概述
Android为XML布局提供了多种类型的组件标签供使用,其中include、merge、ViewStub不常用,这三个标签用于布局优化,本文对这三个标签进行初略讲解。
include
include是包含的意思,顾名思义就是布局重用的意思,也就是一块布局写好了之后,可以在其他布局中重复使用。实际开发中,使用include标签地方不少,包括标题栏、控制面板、进度条、统一的按钮文字等等,凡是共用的布局都可以使用include,大大减少了程序员的工作量,提高了开发效率。
以标题栏为例阐述include的使用。
- 要自定义标题栏titlebar,需要将app主题设为NoActionBar。
<style name="Theme.Content" parent="Theme.MaterialComponents.DayNight.NoActionBar">
- 创建空白布局。
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="Hello World!"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="48dp" />
</LinearLayout>
因为取消了系统默认的标题栏,所以预览图中标题部分是没有的。

3. 自定义标题栏。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="52dp"
android:background="#00BCD4">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:src="@drawable/ic_baseline_keyboard_arrow_left_24" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:text="这是标题"
android:textColor="@color/white"
android:textSize="28dp" />
</RelativeLayout>
自定义标题栏中包含返回按钮和标题。
4. include标题栏
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<include layout="@layout/titlebar" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="Hello World!"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="48dp" />
</LinearLayout>

使用include标签,需要注意一下几点。
- include标签不能作为根布局元素
} else if (TAG_INCLUDE.equals(name)) {
if (parser.getDepth() == 0) {
throw new InflateException("<include /> cannot be the root element");
}
parseInclude(parser, context, parent, attrs);
- include标签内不可以再添加其他元素。
<include
layout="@layout/titlebar" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="Hello World!"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="48dp" />
</include>
像上面的写法虽然不会报错,但是TextView却无法展示出来。
- include只能用在ViewGroup内
if (!(parent instanceof ViewGroup)) {
throw new InflateException("<include /> can only be used inside of a ViewGroup");
}
- 若include添加了一些属性,则会以添加后的为准,且include里面包含的元素也会以添加后的属性为准。
// Apply a theme wrapper, if requested. This is sort of a weird
// edge case, since developers think the <include> overwrites
// values in the AttributeSet of the included View. So, if the
// included View has a theme attribute, we'll need to ignore it.
final TypedArray ta = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, ATTRS_THEME);
final int themeResId = ta.getResourceId(0, 0);
final boolean hasThemeOverride = themeResId != 0;
if (hasThemeOverride) {
context = new ContextThemeWrapper(context, themeResId);
}
ta.recycle();
<include
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
layout="@layout/titlebar" >
</include>
此时页面效果就会发生改变。

- 若include中有设置了id,include包含的视图中也设置了id,则不能通过include自己的id获取include里面的组件
<include
android:id="@+id/include_title"
layout="@layout/titlebar" >
</include>
titlebar.xml中布局如下。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/rl_title"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="52dp"
android:background="#00BCD4">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentLeft="true"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:src="@drawable/ic_baseline_keyboard_arrow_left_24" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_title"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:text="这是标题"
android:textColor="@color/white"
android:textSize="28dp" />
</RelativeLayout>
此时通过rl_title寻找tv_title会出现空指针。
RelativeLayout titleBar = findViewById(R.id.rl_title);
TextView title = titleBar.findViewById(R.id.tv_title);
结果会出现空指针异常。
Caused by: java.lang.NullPointerException: Attempt to invoke virtual method 'android.view.View android.widget.RelativeLayout.findViewById(int)' on a null object reference
at com.example.content.MainActivity.onCreate(MainActivity.java:22)
include标签复用其他布局时,可以视为在布局中又写了一遍,所以获取复用布局里面的元素直接使用findViewById即可。
TextView title = findViewById(R.id.tv_title);
无需借助复用布局的再一次findViewById。
merge
merge翻译过来的意思是合并、融入、融合、兼并的意思,merge标签也就是起这样的作用,用于减少布局层级,防止页面过渡绘制,减少绘制时间,提高性能。
不使用merge
普通布局。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<include layout="@layout/titlebar"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="Hello World!"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:textSize="48dp" />
<include layout="@layout/normal_item"/>
</LinearLayout>
其中normal_item没有使用merge。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="24dp"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:text="第一个普通测试文本"/>
<TextView
android:layout_marginTop="50dp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="24dp"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:text="第二个普通测试文本"/>
</LinearLayout>
结果布局中的树如下:
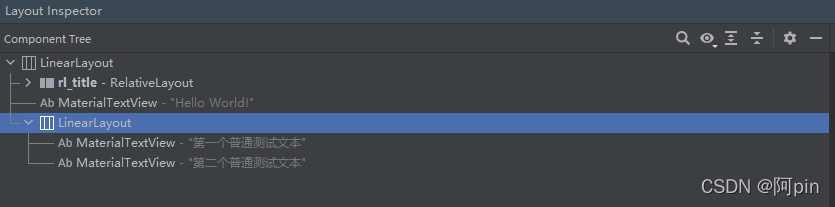
一共有两级组件。
使用merge
使用merge就是将上诉normal_item中LinearLayout改成merge。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<merge xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="24dp"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:text="第一个merge测试文本"/>
<TextView
android:layout_marginTop="50dp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="24dp"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:text="第二个merge测试文本"/>
</merge>
组件树如下:
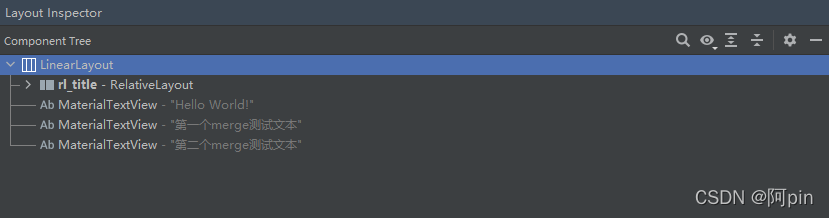
结果发现使用了merge后,merge里面的组件和父容器里面的组件是同一层级,而没有使用merge是两级,所以merge主要功能是用来减少布局层级。
使用merge也需要注意几点。
- merge是一个标签而不是一个view,所以在merge上不需要设置任何属性
<merge xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
像上面的写法其实是没有任何效果的,merge里面的组件是根据使用merge的父容器来的。
- merge必须是根节点元素
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<merge xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="24dp"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:text="第一个merge测试文本"/>
<TextView
android:layout_marginTop="50dp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="24dp"
android:textColor="@color/black"
android:text="第二个merge测试文本"/>
</merge>
否则代码编译的时候会报错。
} else if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name)) {
throw new InflateException("<merge /> must be the root element");
} else {
- merge必须要有父容器
if (TAG_MERGE.equals(name)) {
if (root == null || !attachToRoot) {
throw new InflateException("<merge /> can be used only with a valid "
+ "ViewGroup root and attachToRoot=true");
}
rInflate(parser, root, inflaterContext, attrs, false);
ViewStub
A ViewStub is an invisible, zero-sized View that can be used to lazily inflate layout resources at runtime. When a ViewStub is made visible, or when inflate() is invoked, the layout resource is inflated. The ViewStub then replaces itself in its parent with the inflated View or Views. Therefore, the ViewStub exists in the view hierarchy until setVisibility(int) or inflate() is invoked. The inflated View is added to the ViewStub’s parent with the ViewStub’s layout parameters. Similarly, you can define/override the inflate View’s id by using the ViewStub’s inflatedId property.
简单来讲,ViewStub默认是一个不可见,且宽高都为0的,只有在运行时才会加载(懒加载)的组件。
public ViewStub(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
super(context);
final TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs,
R.styleable.ViewStub, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
saveAttributeDataForStyleable(context, R.styleable.ViewStub, attrs, a, defStyleAttr,
defStyleRes);
mInflatedId = a.getResourceId(R.styleable.ViewStub_inflatedId, NO_ID);
mLayoutResource = a.getResourceId(R.styleable.ViewStub_layout, 0);
mID = a.getResourceId(R.styleable.ViewStub_id, NO_ID);
a.recycle();
setVisibility(GONE);
setWillNotDraw(true);
}
...
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(0, 0);
}
ViewStub默认显示为GONE,宽高都为0,此时也不会绘制。需要显示的时候,需要调用setVisibility()或者Inflate()才可以加载布局。
使用
<ViewStub
android:id="@+id/vs_test"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:inflatedId="@+id/vs_inflate"
android:layout="@layout/viewstub_item" />
其中viewstub_item:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<ListView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/lv_test"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
</ListView>
通过inflatedId就可以获取viewstub_item里面的ListView 。
ViewStub viewStub = findViewById(R.id.vs_test);
// 加载
viewStub.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
// 通过inflatedId获取viewstub_item里面的listView
ListView listView = findViewById(R.id.vs_inflate);
当inflatedId不为NO_ID,也就是设置了id的时候,此时ViewStub的inflatedId就成为了根元素的id,此时可以直接通过findViewById获取ViewStub 里面的元素。
如果没有设置inflatedId时,可以直接通过findViewById(R.id.lv_test)获取ViewStub里面的ListView。也可以通过inflate()直接获取ViewStub里面的ListView。
ViewStub viewStub = findViewById(R.id.vs_test);
// 获取ListView
ListView inflate = (ListView) viewStub.inflate();
if (inflate == null) {
// 未加载
} else {
// 已加载
}
注意:
- 可以通过判断ViewStub的可见性(Visibility)判断是否已加载。
- 如果通过inflate(),则需要通过对inflate获取对象进行判空来判断是否加载。
- 如果设置了inflatedId,则需要通过inflatedId查找目标父容器。
