一、建立开发环境
1、AS简介
Android Studio 是Google开发的一款面向Android开发者的IDE,支持Windows、Mac、Linux等操作系统,基于流行的开发语言java集成开发环境IntelliJ搭建而成的,类似Eclipse ADT。该IDE在2003年5月的Google I/O开发者大会首次露面,当时的测试版本还不够完善,直到2014年12月8日发布了稳定的版本。Android Studio 提供了集成的 Android 开发工具用于开发和调试。
1)基于 Gradle 的灵活构建系统
2)快速且功能丰富的模拟器
3)可针对所有 Android 设备进行开发的统一环境
4)Instant Run,可将变更推送到正在运行的应用,无需构建新的 APK
5)可帮助您构建常用应用功能和导入示例代码的代码模板和 GitHub 集成
6)丰富的测试工具和框架
7)可捕捉性能、易用性、版本兼容性以及其他问题的 Lint 工具
8)C++ 和 NDK 支持
9)内置对 Google 云端平台的支持,可轻松集成 Google Cloud Messaging 和 App 引擎
2、环境的搭建
可参考:https://blog.csdn.net/u014720022/article/details/93320488
系统要求:Win7或更高、内存 最少 4 GB ,建议8 GB RAM、硬盘 4G
1)下载JDK
官网站:https://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/jdk8-downloads-2133151.html
2)下载AS
官方下载地址:https://developer.android.google.cn/studio/
3)安装JDK及Java环境
4)安装Android Studio
5)搭建环境所碰到的坑
安装Android Studio时,无法安装Android Studio的SDK组件
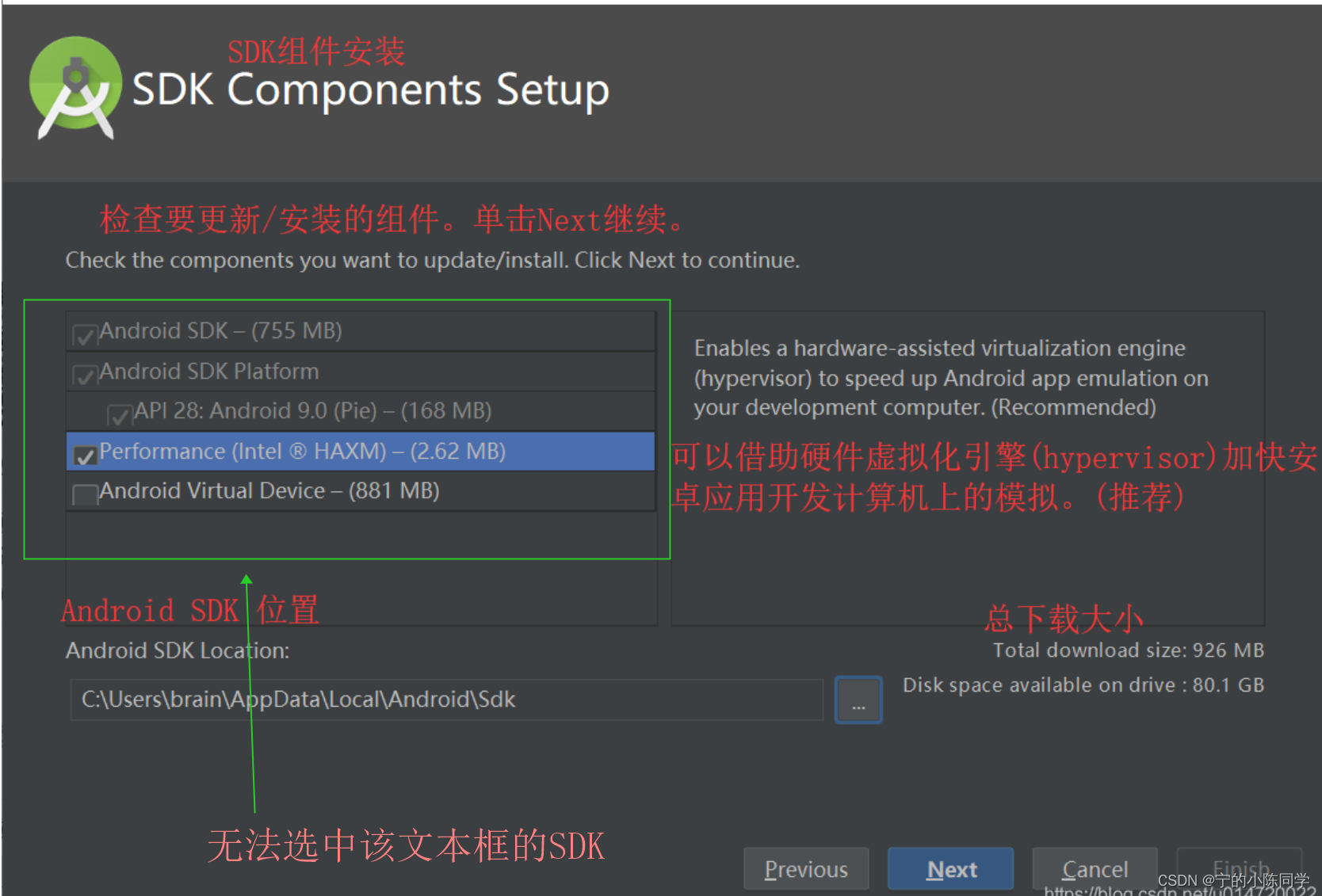
这个问题特别折磨人,经过多次排查和反复安装后发现主要是网络问题导致的,安装前需要关掉防火墙。关掉防火墙后,必须把之前安装的Android Studio卸载掉,再重新进行安装才生效。
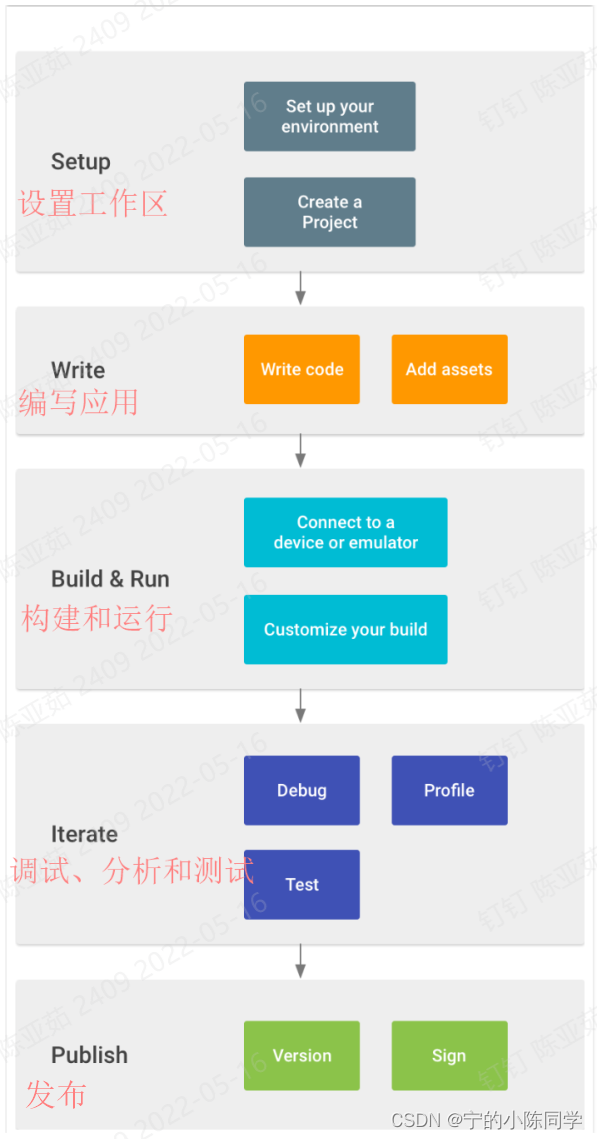
3、开发步骤
二、开发教程-计算器
1、概述
一个简单的Android App开发,这个App是个简单的计算器,支持简单的加减乘除的运算
2、创建应用
1)双击,启动Android Studio
2)创建项目,选择New Project
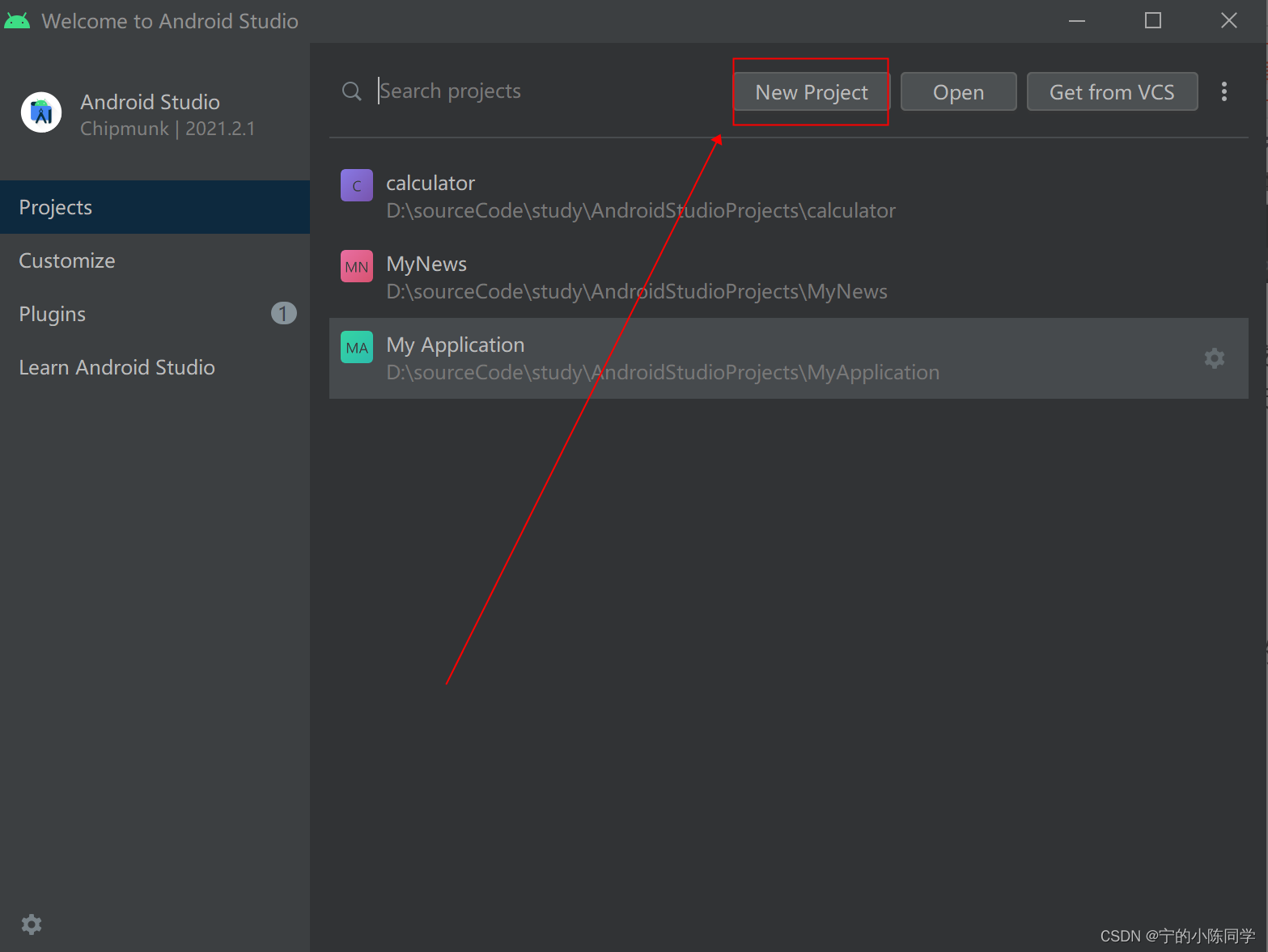
如果是已有的项目,在列表中存在时就直接选择,不存在时点击Open选中对应的文件夹
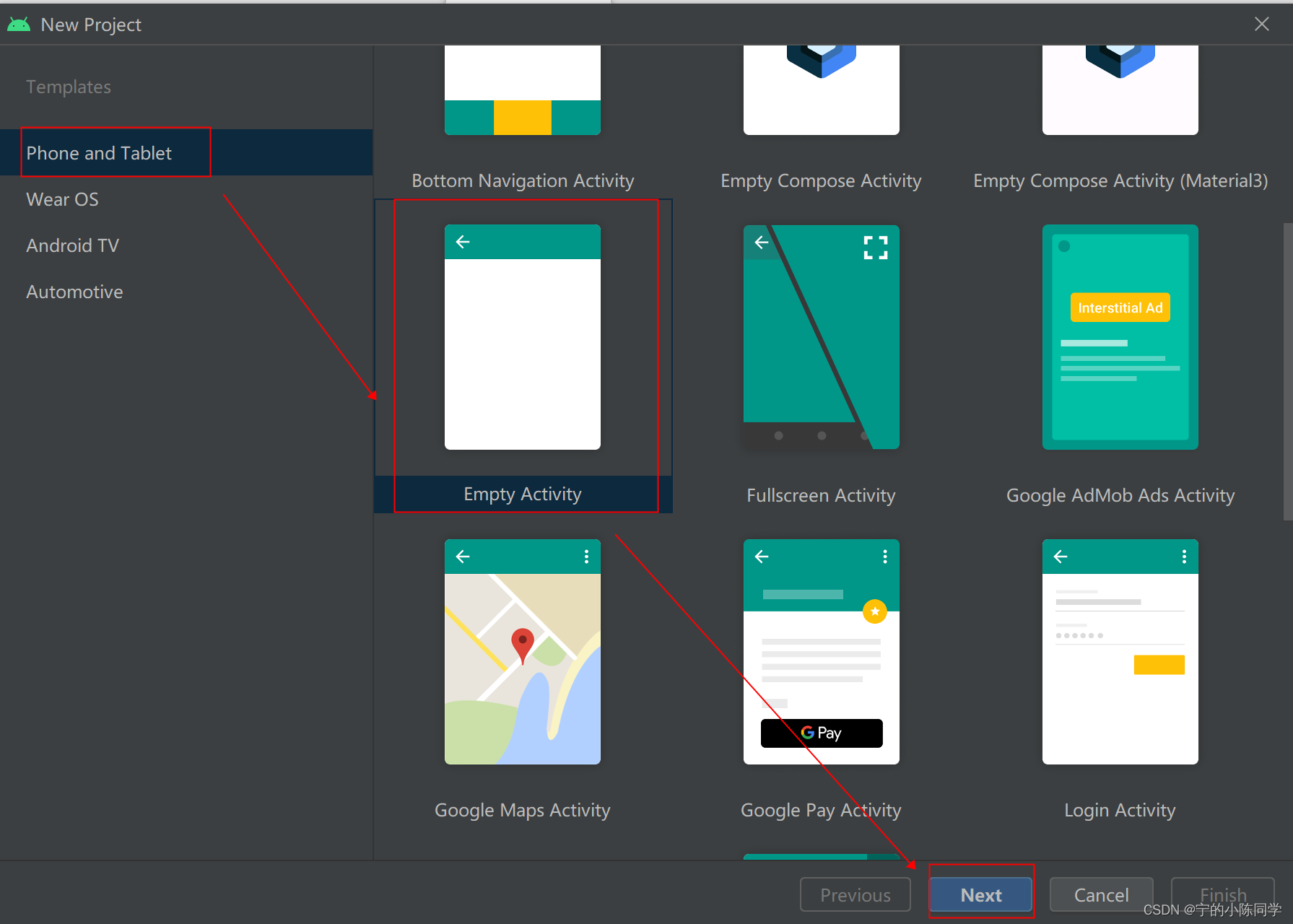
3)选择想要创建的Android版本
建议选择empty activity(空模板),然后点击next
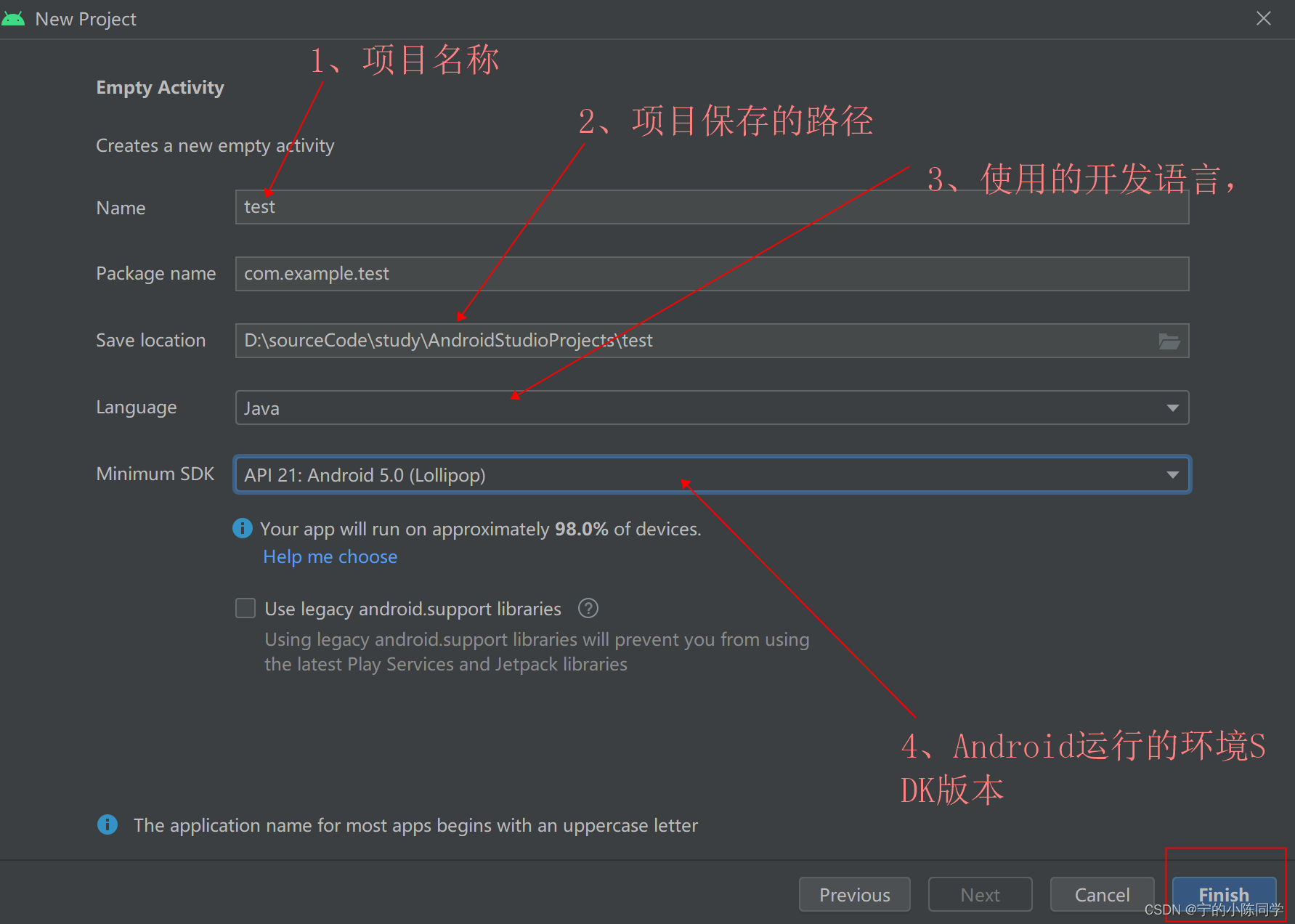
4)填写项目信息
本项目主要使用的开发语言是JAVA。其中,Minimum SDK版本是Andriod虚拟机运行的版本,版本越低运行越快,根据个人要求来选择(我这边是直接选择默认的),然后点击finish
3、项目结构
新手开发,建议还是熟悉下项目的整体结构,更有利于整体的开发。
可参考:http://t.csdn.cn/j8U14
4、熟悉Android Studio
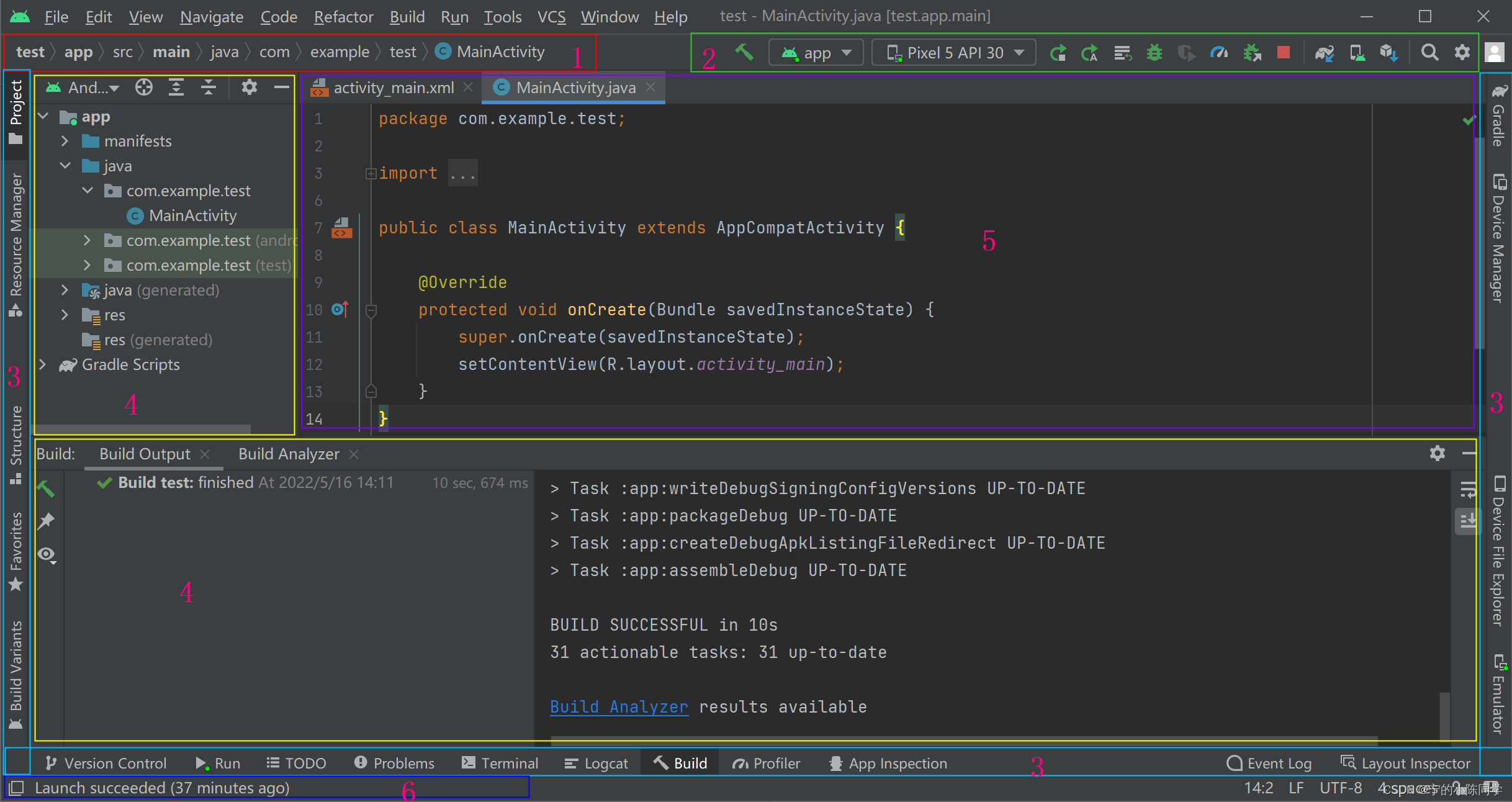
1:导航栏可帮助我们在项目中导航,以及打开文件进行编辑。此区域提供 Project 窗口所示结构的精简视图。
2:工具栏提供执行各种操作的工具,包括运行应用和启动 Android 工具。
3:工具窗口栏在 IDE 窗口外部运行,并且包含可用于展开或折叠各个工具窗口的按钮。
4:工具窗口提供对特定任务的访问,例如项目管理、搜索和版本控制等。我们可以展开和折叠这些窗口。
5:编辑器窗口是创建和修改代码的区域。 编辑器可能因当前文件类型的不同而有所差异。 例如,在查看布局文件时,编辑器显示布局编辑器。
6:状态栏显示项目和 IDE 本身的状态以及任何警告或消息。
5、设置手机模拟机(需联网下载)
1)点击模拟机设置图标,右边弹窗出来选择Virtual,之后点击Create device
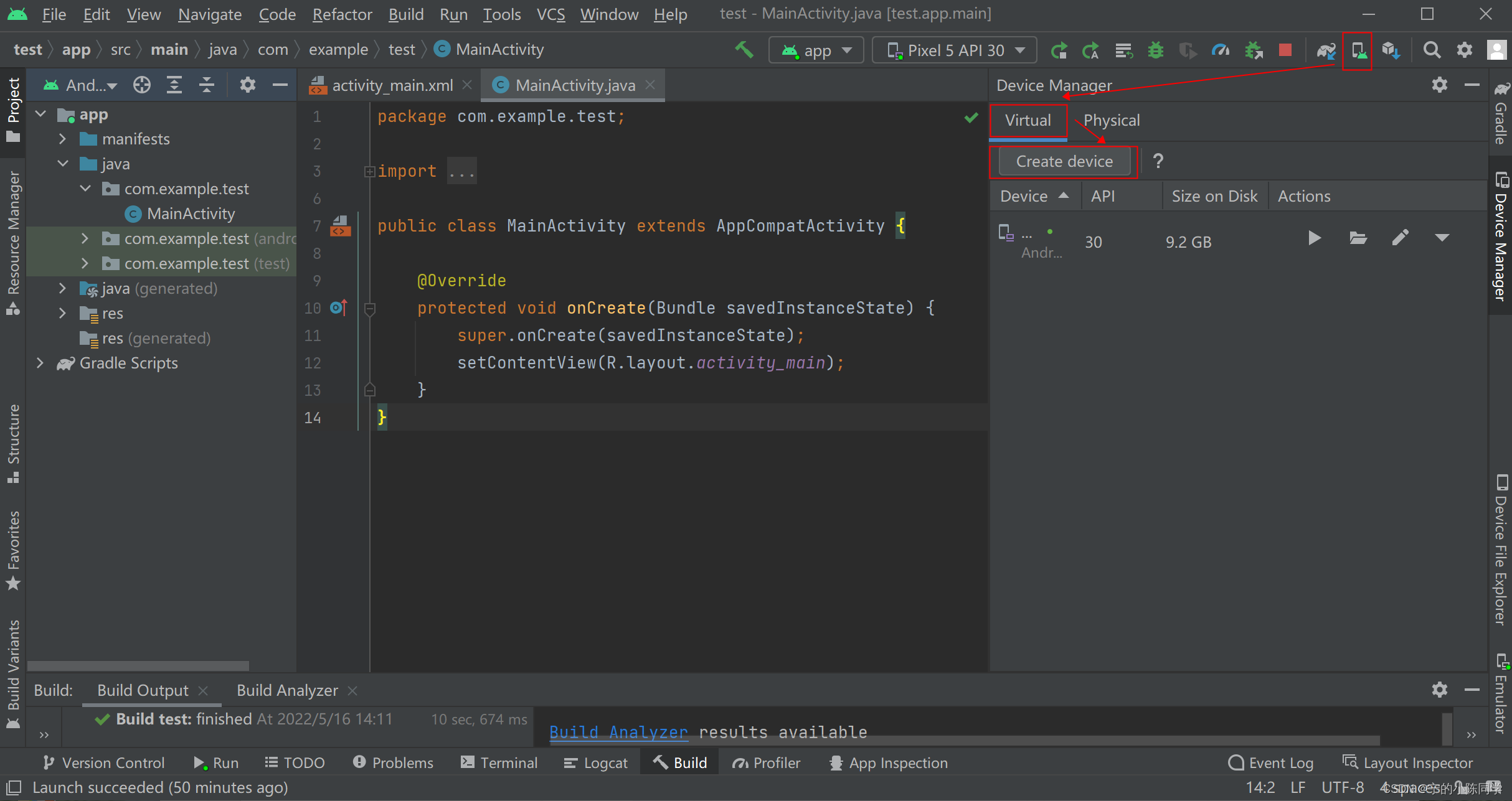
2)点击Phone,选择想要的手机类型,点击next
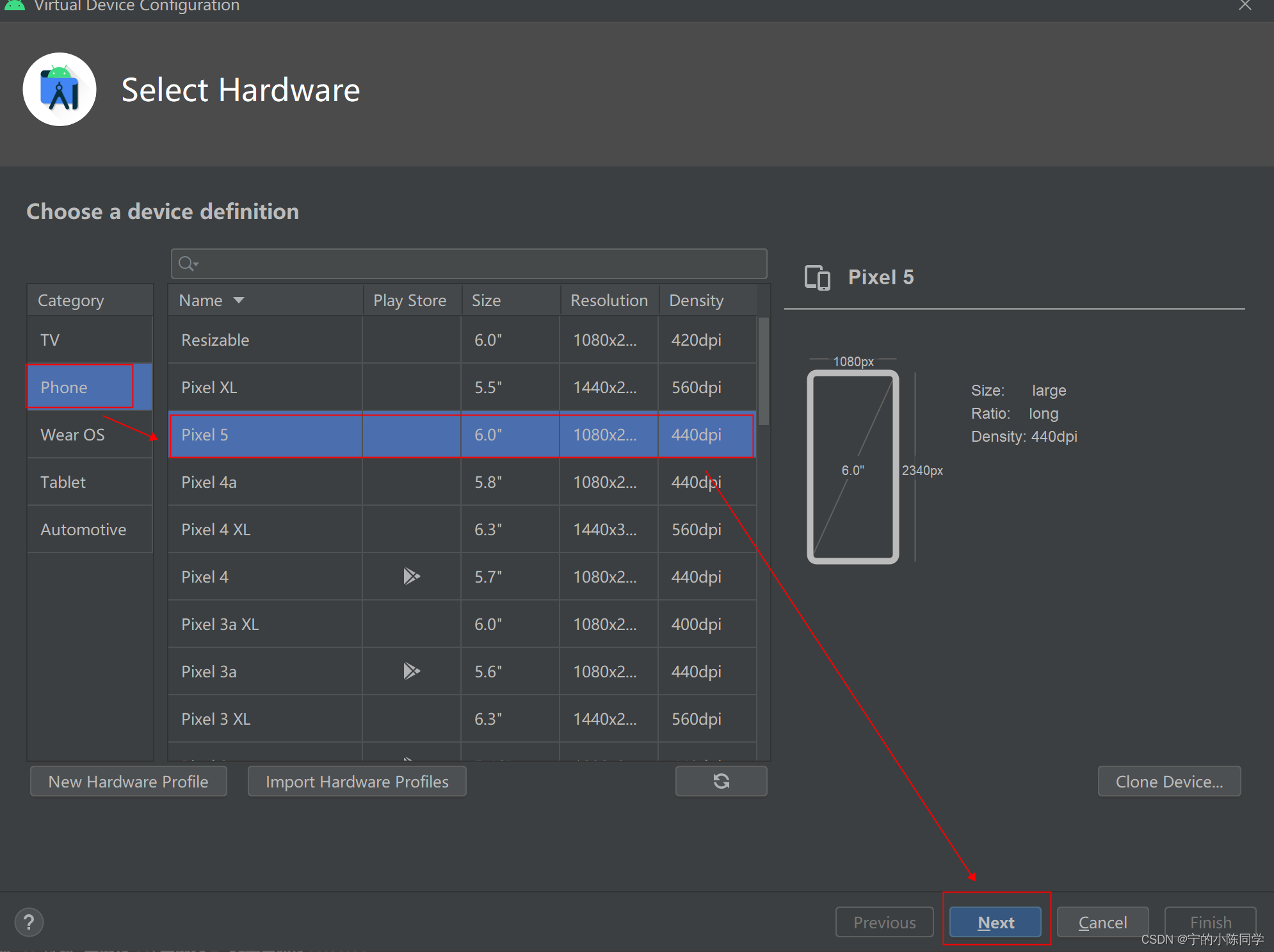
3)选择对应的类型,点击next
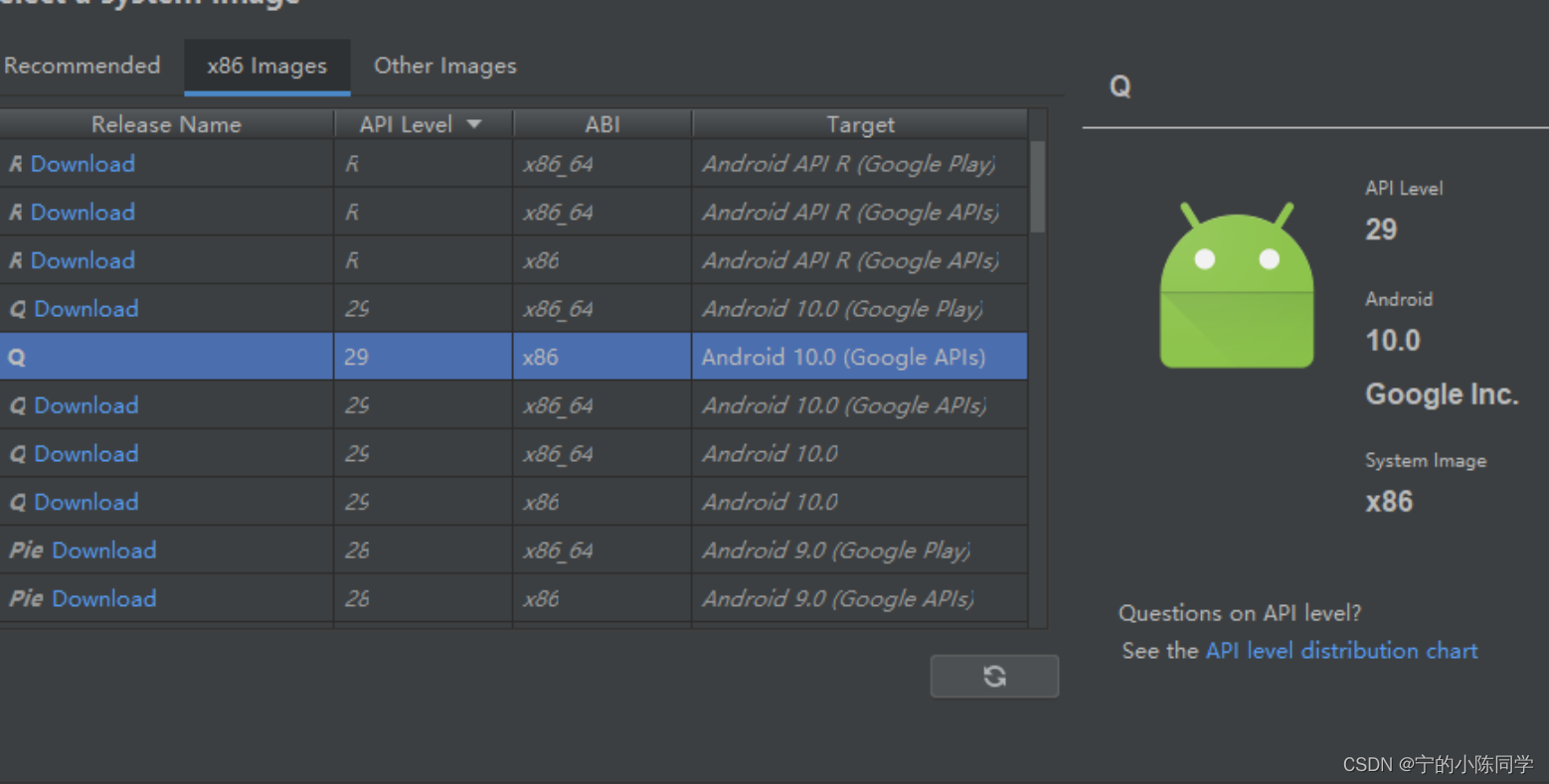
4)给该模拟机命名,点击finish,就会开始下载该模拟机
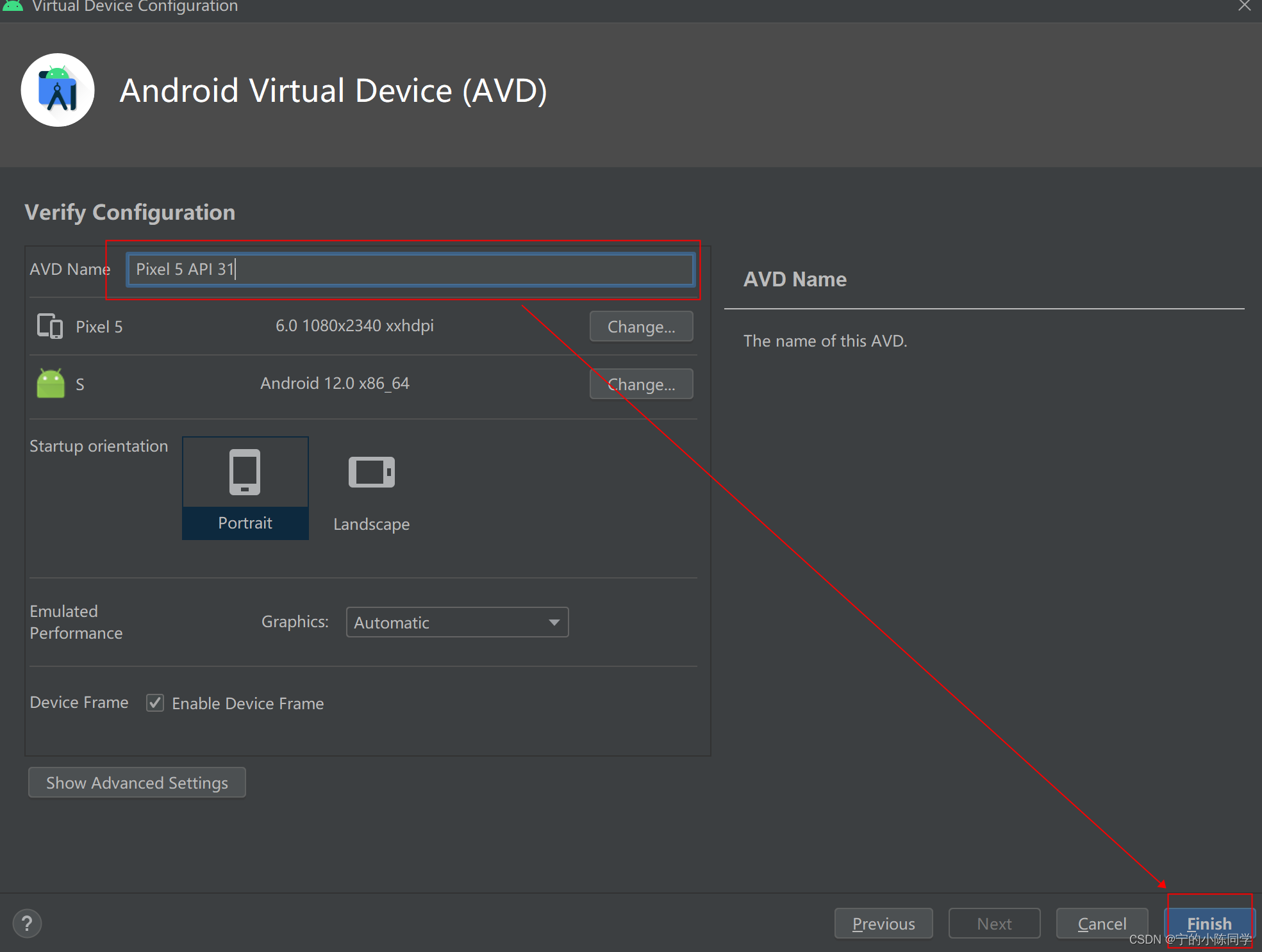
5)测试模拟机是否下载成功
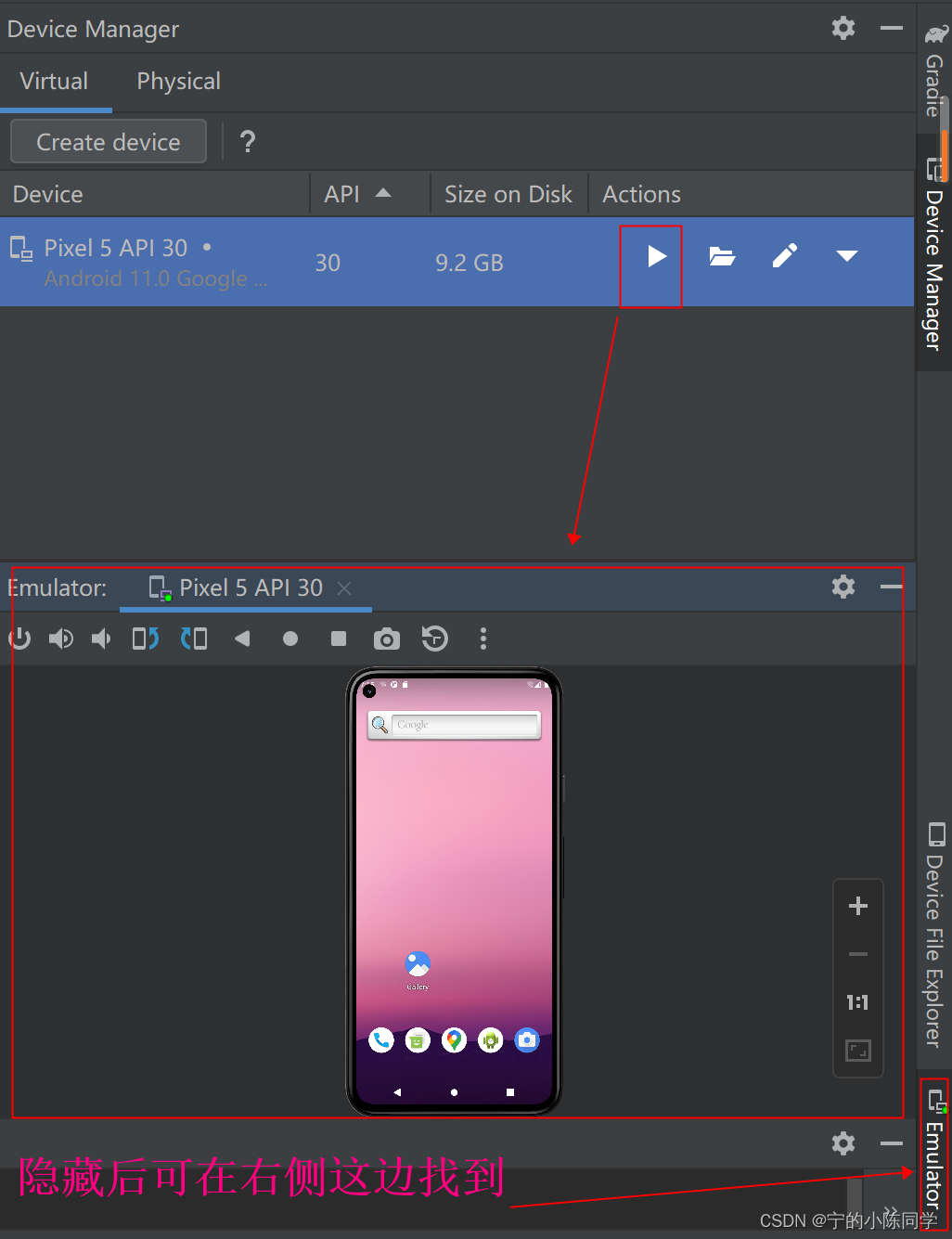
6)调试默认模板的项目,看是否成功。失败的话,可以进入Build看报错原因
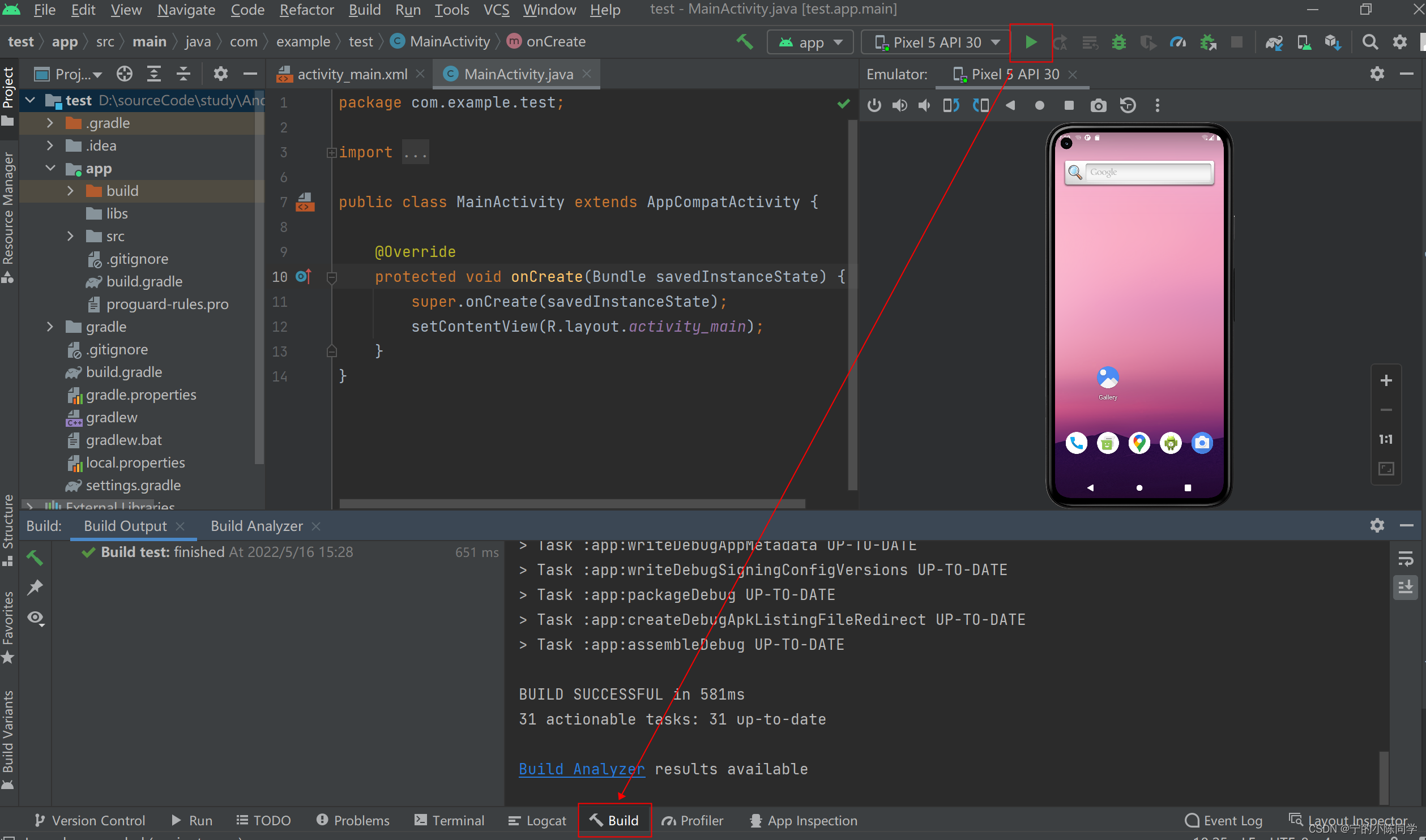
6、开始进入编写项目
写代码的过程中,记得写完一个模块就调试下,看有没有出现bug,及时解决
该项目是个简单的计算器的应用,没有页面间的交互,所以主要的围绕以下的三个文件:
MainActivity.java:提供了用户与屏幕之间的互动,以便于用户进行操作,在里面实现主要的Java代码
activity_main.xml:布局文件,Android的UI界面显示的视图,所有的控件在这里设计
AndroidManifest.xml:Android应用程序的清单文件,是整个Android应用程序的描述文件
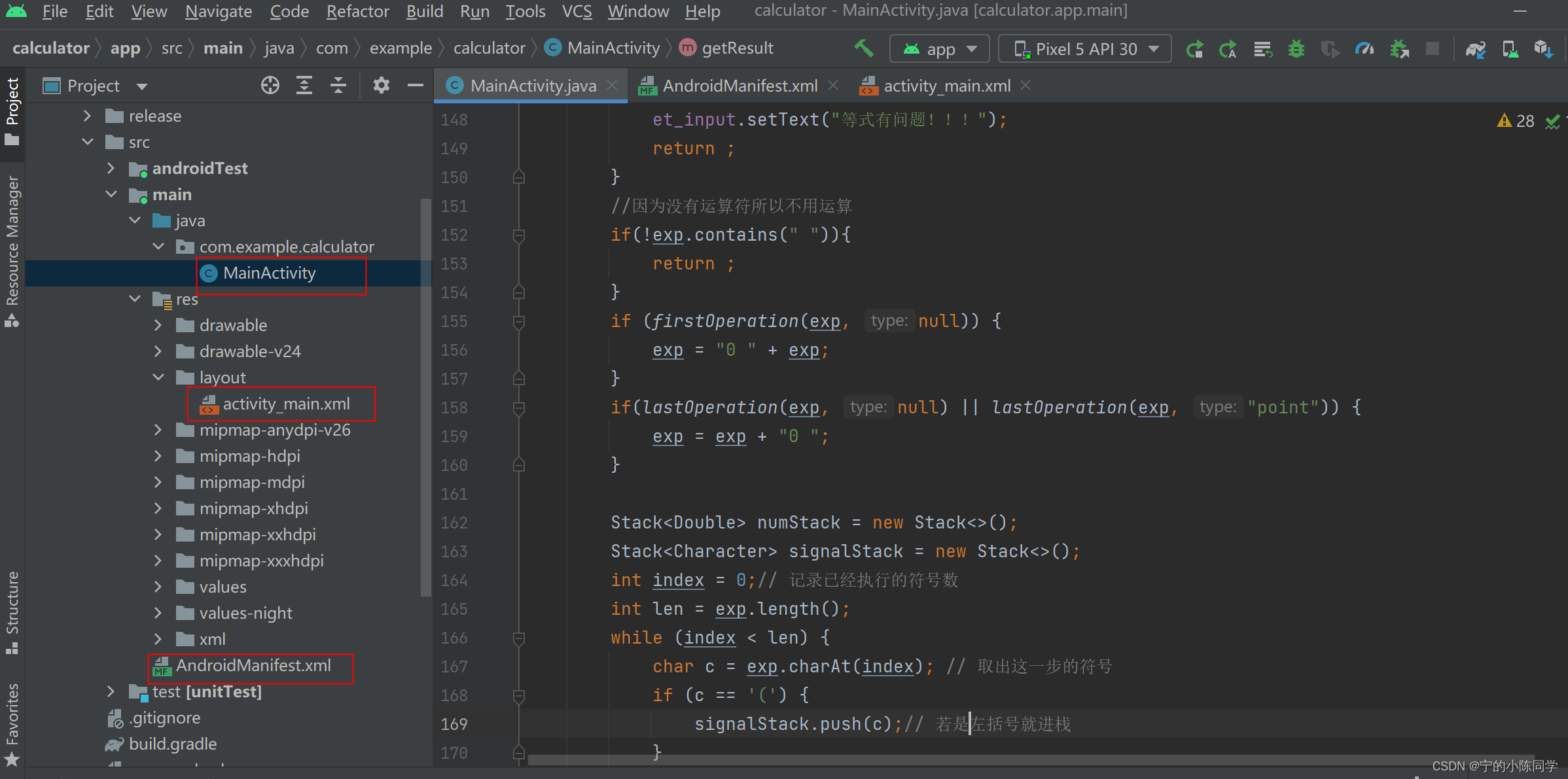
1)activity_main.xml
- 先将android.support.constraint.ConstraintLayout改为LinerLayout线性的,意思就是水平的的结构
- 并加入android:orientation="vertical"意思是将所有组件垂直摆放
- 设置背景色为黑色
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity"
android:background="#000000" >
</LinearLayout>
- 设置数字显示框的样式
<EditText
android:id="@+id/et_input"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="80dp"
android:background="@drawable/white"
android:clickable="false"
android:editable="false"
android:paddingBottom="5dp"
android:textSize="32sp" />
- 结合LinerLayout线性的布局方式,设置各个按钮样式,以下列举两个按钮,其他按钮也是类型此布局
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="30dp"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_clr"
android:layout_width="170dp"
android:layout_height="70dp"
android:text="C"
android:textSize="30sp"
android:paddingRight="15sp"
android:paddingBottom="15sp"
android:background="@drawable/selector"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_del"
android:layout_width="170dp"
android:layout_height="70dp"
android:text="?"
android:textSize="30sp"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:paddingRight="15sp"
android:paddingBottom="15sp"
android:background="@drawable/selector"/>
</LinearLayout>
- 上面的android:id="@+id/btn_del"是为了在MainActivity.java可以准确获取到各个布局的id,便于整个业务交互逻辑的操作
- 上面的android:background是自定义了该布局的样式,主要在drawable文件里创建文件并自己画出样式后,再直接引用,这边便不细说了。
2)MainActivity.java
- 先获取到各个按钮,再进行点击事件监听
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
//创建Button对象 也就是activity_main.xml里所设置的ID
Button btn_0,btn_1,btn_2,btn_3,btn_4,btn_5,btn_6,btn_7,btn_8,btn_9,btn_pt;
Button btn_mul,btn_div,btn_add,btn_sub;
Button btn_clr,btn_del,btn_eq;
Button btn_left,btn_right;
EditText et_input;
Boolean resErr = false;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//实例化对象
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
btn_0= (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_0);
btn_1= (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_1);
btn_2= (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_2);
btn_3= (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_3);
btn_4= (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_4);
btn_5= (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_5);
btn_6= (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_6);
btn_7= (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_7);
btn_8= (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_8);
btn_9= (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_9);
btn_pt= (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_pt);
btn_add= (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_add);
btn_sub= (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_sub);
btn_mul= (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_mul);
btn_div= (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_div);
btn_clr= (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_clr);
btn_del= (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_del);
btn_eq= (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_eq);
et_input= (EditText) findViewById(R.id.et_input);
btn_left= (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_left);
btn_right= (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_right);
//给按钮设置的点击事件
btn_0.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_1.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_2.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_3.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_4.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_5.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_6.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_7.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_8.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_9.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_pt.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_add.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_sub.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_mul.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_div.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_clr.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_del.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_eq.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_left.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_right.setOnClickListener(this);
}
}
- 之后开始进入编写点击事件
左括号:1、若已有输入且前一位不是运算符号,则默认在左括号前面加?
右括号:1、等式必须存在左括号才允许输入;2、若前一位是小数点,则默认在右括号前面加0
加减乘除运算符号:1、前一位必须不是运算符号才允许输入;2、若前一位是小数点,则默认在运算符号前面加0
小数点:1、若在当前输入的位置至前一个运算符号这一串字符串,存在小数点的话,则不允许输入小数点(例如:1.12 - 1 + 2.11);2、若前一位是运算符号或左括号或未输入字符时,默认在小数点前面补0
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
if(resErr) {
et_input.setText("");
resErr = false;
}
String str=et_input.getText().toString();
switch (v.getId()){
case R.id.btn_0:
case R.id.btn_1:
case R.id.btn_2:
case R.id.btn_3:
case R.id.btn_4:
case R.id.btn_5:
case R.id.btn_6:
case R.id.btn_7:
case R.id.btn_8:
case R.id.btn_9:
et_input.setText(str+((Button)v).getText());
break;
case R.id.btn_left:
if(!str.equals("") && !lastOperation(str, null)) {
str = str + " × ";
}
et_input.setText(str+((Button)v).getText());
break;
case R.id.btn_right:
if (str.indexOf("(") != -1) {
if (lastOperation(str, "point")) {
str = str + "0";
}
et_input.setText(str+((Button)v).getText());
}
break;
case R.id.btn_add:
case R.id.btn_sub:
case R.id.btn_mul:
case R.id.btn_div:
if (lastOperation(str, "point")) {
str = str + "0";
}
if(!lastOperation(str, null)) {
et_input.setText(str+" "+((Button)v).getText()+" ");
}
break;
case R.id.btn_pt:
if (!hasPoint(str)) {
if (lastOperation(str, null) || lastOperation(str, "left") || str.equals("")) {
str = str + "0";
}
et_input.setText(str+((Button)v).getText());
}
break;
case R.id.btn_clr:
et_input.setText("");
break;
case R.id.btn_del: //判断是否为空,然后在进行删除
if(str != null && !str.equals("")){
et_input.setText(str.substring(0, str.length() - 1));
}
break;
case R.id.btn_eq: //单独运算最后结果
getResult();//调用下面的方法
break;
}
}
// 判断首位是否为运算符号、小数点
private static Boolean firstOperation(String str, String type) {
String newStr = str.trim();
if (newStr.equals("")) return false;
char firstChar = newStr.charAt(0);
if (type == "point") {
return firstChar == '.';
} else if(type == "left"){
return firstChar == '(';
}else if(type == "right"){
return firstChar == ')';
} else {
return firstChar == '+' || firstChar == '-' || firstChar == '×' || firstChar == '÷';
}
}
// 判断末位是否为运算符号、小数点
private static Boolean lastOperation(String str, String type) {
String newStr = str.trim();
if (newStr.equals("")) return false;
char lastChar = newStr.charAt(newStr.length()-1);
if (type == "point") {
return lastChar == '.';
} else if(type == "left"){
return lastChar == '(';
} else if(type == "right"){
return lastChar == ')';
} else {
return lastChar == '+' || lastChar == '-' || lastChar == '×' || lastChar == '÷';
}
}
// 判断当前输入到运算符前,是否有小数点
private static Boolean hasPoint(String str) {
int index = 0;
String[] operationArr = {"+", "-", "×", "÷"};
for(int i = 0; i < operationArr.length; i++) {
int w = str.lastIndexOf(operationArr[i]);
if (w > index) index = w;
}
String newStr = str.substring(index);
return newStr.indexOf(".") != -1;
}
- 点击计算最终结果
1、左右括号数量不对等,等式有问题
2、第一位是运算符号时,最前面补0
3、最后一位是运算符号或小数点时,最后面补0
4、整体运算逻辑根据进出栈来实现的,共有两个栈:数字numStack 、非数字(运算符号和括号)signalStack 。
遍历计算公式后,
数字的话,进栈numStack
非数字的话,需要先判断其运算等级是否大于signalStack 的最后一位,若大于则进栈signalStack ;而小于的话,numStack 出栈两个数字,signalStack 出栈一个运算符号,计算结果入栈numStack;之后继续判断该非数字的运算等级和signalStack 的最后一位的大小,结果循环上述的,直到其能入栈signalStack
private void getResult() {
String exp=et_input.getText().toString();
if(exp==null||exp.equals("")) return ;
resErr = false;
// 判断括号是否正确
if (getNum(exp, "(") != getNum(exp, ")")) {
resErr = true;
et_input.setText("等式有问题!!!");
return ;
}
//因为没有运算符所以不用运算
if(!exp.contains(" ")){
return ;
}
if (firstOperation(exp, null)) {
exp = "0 " + exp;
}
if(lastOperation(exp, null) || lastOperation(exp, "point")) {
exp = exp + "0 ";
}
Stack<Double> numStack = new Stack<>();
Stack<Character> signalStack = new Stack<>();
int index = 0;// 记录已经执行的符号数
int len = exp.length();
while (index < len) {
char c = exp.charAt(index); // 取出这一步的符号
if (c == '(') {
signalStack.push(c);// 若是左括号就进栈
}
// 否则要先判断优先级
else if (c == '+' || c == '-' || c == '×' || c == '÷') {
int currOperLevel = getOperlevel(c);// 当前符号的优先级
while (true) {
int stackOperLevel = 0;// 栈顶元素的优先级
if (!signalStack.isEmpty()) {
Object obj = signalStack.peek();
stackOperLevel = getOperlevel((char) obj);
}
// 若当前元素优先级大于栈顶元素的优先级则入栈
if (currOperLevel > stackOperLevel) {
signalStack.push(c);
break;// 直到让比自己优先级高的符号都出栈运算了再把自己进栈
} else {// 不能入栈就进行计算
try {
char optemp = '0';
double num1 = 0;
double num2 = 0;
if (!signalStack.isEmpty()) {
optemp = (char) signalStack.pop();// 取出优先级大的那个符号
}
if (!numStack.isEmpty()) {
num1 = (double) numStack.pop();
num2 = (double) numStack.pop();// 取出数据栈中的两个数
}
numStack.push(caculateResult(optemp, num2, num1));// 将算出来的结果数据再次进入数据栈
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
} else if (c == ')') {// 右括号就返回栈顶元素,右括号是不进栈的
while (true) {
char theop = (char) signalStack.pop();
if (theop == '(') {
break;
} else {
try {
double num1 = (double) numStack.pop();
double num2 = (double) numStack.pop();
numStack.push(caculateResult(theop, num2, num1));// 运算括号内的内容
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
} else if (c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
int tempIndex = index + 1;
while (tempIndex < len) {
char temp = exp.charAt(tempIndex);// 取字符串中处于当前字符的下一位
if ((temp >= '0' && temp <= '9') || temp == '.') {
tempIndex++;// 若为数字则继续向后取
} else {
break;// 证明数字去完
}
}
String numstr = exp.substring(index, tempIndex);// 截取这个字符串则为两个符号之间的数字
try {
double numnum = Double.parseDouble(numstr);// 将数字转换成整型便于运算
numStack.push(numnum);
index = tempIndex - 1;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
index++;
}
// 检查符号栈是否为空
while (true) {
Object obj = null;
if (signalStack.isEmpty() == false) {
obj = signalStack.pop();
}
if (obj == null) {
break;// 为空证明运算已结束
} else {// 不为空就出栈运算
char opterTemp = (char) obj;
double num1 = (double) numStack.pop();
double num2 = (double) numStack.pop();
numStack.push(caculateResult(opterTemp, num2, num1));
}
}
double result = (double) numStack.pop();
et_input.setText(result + "");
}
private static int getNum(String originStr, String targetStr){
int res = 0;
int i = originStr.indexOf(targetStr);
while (i != -1){
i = originStr.indexOf(targetStr,i+1);
res++;
}
return res;
}
//计算加减乘除余
private static Double caculateResult(char optemp, double num1, double num2) {
switch (optemp) {
case '+':
return num1 + num2;
case '-':
return num1 - num2;
case '×':
return num1 * num2;
case '÷':
return num1 / num2;
}
return 0.0;
}
//返回符号优先级
private static int getOperlevel(char c) {
switch (c) {
case '+':
case '-':
return 1;
case '×':
case '÷':
return 2;
default:
return 0;
}
}
3)AndroidManifest.xml
- android:icon设置app图标
- android:label设置app名称
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:dataExtractionRules="@xml/data_extraction_rules"
android:fullBackupContent="@xml/backup_rules"
android:icon="@drawable/icons2"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@drawable/ic_launcher_background"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/Theme.Calculator"
tools:targetApi="31">
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
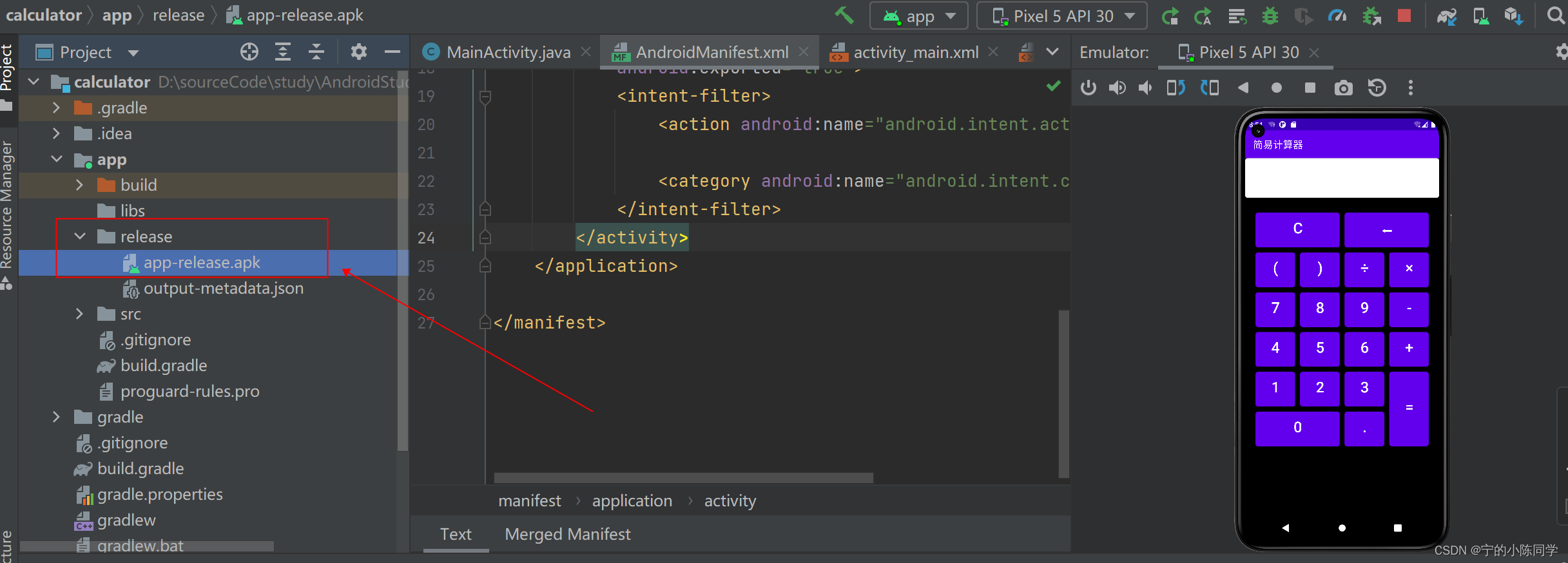
7、发布打包项目为apk
- 菜单栏 -> Build -> Generate Signed APK
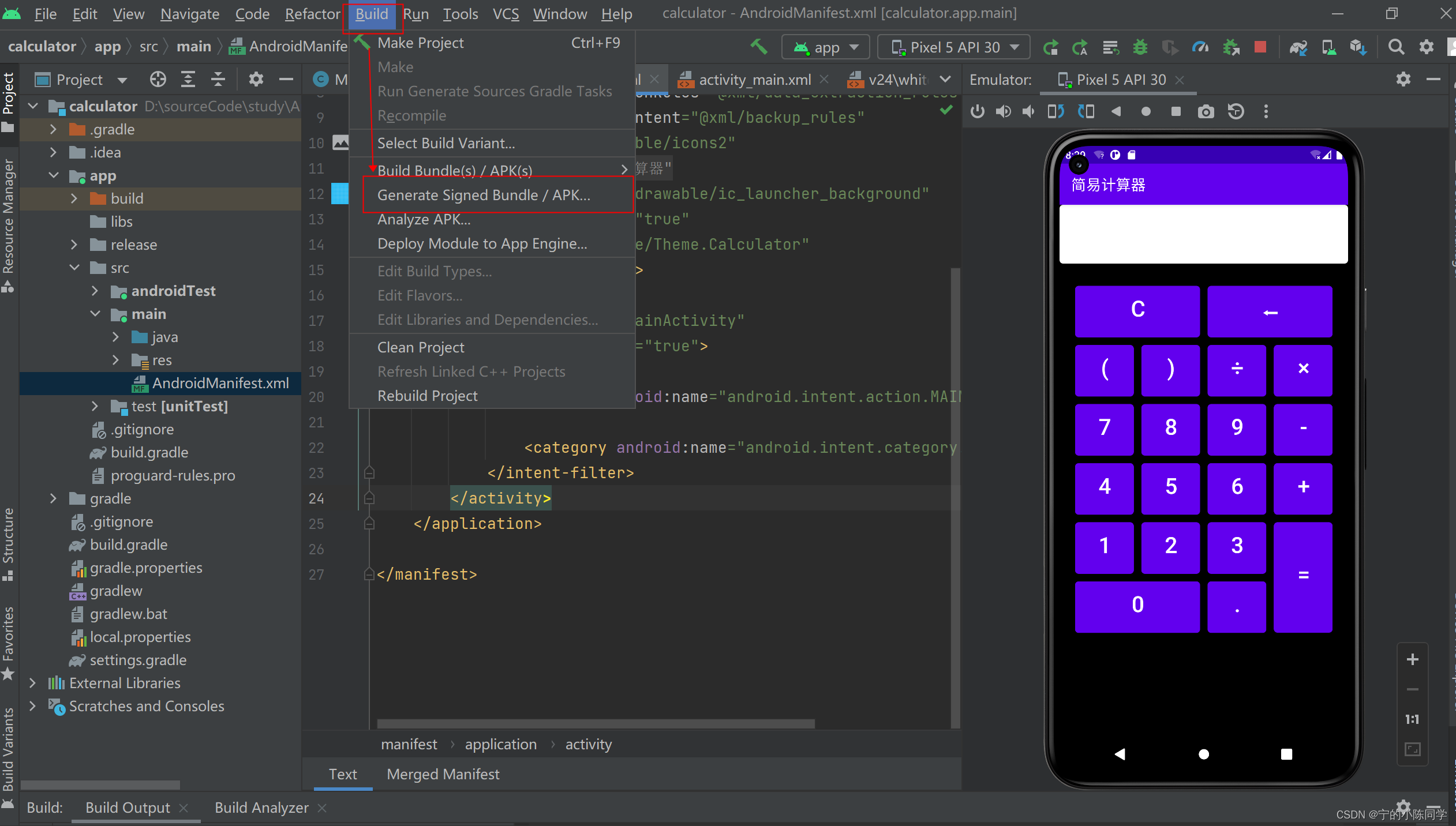
- 选择APK后,点击Next
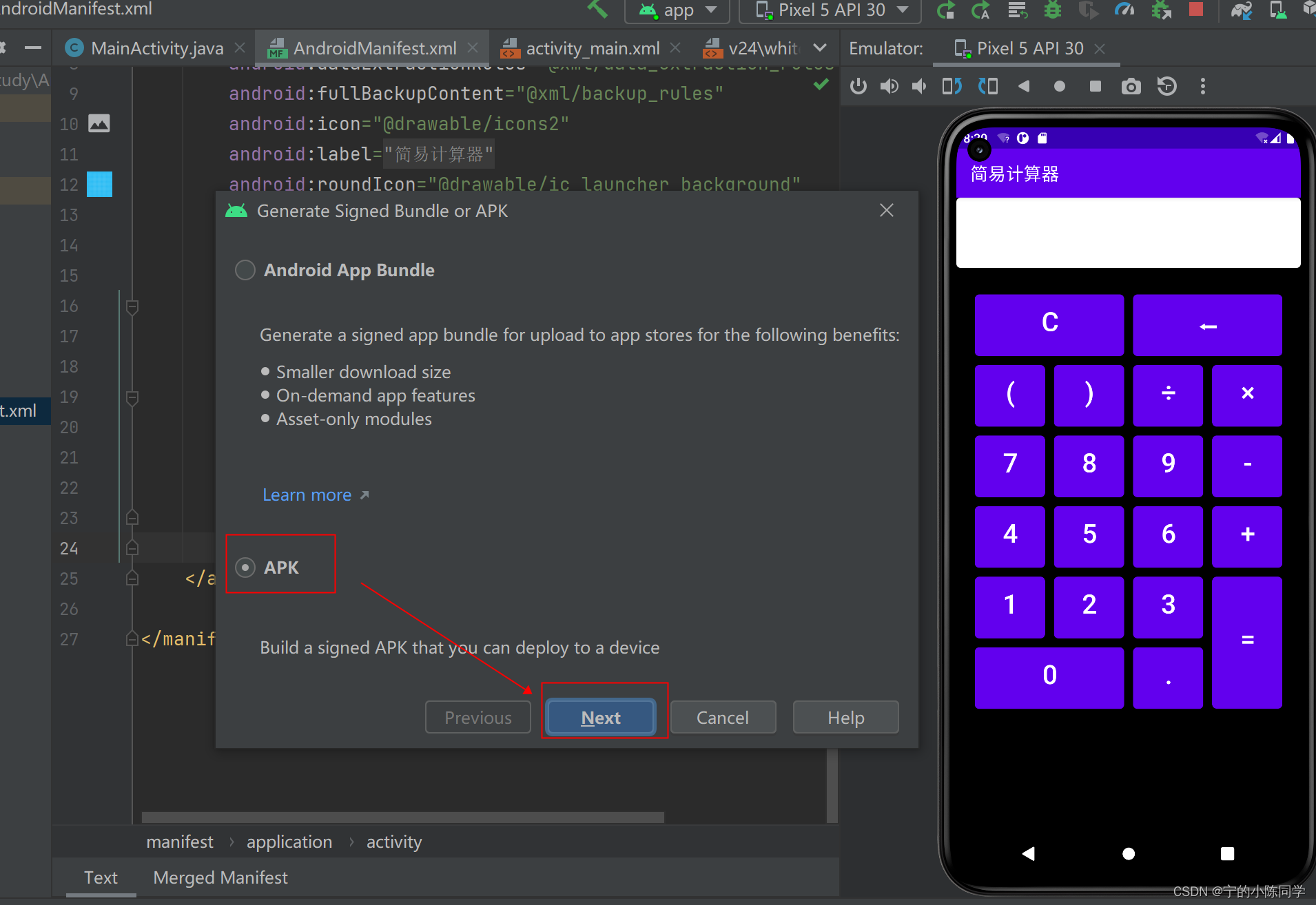
- 点击create new,创建一个密钥库
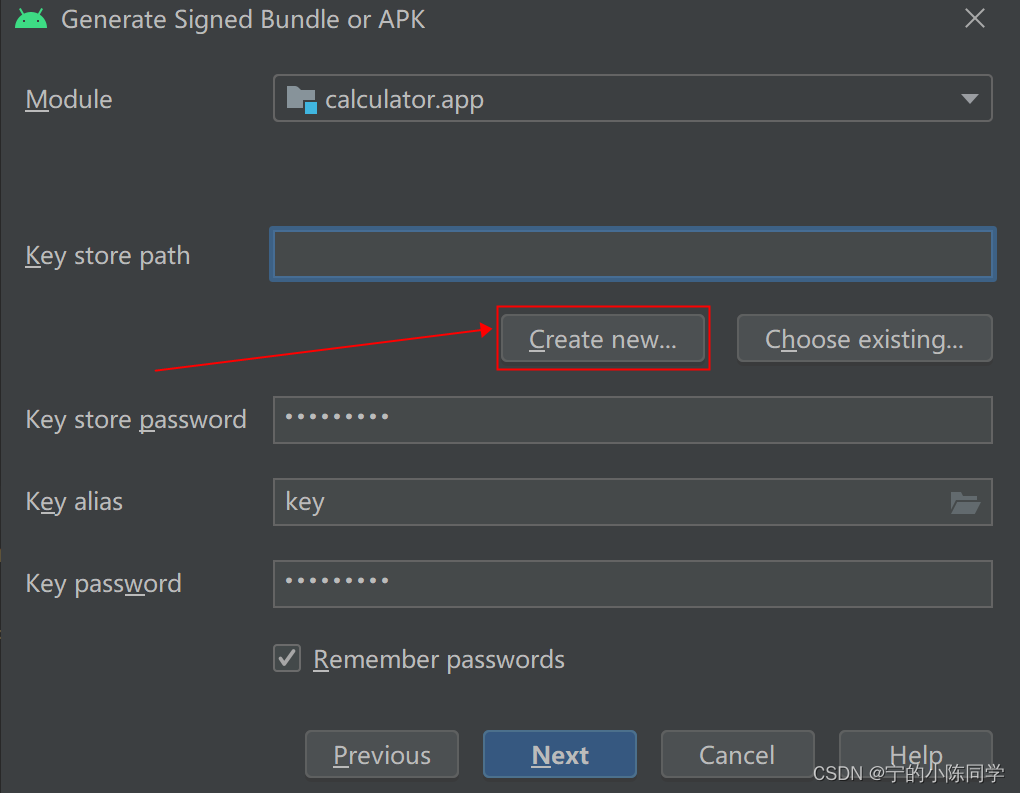
- 填写密钥库后,选择OK
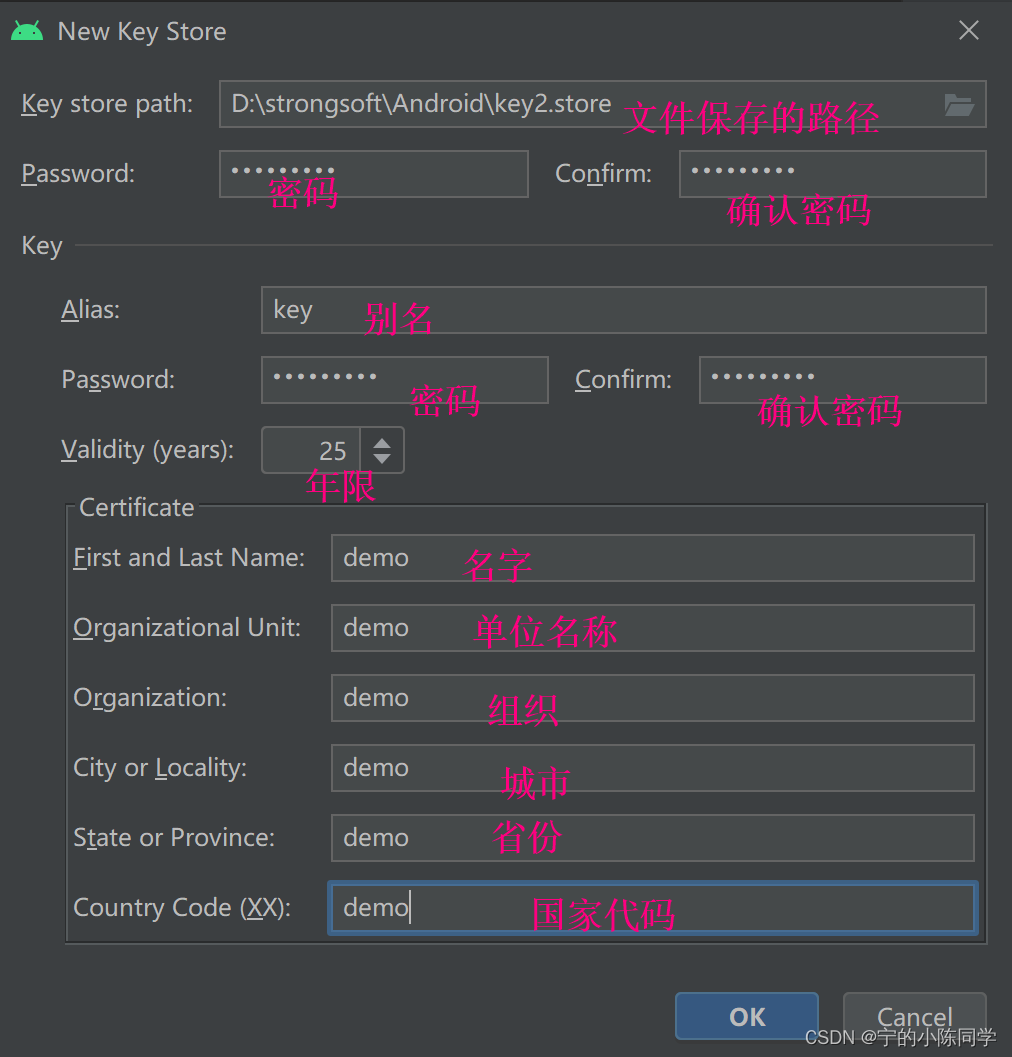
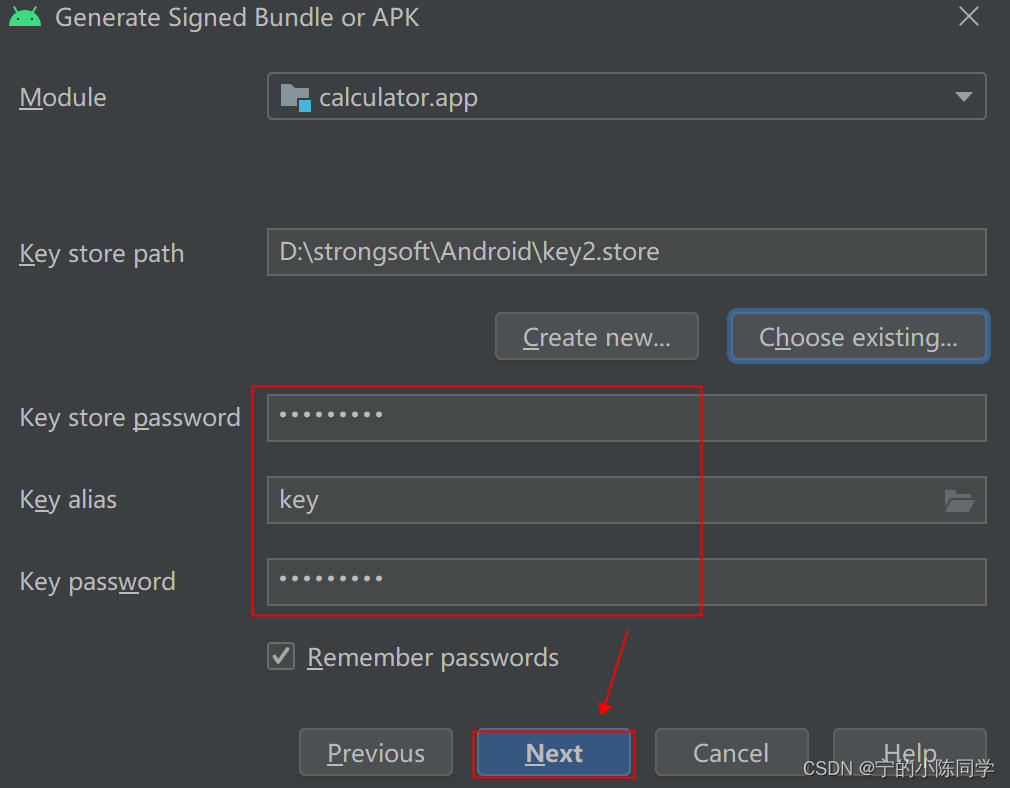
- 填写密钥库的别名,密码,确认密码,点击next
-
- 路径这边是直接默认,选择release后,点击finish
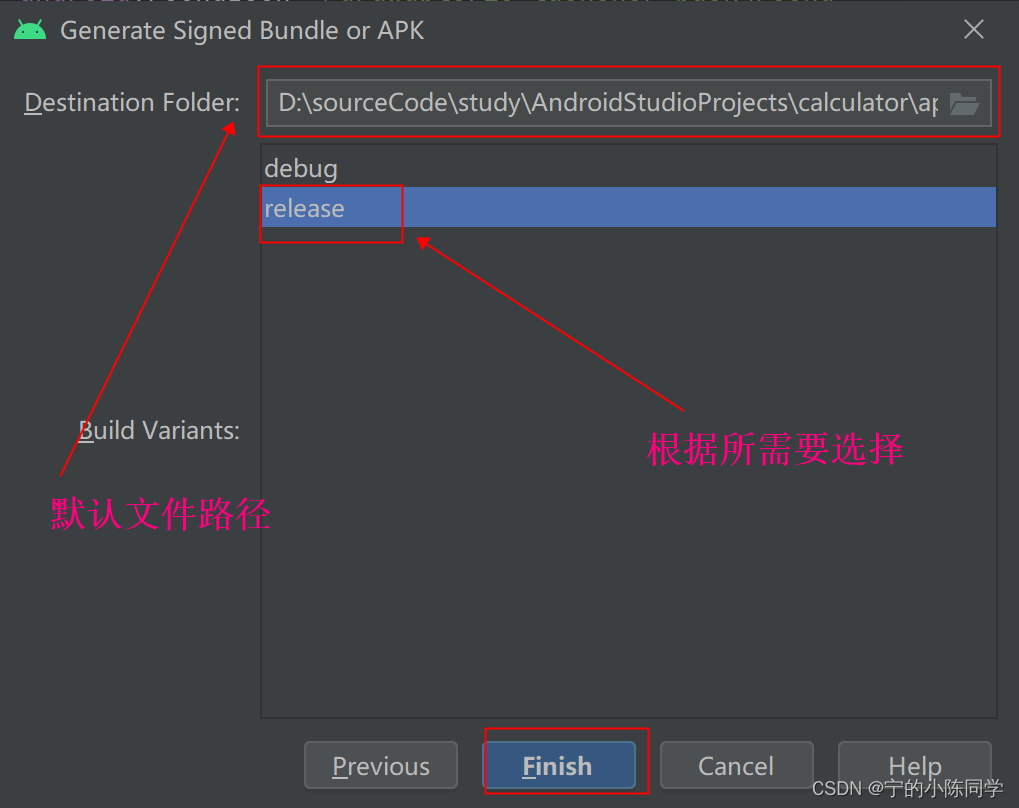
- build没有报错,且有弹出打包成功的弹框说明打包成功
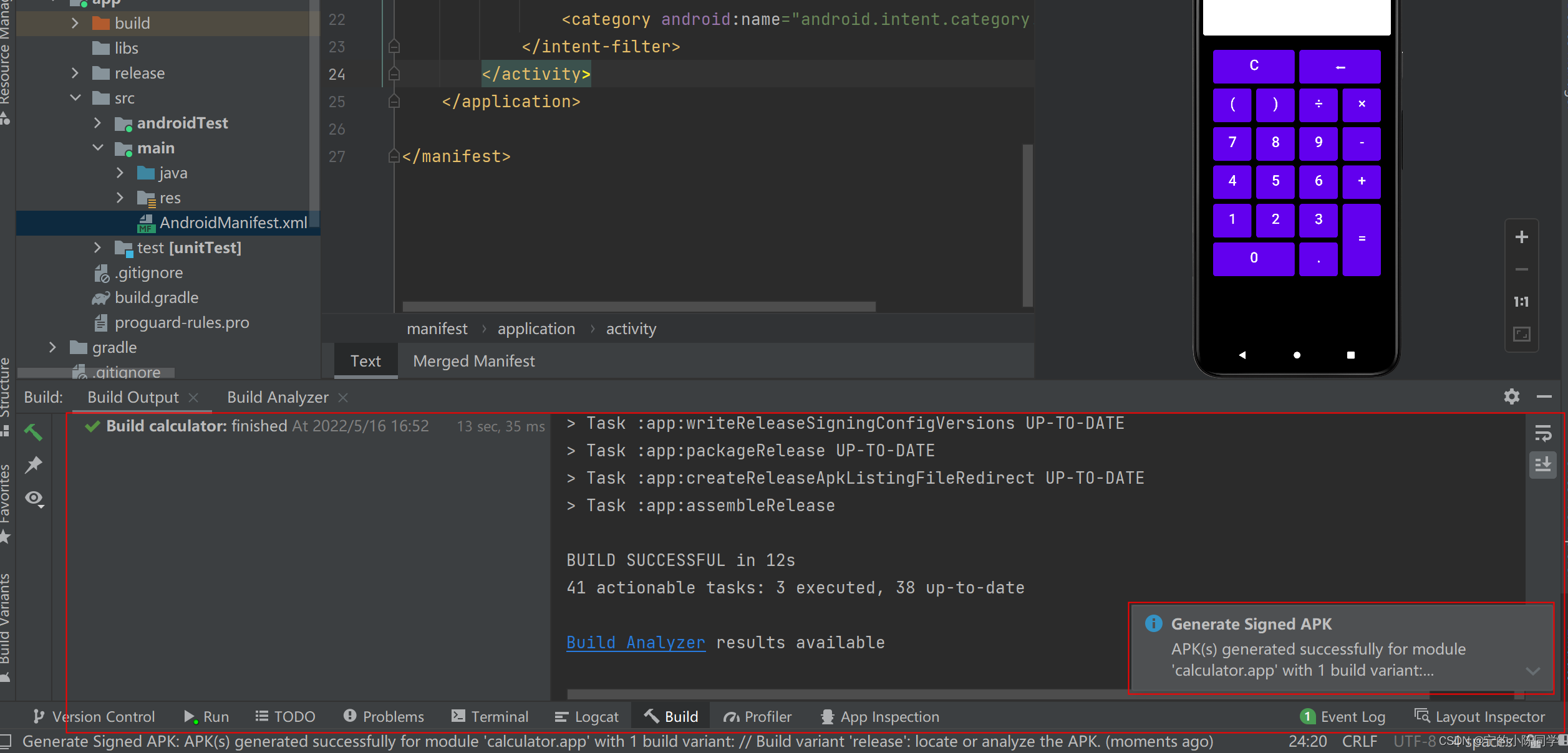
- 可在该文件夹下,看到打包成功的apk文件