Moya和高阶函数
1.Moya
1.1 Moya简介
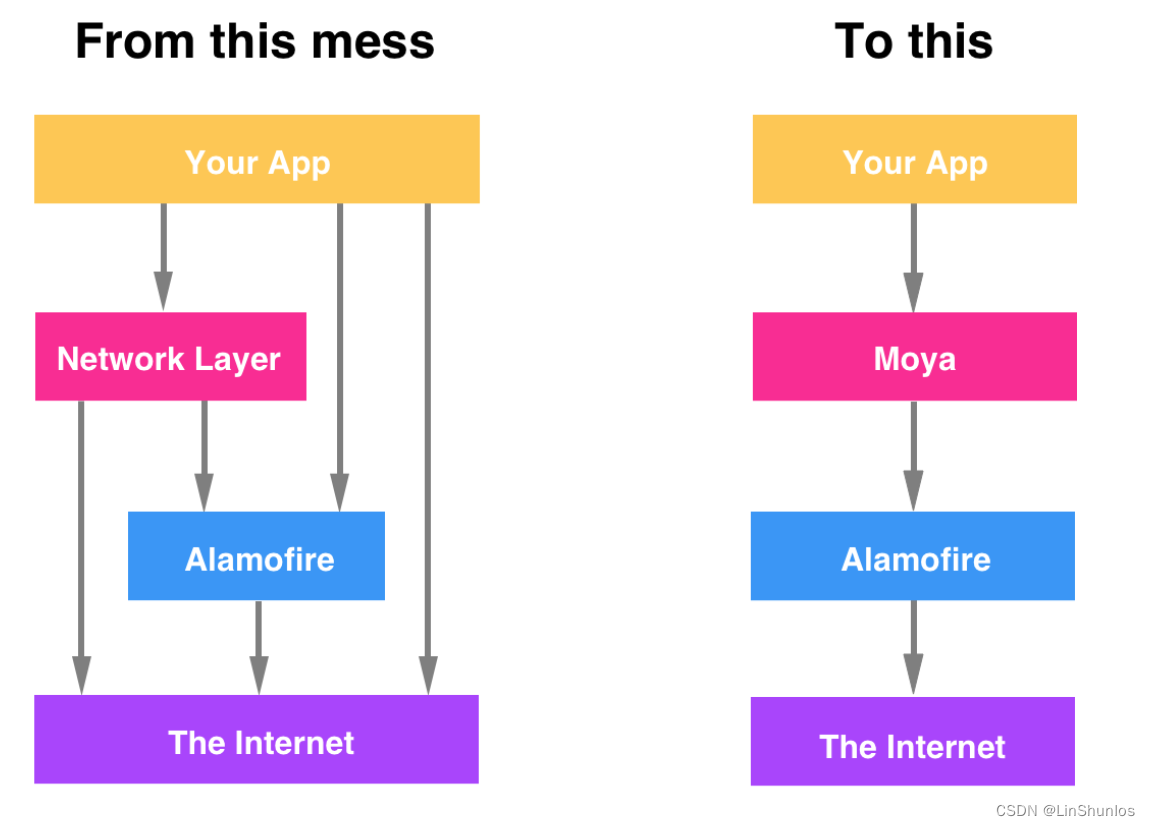
我们日常都会和网络打交道不管是使用 AFN 还是 Alamofire ,虽然这两者都封装了 URLSession ,不用让我们使用官方繁琐的 API。久而久之我们会发现我们的APP中到处都散落着和 AFN 、 Alamofire 相关的代码,不便于统 一的管理,而且很多代码内容是重复的,于是我们就会新建一个中间层 Network layer 来统一 管理我们代码中 AFN 、 Alamofire 的使用。
于此同时我们仅仅希望我们的App只和我们的 Network layer 打交道,不用关系底层使用的那个 三方的网络库,即使进行迁移,也应该对我们的上层业务逻辑毫无变化,因为我们都是通过Network layer 来耦合业务逻辑的。
但是因为抽象的颗粒度不够,我们往往写着写着就会出现越过 Network layer , 直接和我们的三 方网络库打交道,这样就违背了我们设计的原则,而 Moya 就是对网络业务逻辑的抽象,我们 只需要遵循相关协议,就可以发起网络请求,而不用关系底层细节
1.2 Moya 是如何一步步构建出来的?
Moya 的模块可以大致分成这几类:
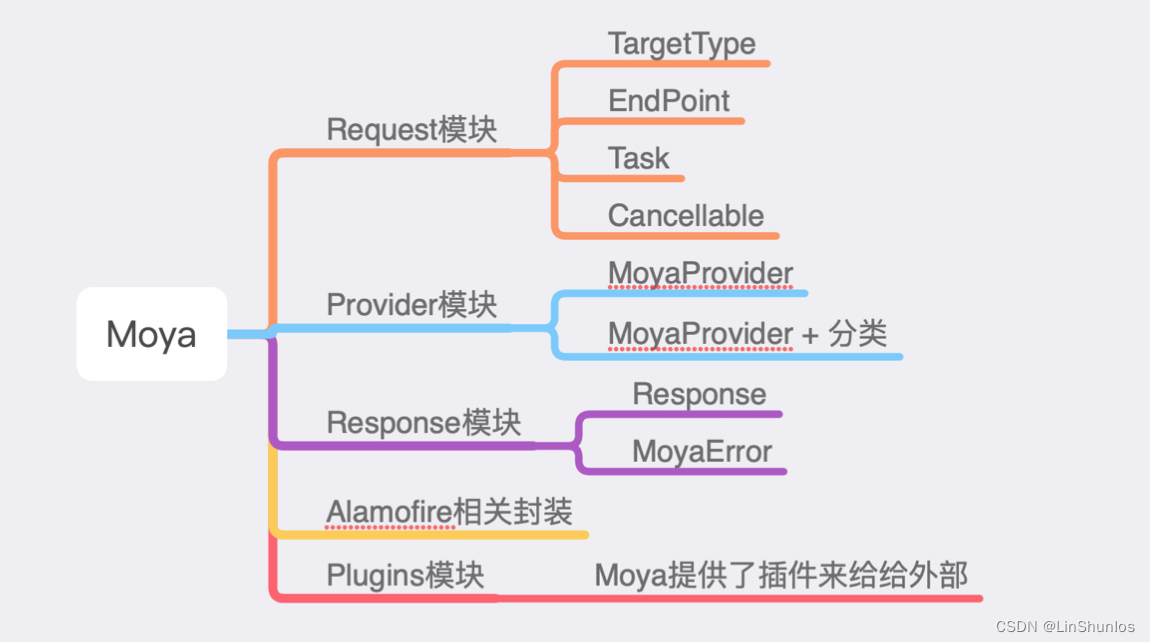
其次 Moya 主要的数据处理流程可以用下面这张图来表示Moya流程图,对于这张图我们一 点点来分析,我们先来看第一个阶段链接:
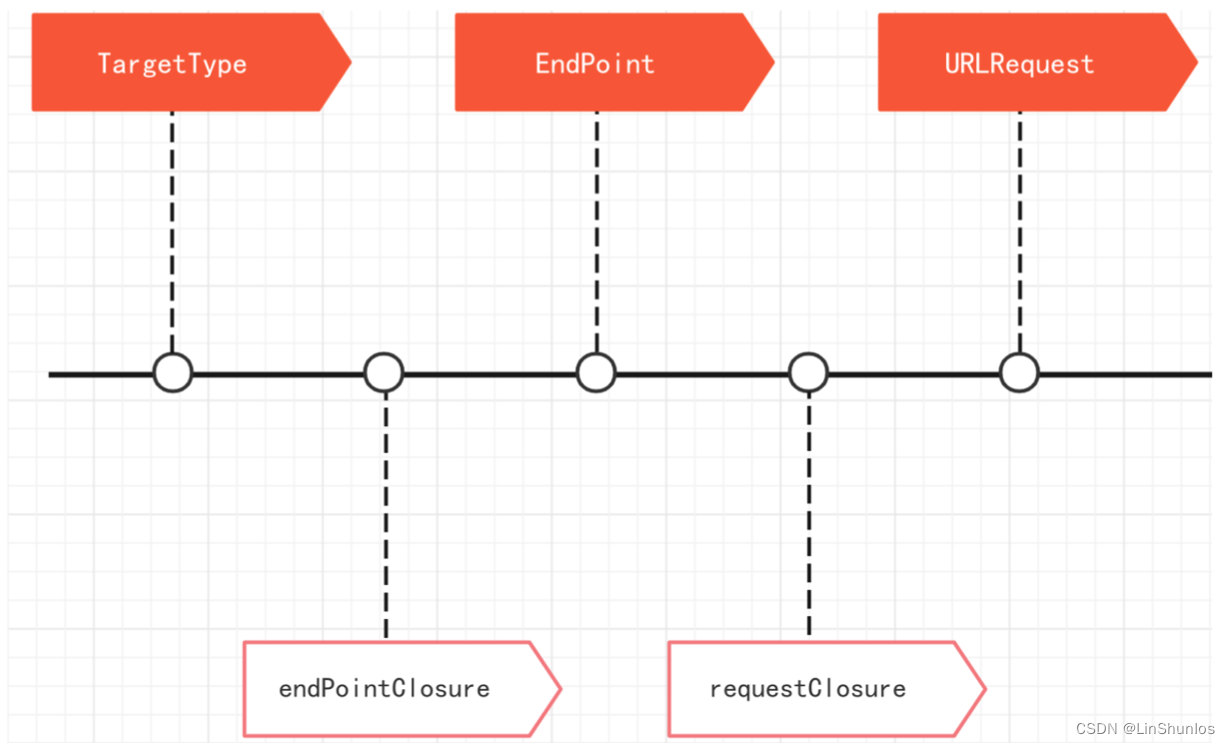
第一步创建了一个遵守 TargetType 协议的枚举,这个过程中我们完成网络请求的基本配置;

接下来通过 endpointClosure 的加工生成了一个 endPoint ,点击进入EndPoint的文件中,可以看到这里是对 TargetType 的一层再包装,其中endpointClosure的代码如下
public typealias EndpointClosure = (Target) -> Endpoint
public let endpointClosure: EndpointClosure
@escaping EndpointClosure = MoyaProvider.defaultEndpointMapping
final class func defaultEndpointMapping(for target: Target) -> Endpoint {
Endpoint(
url: URL(target: target).absoluteString,
sampleResponseClosure: { .networkResponse(200, target.sampleData) }
method: target.method,
task: target.task,
httpHeaderFields: target.headers
)
}
EndpointClosure = {(Target)->Endpoint in
Endpoint(
url: URL(target: target).absoluteString,
sampleResponseClosure: { .networkResponse(200, target.sampleDat
method: target.method,
task: target.task,
httpHeaderFields: target.headers
)
}
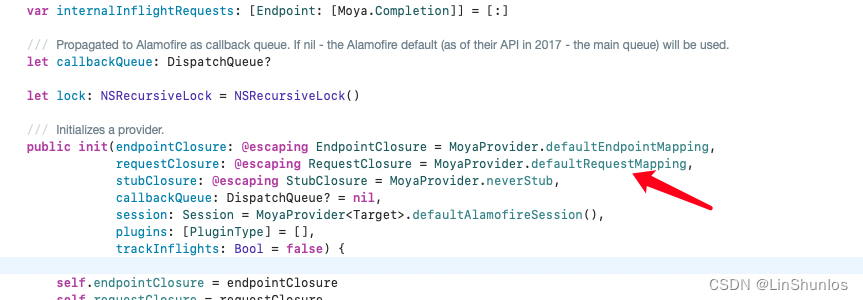
以上就是关于 TargetType 通过 endpointClosure 转化为 endPoint 的过程。下一步就是利用 requestClosure ,传入 endPoint ,然后生成 request 。request 生成过程和 endPoint 很相似。整体上使用 do-catch 语句来初始化一个 urlRequest,根据不同结果向闭包传入不同的参数。一开始使用 try 来调用 endpoint.urlRequest() ,如果抛出错误,会切换到 catch 语句中去。至于 endpoint.urlRequest() 它其实做的事情很简单,就是根据前面说到的 endpoint 的那些属性来初始化一个 NSURLRequest 的对象。
/// Closure that decides if and what request should be performed.
public typealias RequestResultClosure = (Result<URLRequest, MoyaError>) -> Void
/// Closure that resolves an `Endpoint` into a `RequestResult`.
public typealias RequestClosure = (Endpoint, @escaping RequestResultClosure) -> Void
/// A closure deciding if and what request should be performed.
public let requestClosure: RequestClosure
@escaping RequestClosure = MoyaProvider.defaultRequestMapping,
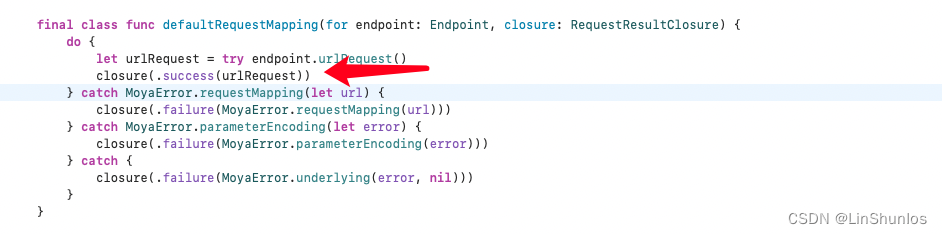
final class func defaultRequestMapping(for endpoint: Endpoint, closure: RequestResultClosure) {
do {
let urlRequest = try endpoint.urlRequest()
closure(.success(urlRequest))
} catch MoyaError.requestMapping(let url) {
closure(.failure(MoyaError.requestMapping(url)))
} catch MoyaError.parameterEncoding(let error) {
closure(.failure(MoyaError.parameterEncoding(error)))
} catch {
closure(.failure(MoyaError.underlying(error, nil)))
}
}
生成了 Request 之后,就交给 Provider 来发起网络请求了
@discardableResult
open func request(_ target: Target,
callbackQueue: DispatchQueue? = .none,
progress: ProgressBlock? = .none,
completion: @escaping Completion) -> Cancellable {
let callbackQueue = callbackQueue ?? self.callbackQueue
return requestNormal(target, callbackQueue: callbackQueue, progress: progress, completion: completion)
}
看到上面发起请求调用了 requestNormal 方法。
func requestNormal(_ target: Target, callbackQueue: DispatchQueue?, progress: Moya.ProgressBlock?, completion: @escaping Moya.Completion) -> Cancellable {
let endpoint = self.endpoint(target)
let stubBehavior = self.stubClosure(target)
let cancellableToken = CancellableWrapper()
// Allow plugins to modify response
let pluginsWithCompletion: Moya.Completion = { result in
let processedResult = self.plugins.reduce(result) { $1.process($0, target: target) }
completion(processedResult)
}
if trackInflights {
var inflightCompletionBlocks = self.inflightRequests[endpoint]
inflightCompletionBlocks?.append(pluginsWithCompletion)
self.internalInflightRequests[endpoint] = inflightCompletionBlocks
if inflightCompletionBlocks != nil {
return cancellableToken
} else {
self.internalInflightRequests[endpoint] = [pluginsWithCompletion]
}
}
let performNetworking = { (requestResult: Result<URLRequest, MoyaError>) in
if cancellableToken.isCancelled {
self.cancelCompletion(pluginsWithCompletion, target: target)
return
}
var request: URLRequest!
switch requestResult {
case .success(let urlRequest):
request = urlRequest
case .failure(let error):
pluginsWithCompletion(.failure(error))
return
}
let networkCompletion: Moya.Completion = { result in
if self.trackInflights {
self.inflightRequests[endpoint]?.forEach { $0(result) }
self.internalInflightRequests.removeValue(forKey: endpoint)
} else {
pluginsWithCompletion(result)
}
}
cancellableToken.innerCancellable = self.performRequest(target, request: request, callbackQueue: callbackQueue, progress: progress, completion: networkCompletion, endpoint: endpoint, stubBehavior: stubBehavior)
}
requestClosure(endpoint, performNetworking)
return cancellableToken
}
endPoint 这个我们再上面的代码分析中已经说过了,stub 是有关测试桩的代码这里我们都暂且忽略,cancellableToken 是取消的标识,如果有取消的标识,那么isCancelled就会为true。
internal class CancellableWrapper: Cancellable {
internal var innerCancellable: Cancellable = SimpleCancellable()
var isCancelled: Bool { innerCancellable.isCancelled }
internal func cancel() {
innerCancellable.cancel()
}
}
internal class SimpleCancellable: Cancellable {
var isCancelled = false
func cancel() {
isCancelled = true
}
}
CancellableWrapper 是对 SimpleCancellable 的又一层包装,都遵循了 Cancellable 的协议, 这里我们也可以遵循自己定义的协议,所以这里我们可以看到当前的 Class 都是 internal。接下来就是 performNetworking 这个闭包表达式的分析,我们先一步步来看
如果取消请求,则调用取消完成的回调, 直接 return,不再执行闭包内下面的语句。否则就调用
requestClosure(endpoint, performNetworking)
requestClosure的默认实现是MoyaProvider.defaultRequestMapping。
那么如果请求成功,就会调用closure
2. 高阶函数
高阶函数的本质也是函数,有两个特点
- 接受函数或者是闭包作为参数
- 返回值是一个函数或者是闭包
2.1 Map
对数组进行循环,并对数组中的每个元素采取相同的操作,然后返回数组。
看到map接受闭包作为参数,并且返回值是范型集合。

这里可以使用map将字符串全都变成大写
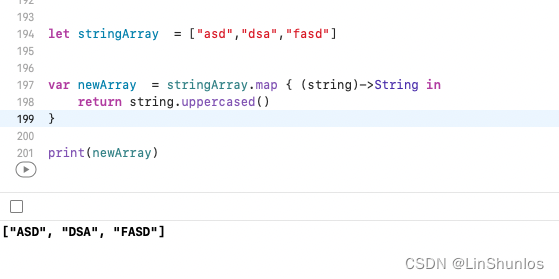
简写:

2.2 flatMap
flatMap接受闭包作为参数,返回当前元素的集合。

flatMap 中的闭包的参数同样是 Sequence 中的元素类型,但其返回类型为
SegmentOfResult。在函数体的范型定义中, SegmentOfResult 的类型其实就是 Sequence
而 flatMap 函数返回的类型是: SegmentOfResult.Element 的数组。从函数的返回值来看,与
map 的区别在于 flatMap 会将 Sequence 中的元素进行 “压平”,返回的类型会是
Sequence 中元素类型的数组,而 map 返回的这是闭包返回类型的数组。
相比较我们的 map 来说,flatMap 最主要的两个作用一个是压平数组,一个是过滤数组空值。

2.3 compactMap
当转换闭包返回可选值并且你期望得到的结果为非可选值的序列 时,使用 compactMap 。
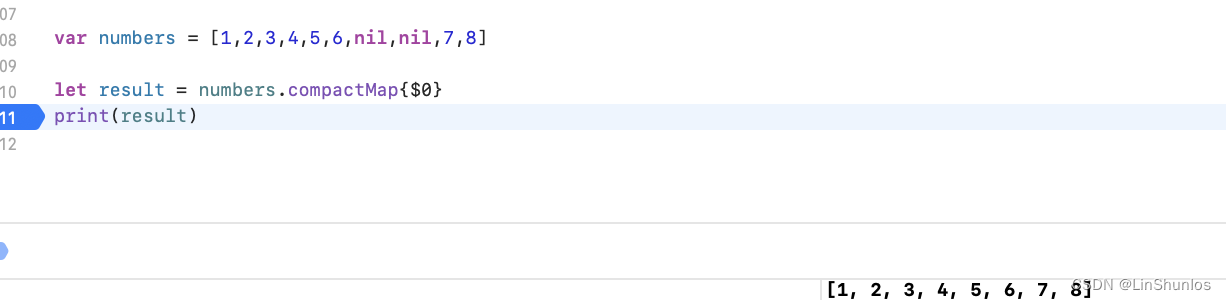
其实flatMap也能做到同样的效果,但是系统推荐使用compactMap。

2.4 filter
遍历数组,过滤不满足条件的元素后返回满足条件的元素组成的数组,也就是允许调用者传入一个闭包来过滤集合中的元素。
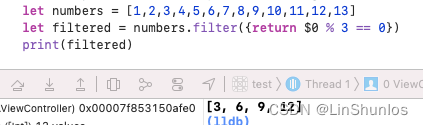
2.5 reduce
reduce 把集合中所有的值结合起来返回一个新的值。
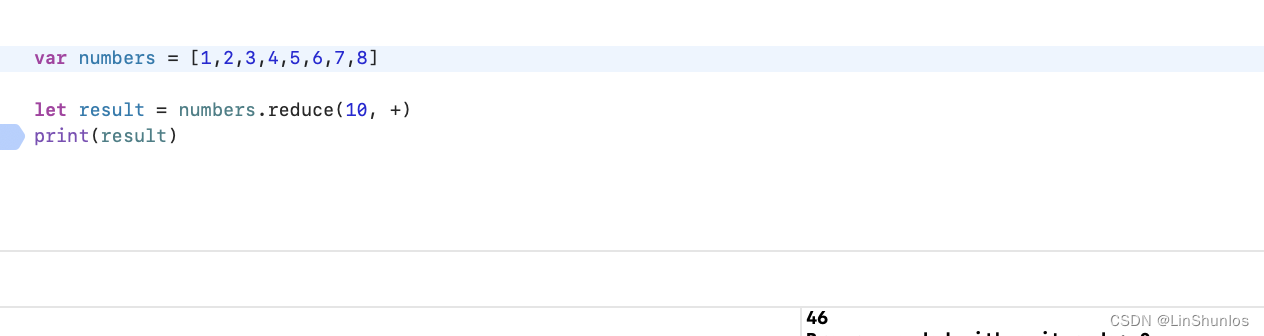
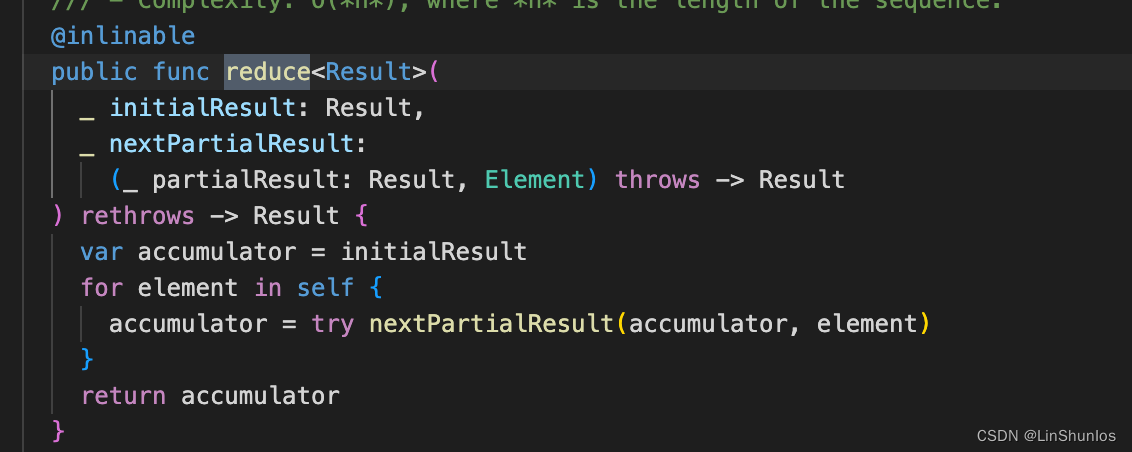
查看reduce的源代码,首先这里传入一个初始值,然后传入一个闭包表达式,返回值和初始值的类型一样为泛型Result。这里将初始值赋值给accumulator,然后遍历数组中的element执行nextPartialResult。
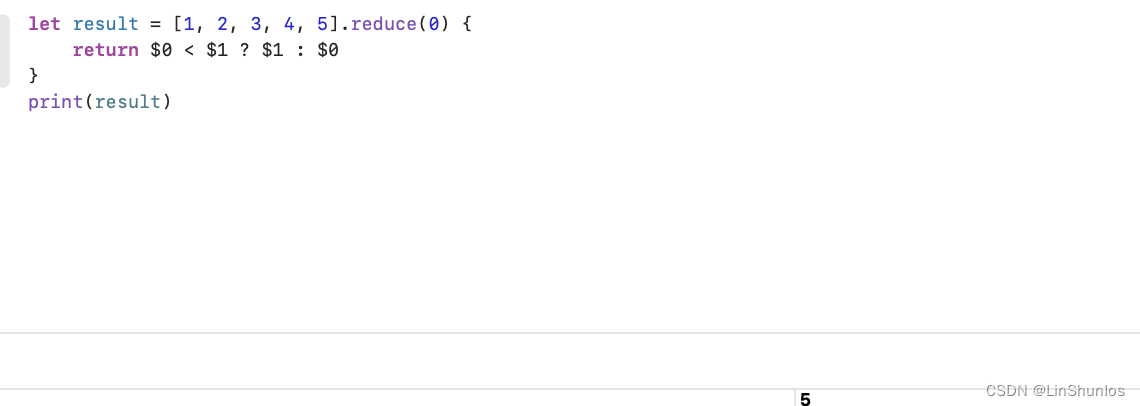
那么如果我们想要找到数组中的最大值,我们也可以使用reduce。
那么如果想要逆转一个数组,也可以使用reduce

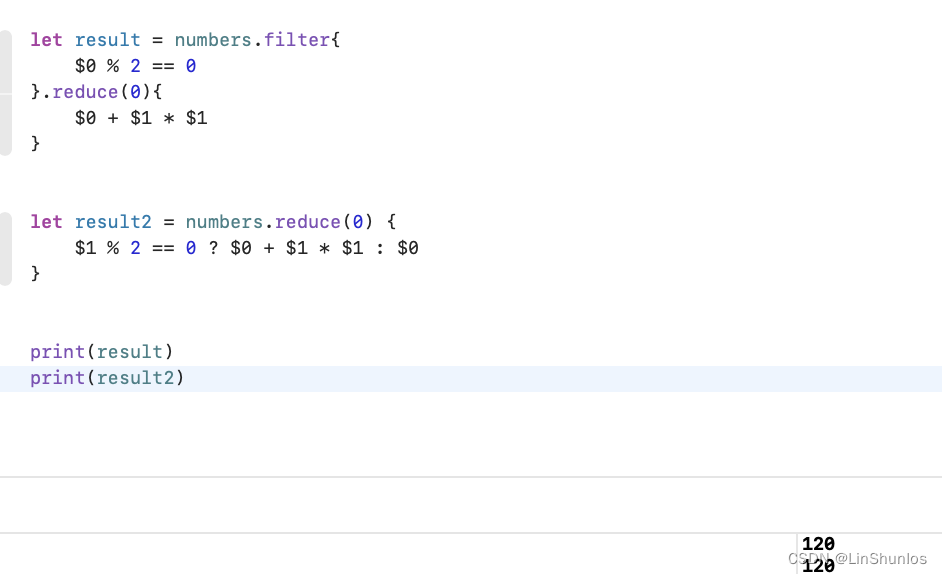
2.6 高阶函数链式调用
计算数组中偶数的平方和
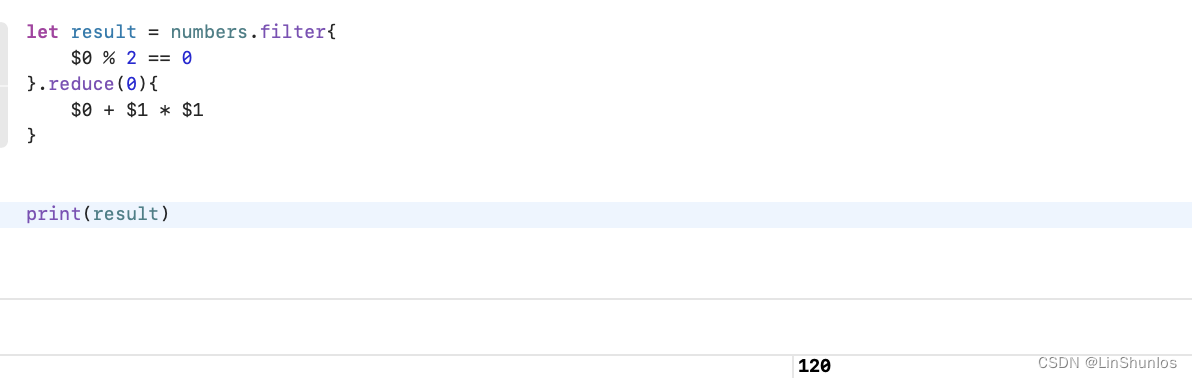
也可以只使用reduce来完成。