百度:
ptrace()系统调用提供了一种方法可以使得追踪者(tracer)来对被追踪者(tracee)进行观察与控制。具体表现为可以检查tracee中内存以及寄存器的值。ptrace首要地被用于实现断点debug与系统调用追踪。
首先,tracee process必须要被tracer attach上(也就是我们启动gdb后的 attach pid),需要注意的是,attach和后续的命令是针对每个线程来说的。如果是一个多线程的程序,每个线程都要被单独的attach才行。这里主要强调了,tracee(被追踪者)是一个单独的thread,而非一个整个的多线程程序。
当追踪时,tracee每次发送一个信号就会停一次,即使这个signal会被忽略掉。而tracer将会捕捉到tracee的下一个调用(通过waitpid或wait类似系统调用)。而这个调用将会告诉tracer,tracee停止的原因以及相关信息。所以当tracee停下来,tracer可以通过ptrace的多种模式来进行监控甚至修改tracee,然后tracer会告诉tracee继续运行。
ptrace四个参数的含义解释如下:
request :request的值确定要执行的操作
第二参数 pid :指示ptrace要跟踪的进程。
第三参数 addr :指定ptrace要读取or监控的内存地址。
第四参数 data :如果我们要向目标进程写入数据,那么data是我们要写入的数据;如果我们从目标进程中读出数据,那么读出的数据放在data。
运行:
- 在ARM架构的系统中运行test。
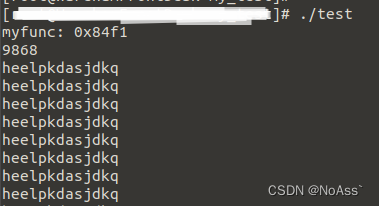
- 运行ptrace程序。
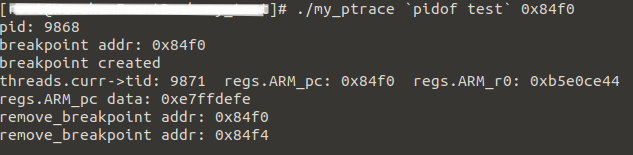
breakpoints(断点):
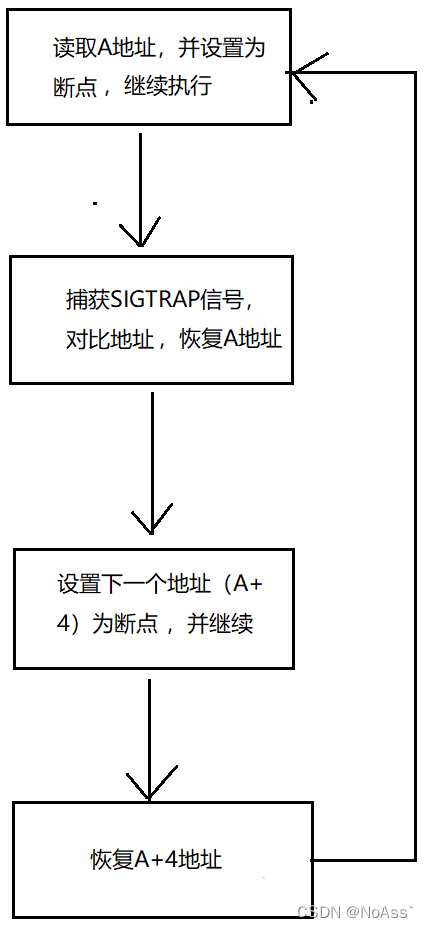
断点不是ptrace中的一部分,是通过将中断指令写入到某个地址,当程序执行到该地址时,就会产生SIGTRAP信号,正常情况下程序就会因为信号而崩溃,但是ptrace会捕获到该信号,就形成了断点。大致流程:
1. 读取A地址的指令,保存到指令结构体中。
2. 将中断指令写入到A地址中。
3. 当程序执行到A地址时,CPU会产生一个SIGTRAP信号,ptrace捕获到该信号,比较指令结构体中保存的地址,判断是否是对应的地址,找到对应地址后,恢复A地址的指令。
4. 恢复地址后,将中断指令写入到下一个地址(A+4),并执行下一步,目的是继续循环让A地址设置为断点。
5. 下一个地址(A+4)恢复到原来的指令,继续执行,等到循环断点。
如图所示,循环断到某地址:
代码简介:
每个架构的中断指令都不一样,由于本人用的是ARM小端的系统,所以是0xFE,0xDE,0xFF,0xE7。
/*ARM小端*/
static uint8_t break_instr[] = {0xFE,0xDE,0xFF,0xE7};
/*
// ARM大端
static uint8_t break_instr[] = {0xE7,0xFF,0xDE,0xFE};
// THUMB小端
static uint8_t break_instr[] = {0xfe,0xdf};
// THUMB大端
static uint8_t break_instr[] = {0xdf,0xfe};
*/
/*
// MIPS中断指令
#define BIG_BREAKPOINT {0, 0x5, 0, 0xd}
#define LITTLE_BREAKPOINT {0xd, 0, 0x5, 0}
#define PMON_BIG_BREAKPOINT {0, 0, 0, 0xd}
#define PMON_LITTLE_BREAKPOINT {0xd, 0, 0, 0}
#define IDT_BIG_BREAKPOINT {0, 0, 0x0a, 0xd}
#define IDT_LITTLE_BREAKPOINT {0xd, 0x0a, 0, 0}
#define MIPS16_BIG_BREAKPOINT {0xe8, 0xa5}
#define MIPS16_LITTLE_BREAKPOINT {0xa5, 0xe8}
*/
使用PTRACE_PEEKDATA读取地址的指令,并保存。再用PTRACE_POKEDATA将中断指令写入到地址中。
/*设置断点*/
char set_breakpoint(pid_t tid, size_t addr)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < BREAKPOINT_NUMBER; i++){
if (breakpoints[i].addr == 0)
{
// 读取addr地址中的数据
size_t data = ptrace(PTRACE_PEEKDATA, tid, (void *)addr, NULL);
breakpoints[i].orig_data = data;
breakpoints[i].addr = addr;
memcpy((void *)&data, break_instr, sizeof(break_instr));
// 将中断指令写入到对应的地址
ptrace(PTRACE_POKEDATA, tid, (void *)addr, data);
break;
}
}
if (i == BREAKPOINT_NUMBER)
return 0;
else
return 1;
}
还原之前的指令,否证会一直断在该地址。
// 移除断点
char remove_breakpoint(pid_t tid, size_t addr)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < BREAKPOINT_NUMBER; i++)
if (breakpoints[i].addr == addr)
{
/*还原原来的数据*/
ptrace(PTRACE_POKEDATA, tid, (void *)addr, breakpoints[i].orig_data);
breakpoints[i].addr = 0;
printf("remove_breakpoint addr: 0x%lx\n",addr);
break;
}
if (i == BREAKPOINT_NUMBER){
printf("BREAKPOINT_NUMBER error\n");
return 0;
}
else
return 1;
}
继续执行,相当于gdb命令中的 c 命令,一值运行下去,直到有信号中断该程序。
for (int i = 0, n = 0; i < THREAD_NUMBER && n < threads.len; i++){
if (threads.t[i].tid)
{
ptrace(PTRACE_CONT, threads.t[i].tid, 0, 0);
n++;
}
}
阻塞等待要中断的pid号,如果没有遇到捕获到信号,则会阻塞在这里。
int stat;
pid_t tid = waitpid(-1, &stat, __WALL);
完整代码:
test.c
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <pthread.h>
void hello(char **h){
printf("%s\n",*h);
}
void myfunc(void* arg){
//打印子线程id
char *a = "heelpkdasjdkq";
char **b = &a;
for(int i=0; i<2000;i++){
hello(b);
sleep(2);
}
return;
}
int main(){
void(*pgo1)(void* a) = hello;
//打印hello函数的地址,真实的hello的地址是打印出来的-1
printf("myfunc: %p\n",pgo1);
pthread_t ptid;
//打印自身的pid
printf("%d\n",getpid());
//创建10个线程
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
int ret = pthread_create(&ptid, NULL, myfunc, NULL);
if (ret != 0){
printf("pthread err %d\n", ret);
}
}
sleep(200);
return 0;
}
my_ptrace.h
#include <dirent.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <syscall.h>
#include <sys/ptrace.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/user.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/user.h>
#include <sys/syscall.h> /* SYS_write */
#include <asm/ptrace.h>
#include <assert.h>
#define THREAD_NUMBER 64
#define BREAKPOINT_NUMBER 64
struct thread_id_t
{
pid_t pid;
pid_t tid;
int stat;
};
struct thread_list_t
{
struct thread_id_t t[THREAD_NUMBER];
struct thread_id_t *curr;
int len;
} threads;
struct debug_breakpoint_t
{
size_t addr;
size_t orig_data;
} breakpoints[BREAKPOINT_NUMBER];
/*ARM小端*/
static uint8_t break_instr[] = {0xFE,0xDE,0xFF,0xE7};
/*
// ARM大端
static uint8_t break_instr[] = {0xE7,0xFF,0xDE,0xFE};
// THUMB小端
static uint8_t break_instr[] = {0xfe,0xdf};
// THUMB大端
static uint8_t break_instr[] = {0xdf,0xfe};
*/
/*
// MIPS中断指令
#define BIG_BREAKPOINT {0, 0x5, 0, 0xd}
#define LITTLE_BREAKPOINT {0xd, 0, 0x5, 0}
#define PMON_BIG_BREAKPOINT {0, 0, 0, 0xd}
#define PMON_LITTLE_BREAKPOINT {0xd, 0, 0, 0}
#define IDT_BIG_BREAKPOINT {0, 0, 0x0a, 0xd}
#define IDT_LITTLE_BREAKPOINT {0xd, 0x0a, 0, 0}
#define MIPS16_BIG_BREAKPOINT {0xe8, 0xa5}
#define MIPS16_LITTLE_BREAKPOINT {0xa5, 0xe8}
*/
/*
// x86-64
static unsigned char breakpoint[] = { 0xcc };
*/
/*设置断点*/
char set_breakpoint(pid_t tid, size_t addr);
// 移除断点
char remove_breakpoint(pid_t tid, size_t addr);
/*将tid设置为当前线程*/
void set_curr_thread(pid_t tid);
int resume_from_breakpoint(pid_t pid);
/*获取当前pid的全部线程信息*/
int init_tids(const pid_t pid);
my_ptrace.c
#include "my_ptrace.h"
/*设置断点*/
char set_breakpoint(pid_t tid, size_t addr)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < BREAKPOINT_NUMBER; i++){
if (breakpoints[i].addr == 0)
{
// 读取addr地址中的数据
size_t data = ptrace(PTRACE_PEEKDATA, tid, (void *)addr, NULL);
breakpoints[i].orig_data = data;
breakpoints[i].addr = addr;
memcpy((void *)&data, break_instr, sizeof(break_instr));
// 将中断指令写入到对应的地址
ptrace(PTRACE_POKEDATA, tid, (void *)addr, data);
break;
}
}
if (i == BREAKPOINT_NUMBER)
return 0;
else
return 1;
}
// 移除断点
char remove_breakpoint(pid_t tid, size_t addr)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < BREAKPOINT_NUMBER; i++)
if (breakpoints[i].addr == addr)
{
/*还原原来的数据*/
ptrace(PTRACE_POKEDATA, tid, (void *)addr, breakpoints[i].orig_data);
breakpoints[i].addr = 0;
printf("remove_breakpoint addr: 0x%lx\n",addr);
break;
}
if (i == BREAKPOINT_NUMBER){
printf("BREAKPOINT_NUMBER error\n");
return 0;
}
else
return 1;
}
/*将pid设置为当前线程*/
void set_curr_thread(pid_t tid)
{
for (int i = 0; i < THREAD_NUMBER; i++)
if (threads.t[i].tid == tid)
{
threads.curr = &threads.t[i];
break;
}
}
int resume_from_breakpoint(pid_t pid)
{
struct pt_regs regs = {0};
int wait_status;
int f = 0;
char ret = -1;
// 获取对应寄存器的值
ptrace(PTRACE_GETREGS, threads.curr->tid, 0, ®s);
printf("threads.curr->tid: %d regs.ARM_pc: 0x%lx regs.ARM_r0: 0x%lx\n",threads.curr->tid,regs.ARM_pc, regs.ARM_r0);
size_t data = ptrace(PTRACE_PEEKDATA, threads.curr->tid, (void *)(regs.ARM_pc), NULL);
printf("regs.ARM_pc data: 0x%lx\n",data);
size_t addr = 0;
int i;
// 判断地址是否是要设置断点的地址
for (i = 0; i < BREAKPOINT_NUMBER; i++){
if (breakpoints[i].addr == regs.ARM_pc)
{
addr = breakpoints[i].addr;
break;
}
}
if (!addr){
return -1;
}
// 移除中断
ret = remove_breakpoint(threads.curr->tid, addr);
if (!ret){
printf("remove_breakpoint error\n");
return -1;
}
// 设置下一步的断点
ret = set_breakpoint(threads.curr->tid, addr+4);
if (!ret){
printf("breakpoint error\n");
return -1;
}
// 继续 相当于执行下一步
for (int i = 0, n = 0; i < THREAD_NUMBER && n < threads.len; i++){
if (threads.t[i].tid)
{
ptrace(PTRACE_CONT, threads.t[i].tid, 0, 0);
n++;
}
}
// 等待中断
waitpid(threads.curr->tid, &threads.curr->stat, __WALL);
WIFEXITED(threads.curr->stat);
if (!WIFSTOPPED(threads.curr->stat))
{
printf("threads.curr->tid2: %d exit\n",threads.curr->tid);
}
ret = remove_breakpoint(threads.curr->tid, addr+4);
if (!ret){
printf("remove_breakpoint error\n");
return -1;
}
// 重新设置中断
ret = set_breakpoint(threads.curr->tid, addr);
if (!ret){
printf("breakpoint error\n");
return -1;
}
// 继续
for (int i = 0, n = 0; i < THREAD_NUMBER && n < threads.len; i++){
if (threads.t[i].tid)
{
ptrace(PTRACE_CONT, threads.t[i].tid, 0, 0);
n++;
}
}
// 等待中断
int stat;
pid_t tid = waitpid(-1, &stat, __WALL);
if (tid < 0)
return -1;
threads.curr->stat = stat;
set_curr_thread(tid);
if (WIFEXITED(threads.curr->stat))
{
threads.curr->pid = 0;
threads.curr->tid = 0;
threads.curr = NULL;
threads.len--;
}
if (!WIFSTOPPED(threads.curr->stat))
{
printf("threads.curr->tid4: %d exit\n",threads.curr->tid);
}
return 1;
}
/*获取当前pid的全部线程信息*/
int init_tids(const pid_t pid)
{
char dirname[64];
DIR *dir;
struct dirent *ent;
int i = 0;
// 通过/proc/xxx/task 下的文件夹名称得到线程号
snprintf(dirname, sizeof dirname, "/proc/%d/task/", (int)pid);
dir = opendir(dirname);
if (!dir){
perror("opendir()");
return 0;
}
while ((ent = readdir(dir)) != NULL)
{
if (ent->d_name[0] == '.')
continue;
threads.t[i].pid = pid;
threads.t[i].tid = atoi(ent->d_name);
threads.len++;
i++;
}
closedir(dir);
return 1;
}
void run_debugger(pid_t child_pid, size_t addr)
{
printf("pid: %d\n", child_pid);
// 设置断点
printf("breakpoint addr: 0x%lx\n",addr);
char ret = set_breakpoint(threads.curr->tid, addr);
if (ret)
printf("breakpoint created\n");
else{
printf("breakpoint error\n");
return;
}
for (int i = 0, n = 0; i < THREAD_NUMBER && n < threads.len; i++){
if (threads.t[i].tid)
{
ptrace(PTRACE_CONT, threads.t[i].tid, NULL, NULL);
n++;
}
}
int wait_status;
pid_t tid = waitpid(-1, &wait_status, __WALL);
set_curr_thread(tid);
while (1) {
int rc = resume_from_breakpoint(tid);
printf("\n");
if (rc) {
continue;
}
else {
printf("unexpected: %d\n", rc);
break;
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
pid_t pid;
if (argc < 3) {
fprintf(stderr, "sudo ./my_ptrace (pid) (addr)\n");
return -1;
}
pid = atoi(argv[1]);
if (pid > 0) {
if(init_tids(pid) == 0){
return 0;
}
for (int i = 0, n = 0; i < THREAD_NUMBER && n < threads.len; i++){
if (threads.t[i].tid)
{
// ATTACH 目标pid
if (ptrace(PTRACE_ATTACH, threads.t[i].tid, NULL, NULL) < 0)
{
perror("ptrace()");
return -1;
}
if (waitpid(threads.t[i].tid, &threads.t[i].stat, __WALL) < 0)
{
perror("waitpid");
return -1;
}
ptrace(PTRACE_SETOPTIONS, threads.t[i].tid, NULL, PTRACE_O_TRACECLONE);
n++;
}
}
threads.curr = &threads.t[0];
size_t addr = (size_t) strtol(argv[2], NULL, 16);
run_debugger(pid, addr);
}
else {
printf("pid :%d\n",pid);
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
Makefile
CC = arm-linux-gnueabihf-gcc
CCFLAGS = -std=gnu99 -Wall -O0 -g -o
EXECUTABLES = my_ptrace
.PHONY: all clean
all:
$(CC) $(CCFLAGS) my_ptrace my_ptrace.c my_ptrace.h
$(CC) $(CCFLAGS) test test.c -lpthread
clean:
rm -f $(EXECUTABLES) *.o *.a test
坑点:
不可以使用PTRACE_SINGLESTEP,单步执行,否证会返回负数,并出错。所以只可以通过设置下一个地址为断点,然后PTRACE_CONT。x86架构可以使用PTRACE_SINGLESTEP,ARM架构不知道为什么不可以。

参考:
http://note.iawen.com/note/programming/gdb_ptrace
https://bbs.pediy.com/thread-265599.htm
https://blog.csdn.net/Rong_Toa/article/details/112155847
