背景
最近在跟进项目,项目主要是使用Kotlin为主要语言编写的。借此机会好好了解和学习Kotlin,主要是一个数据视图分离的处理及采用MVVM模式设计的项目。
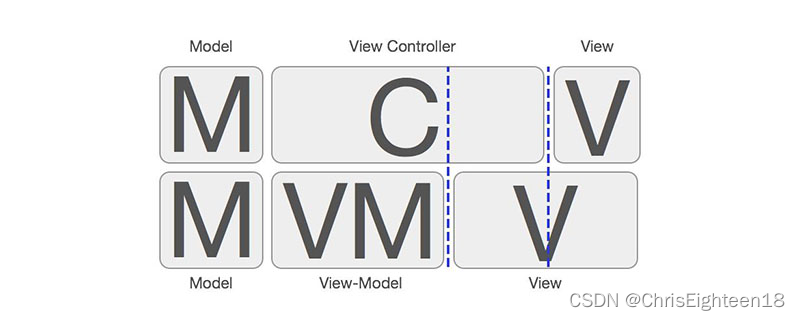
MVC和MVVM区别
ViewModel 概览 - google 官网文档
KOTLIN中CLASS、OBJECT、COMPANION OBJECT区别示例
object相当于一个单例类直接调用,而class需要new出来()才能使用;companion object相当于class内的单例资源
代码了解
提供一个ViewModel对视图进行处理;
其中代码中有SharedFlow,,可以参考Android SharedFlow详解
可以简单理解为数据的发收等等处理。
如下提供一个登录的ViewModel使用:
import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModel
import androidx.lifecycle.viewModelScope
import im.zego.takeaguess.data.local.TokenStore
import im.zego.takeaguess.ui.utils.UiEvent
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.MutableSharedFlow
import kotlinx.coroutines.flow.asSharedFlow
import kotlinx.coroutines.launch
class LoginViewModel : ViewModel() {
// 有下划线发送事件,无就只能接收事件
private val _loginEvent = MutableSharedFlow<UiEvent<Unit>>()
val loginEvent = _loginEvent.asSharedFlow()
fun login() {
viewModelScope.launch {
_loginEvent.emit(UiEvent.Loading)
TokenStore.refreshAndGetToken().onSuccess {
_loginEvent.emit(UiEvent.Success(Unit))
}.onFailure {
_loginEvent.emit(UiEvent.Failure(it))
}
}
}
}
而Activity就是属于View的部分,那么和Model的交互重任就交给上述的ViewModel实现。
/**
* Kotlin 活动对象,采用数据捆绑的新方式实现对View的控制;
* 参考官方文档记录:
* https://developer.android.google.cn/topic/libraries/view-binding#kotlin
*/
class LoginActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
//lateinit 关键词-延迟赋值,var是必须要先赋值
private lateinit var binding: ActivityLoginBinding
private val viewModel: LoginViewModel by viewModels()
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
binding = ActivityLoginBinding.inflate(layoutInflater)
setTransparentStyle(binding.root)
setContentView(binding.root)
initView()
}
private fun initView() {
with(binding) {
// 在这个作用域里面的代码都可以省略 (binding.)
// binding.etUserName -> etUserName
etUserName.setText("HelloWorld")
btEnter.setOnNotFastClickListener {
val userName = etUserName.text.toString()
if (userName.isNotBlank()) {
AccountStore.userName = userName
viewModel.login()
}
}
}
lifecycleScope.launch {
viewModel.loginEvent.collect { event ->
when(event) {
UiEvent.Loading -> {
showProgressDialog()
}
is UiEvent.Failure -> {
showToast(event.throwable)
dismissProgressDialog()
}
is UiEvent.Success -> {
HomeActivity.open(this@LoginActivity)
dismissProgressDialog()
}
}
}
}
}
}
解析
这里也使用了kotlin的扩展函数:
etUserName.setText("HelloWorld")
btEnter.setOnNotFastClickListener {
val userName = etUserName.text.toString()
if (userName.isNotBlank()) {
AccountStore.userName = userName
viewModel.login()
}
}
setOnNotFastClickListener是基于如下的方式实现:
import android.view.View
fun View.setOnNotFastClickListener(
time: Long = 300,
listener: View.OnClickListener
) {
var lastTime: Long = 0
this.setOnClickListener {
val currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis()
if (currentTime - lastTime > time) {
listener.onClick(it)
lastTime = currentTime
}
}
}
使用了数据的交互传递:lifecycleScope挂起个线程:
CoroutineScope tied to this LifecycleOwner’s Lifecycle.
This scope will be cancelled when the Lifecycle is destroyed.
This scope is bound to Dispatchers.Main.immediate.
lifecycleScope.launch {
viewModel.loginEvent.collect { event ->
when(event) {
UiEvent.Loading -> {
showProgressDialog()
}
is UiEvent.Failure -> {
showToast(event.throwable)
dismissProgressDialog()
}
is UiEvent.Success -> {
HomeActivity.open(this@LoginActivity)
dismissProgressDialog()
}
}
}
}
以上的代码是接收方。发送方emit如下在ViewModel中根据相关调用的反馈进行变动:
fun login() {
viewModelScope.launch {
_loginEvent.emit(UiEvent.Loading)
TokenStore.refreshAndGetToken().onSuccess {
_loginEvent.emit(UiEvent.Success(Unit))
}.onFailure {
_loginEvent.emit(UiEvent.Failure(it))
}
}
}
这样就形成一个闭环了。关键就是要绑定到一块:
private val viewModel: LoginViewModel by viewModels()