?一.View的measure过程
View的measure过程是由View的measure方法完成的,他是一个被final关键字修饰的方法,我们无法重写该方法,但是measure方法中会调用onMeasure方法来设置计算后的宽高,onMeasure方法是可以被重写的:
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}getDefaultSize方法:
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = size;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
result = size;
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}可以看到EXACTLY和AT_MOST两种模式下都是以specSize作为返回值,而这个specSize就是View测量后的大小。如果View采用AT_MOST模式即wrap_content来绘制那么结合上一篇文章中的图例:
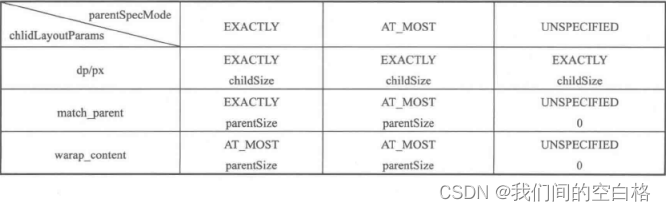
?可以知道View最终在父布局中的绘制会以parentSize作为specSize的实际大小,即我们自定义的直接继承自View的View在布局中使用wrap_content的效果和match_parent是一样的,而解决这个问题的方式就需要重写onMeasure方法来对wrap_content做特殊处理:
override fun onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec: Int, heightMeasureSpec: Int) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec)
val widthSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec)
val widthSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec)
val heightSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec)
val heightSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec)
if (widthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST && heightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
setMeasuredDimension(mWidth, mHeight)
} else if (widthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
setMeasuredDimension(mWidth, heightSpecSize)
} else if (heightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
setMeasuredDimension(widthSpecSize, mHeight)
}
}重写的onMeasure方法中我们需要提供一个View在wrap_content情况下使用的宽高mWidth和mHeight,非wrap_content的场景下就直接使用系统提供的测量值widthSpecSize/heightSpecSize即可。具体mWidth和mHeight该怎么取值要根据实际使用场景来定,参考TextView的onMeasure方法部分源码:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int width;
int height;
...
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
// Parent has told us how big to be. So be it.
width = widthSize;
} else {//AT_MOST
...
if (boring == null || boring == UNKNOWN_BORING) {
if (des < 0) {
des = (int) Math.ceil(Layout.getDesiredWidthWithLimit(mTransformed, 0,
mTransformed.length(), mTextPaint, mTextDir, widthLimit));
}
width = des;
} else {
width = boring.width;
}
final Drawables dr = mDrawables;
if (dr != null) {
width = Math.max(width, dr.mDrawableWidthTop);
width = Math.max(width, dr.mDrawableWidthBottom);
}
...
}
...
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
// Parent has told us how big to be. So be it.
height = heightSize;
mDesiredHeightAtMeasure = -1;
} else {//AT_MOST
int desired = getDesiredHeight();
height = desired;
mDesiredHeightAtMeasure = desired;
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
height = Math.min(desired, heightSize);
}
}
...
setMeasuredDimension(width, height);
}可以看到TextView对AT_MOST模式下的宽高都进行了重新定义,具体赋值逻辑太过复杂就不细说了。
二.ViewGroup的measure过程
ViewGroup是一个继承自View的抽象类,它并没有实现onMeasure方法,这是因为ViewGroup作为一个父类他不能对不同需求和场景下的子类布局作统一测量,就像LinearLayout和RelativeLayout一样是两种完全不同的布局方式,他们的测量方式需要他们自己去实现。但是ViewGroup也提供了一个measureChildren方法:
protected void measureChildren(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
final int size = mChildrenCount;
final View[] children = mChildren;
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
final View child = children[i];
if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) != GONE) {
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
}逻辑上很简单,就是按顺序调用measureChild方法来测量子View:
protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec) {
final LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom, lp.height);
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}measureChild方法和上一篇文章提到的measureChildWithMargins方法原理是一样的,只不过没有把子View的外边距加进去。不过这个measureChildren方法在已知的几种布局中只在AbsoluteLayout布局中有使用,而AbsoluteLayout作为最简单粗暴的一种布局也是几乎没有使用场景,所以可以看出对于子View的测量LinearLayout、RelativeLayout等常用布局都是需要自己去实现的。下面以LinearLayout的onMeasure方法为例:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {
measureVertical(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
} else {
measureHorizontal(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}measureVertical方法:
void measureVertical(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
...
for (int i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
final View child = getVirtualChildAt(i);
if (child == null) {
mTotalLength += measureNullChild(i);
continue;
}
...
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY && useExcessSpace) {
// Optimization: don't bother measuring children who are only
// laid out using excess space. These views will get measured
// later if we have space to distribute.
final int totalLength = mTotalLength;
mTotalLength = Math.max(totalLength, totalLength + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
skippedMeasure = true;
} else {
if (useExcessSpace) {
// The heightMode is either UNSPECIFIED or AT_MOST, and
// this child is only laid out using excess space. Measure
// using WRAP_CONTENT so that we can find out the view's
// optimal height. We'll restore the original height of 0
// after measurement.
lp.height = LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT;
}
// Determine how big this child would like to be. If this or
// previous children have given a weight, then we allow it to
// use all available space (and we will shrink things later
// if needed).
final int usedHeight = totalWeight == 0 ? mTotalLength : 0;
measureChildBeforeLayout(child, i, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, usedHeight);
final int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
if (useExcessSpace) {
// Restore the original height and record how much space
// we've allocated to excess-only children so that we can
// match the behavior of EXACTLY measurement.
lp.height = 0;
consumedExcessSpace += childHeight;
}
final int totalLength = mTotalLength;
mTotalLength = Math.max(totalLength, totalLength + childHeight + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin + getNextLocationOffset(child));
...
}
}
}可以看到LinearLayout会按序遍历每一个子View,并调用measureChildBeforeLayout方法来测量子View,测量完成后获取子View的measuredHeight累加到mTotalLength中作为最后LinearLayout的总高度。所有的子View都测量完成后,LinearLayout会用mTotalLength来测量自身的高度:
mTotalLength += mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom;
int heightSize = mTotalLength;
// Check against our minimum height
heightSize = Math.max(heightSize, getSuggestedMinimumHeight());
// Reconcile our calculated size with the heightMeasureSpec
int heightSizeAndState = resolveSizeAndState(heightSize, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
setMeasuredDimension(resolveSizeAndState(maxWidth, widthMeasureSpec, childState),
heightSizeAndState);这里的resolveSizeAndState方法就是对不同测量模式下的LinearLayout高度分情况处理:
public static int resolveSizeAndState(int size, int measureSpec, int childMeasuredState) {
final int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
final int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
final int result;
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (specSize < size) {
result = specSize | MEASURED_STATE_TOO_SMALL;
} else {
result = size;
}
break;
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
default:
result = size;
}
return result | (childMeasuredState & MEASURED_STATE_MASK);
}当LinearLayout采用match_parent时就直接使用测量的specSize,如果采用wrap_content就使用累加得到的总高度值mTotalHeight,当然这个值也要小于等于父布局给的剩余高度,否则仍然以specSize作为LinearLayout的最终高度。
三.获取measure后的宽高
对于获取measure后的宽高View直接给我们提供了getMeasuredWidth/getMeasuredHeight方法,但是应该在什么时候使用这俩方法呢,首先View在很多情况下会出现多次测量的情况,所以在onMeasure方法中获取的measuredWidth/measuredHeight往往并不是最终正确的宽高,而onLayout是在onMeasure完全结束的情况下执行的,所以一般我们会在onLayout方法中去拿到最终的measuredWidth/measuredHeight。
如果在activity的声明周期方法里面去getMeasuredWidth/getMeasuredHeight会得到正确的宽高吗?答案往往是否定的,因为整个measure的过程和页面的生命周期并没有绑定,当我们在onStart、onResume方法里面去获取宽高时可能View还没有measure结束而获取到一个默认值0。Android为我们提供了以下几种方式去拿到正确的measuredWidth/measuredHeight:
1.onWindowFocusChanged
class DemoView(context: Context?, attrs: AttributeSet?) : View(context, attrs) {
...
override fun onWindowFocusChanged(hasWindowFocus: Boolean) {
super.onWindowFocusChanged(hasWindowFocus)
if (hasWindowFocus) {
val width = this.measuredWidth
val height = this.measuredHeight
}
}
...
}这个回调在activity中也是可以设置的,但是需要注意的是它和activity的生命周期存在关联,可能会出现频繁回调的情况,当activity频繁的触发onResume和onPause时onWindowFocusChanged也会频繁的触发回调
2.view.post
View通过post方法把一个Runnable任务加到主线程消息队列的末尾,当这个Runnable执行时View早已经初始化好了:
btn1.post {
val width = btn1.measuredWidth
val height = btn1.measuredHeight
}3.ViewTreeObserver
ViewTreeObserver提供了很多和视图树状态有关的接口,很多都是可以用来获取measuredWidth/measuredHeight,以OnGlobalLayoutListener为例:
class DemoView(context: Context?, attrs: AttributeSet?) : View(context, attrs) {
...
init {
viewTreeObserver.addOnGlobalLayoutListener(object:ViewTreeObserver.OnGlobalLayoutListener{
override fun onGlobalLayout() {
viewTreeObserver.removeOnGlobalLayoutListener(this)
val width = this@DemoView.measuredWidth
val height = this@DemoView.measuredHeight
}
})
}
...
}当view树的状态改变或者里面的view可见性发生变化都会触发OnGlobalLayoutListener回调,此时measuredWidth/measuredHeight将是准确的。
4.measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec)
通过手动对View进行measure来指定width和height,但是这里需要根据LayoutParams来分情况处理:
.match_parent
这种情况下无法直接手动measure,因为我们需要知道父布局的剩余空间大小parentSize,而在当前View中我们是无法知道父布局的剩余空间大小情况的
.具体数值dp/px
例如宽高都是100px:
class DemoView(context: Context?, attrs: AttributeSet?) : View(context, attrs) {
...
init {
val widthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(100, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY)
val heightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(100, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY)
this.measure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec)
}
...
}.wrap_content
class DemoView(context: Context?, attrs: AttributeSet?) : View(context, attrs) {
...
init {
val widthMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec((1 shl 30) - 1, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST)
val heightMeasureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec((1 shl 30) - 1, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST)
this.measure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec)
}
...
}当使用AT_MOST模式时,我们可以指定specSize为其所能达到的最大值即measureSpec表示具体尺寸的后三十位全为1,所以specSize=1*10的30次方-1,用kotlin的代码表示就是(1 shl 30) - 1,java的代码表示就是(1 << 30) - 1。