ESP32 DEVKIT V1 引脚
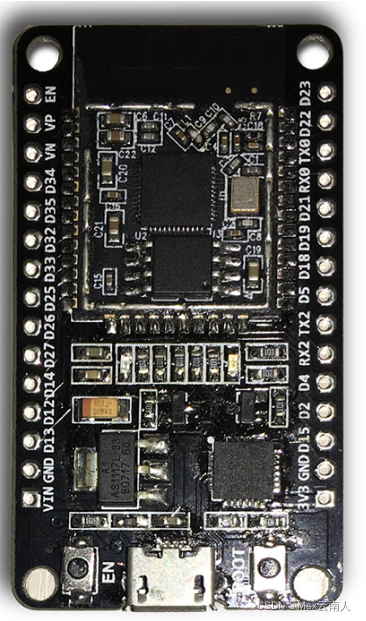
引脚定义查看:ESP32 DEVKILTv1(devkitv1)开发板全解析!!!(搭载芯片为ESP32D0WDQ6)
1.44寸TFT引脚
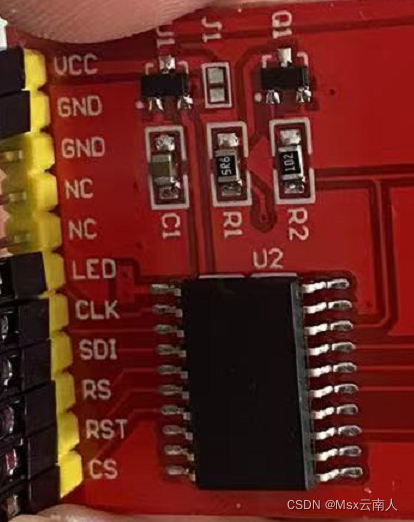

引脚分析
| 串口 | 功能 |
| VCC | 电源正 |
| GND | 电源地 |
| GND | 电源地 |
| NC | 无定义,保留,不需要接线 |
| NC | 无定义,保留,不需要接线 |
| LED | LCD背光控制信号 |
| CLK | LCD SPI总线时钟引脚 |
| SDI | LCD SPI总线数据引脚 |
| RS | LCD寄存器/数据选择控制引脚 |
| RST | LCD 复位控制引脚 |
| CS | LCD片选控制引脚 |
ESP32和1.44TFT引脚接法
| ESP32- DEVKIT V1 | 1.44寸TFT |
| 3V3 | VCC |
| GND(同一面) | GND |
| - | GND |
| - | NC |
| - | NC |
| D15 | LED |
| D18 | CLK |
| D23 | SDI |
| D4 | RS |
| D2 | RST |
| D14 | CS |
?TFT_eSPI库示例代码
User_Setup.h
// USER DEFINED SETTINGS
// Set driver type, fonts to be loaded, pins used and SPI control method etc
//
// See the User_Setup_Select.h file if you wish to be able to define multiple
// setups and then easily select which setup file is used by the compiler.
//
// If this file is edited correctly then all the library example sketches should
// run without the need to make any more changes for a particular hardware setup!
// Note that some sketches are designed for a particular TFT pixel width/height
// ##################################################################################
//
// Section 1. Call up the right driver file and any options for it
//
// ##################################################################################
// Define STM32 to invoke optimised processor support (only for STM32)
//#define STM32
// Defining the STM32 board allows the library to optimise the performance
// for UNO compatible "MCUfriend" style shields
//#define NUCLEO_64_TFT
//#define NUCLEO_144_TFT
// Tell the library to use 8 bit parallel mode (otherwise SPI is assumed)
//#define TFT_PARALLEL_8_BIT
// Display type - only define if RPi display
//#define RPI_DISPLAY_TYPE // 20MHz maximum SPI
// Only define one driver, the other ones must be commented out
//#define ILI9341_DRIVER
#define ST7735_DRIVER // Define additional parameters below for this display
//#define ILI9163_DRIVER // Define additional parameters below for this display
//#define S6D02A1_DRIVER
//#define RPI_ILI9486_DRIVER // 20MHz maximum SPI
//#define HX8357D_DRIVER
//#define ILI9481_DRIVER
//#define ILI9486_DRIVER
//#define ILI9488_DRIVER // WARNING: Do not connect ILI9488 display SDO to MISO if other devices share the SPI bus (TFT SDO does NOT tristate when CS is high)
//#define ST7789_DRIVER // Full configuration option, define additional parameters below for this display
//#define ST7789_2_DRIVER // Minimal configuration option, define additional parameters below for this display
//#define R61581_DRIVER
//#define RM68140_DRIVER
//#define ST7796_DRIVER
// Some displays support SPI reads via the MISO pin, other displays have a single
// bi-directional SDA pin and the library will try to read this via the MOSI line.
// To use the SDA line for reading data from the TFT uncomment the following line:
// #define TFT_SDA_READ // This option is for ESP32 ONLY, tested with ST7789 display only
// For ST7789 and ILI9341 ONLY, define the colour order IF the blue and red are swapped on your display
// Try ONE option at a time to find the correct colour order for your display
#define TFT_RGB_ORDER TFT_RGB // Colour order Red-Green-Blue
// #define TFT_RGB_ORDER TFT_BGR // Colour order Blue-Green-Red
// For M5Stack ESP32 module with integrated ILI9341 display ONLY, remove // in line below
// #define M5STACK
// For ST7789, ST7735 and ILI9163 ONLY, define the pixel width and height in portrait orientation
// #define TFT_WIDTH 80
#define TFT_WIDTH 128
// #define TFT_WIDTH 240 // ST7789 240 x 240 and 240 x 320
#define TFT_HEIGHT 160
// #define TFT_HEIGHT 128
// #define TFT_HEIGHT 240 // ST7789 240 x 240
// #define TFT_HEIGHT 320 // ST7789 240 x 320
// For ST7735 ONLY, define the type of display, originally this was based on the
// colour of the tab on the screen protector film but this is not always true, so try
// out the different options below if the screen does not display graphics correctly,
// e.g. colours wrong, mirror images, or tray pixels at the edges.
// Comment out ALL BUT ONE of these options for a ST7735 display driver, save this
// this User_Setup file, then rebuild and upload the sketch to the board again:
// #define ST7735_INITB
// #define ST7735_GREENTAB
#define ST7735_GREENTAB2
// #define ST7735_GREENTAB3
// #define ST7735_GREENTAB128 // For 128 x 128 display
// #define ST7735_GREENTAB160x80 // For 160 x 80 display (BGR, inverted, 26 offset)
// #define ST7735_REDTAB
// #define ST7735_BLACKTAB
// #define ST7735_REDTAB160x80 // For 160 x 80 display with 24 pixel offset
// If colours are inverted (white shows as black) then uncomment one of the next
// 2 lines try both options, one of the options should correct the inversion.
// #define TFT_INVERSION_ON
#define TFT_INVERSION_OFF
// If a backlight control signal is available then define the TFT_BL pin in Section 2
// below. The backlight will be turned ON when tft.begin() is called, but the library
// needs to know if the LEDs are ON with the pin HIGH or LOW. If the LEDs are to be
// driven with a PWM signal or turned OFF/ON then this must be handled by the user
// sketch. e.g. with digitalWrite(TFT_BL, LOW);
#define TFT_BACKLIGHT_ON HIGH // HIGH or LOW are options
// ##################################################################################
//
// Section 2. Define the pins that are used to interface with the display here
//
// ##################################################################################
// We must use hardware SPI, a minimum of 3 GPIO pins is needed.
// Typical setup for ESP8266 NodeMCU ESP-12 is :
//
// Display SDO/MISO to NodeMCU pin D6 (or leave disconnected if not reading TFT)
// Display LED to NodeMCU pin VIN (or 5V, see below)
// Display SCK to NodeMCU pin D5
// Display SDI/MOSI to NodeMCU pin D7
// Display DC (RS/AO)to NodeMCU pin D3
// Display RESET to NodeMCU pin D4 (or RST, see below)
// Display CS to NodeMCU pin D8 (or GND, see below)
// Display GND to NodeMCU pin GND (0V)
// Display VCC to NodeMCU 5V or 3.3V
//
// The TFT RESET pin can be connected to the NodeMCU RST pin or 3.3V to free up a control pin
//
// The DC (Data Command) pin may be labeled AO or RS (Register Select)
//
// With some displays such as the ILI9341 the TFT CS pin can be connected to GND if no more
// SPI devices (e.g. an SD Card) are connected, in this case comment out the #define TFT_CS
// line below so it is NOT defined. Other displays such at the ST7735 require the TFT CS pin
// to be toggled during setup, so in these cases the TFT_CS line must be defined and connected.
//
// The NodeMCU D0 pin can be used for RST
//
//
// Note: only some versions of the NodeMCU provide the USB 5V on the VIN pin
// If 5V is not available at a pin you can use 3.3V but backlight brightness
// will be lower.
// ###### EDIT THE PIN NUMBERS IN THE LINES FOLLOWING TO SUIT YOUR ESP8266 SETUP ######
// For NodeMCU - use pin numbers in the form PIN_Dx where Dx is the NodeMCU pin designation
//#define TFT_CS PIN_D8 // Chip select control pin D8
//#define TFT_DC PIN_D3 // Data Command control pin
//#define TFT_RST PIN_D4 // Reset pin (could connect to NodeMCU RST, see next line)
//#define TFT_RST -1 // Set TFT_RST to -1 if the display RESET is connected to NodeMCU RST or 3.3V
//#define TFT_BL PIN_D1 // LED back-light (only for ST7789 with backlight control pin)
//#define TOUCH_CS PIN_D2 // Chip select pin (T_CS) of touch screen
//#define TFT_WR PIN_D2 // Write strobe for modified Raspberry Pi TFT only
// ###### FOR ESP8266 OVERLAP MODE EDIT THE PIN NUMBERS IN THE FOLLOWING LINES ######
// Overlap mode shares the ESP8266 FLASH SPI bus with the TFT so has a performance impact
// but saves pins for other functions. It is best not to connect MISO as some displays
// do not tristate that line wjen chip select is high!
// On NodeMCU 1.0 SD0=MISO, SD1=MOSI, CLK=SCLK to connect to TFT in overlap mode
// On NodeMCU V3 S0 =MISO, S1 =MOSI, S2 =SCLK
// In ESP8266 overlap mode the following must be defined
//#define TFT_SPI_OVERLAP
// In ESP8266 overlap mode the TFT chip select MUST connect to pin D3
//#define TFT_CS PIN_D3
//#define TFT_DC PIN_D5 // Data Command control pin
//#define TFT_RST PIN_D4 // Reset pin (could connect to NodeMCU RST, see next line)
//#define TFT_RST -1 // Set TFT_RST to -1 if the display RESET is connected to NodeMCU RST or 3.3V
// ###### EDIT THE PIN NUMBERS IN THE LINES FOLLOWING TO SUIT YOUR ESP32 SETUP ######
// For ESP32 Dev board (only tested with ILI9341 display)
// The hardware SPI can be mapped to any pins
//#define TFT_MISO 19
#define TFT_MOSI 23
#define TFT_SCLK 18
#define TFT_CS 14 // Chip select control pin
#define TFT_DC 4 // Data Command control pin
#define TFT_RST 2 // Reset pin (could connect to RST pin)
//#define TFT_RST -1 // Set TFT_RST to -1 if display RESET is connected to ESP32 board RST
//#define TFT_BL 32 // LED back-light (only for ST7789 with backlight control pin)
//#define TOUCH_CS 21 // Chip select pin (T_CS) of touch screen
//#define TFT_WR 22 // Write strobe for modified Raspberry Pi TFT only
// For the M5Stack module use these #define lines
//#define TFT_MISO 19
//#define TFT_MOSI 23
//#define TFT_SCLK 18
//#define TFT_CS 14 // Chip select control pin
//#define TFT_DC 27 // Data Command control pin
//#define TFT_RST 33 // Reset pin (could connect to Arduino RESET pin)
//#define TFT_BL 32 // LED back-light (required for M5Stack)
// ###### EDIT THE PINs BELOW TO SUIT YOUR ESP32 PARALLEL TFT SETUP ######
// The library supports 8 bit parallel TFTs with the ESP32, the pin
// selection below is compatible with ESP32 boards in UNO format.
// Wemos D32 boards need to be modified, see diagram in Tools folder.
// Only ILI9481 and ILI9341 based displays have been tested!
// Parallel bus is only supported on ESP32
// Uncomment line below to use ESP32 Parallel interface instead of SPI
//#define ESP32_PARALLEL
// The ESP32 and TFT the pins used for testing are:
//#define TFT_CS 33 // Chip select control pin (library pulls permanently low
//#define TFT_DC 15 // Data Command control pin - must use a pin in the range 0-31
//#define TFT_RST 32 // Reset pin, toggles on startup
//#define TFT_WR 4 // Write strobe control pin - must use a pin in the range 0-31
//#define TFT_RD 2 // Read strobe control pin
//#define TFT_D0 12 // Must use pins in the range 0-31 for the data bus
//#define TFT_D1 13 // so a single register write sets/clears all bits.
//#define TFT_D2 26 // Pins can be randomly assigned, this does not affect
//#define TFT_D3 25 // TFT screen update performance.
//#define TFT_D4 17
//#define TFT_D5 16
//#define TFT_D6 27
//#define TFT_D7 14
// ##################################################################################
//
// Section 3. Define the fonts that are to be used here
//
// ##################################################################################
// Comment out the #defines below with // to stop that font being loaded
// The ESP8366 and ESP32 have plenty of memory so commenting out fonts is not
// normally necessary. If all fonts are loaded the extra FLASH space required is
// about 17Kbytes. To save FLASH space only enable the fonts you need!
#define LOAD_GLCD // Font 1. Original Adafruit 8 pixel font needs ~1820 bytes in FLASH
#define LOAD_FONT2 // Font 2. Small 16 pixel high font, needs ~3534 bytes in FLASH, 96 characters
#define LOAD_FONT4 // Font 4. Medium 26 pixel high font, needs ~5848 bytes in FLASH, 96 characters
#define LOAD_FONT6 // Font 6. Large 48 pixel font, needs ~2666 bytes in FLASH, only characters 1234567890:-.apm
#define LOAD_FONT7 // Font 7. 7 segment 48 pixel font, needs ~2438 bytes in FLASH, only characters 1234567890:-.
#define LOAD_FONT8 // Font 8. Large 75 pixel font needs ~3256 bytes in FLASH, only characters 1234567890:-.
//#define LOAD_FONT8N // Font 8. Alternative to Font 8 above, slightly narrower, so 3 digits fit a 160 pixel TFT
#define LOAD_GFXFF // FreeFonts. Include access to the 48 Adafruit_GFX free fonts FF1 to FF48 and custom fonts
// Comment out the #define below to stop the SPIFFS filing system and smooth font code being loaded
// this will save ~20kbytes of FLASH
#define SMOOTH_FONT
// ##################################################################################
//
// Section 4. Other options
//
// ##################################################################################
// Define the SPI clock frequency, this affects the graphics rendering speed. Too
// fast and the TFT driver will not keep up and display corruption appears.
// With an ILI9341 display 40MHz works OK, 80MHz sometimes fails
// With a ST7735 display more than 27MHz may not work (spurious pixels and lines)
// With an ILI9163 display 27 MHz works OK.
// #define SPI_FREQUENCY 1000000
// #define SPI_FREQUENCY 5000000
// #define SPI_FREQUENCY 10000000
// #define SPI_FREQUENCY 20000000
#define SPI_FREQUENCY 27000000 // Actually sets it to 26.67MHz = 80/3
// #define SPI_FREQUENCY 40000000
// #define SPI_FREQUENCY 80000000
// Optional reduced SPI frequency for reading TFT
#define SPI_READ_FREQUENCY 20000000
// The XPT2046 requires a lower SPI clock rate of 2.5MHz so we define that here:
#define SPI_TOUCH_FREQUENCY 2500000
// The ESP32 has 2 free SPI ports i.e. VSPI and HSPI, the VSPI is the default.
// If the VSPI port is in use and pins are not accessible (e.g. TTGO T-Beam)
// then uncomment the following line:
//#define USE_HSPI_PORT
// Comment out the following #define if "SPI Transactions" do not need to be
// supported. When commented out the code size will be smaller and sketches will
// run slightly faster, so leave it commented out unless you need it!
// Transaction support is needed to work with SD library but not needed with TFT_SdFat
// Transaction support is required if other SPI devices are connected.
// Transactions are automatically enabled by the library for an ESP32 (to use HAL mutex)
// so changing it here has no effect
// #define SUPPORT_TRANSACTIONS
?代码
/*
An example analogue clock using a TFT LCD screen to show the time
use of some of the drawing commands with the ST7735 library.
For a more accurate clock, it would be better to use the RTClib library.
But this is just a demo.
Uses compile time to set the time so a reset will start with the compile time again
Gilchrist 6/2/2014 1.0
Updated by Bodmer
*/
#include <TFT_eSPI.h> // Graphics and font library for ST7735 driver chip
#include <SPI.h>
TFT_eSPI tft = TFT_eSPI(); // Invoke library, pins defined in User_Setup.h
#define TFT_GREY 0xBDF7
float sx = 0, sy = 1, mx = 1, my = 0, hx = -1, hy = 0; // Saved H, M, S x & y multipliers
float sdeg=0, mdeg=0, hdeg=0;
uint16_t osx=64, osy=64, omx=64, omy=64, ohx=64, ohy=64; // Saved H, M, S x & y coords
uint16_t x0=0, x1=0, yy0=0, yy1=0;
uint32_t targetTime = 0; // for next 1 second timeout
static uint8_t conv2d(const char* p) {
uint8_t v = 0;
if ('0' <= *p && *p <= '9')
v = *p - '0';
return 10 * v + *++p - '0';
}
uint8_t hh=conv2d(__TIME__), mm=conv2d(__TIME__+3), ss=conv2d(__TIME__+6); // Get H, M, S from compile time
boolean initial = 1;
void setup(void) {
tft.init();
tft.setRotation(0);
tft.fillScreen(TFT_GREY);
tft.setTextColor(TFT_GREEN, TFT_GREY); // Adding a black background colour erases previous text automatically
// Draw clock face
tft.fillCircle(64, 64, 61, TFT_BLUE);
tft.fillCircle(64, 64, 57, TFT_BLACK);
// Draw 12 lines
for(int i = 0; i<360; i+= 30) {
sx = cos((i-90)*0.0174532925);
sy = sin((i-90)*0.0174532925);
x0 = sx*57+64;
yy0 = sy*57+64;
x1 = sx*50+64;
yy1 = sy*50+64;
tft.drawLine(x0, yy0, x1, yy1, TFT_BLUE);
}
// Draw 60 dots
for(int i = 0; i<360; i+= 6) {
sx = cos((i-90)*0.0174532925);
sy = sin((i-90)*0.0174532925);
x0 = sx*53+64;
yy0 = sy*53+64;
tft.drawPixel(x0, yy0, TFT_BLUE);
if(i==0 || i==180) tft.fillCircle(x0, yy0, 1, TFT_CYAN);
if(i==0 || i==180) tft.fillCircle(x0+1, yy0, 1, TFT_CYAN);
if(i==90 || i==270) tft.fillCircle(x0, yy0, 1, TFT_CYAN);
if(i==90 || i==270) tft.fillCircle(x0+1, yy0, 1, TFT_CYAN);
}
tft.fillCircle(65, 65, 3, TFT_RED);
// Draw text at position 64,125 using fonts 4
// Only font numbers 2,4,6,7 are valid. Font 6 only contains characters [space] 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 : . a p m
// Font 7 is a 7 segment font and only contains characters [space] 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 : .
tft.drawCentreString("Time flies",64,130,4);
targetTime = millis() + 1000;
}
void loop() {
if (targetTime < millis()) {
targetTime = millis()+1000;
ss++; // Advance second
if (ss==60) {
ss=0;
mm++; // Advance minute
if(mm>59) {
mm=0;
hh++; // Advance hour
if (hh>23) {
hh=0;
}
}
}
// Pre-compute hand degrees, x & y coords for a fast screen update
sdeg = ss*6; // 0-59 -> 0-354
mdeg = mm*6+sdeg*0.01666667; // 0-59 -> 0-360 - includes seconds
hdeg = hh*30+mdeg*0.0833333; // 0-11 -> 0-360 - includes minutes and seconds
hx = cos((hdeg-90)*0.0174532925);
hy = sin((hdeg-90)*0.0174532925);
mx = cos((mdeg-90)*0.0174532925);
my = sin((mdeg-90)*0.0174532925);
sx = cos((sdeg-90)*0.0174532925);
sy = sin((sdeg-90)*0.0174532925);
if (ss==0 || initial) {
initial = 0;
// Erase hour and minute hand positions every minute
tft.drawLine(ohx, ohy, 65, 65, TFT_BLACK);
ohx = hx*33+65;
ohy = hy*33+65;
tft.drawLine(omx, omy, 65, 65, TFT_BLACK);
omx = mx*44+65;
omy = my*44+65;
}
// Redraw new hand positions, hour and minute hands not erased here to avoid flicker
tft.drawLine(osx, osy, 65, 65, TFT_BLACK);
tft.drawLine(ohx, ohy, 65, 65, TFT_WHITE);
tft.drawLine(omx, omy, 65, 65, TFT_WHITE);
osx = sx*47+65;
osy = sy*47+65;
tft.drawLine(osx, osy, 65, 65, TFT_RED);
tft.fillCircle(65, 65, 3, TFT_RED);
}
}
Arduino添加ESP32开发板
https://blog.csdn.net/Naisu_kun/article/details/84958561
参考:
Arduino环境下ESP32+1.8'128X160 RGB_TFT(ST7735S)三种库的配置及示例程序效果_大头工程师笔记的博客-CSDN博客_esp32 st7735s