在看视频的过程中, 很多用户会发弹幕, 当前用户可以设置过滤敏感词和敏感用户,? 设置后, 命中敏感词和敏感用户的弹幕就不会显示.?
- 敏感词和敏感用户的设置上限为各100.
- 由客户端进行过滤,
- 不区分大小写, 比如用户设置了"abc",? 其他用户发送了"ABC"或者"Abc", 都不显示.
过滤敏感用户
服务器对发送弹幕的用户ID做了16位的md5, 比如用户ID为12345, 经过16位MD5加密后为EA8A706C4C34A168, 客户端使用弹幕发送者的ID和数组(最多100个)中的敏感用户ID进行匹配,如果匹配到了就不展示该弹幕.
一开始的做法, 服务器返回了敏感用户的数组, 客户端使用数组的-?containsObject进行处理, 功能是可以完成, 但是由于containsObject 内部实现是做了一次O(N)的遍历, 假设有1W个敏感用户, 每条弹幕都需要循环1W次, 效率很差, 我们采用了生成一个NSSet, 使用Set的containsObject 进行判断, 这样时间复杂度就降到了O(1).
过滤敏感词
由于需要忽略弹幕中的大小写, 直接使用[NSString containsString:@""] 是不行的,? 经过一顿搜索, 使用谓词?可以忽略敏感词里的大小写.? 假设 @"abc" 为敏感词
NSPredicate *pred = [NSPredicate predicateWithFormat:@"SELF CONTAINS [cd] %@",@"abc"];
BOOL result1 = [pred evaluateWithObject:@"Abc"];
BOOL result2 = [pred evaluateWithObject:@"ABCD"];
BOOL result3 = [pred evaluateWithObject:@"ABC"];
BOOL result4 = [pred evaluateWithObject:@"AC"];
// 打印结果 1 1 1 0
NSLog(@"%d %d %d %d",result1, result2, result3, result4);可以达成效果,? 很快写下了这样的代码. 自测通过, 继续做其他功能 ...
// self.keyWordArray 为用户设置的敏感词构成的数组
// self.danMu 为其他用户发送的弹幕, 判断此条弹幕是否合法
for (NSString *keyWord in self.keyWordArray) {
NSPredicate *pred = [NSPredicate predicateWithFormat:@"SELF CONTAINS [cd] %@",keyWord];
BOOL result = [pred evaluateWithObject:self.danMu];
if (result) {
NSLog(@"方案1 -- %@",keyWord);
}
}提测之后, 测试环境一切正常, 但是到了正式环境上, 发现弹幕存在卡顿,? 由于测试环境的弹幕普遍不多(基本不超过100条),? 而正式环境上的弹幕很多都是几千条,在一个3W条弹幕的视频进行测试, 可以感受到明显的卡顿.
抓紧时间进行优化
- 优化判断时机,?
- 缓存NSPredicate对象
优化判断时机,
之前的做法是在开始播放后进行全量的数据判断, 比如说总计有1W条弹幕, 开始播放后, 立即逐个判断弹幕是否合法, 然后存到新数组中, 从新数组中查找弹幕进行展示, 这样的做法就是会导致刚开始播放CPU很高, 而且所有数据处理完成后才能展示弹幕, 在加过滤功能之前, 只要开始播放就可以展示弹幕, 而现在要等2-3S才能开始展示弹幕.
修改判断的时机, 在每次取出弹幕的时候进行判断, 比如这1s取出100条弹幕, 那只判断这100条弹幕是否合法, 不判断全量数据, 虽然判断的总数没有变化, 但是每次判断量很小, 弹幕可以很快出现. 把一个CPU占用的高峰, 分配到了播放的过程中, 平滑CPU的波动.
缓存NSPredicate对象
使用xcode -> instrument查看CPU占用, 发现生成谓词对象和使用谓词判断占用了很多cpu时间, 由于谓词对象是和服务器返回的敏感词绑定的, 而且在播放的过程中没有变化, 可以使用数组来缓存谓词对象, 不需要在每次判断生成一次.
假设总计有1W条弹幕+100个敏感词?进行判断, 那么原始的写法会生成 100W 个临时谓词变量
如果采用缓存谓词对象后, 只需在服务器返回数据后生成100次即可, 后续都是取出谓词进行判断, 可以节省大约100W次谓词生成占用的CPU消耗.
弹幕数量越多, 缓存的优势越明显.
for (NSString *keyWord in self.keyWordArray) {
// 生成谓词对象很费时间
NSPredicate *pred = [NSPredicate predicateWithFormat:@"SELF CONTAINS [cd] %@",keyWord];
BOOL result = [pred evaluateWithObject:self.danMu];
}
优化后写法 🔽🔽🔽
for (NSString *keyWord in self.keyWordArray) {
// 数组缓存谓词对象, 取出谓词进行判断
NSPredicate *pred = [self.predArray objectAtIndex:i];
BOOL result = [pred evaluateWithObject:self.danMu];
}由于多用了缓存, 自然关心一下内存的增长, 如果缓存的谓词对象太大, 导致内存上升几十M,甚至上百M, 那么这个方案,肯定不会通过.
新建一个项目进行验证, 无关因素少, 验证后发现 100个谓词的大小可以忽略不计,
- 原始内存占用 ?106M
- 缓存数据后占用 ?319M,
- 缓存谓词占用增量为213M, 总计缓存100W个谓词对象,平均1W个谓词对象占用2.13M,
- 单个谓词占用约0.2K,实际项目中100个内存占用约20K,可忽略不计
经过了这2个优化, 播放的卡顿已经没有了,按时上线.
以为这就完事了, NO,NO,NO, 虽然经过了优化, 但是谓词判断是否包含占用还是有点大, 就是这一行. 这个是每条弹幕都会调用的, 再找找有没有其他方案进行优化.
BOOL result = [pred evaluateWithObject:self.danMu];
在xcode中搜索是不区分大小写的, 而且搜索很快, 比如搜索 ABC, 是可以搜出来 abc, Abc, ABc, 那么系统应该提供出了类似的api,? 在NSString下搜索contain, 找到了这2个API,?
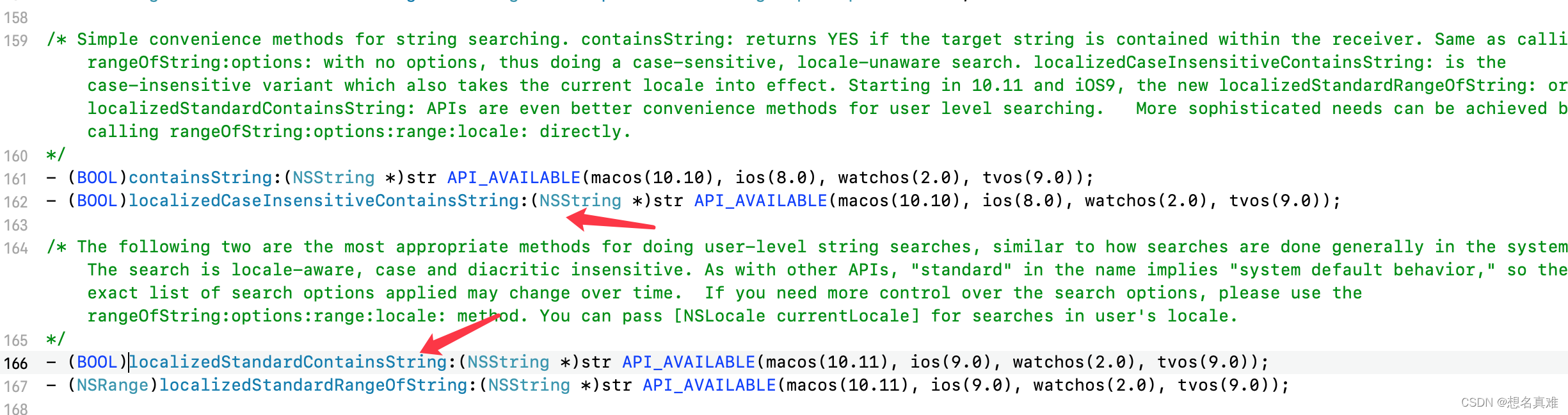
-
- (BOOL)localizedCaseInsensitiveContainsString:(NSString *)str;
返回一个布尔值,通过执行不区分大小写、区分区域设置的搜索,指示该字符串是否包含给定字符串。 -
- (BOOL)localizedStandardContainsString:(NSString *)str;
返回一个布尔值,该值指示字符串是否包含给定字符串,方法是执行不区分大小写和变音符号的区域设置搜索。
通过阅读官方的注释文档, 2个方法很接近, 区别在于是否区分变音符号, 对中文和英文来说应该没有区别. 这2个api最终都会调用此方法.?
- (NSRange)rangeOfString:(NSString *)searchString options:(NSStringCompareOptions)mask range:(NSRange)rangeOfReceiverToSearch locale:(nullable NSLocale *)locale
其中有2个参数着重说下?NSStringCompareOptions 和 NSLocale,?
typedef NS_OPTIONS(NSUInteger, NSStringCompareOptions) {
NSCaseInsensitiveSearch = 1,
NSLiteralSearch = 2, /* Exact character-by-character equivalence */
NSBackwardsSearch = 4, /* Search from end of source string */
NSAnchoredSearch = 8, /* Search is limited to start (or end, if NSBackwardsSearch) of source string */
NSNumericSearch = 64, /* Added in 10.2; Numbers within strings are compared using numeric value, that is, Foo2.txt < Foo7.txt < Foo25.txt; only applies to compare methods, not find */
NSDiacriticInsensitiveSearch API_AVAILABLE(macos(10.5), ios(2.0), watchos(2.0), tvos(9.0)) = 128, /* If specified, ignores diacritics (o-umlaut == o) */
NSWidthInsensitiveSearch API_AVAILABLE(macos(10.5), ios(2.0), watchos(2.0), tvos(9.0)) = 256, /* If specified, ignores width differences ('a' == UFF41) */
NSForcedOrderingSearch API_AVAILABLE(macos(10.5), ios(2.0), watchos(2.0), tvos(9.0)) = 512, /* If specified, comparisons are forced to return either NSOrderedAscending or NSOrderedDescending if the strings are equivalent but not strictly equal, for stability when sorting (e.g. "aaa" > "AAA" with NSCaseInsensitiveSearch specified) */
NSRegularExpressionSearch API_AVAILABLE(macos(10.7), ios(3.2), watchos(2.0), tvos(9.0)) = 1024 /* Applies to rangeOfString:..., stringByReplacingOccurrencesOfString:..., and replaceOccurrencesOfString:... methods only; the search string is treated as an ICU-compatible regular expression; if set, no other options can apply except NSCaseInsensitiveSearch and NSAnchoredSearch */
};- NSCaseInsensitiveSearch = 1,//不区分大小写的搜索
- NSLiteralSearch = 2, ? ? ? ?/* 精确的逐个字符串等价, - isEqualToString, Exact character-by-character equivalence */
- NSBackwardsSearch = 4, ? ? ?/*从源字符串的末尾搜索、 Search from end of source string */
- NSAnchoredSearch = 8, ? ? ? /*搜索仅限于开始(或结束,如果是从末尾开始的搜索)源字符串 Search is limited to start (or end, if NSBackwardsSearch) of source string */
- NSNumericSearch = 64, ? ? ? /*。用字符串中的数字的值进行比较, Added in 10.2; Numbers within strings are compared using numeric value, that is, Foo2.txt < Foo7.txt < Foo25.txt; only applies to compare methods, not find */
- NSDiacriticInsensitiveSearch = 128, /*搜索忽略变音符号。 If specified, ignores diacritics (o-umlaut == o) */
- NSWidthInsensitiveSearch = 256 /* 搜索忽略具有全宽和半宽形式的字符的宽度差异,例如在东亚字符串集。If specified, ignores width differences ('a' == UFF41) */
- NSForcedOrderingSearch = 512 /* 如果字符串是等效的但不是严格相等的,比较会被强制返回same,例如 "aaa"和"AAA" 会返回same。 */
- NSRegularExpressionSearch = 1024?/* 只在rangeOfString:...、stringByReplacingOccurrencesOfString:...和replaceOccurrencesOfString:...方法中适用。搜索字符串被视为与ICU兼容的正则表达式。如果设置了这个选项,那么其余选项除了NSCaseInsensitiveSearch和NSAnchoredSearch,别的都不能使用 */
看来这2个的api差别就在于有没有设置NSDiacriticInsensitiveSearch ,? 同时还发现支持忽略标点符号,设置NSWidthInsensitiveSearch, 就可以忽略中文英文标点.
至于NSLocale, 就参考这篇文章??NSLocale的重要性和用法简介 - 简书
到此, 我们已经有4个方案了, 对比一下4个方案的性能,?
- 使用谓词, 不缓存谓词, 每次使用临时变量
- 使用谓词, 缓存谓词, 把谓词对象缓存到集合中
- 使用NSString的方法, 使用支持变音的版本, ios9之后可用
- 使用NSString的方法, 使用不支持变音的版本, ios 8之后可用
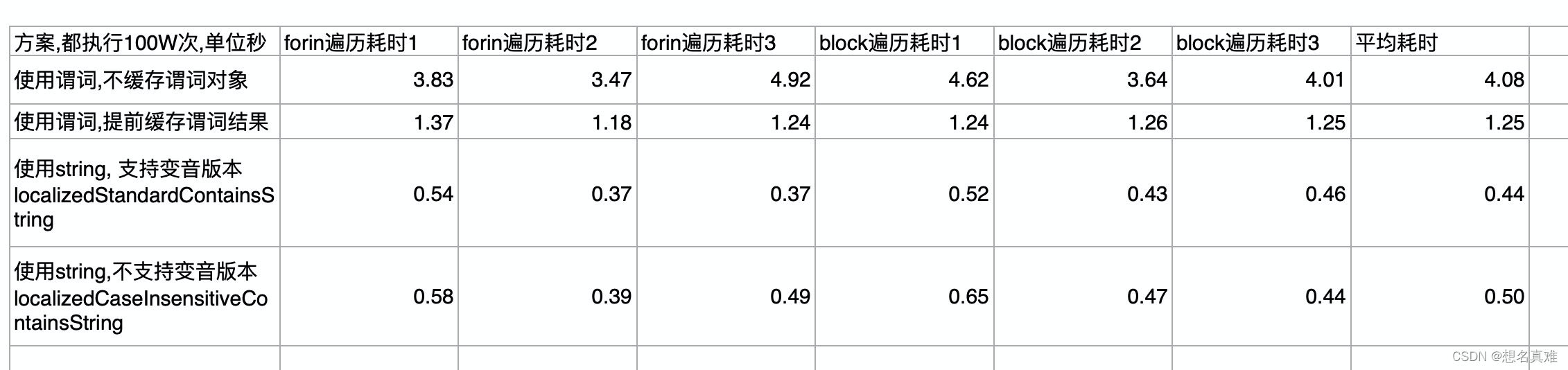
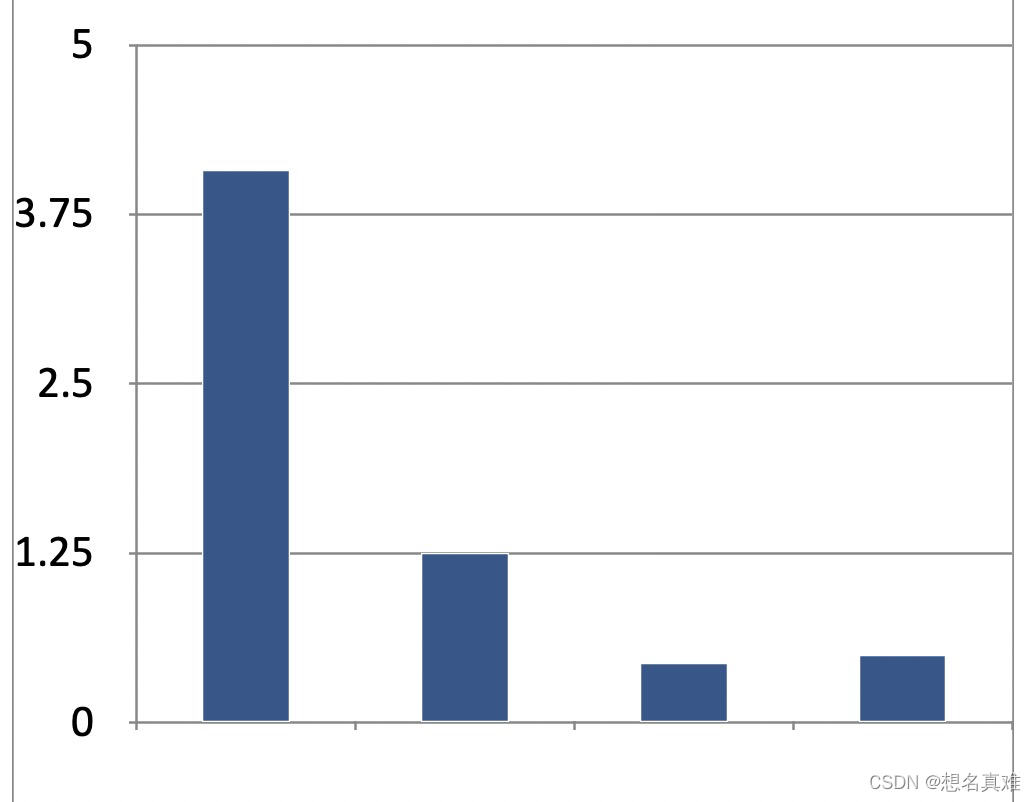
总体来看,
- 使用String的效率比使用谓词要高效很多,
即使缓存谓词, 使用谓词判断的耗时还是使用String判断的2倍以上, 所以, 可以考虑使用谓词方案替换成使用string的方案. 而2个string方案效率差别不大. - 使用谓词的好处也是有的, 就是比较灵活, 可以自由组合判断条件, 这点是String做不到的.
- 使用谓词缓存, 可以提升3倍左右的效率.弹幕数量越多, 缓存的优势越明显.
- 2个string版本中, 变音版本效率略高, 可能系统在ios9之后偷偷优化了实现, 推荐使用
- 使用forin遍历效率比block遍历的效率略高一点点, 但是差别不大. 实际开发中基本无感觉
?最后, 附上压力测试的代码:?
#import "ViewController.h"
@interface ViewController ()
/// 敏感词数组
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSArray *keyWordArray;
/// 用户发送的文案
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *danMu;
// 遍历使用的方式
@property (nonatomic, assign) NSInteger type;
// 缓存谓词对象
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSArray <NSPredicate *>*predArray;
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
// 模拟数据,压力测试, 假设有100W条敏感词
NSMutableArray *array = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:10000];
for (NSInteger i = 0; i<10000 * 100; i++) {
[array addObject:NSUUID.UUID.UUIDString];
}
[array addObject:@"敏感词1a"];
self.keyWordArray = [array copy];
self.danMu = @"来了,敏感词1A";
self.type = 1;
// 提前处理好谓词数组
NSMutableArray *predArray = [NSMutableArray arrayWithCapacity:self.keyWordArray.count];
for (NSString *keyWord in self.keyWordArray) {
NSPredicate *pred = [NSPredicate predicateWithFormat:@"SELF CONTAINS [cd] %@",keyWord];
[predArray addObject:pred];
}
self.predArray = [predArray copy];
#pragma mark - 开始测试
// 100W条数据 3.83S, 3.47S 4.92S forin遍历
// 100W条数据 4.62S, 3.64S 4.01S block遍历, 使用block遍历还要略慢一点
// 缓存谓词结果后,100W条数据 0.67S 0.83S 0.71S, 比下面的2种方案性能还是差, 但是在可接受范围内
CFTimeInterval start = CACurrentMediaTime();
[self test1];
CFTimeInterval end = CACurrentMediaTime();
NSLog(@"方案1 %@",@(end-start));
// 提前处理好谓词缓存
// 100W条数据 1.37S 1.18S 1.24S forin遍历
// 100W条数据 1.24S 1.26S 1.25S block遍历
// 原始内存占用 106M
// 缓存数据后占用 319M,
// 缓存占用增量为213M,缓存100W个对象,平均1W个对象占用2.13M,单个谓词占用0.2K,实际项目中100个内存占用约20K, 可忽略不计
start = CACurrentMediaTime();
[self test11];
end = CACurrentMediaTime();
NSLog(@"方案11 %@",@(end-start));
// 100W条数据 0.54S 0.37S 0.37S forin遍历
// 100W条数据 0.52S 0.43S 0.46S block遍历
start = CACurrentMediaTime();
[self test2];
end = CACurrentMediaTime();
NSLog(@"方案2 %@",@(end-start));
// 100W条数据 0.58S 0.39S 0.49S forin遍历
// 100W条数据 0.65S 0.44S 0.47S block遍历
start = CACurrentMediaTime();
[self test3];
end = CACurrentMediaTime();
NSLog(@"方案3 %@",@(end-start));
#pragma mark 结束测试
}
- (void)test1 {
// 方案1, 使用谓词,可以比较,不区分大小写
if (self.type == 0) {
for (NSString *keyWord in self.keyWordArray) {
// 生成谓词对象很费时间,可以用数组缓存谓词对象
NSPredicate *pred = [NSPredicate predicateWithFormat:@"SELF CONTAINS [cd] %@",keyWord];
BOOL result = [pred evaluateWithObject:self.danMu];
if (result) {
NSLog(@"方案1 -- %@",keyWord);
}
}
} else if (self.type == 1) {
[self.keyWordArray enumerateObjectsUsingBlock:^(NSString * _Nonnull keyWord, NSUInteger idx, BOOL * _Nonnull stop) {
NSPredicate *pred = [NSPredicate predicateWithFormat:@"SELF CONTAINS [cd] %@",keyWord];
BOOL result = [pred evaluateWithObject:self.danMu];
if (result) {
NSLog(@"方案1 -- %@",keyWord);
}
}];
}
}
- (void)test11 {
// 方案11, 使用谓词,缓存谓词结果
if (self.type == 0) {
NSInteger i = 0;
for (NSString *keyWord in self.keyWordArray) {
// 生成谓词对象很费时间,可以用数组缓存谓词对象
NSPredicate *pred = [self.predArray objectAtIndex:i];
BOOL result = [pred evaluateWithObject:self.danMu];
if (result) {
NSLog(@"方案11 -- %@",keyWord);
}
i++;
}
} else if (self.type == 1) {
[self.keyWordArray enumerateObjectsUsingBlock:^(NSString * _Nonnull keyWord, NSUInteger idx, BOOL * _Nonnull stop) {
NSPredicate *pred = [self.predArray objectAtIndex:idx];
BOOL result = [pred evaluateWithObject:self.danMu];
if (result) {
NSLog(@"方案11 -- %@",keyWord);
}
}];
}
}
// 支持变音版本
- (void)test2 {
if (self.type == 0) {
for (NSString *keyWord in self.keyWordArray) {
BOOL result = [self.danMu localizedStandardContainsString:keyWord];
if (result) {
NSLog(@"方案2 -- %@",keyWord);
}
}
} else if (self.type == 1) {
[self.keyWordArray enumerateObjectsUsingBlock:^(NSString * _Nonnull keyWord, NSUInteger idx, BOOL * _Nonnull stop) {
BOOL result = [self.danMu localizedStandardContainsString:keyWord];
if (result) {
NSLog(@"方案2 -- %@",keyWord);
}
}];
}
}
// 不支持变音版本
- (void)test3 {
if (self.type == 0) {
for (NSString *keyWord in self.keyWordArray) {
BOOL result = [self.danMu localizedCaseInsensitiveContainsString:keyWord];
if (result) {
NSLog(@"方案3 -- %@",keyWord);
}
}
} else if (self.type == 1) {
[self.keyWordArray enumerateObjectsUsingBlock:^(NSString * _Nonnull keyWord, NSUInteger idx, BOOL * _Nonnull stop) {
BOOL result = [self.danMu localizedCaseInsensitiveContainsString:keyWord];
if (result) {
NSLog(@"方案3 -- %@",keyWord);
}
}];
}
}
// 忽略大小写进行比较是否相等,
- (void)test10 {
NSComparisonResult result = [@"abc" caseInsensitiveCompare:@"ABc"];
// a < b , NSOrderedAscending. -1
// a == b , NSOrderedSame. 0
// a > b , NSOrderedDescending. 1
NSLog(@"caseInsensitiveCompare -- %zd",result);
}
@end