1 IMS启动过程
IMS的启动还是从SystemServer的startOtherServices方法中启动的。
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/reader/InputReader.cpp
private void startOtherServices(@NonNull TimingsTraceAndSlog t) {
...
t.traceBegin("StartInputManager");
inputManager.setWindowManagerCallbacks(wm.getInputManagerCallback());
inputManager.start();
t.traceEnd();
...
}
这里调用InputManagerService的start方法。
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/reader/InputReader.cpp
public void start() {
Slog.i(TAG, "Starting input manager");
mNative.start(); //1
// Add ourselves to the Watchdog monitors.
Watchdog.getInstance().addMonitor(this); //2
registerPointerSpeedSettingObserver();
registerShowTouchesSettingObserver();
registerAccessibilityLargePointerSettingObserver();
registerLongPressTimeoutObserver();
registerMaximumObscuringOpacityForTouchSettingObserver();
registerBlockUntrustedTouchesModeSettingObserver();
mContext.registerReceiver(new BroadcastReceiver() {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
updatePointerSpeedFromSettings();
updateShowTouchesFromSettings();
updateAccessibilityLargePointerFromSettings();
updateDeepPressStatusFromSettings("user switched");
}
}, new IntentFilter(Intent.ACTION_USER_SWITCHED), null, mHandler);
updatePointerSpeedFromSettings();
updateShowTouchesFromSettings();
updateAccessibilityLargePointerFromSettings();
updateDeepPressStatusFromSettings("just booted");
updateMaximumObscuringOpacityForTouchFromSettings();
updateBlockUntrustedTouchesModeFromSettings();
}
注释1处调用native的start方法,注释2处将自身添加到watchdog中进行监测。
frameworks/base/services/core/jni/com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp
static void nativeStart(JNIEnv* env, jobject nativeImplObj) {
NativeInputManager* im = getNativeInputManager(env, nativeImplObj);
status_t result = im->getInputManager()->start();
if (result) {
jniThrowRuntimeException(env, "Input manager could not be started.");
}
}
这里获取native中的InputManager对象,并调用其中的start方法。
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/InputManager.cpp
status_t InputManager::start() {
status_t result = mDispatcher->start(); //1
if (result) {
ALOGE("Could not start InputDispatcher thread due to error %d.", result);
return result;
}
result = mReader->start(); //2
if (result) {
ALOGE("Could not start InputReader due to error %d.", result);
mDispatcher->stop();
return result;
}
return OK;
}
注释1处调用了InputDispatcher的start函数,注释2处调用了InputReader的start函数。
2 InputDispatcher的启动
由上面的InputManager的start方法中调用了InputDispatcher的start函数。
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
status_t InputDispatcher::start() {
if (mThread) {
return ALREADY_EXISTS;
}
mThread = std::make_unique<InputThread>(
"InputDispatcher", [this]() { dispatchOnce(); }, [this]() { mLooper->wake(); });
return OK;
}
创建了单独的线程运行,InputThread构造函数接收三个参数,第一个参数是线程名,第二个参数是执行threadLoop时的回调函数,第三个参数是线程销毁前唤醒线程的回调。
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/InputThread.cpp
namespace {
// Implementation of Thread from libutils.
class InputThreadImpl : public Thread {
public:
explicit InputThreadImpl(std::function<void()> loop)
: Thread(/* canCallJava */ true), mThreadLoop(loop) {} //1
~InputThreadImpl() {}
private:
std::function<void()> mThreadLoop;
bool threadLoop() override { //2
mThreadLoop();
return true;
}
};
} // namespace
InputThread::InputThread(std::string name, std::function<void()> loop, std::function<void()> wake)
: mName(name), mThreadWake(wake) { //3
mThread = new InputThreadImpl(loop); //4
mThread->run(mName.c_str(), ANDROID_PRIORITY_URGENT_DISPLAY);
}
注释3处是InputThread的构造函数,这里对传入的第一个和第三个参数进行了初始化,然后注释4处创建InputThreadImpl对象,并调用其run方法。创建InputThreadImpl对象的时候调用注释1处构造函数,传入的是threadLoop中执行的方法,threadLoop是重写native的Thread中的方法,返回true并且没有调用requestExit函数,就会一直循环threadLoop中的函数,即dispatchOnce函数。
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce() {
nsecs_t nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MAX;
{ // acquire lock
std::scoped_lock _l(mLock);
mDispatcherIsAlive.notify_all();
// Run a dispatch loop if there are no pending commands.
// The dispatch loop might enqueue commands to run afterwards.
if (!haveCommandsLocked()) { //1
dispatchOnceInnerLocked(&nextWakeupTime); //2
}
// Run all pending commands if there are any.
// If any commands were run then force the next poll to wake up immediately.
if (runCommandsLockedInterruptable()) {
nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MIN;
}
// If we are still waiting for ack on some events,
// we might have to wake up earlier to check if an app is anr'ing.
const nsecs_t nextAnrCheck = processAnrsLocked();
nextWakeupTime = std::min(nextWakeupTime, nextAnrCheck);
// We are about to enter an infinitely long sleep, because we have no commands or
// pending or queued events
if (nextWakeupTime == LONG_LONG_MAX) {
mDispatcherEnteredIdle.notify_all();
}
} // release lock
// Wait for callback or timeout or wake. (make sure we round up, not down)
nsecs_t currentTime = now(); //3
int timeoutMillis = toMillisecondTimeoutDelay(currentTime, nextWakeupTime); //4
mLooper->pollOnce(timeoutMillis);
}
注释1处用于检查InputDispatcher的缓存队列中是否有等待处理的命令,如果没有就会调用注释2处的dispatchOnceInnerLocked函数进行窗口的分发。注释3处获取当前时间,注释4处得出休眠时间,然后调用pollOnce进入休眠,当InputReader有输入事件时,会唤醒InputDispatcher,重新进行事件的分发。
3 InputReader处理事件流程
InputReader的具体处理流程如下图所示:
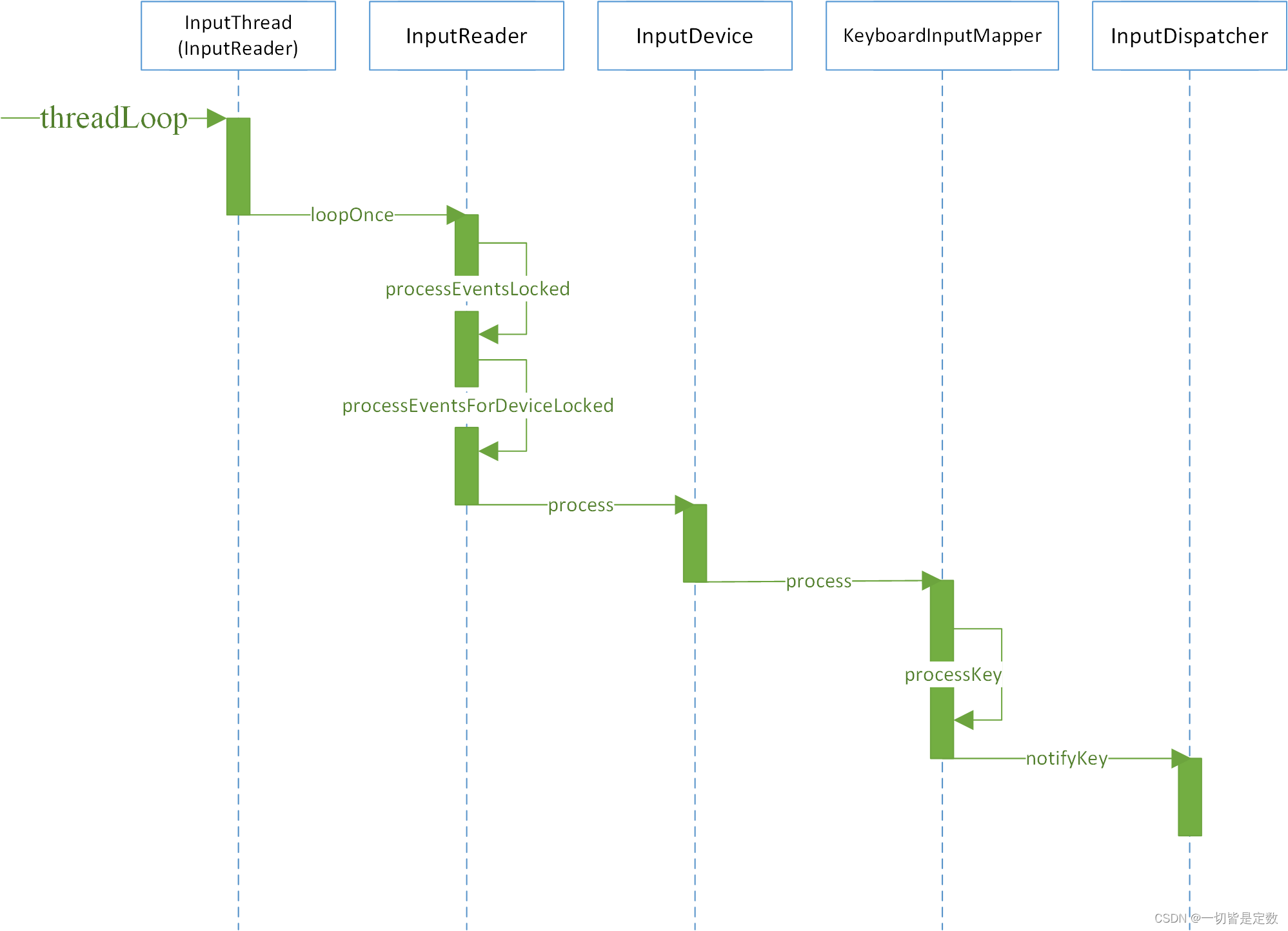 接下来进行详细的分析。
接下来进行详细的分析。
InputReader也是在InputManager的start方法中启动的,与InputDispatcher一样,会创建一个InputThread在单独的线程中运行。
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/reader/InputReader.cpp
status_t InputReader::start() {
if (mThread) {
return ALREADY_EXISTS;
}
mThread = std::make_unique<InputThread>(
"InputReader", [this]() { loopOnce(); }, [this]() { mEventHub->wake(); });
return OK;
}
threadLoop中执行的是loopOnce函数
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/reader/InputReader.cpp
void InputReader::loopOnce() {
...
size_t count = mEventHub->getEvents(timeoutMillis, mEventBuffer, EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE); //1
{ // acquire lock
std::scoped_lock _l(mLock);
mReaderIsAliveCondition.notify_all();
if (count) {
processEventsLocked(mEventBuffer, count); //2
}
...
}
注释1处调用EvnetHub的getEvents函数获取事件信息,存储到mEventBuffer中。事件信息主要有两种,一种是设备节点的增删事件,一种是原始输入事件。注释2处processEventsLocked函数用于处理原始输入事件,并将其交给InputDispatcher来处理。
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/reader/InputReader.cpp
void InputReader::processEventsLocked(const RawEvent* rawEvents, size_t count) {
for (const RawEvent* rawEvent = rawEvents; count;) {
int32_t type = rawEvent->type;
size_t batchSize = 1;
if (type < EventHubInterface::FIRST_SYNTHETIC_EVENT) { //1
int32_t deviceId = rawEvent->deviceId;
while (batchSize < count) {
if (rawEvent[batchSize].type >= EventHubInterface::FIRST_SYNTHETIC_EVENT ||
rawEvent[batchSize].deviceId != deviceId) {
break;
}
batchSize += 1;
}
if (DEBUG_RAW_EVENTS) {
ALOGD("BatchSize: %zu Count: %zu", batchSize, count);
}
processEventsForDeviceLocked(deviceId, rawEvent, batchSize);
} else {
switch (rawEvent->type) { //2
case EventHubInterface::DEVICE_ADDED:
addDeviceLocked(rawEvent->when, rawEvent->deviceId);
break;
case EventHubInterface::DEVICE_REMOVED:
removeDeviceLocked(rawEvent->when, rawEvent->deviceId);
break;
case EventHubInterface::FINISHED_DEVICE_SCAN:
handleConfigurationChangedLocked(rawEvent->when);
break;
default:
ALOG_ASSERT(false); // can't happen
break;
}
}
count -= batchSize;
rawEvent += batchSize;
}
}
该函数中会遍历mEventBuffer中存储的输入事件,注释1处处理原始输入事件,注释2处处理设备事件。事件存储在RawEvent里面,设备事件分为DEVICE_ADDED、DEVICE_REMOVED和FINISHED_DEVICE_SCAN,其中DEVICE_ADDED事件,InputReader会创建InputDevice对象,用来存储设备信息,并将其方法添加到mDevice中。
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/reader/include/InputReader.h
std::unordered_map<int32_t /*eventHubId*/, std::shared_ptr<InputDevice>> mDevices
GUARDED_BY(mLock);
mDevices的定义,是一个map集合,保存着eventHubId和InputDevice对象。
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/reader/InputReader.cpp
void InputReader::addDeviceLocked(nsecs_t when, int32_t eventHubId) {
...
std::shared_ptr<InputDevice> device = createDeviceLocked(eventHubId, identifier);
...
mDevices.emplace(eventHubId, device);
...
}
这里创建了InputDevice对象,并使用emplace将该对象添加到了mDevices集合中。
对于原始输入事件,调用processEventsForDeviceLocked函数进行处理。
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/reader/InputReader.cpp
void InputReader::processEventsForDeviceLocked(int32_t eventHubId, const RawEvent* rawEvents,
size_t count) {
auto deviceIt = mDevices.find(eventHubId); //1
if (deviceIt == mDevices.end()) {
ALOGW("Discarding event for unknown eventHubId %d.", eventHubId);
return;
}
std::shared_ptr<InputDevice>& device = deviceIt->second; //2
if (device->isIgnored()) {
// ALOGD("Discarding event for ignored deviceId %d.", deviceId);
return;
}
device->process(rawEvents, count); //3
}
注释1处根据eventHubId查询map集合中是否有该key,如果没有则返回,有则在注释2处将value值取出,是InputDevice类型的。在注释3处调用process函数执行处理。
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/reader/InputDevice.cpp
void InputDevice::process(const RawEvent* rawEvents, size_t count) {
// Process all of the events in order for each mapper.
// We cannot simply ask each mapper to process them in bulk because mappers may
// have side-effects that must be interleaved. For example, joystick movement events and
// gamepad button presses are handled by different mappers but they should be dispatched
// in the order received.
for (const RawEvent* rawEvent = rawEvents; count != 0; rawEvent++) {
if (DEBUG_RAW_EVENTS) {
ALOGD("Input event: device=%d type=0x%04x code=0x%04x value=0x%08x when=%" PRId64,
rawEvent->deviceId, rawEvent->type, rawEvent->code, rawEvent->value,
rawEvent->when);
}
if (mDropUntilNextSync) { //1
if (rawEvent->type == EV_SYN && rawEvent->code == SYN_REPORT) {
mDropUntilNextSync = false;
if (DEBUG_RAW_EVENTS) {
ALOGD("Recovered from input event buffer overrun.");
}
} else {
if (DEBUG_RAW_EVENTS) {
ALOGD("Dropped input event while waiting for next input sync.");
}
}
} else if (rawEvent->type == EV_SYN && rawEvent->code == SYN_DROPPED) {
ALOGI("Detected input event buffer overrun for device %s.", getName().c_str());
mDropUntilNextSync = true;
reset(rawEvent->when);
} else {
for_each_mapper_in_subdevice(rawEvent->deviceId, [rawEvent](InputMapper& mapper) {
mapper.process(rawEvent); //2
});
}
--count;
}
}
注释1处的mDropUntilNextSync的值默认为false,如果设备的输入缓冲区溢出,该值会被设置为true,如果恢复,会重新置为false。原始输入事件类型有很多,如键盘输入事件、触摸输入事件等,这些类别都会由单独的InputMapper的子类来进行处理。
注释2处遍历所有的Mapper类型,选择合适的Mapper处理事件,for_each_mapper_in_subdevice是一个内联函数,用于遍历所有的Mapper,InputReader将输入事件交由合适的InputMapper处理,至于是哪个InputMapper,InputReader并不关心。
这里以键盘输入事件为例,执行的是KeyboardInputMapper的process函数
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/reader/mapper/KeyboardInputMapper.cpp
void KeyboardInputMapper::process(const RawEvent* rawEvent) {
switch (rawEvent->type) {
case EV_KEY: { //1
int32_t scanCode = rawEvent->code;
int32_t usageCode = mCurrentHidUsage;
mCurrentHidUsage = 0;
if (isKeyboardOrGamepadKey(scanCode)) {
processKey(rawEvent->when, rawEvent->readTime, rawEvent->value != 0, scanCode,
usageCode); //2
}
break;
}
case EV_MSC: { //3
if (rawEvent->code == MSC_SCAN) {
mCurrentHidUsage = rawEvent->value;
}
break;
}
case EV_SYN: { //4
if (rawEvent->code == SYN_REPORT) {
mCurrentHidUsage = 0;
}
}
}
}
注释3处为其他事件的处理,注释4处为同步事件的处理。主要还是关注注释1处,按键类型事件,调用注释2处processKey函数进行处理。
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/reader/mapper/KeyboardInputMapper.cpp
void KeyboardInputMapper::processKey(nsecs_t when, nsecs_t readTime, bool down, int32_t scanCode,
int32_t usageCode) {
...
NotifyKeyArgs args(getContext()->getNextId(), when, readTime, getDeviceId(), mSource,
getDisplayId(), policyFlags,
down ? AKEY_EVENT_ACTION_DOWN : AKEY_EVENT_ACTION_UP,
AKEY_EVENT_FLAG_FROM_SYSTEM, keyCode, scanCode, keyMetaState, downTime);
getListener().notifyKey(&args);
}
这里会对键盘输入事件进行加工,并将加工后的数据封装到NotifyKeyArgs类型的对象中。getListener是InputMapper.h中的一个内联函数,返回的是InputListenerInterface类型的对象。InputDispatcherListener继承了InputListenerInterface,而InputDispatcher继承了InputDispatcherListener,所以这里调用的实际是INputDispatcher的notifyKey函数。
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::notifyKey(const NotifyKeyArgs* args) {
if (DEBUG_INBOUND_EVENT_DETAILS) {
ALOGD("notifyKey - eventTime=%" PRId64 ", deviceId=%d, source=0x%x, displayId=%" PRId32
"policyFlags=0x%x, action=0x%x, "
"flags=0x%x, keyCode=0x%x, scanCode=0x%x, metaState=0x%x, downTime=%" PRId64,
args->eventTime, args->deviceId, args->source, args->displayId, args->policyFlags,
args->action, args->flags, args->keyCode, args->scanCode, args->metaState,
args->downTime);
}
if (!validateKeyEvent(args->action)) {
return;
}
uint32_t policyFlags = args->policyFlags;
int32_t flags = args->flags;
int32_t metaState = args->metaState;
// InputDispatcher tracks and generates key repeats on behalf of
// whatever notifies it, so repeatCount should always be set to 0
constexpr int32_t repeatCount = 0;
if ((policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_VIRTUAL) || (flags & AKEY_EVENT_FLAG_VIRTUAL_HARD_KEY)) {
policyFlags |= POLICY_FLAG_VIRTUAL;
flags |= AKEY_EVENT_FLAG_VIRTUAL_HARD_KEY;
}
if (policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_FUNCTION) {
metaState |= AMETA_FUNCTION_ON;
}
policyFlags |= POLICY_FLAG_TRUSTED;
int32_t keyCode = args->keyCode;
accelerateMetaShortcuts(args->deviceId, args->action, keyCode, metaState);
KeyEvent event;
event.initialize(args->id, args->deviceId, args->source, args->displayId, INVALID_HMAC,
args->action, flags, keyCode, args->scanCode, metaState, repeatCount,
args->downTime, args->eventTime);
android::base::Timer t;
mPolicy->interceptKeyBeforeQueueing(&event, /*byref*/ policyFlags);
if (t.duration() > SLOW_INTERCEPTION_THRESHOLD) {
ALOGW("Excessive delay in interceptKeyBeforeQueueing; took %s ms",
std::to_string(t.duration().count()).c_str());
}
bool needWake = false;
{ // acquire lock
mLock.lock();
if (shouldSendKeyToInputFilterLocked(args)) { //1
mLock.unlock();
policyFlags |= POLICY_FLAG_FILTERED;
if (!mPolicy->filterInputEvent(&event, policyFlags)) {
return; // event was consumed by the filter
}
mLock.lock();
}
std::unique_ptr<KeyEntry> newEntry =
std::make_unique<KeyEntry>(args->id, args->eventTime, args->deviceId, args->source,
args->displayId, policyFlags, args->action, flags,
keyCode, args->scanCode, metaState, repeatCount,
args->downTime); //2
needWake = enqueueInboundEventLocked(std::move(newEntry)); //3
mLock.unlock();
} // release lock
if (needWake) {
mLooper->wake(); //4
}
}
注释1处如果事件被InputFilter过滤,如果事件被过滤器拦截,则返回。注释2之前的会将上面存储在NotifyKeyArgs中的按键数据重新获取并封装到注释2处的KeyEntry对象中,代表一次按键的数据。然后会在注释3处判断当前的按键数据是否需要唤醒InputDispatcher的处理线程进行分发处理,如果需要则会在注释4处唤醒InputDispatcher线程进行处理。