter<String> adapter = new ArrayAdapter<String>(
this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_single_choice,songs
);
setListAdapter(adapter);
}
@Override
protected void onListItemClick(ListView l,View v,int position,long id){
super.onListItemClick(l,v,position,id);
String s = l.getItemAtPosition(position).toString();
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, s, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
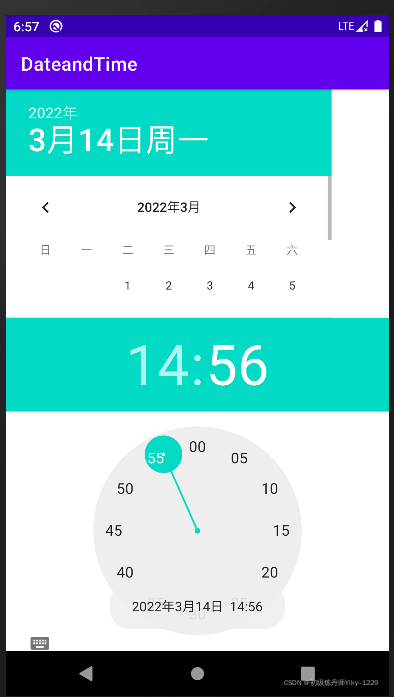
1.3.7 日期、时间拾取器
为了让用户能够选择日期和时间,Android 提供了日期、时间拾取器,分别是DatePicker组件和TimePicker组件。这两个组件使用比较简单,可以在Android Studio的可视化界面设计器中,选择对应的组件并拖曳到布局文件中。为了可以在程序中获取用户选择的日期、时间,还需要为DatePicker和TimePicker组件添加事件监听器。其中,DatePicker组件对应的事件监听器是OnDateChangedListener,而TimePicker组件对应的事件监听器是
OnTimeChangedListener。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical"
>
<DatePicker
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/datePicker1"
android:layout_weight="6"
/>
<TimePicker
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/timePicker"
android:layout_weight="1"
/>
</LinearLayout>
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
int year;
int month;
int day;
int hour;
int minute;
int second;
//时间显示函数
private void show(int year,int month,int day,int hour,int minute){
String dtstr=year+"年"+(month+1)+"月"+day+"日 "+hour+":"+minute;//获取拾取器设置的日期与时间 ,DatePicker获取到的月份是0~11所以+1
Toast.makeText(this, dtstr, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
DatePicker datePicker = (DatePicker) findViewById(R.id.datePicker1);
TimePicker timePicker = (TimePicker) findViewById(R.id.timePicker);
timePicker.setIs24HourView(true);//设置为24小时制
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
year = calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR);
month = calendar.get(Calendar.MONTH);
day = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
hour = calendar.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY);
minute = calendar.get(Calendar.MINUTE);
//初始化日期拾取器,并指定监听器
datePicker.init(year, month, day, new DatePicker.OnDateChangedListener() {
@Override
public void onDateChanged(DatePicker view, int year, int monthOfYear, int dayOfMonth) {
MainActivity.this.year=year;//改变year的值
MainActivity.this.month=monthOfYear;//改变month的值
MainActivity.this.day=dayOfMonth;//改变day的值
show(year,monthOfYear,dayOfMonth,hour,minute);
}
});
//时间拾取器的监听器
timePicker.setOnTimeChangedListener(new TimePicker.OnTimeChangedListener() {
@Override
public void onTimeChanged(TimePicker view, int hourOfDay, int minute) {
MainActivity.this.hour=hourOfDay;
MainActivity.this.minute=minute;
show(year,month,day,hourOfDay,minute);
}
});
}
}
1.3.8 计时器
计时器(Chronometer) 组件可显示从某个起始时间开始,- 共过去了多长时间的文本。由于该组件继承自TextView,所以它以文本的形式显示内容。使用该组件也比较简单,通常只需要使用以下5个方法。
setBase(): 用于设置计时器的起始时间。
setFormat(): 用于设置显示时间的格式。
start(): 用于指定开始计时。
stop(): 用于指定停止计时。
setOnChronometerTickListener(): 用于为计时器绑定事件监听器,当计时器改变时触发该监听器。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
>
<Chronometer
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/chronometer01"
android:text="计时器"
/>
</LinearLayout>
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Chronometer ch = (Chronometer) findViewById(R.id.chronometer01);//设置计时器组件
ch.setBase(SystemClock.elapsedRealtime());//设置当前时间为起始时间
ch.setFormat("已用时间:%s");//设置时间显示的格式
ch.start();//开启计时器
//添加监听器
ch.setOnChronometerTickListener(new Chronometer.OnChronometerTickListener() {
@Override
public void onChronometerTick(Chronometer chronometer) {
if (SystemClock.elapsedRealtime()-ch.getBase()>=1000000){
ch.stop();
}
}
});
}
}
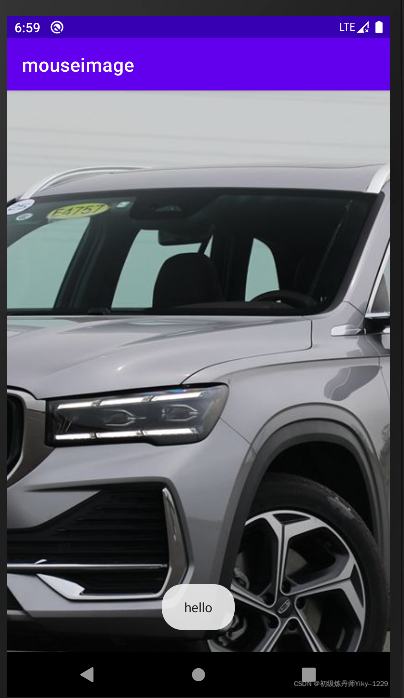
1.3.9 案例:实现跟踪鼠标单击状态的图片按钮
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:gravity="center"
>
<ImageButton
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/start"
android:src="@drawable/button_state"
/>
</LinearLayout>
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
ImageButton imageButton = (ImageButton) findViewById(R.id.start);
imageButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "hello", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
}
}


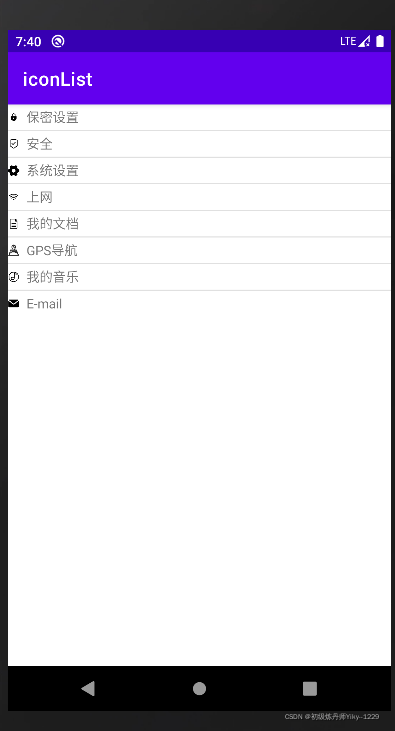
1.3.10 案例:实现带图标的ListView
res/layout/main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
>
<ListView
android:id="@+id/listView1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
tools:ignore="MissingConstraints" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
res/layout/items.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal"
tools:ignore="MissingDefaultResource">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/image"
android:paddingRight="10px"
android:paddingTop="20px"
android:paddingBottom="20px"
android:adjustViewBounds="true"
android:maxWidth="72px"
android:maxHeight="72px"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/title"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="10px"
android:gravity="center"
/>
</LinearLayout>
java
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
ListView listView = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.listView1);
int[] imageId = {R.drawable.secret, R.drawable.safe, R.drawable.set,
R.drawable.wifi, R.drawable.doc, R.drawable.gps, R.drawable.music,
R.drawable.email
};//保存图片id的数组
String[] title = {"保密设置", "安全", "系统设置", "上网", "我的文档",
"GPS导航", "我的音乐", "E-mail"};//列表项文字
List<Map<String, Object>> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i=0;i<imageId.length;i++){
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("image",imageId[i]);
map.put("title",title[i]);
list.add(map);
}
SimpleAdapter adapter = new SimpleAdapter(this, list, R.layout.items, new String[]{
"title", "image"}, new int[]{R.id.title,R.id.image});
listView.setAdapter(adapter);
}
}