一、什么是深度链接(Deeplink)技术?
“Deeplink”又名“深度链接”,是一种能将用户直接从网页带到App指定页面的技术。
目前广义上的“深度链接”概念包含了 DeepLink 和 Deferred Deeplink,主要触发场景分为两种:
- 用户已安装目标App情况下:在web网页点击链接,就能直接跳转到App内指定页面。
- 用户未安装目标App情况下:在web网页点击链接,会先跳转应用商店,下载后首次打开App,会自动跳转到指定页面。
1.深度链接
- 什么是深度链接?
深度链接(DeepLink):对于已经安装了的APP,把需要的参数通过URL的形式传递给APP,指向特定的App页面。是从外部链接到APP内部的直接跳转。
- 深度链接的原理
DeepLink,本质上是使用URI的Schema,移动操作系统提供解析schema的功能,判断schema属于哪个app,唤起并将参数传递给APP.
- URL Scheme的协议样式如下:? ?
Scheme://host:port/path?query
● Scheme:代表Scheme协议名称,可自定义
● host:代表Scheme作用的地址域
● port:代表该路径的端口号
● path:代表的是想要跳转的指定页面(路径)
● query:代表想要传递的参数
工作流程是:当用户点击此类深度链接时—>操作系统提供解析URL Scheme的能力—>判断属于哪个App、是否安装了App—>唤醒App并传递需要的参数。
Demo用例:
首先,自行定义一个网页,这涉及到前端的内容,本人学识浅薄,怎么去写个网页,这大家可以到网上搜。
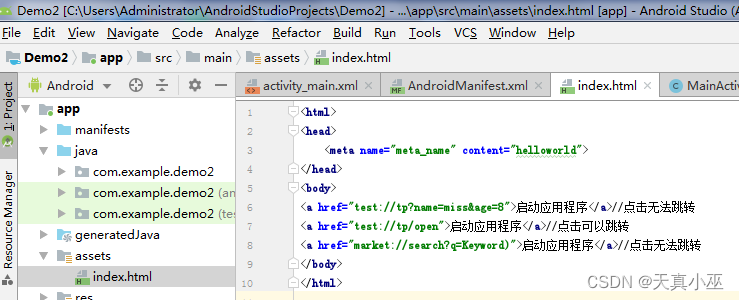
?然后便是manifests配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.demo2">
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/Theme.AppCompat.NoActionBar">
<activity
android:name=".MainActivitywhat"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW"/>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.BROWSABLE"/>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"/>
<data android:scheme="test" android:host="tp" android:pathPrefix="/open"/>
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>这里,是通过Intent隐式意图实现。
lv_0_20220907173127
2.延迟深度链接
1.从当前应用跳转到应用商店。
package com.example.myapplication;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Button button = findViewById(R.id.button);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
gotoStore();
}
});
}
public void gotoStore(){
Uri uri = Uri.parse("market://search?");
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, uri);
startActivity(intent);
}
}
2.判断应用是否安装,如果安装则直接打开对应的app,否则,跳转到应用商店下载。
修改后的代码:
package com.example.myapplication;
import androidx.annotation.RequiresApi;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.pm.PackageManager;
import android.content.pm.VersionedPackage;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.os.Build;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import java.util.List;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Button button = findViewById(R.id.button);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener()
{
@RequiresApi(api = Build.VERSION_CODES.O)
public void onClick(View view) {
if(checkAppInstall("com.example.demo2"))
{
//打开已经安装的app
ComponentName componentName=new ComponentName("com.example.demo2","com.example.demo2.MainActivitywhat");
Intent intent=new Intent();
intent.setComponent(componentName);
startActivity(intent);
}
else
{ //跳转应用商店
gotoStore();
}
}
});
}
@RequiresApi(api = Build.VERSION_CODES.O)
public boolean checkAppInstall( String PackName){
PackageManager pm=getPackageManager();
boolean installed=false;
try {
pm.getPackageInfo(PackName,PackageManager.GET_ACTIVITIES);
installed=true;
} catch (PackageManager.NameNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
installed =false;
}
return installed;
}
public void gotoStore(){
Uri uri = Uri.parse("market://search?");
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW, uri);
startActivity(intent);
}
}