零基础学Linux内核系列文章目录
前置知识篇
1. 进程
2. 线程
进程间通信篇
1. IPC概述
2. 信号
3. 消息传递
4. 同步
5. 共享内存区
编译相关篇
1. GCC编译
2. 静态链接与动态链接
3. makefile入门基础
设备驱动篇
1. 设备驱动概述
2. 内核模块_理论篇
3. 内核模块_实验篇
4. 字符设备_理论篇1
5. 字符设备_理论篇2
6. 字符设备_实验篇1
7. 字符设备_实验篇2
8. 设备模型
9. 平台设备驱动
10. 设备树_添加设备节点信息
11. 设备树_获取设备节点信息
一、前言
本节主要介绍在得到一个设备树文件之后,如何使用代码去查找某个节点并获取该节点的各个属性。
二、前置条件
无
三、本文参考资料
《 [野火]i.MX Linux开发实战指南》
百度
四、正文部分
在设备树中“节点”对应实际硬件中的设备,
我们在设备树中添加了一个“led”节点,正常情况下我们可以从这个节点获取编写led驱动所用到的所有信息,
例如led相关控制寄存器地址、 led时钟控制寄存器地址等等。
这一小节我们就开始学习如何从设备树的设备节点获取我们想要的数据。
内核提供了一组函数用于从设备节点获取资源(设备节点中定义的属性)的函数,这些函数以of_开头,称为OF操作函数。(“open firmware”即开放固件。)
4.1 查找节点函数
这里介绍了7个寻找节点函数,这7个函数有一个共同特点—— 返回值类型相同 。
只要找到了节点就会返回节点对应的device_node结构体,在驱动程序中我们就是通过这个device_node获取设备节点的属性信息、顺藤摸瓜查找它的父、子节点等等。
第一函数of_find_node_by_path与后面六个不同,它是通过节点路径寻找节点的,“节点路径”是从设备树源文件(.dts)中得到的。
而中间四个函数是根据节点属性在某一个节点之后查找符合要求的设备节点,这个“某一个节点”是设备节点结构体(device_node),也就是说这个节点是 已经找到的 。
最后两个函数与中间四个类似,只不过最后两个没有使用节点属性而是根据父、子关系查找。
这个过程可以理解为**把设备树中的设备节点“获取”到驱动中**。
4.1.1 根据节点路径寻找节点函数
static inline struct device_node *of_find_node_by_path(const char *path)
- 参数:
path: 指定节点在设备树中的路径。(从设备树源文件(.dts)中得到的) - 返回值:
device_node: 结构体指针,如果查找失败则返回NULL,否则返回device_node类型的结构体指针,它保存着设备节点的信息。
device_node结构体如下所示。struct device_node { /* 节点中属性为name的值 */ const char *name; /* 节点中属性为device_type的值 */ const char *type; phandle phandle; /* 节点的名字,在device_node结构体后面放一个字符串,full_name指向它 */ const char *full_name; struct fwnode_handle fwnode; /* 链表,连接该节点的所有属性 */ struct property *properties; struct property *deadprops; /* 指向父 / 子 / 兄弟节点 */ struct device_node *parent; struct device_node *child; struct device_node *sibling; #if defined(CONFIG_OF_KOBJ) struct kobject kobj; #endif unsigned long _flags; void *data; #if defined(CONFIG_SPARC) const char *path_component_name; unsigned int unique_id; struct of_irq_controller *irq_trans; #endif };
得到device_node结构体之后我们就可以使用其他of 函数获取节点的详细信息。
4.1.2 根据节点名字寻找节点函数
struct device_node *of_find_node_by_name(struct device_node *from, const char *name)
- 参数:
- from: 指定从哪个节点开始查找,它本身并不在查找行列中,只查找它后面的节点,如果设置为NULL表示从根节点开始查找。
- name:要寻找的节点名。
- 返回值:
device_node: 结构体指针,如果查找失败则返回NULL,否则返回device_node类型的结构体指针,它保存着设备节点的信息。
4.1.3 根据节点类型寻找节点函数
struct device_node *of_find_node_by_type(struct device_node *from, const char *type)
- 参数:
- from:指定从哪个节点开始查找,它本身并不在查找行列中,只查找它后面的节点,如果设置为NULL表示从根节点开始查找。
- type:要查找节点的类型,这个类型就是device_node-> type。
- 返回值:
device_node: device_node类型的结构体指针,保存获取得到的节点。同样,如果失败返回NULL。
4.1.4 根据节点类型和compatible属性寻找节点函数
struct device_node *of_find_compatible_node(struct device_node *from, const char *type, const char *compatible)
相比of_find_node_by_name函数增加了一个compatible属性作为筛选条件。
- 参数:
- from:指定从哪个节点开始查找,它本身并不在查找行列中,只查找它后面的节点,如果设置为NULL表示从根节点开始查找。
- type:要查找节点的类型,这个类型就是device_node-> type。
- compatible:要查找节点的compatible属性。
- 返回值:
device_node: device_node类型的结构体指针,保存获取得到的节点。同样,如果失败返回NULL。
4.1.5 根据匹配表寻找节点函数
static inline struct device_node *of_find_matching_node_and_match(
struct device_node *from,
const struct of_device_id *matches,
const struct of_device_id **match)
可以看到,该结构体包含了更多的匹配参数,也就是说相比前三个寻找节点函数,这个函数匹配的参数更多,对节点的筛选更细。
- 参数:
- from:指定从哪个节点开始查找,它本身并不在查找行列中,只查找它后面的节点,如果设置为NULL表示从根节点开始查找。
- matches:源匹配表(of_device_id),查找与该匹配表想匹配的设备节点。
- match:查找得到的结果(找到的匹配的 of_device_id)
of_device_id: 结构体如下。 struct of_device_id { /* 节点中属性为name的值 */ char name[32]; /* 节点中属性为device_type的值 */ char type[32]; /* 节点的名字,在device_node结构体后面放一个字符串,full_name指向它 */ char compatible[128]; /* 链表,连接该节点的所有属性 */ const void *data; }; - 返回值:
device_node: device_node类型的结构体指针,保存获取得到的节点。同样,如果失败返回NULL。
4.1.6 寻找父节点函数
struct device_node *of_get_parent(const struct device_node *node)
- 参数:
node:指定谁(节点)要查找父节点(即子节点)。 - 返回值:
device_node: device_node类型的结构体指针,保存获取得到的节点。同样,如果失败返回NULL。
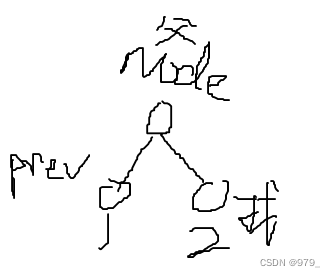
4.1.7 寻找子节点函数
struct device_node *of_get_next_child(const struct device_node *node, struct device_node *prev)
-
参数:
- node:指定谁(节点)要查找它的子节点(即父节点)。
- prev:前一个子节点,寻找的是prev节点之后的节点。
这是一个迭代寻找过程,例如寻找第二个子节点,这里就要填第一个子节点。参数为NULL 表示寻找第一个子节点。
-
返回值:
device_node:device_node类型的结构体指针,保存获取得到的节点。同样,如果失败返回NULL。
?
4.2 提取属性值的of函数
“获取”成功后我们再通过一组of函数从设备节点结构体(device_node)中获取我们想要的设备节点属性信息。
4.2.1 查找节点属性函数(可获取所有属性)
struct property *of_find_property(const struct device_node *np,
const char *name,
int *lenp)
-
参数:
- np:指定要获取哪个设备节点的属性信息。
- name:属性名。
- lenp:获取得到的属性值的大小,这个指针作为输出参数,这个参数“带回”的值是实际获取得到的属性大小。
-
返回值:
property:获取得到的属性。- property结构体,我们把它称为节点属性结构体,如下所示。失败返回NULL。
- 从这个结构体中我们就可以得到想要的属性值了。
struct property { char *name; //属性名 int length; //属性长度 void *value; //属性值 struct property *next; //下一个属性 #if defined(CONFIG_OF_DYNAMIC) || defined(CONFIG_SPARC) unsigned long _flags; #endif #if defined(CONFIG_OF_PROMTREE) unsigned int unique_id; #endif #if defined(CONFIG_OF_KOBJ) struct bin_attribute attr; #endif };
4.2.2 读取整型属性函数
读取属性函数是一组函数,分别为读取8、16、32、64位数据。(即非字符串属性)
/* 8位整数读取函数 */
static inline int of_property_read_u8_array(const struct device_node *np,
const char *propname,
u8 *out_values, size_t sz)
/* 16位整数读取函数 */
static inline int of_property_read_u16_array(const struct device_node *np,
const char *propname,
u16 *out_values, size_t sz)
/* 32位整数读取函数 */
static inline int of_property_read_u32_array(const struct device_node *np,
const char *propname,
u32 *out_values, size_t sz)
/* 64位整数读取函数 */
static inline int of_property_read_u64_array(const struct device_node *np,
const char *propname,
u64 *out_values, size_t sz)
- 参数:
- np:指定要读取哪个设备节点的属性信息,也就是说读取那个设备节点的数据。
- propname:指定要获取设备节点的哪个属性。
- out_values:这是一个输出参数,是函数的“返回值”,保存读取得到的数据。
- sz:这是一个输入参数,它用于设置读取的长度。
- 返回值:
成功返回0
错误返回错误状态码(非零值),-EINVAL(属性不存在),-ENODATA(没有要读取的数据),-EOVERFLOW(属性值列表太小)。
4.2.3 简化后的读取整型属性函数
这里的函数是对读取整型属性函数的简单封装,将读取长度设置为1。
用法与读取属性函数完全一致,这里不再赘述。
/* 8位整数读取函数 */
static inline int of_property_read_u8(const struct device_node *np,
const char *propname,
u8 *out_value)
/* 16位整数读取函数 */
static inline int of_property_read_u16(const struct device_node *np,
const char *propname,
u16 *out_value)
/* 32位整数读取函数 */
static inline int of_property_read_u32(const struct device_node *np,
const char *propname,
u32 *out_value)
/* 64位整数读取函数 */
static inline int of_property_read_u64(const struct device_node *np,
const char *propname,
u64 *out_value)
4.2.4 读取字符串属性函数
在设备节点中存在很多字符串属性,例如compatible、status、type等等,
这些属性可以使用查找节点属性函数of_find_property来获取,但是这样比较繁琐。
内核提供了一组用于读取字符串属性的函数,介绍如下:
static inline int of_property_read_string(const struct device_node *np,
const char *propname,
const char **out_string)
- 参数:
- np: 指定要获取哪个设备节点的属性信息。
- propname: 属性名。
- out_string: 获取得到字符串指针,这是一个“输出”参数,带回一个字符串指针。
也就是字符串属性值的首地址。
这个地址是“属性值”在 内存中的真实位置 ,也就是说我们可以通过对地址操作获取整个字符串属性
(一个字符串属性可能包含多个字符串,这些字符串在内存中连续存储,使用’0’分隔)。
- 返回值:
成功返回0
失败返回错误状态码。
这个函数使用相对繁琐,推荐使用下面这个函数。
static inline int of_property_read_string_index(const struct device_node *np,
const char *propname,
int index, const char **output)
相比前面的函数增加了参数index,它用于指定读取属性值中第几个字符串,index从零开始计数。
第一个函数只能得到属性值所在地址,也就是第一个字符串的地址,其他字符串需要我们手动修改移动地址,非常麻烦,推荐使用第二个函数。
4.2.5 读取布尔型属性函数
在设备节点中一些属性是BOOL型,当然内核会提供读取BOOL型属性的函数,介绍如下:
static inline bool of_property_read_bool(const struct device_node *np,
const char *propname)
- 参数:
- np: 指定要获取那个设备节点的属性信息。
- propname: 属性名。
- 返回值:
这个函数不按套路出牌,它不是读取某个布尔型属性的值,仅仅是读取这个属性存在或者不存在。
如果想要或取值,可以使用之前讲解的“全能”函数查找节点属性函数of_find_property。
?
4.3 内存映射相关of函数
在设备树的设备节点中大多会包含一些内存相关的属性,比如常用的reg属性。
通常情况下,得到寄存器地址之后我们还要通过ioremap函数将物理地址转化为虚拟地址。
现在内核提供了of函数,自动完成物理地址到虚拟地址的转换。
介绍如下:
void __iomem *of_iomap(struct device_node *np, int index)
- 参数:
- np: 指定要获取那个设备节点的属性信息。
- index: 通常情况下reg属性包含多段,index 用于指定映射那一段,标号从0开始。
- 返回值:
成功,得到转换得到的地址。(即设备树中的地址值转换为虚拟地址后的结果)
失败返回NULL。
内核也提供了常规获取地址的of函数,这些函数得到的值就是我们在设备树中设置的地址值。介绍如下:
int of_address_to_resource(struct device_node *node, int index,
struct resource *r)
- 参数:
- np: 指定要获取那个设备节点的属性信息。
- index: 通常情况下reg属性包含多段,index 用于指定映射那一段,标号从0开始。
- r: 这是一个resource结构体,是“输出参数”用于返回得到的地址信息。
struct resource { resource_size_t start; //起始地址 resource_size_t end; //结束地址 const char *name; //属性名字 unsigned long flags; unsigned long desc; struct resource *parent, *sibling, *child; }; - 返回值:
成功返回0
失败返回错误状态码。
?
4.4 获取节点属性实验
本实验是一个简化的字符设备驱动,在驱动中没有实际操作硬件,仅在.open 函数中调用of函数获取设备树节点中的属性,获取成功后打印获取得到的内容。
程序源码如下所示,这里只列出了.open函数中的内容,其他与字符设备驱动类似,完整内容请参考本章配套源码“补充”。
/*.open 函数*/
static int led_chr_dev_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
int error_status = -1;
printk("\n open form device \n");
/* 获取DTS属性信息 */
/* 使用“of_find_node_by_path”函数寻找“led_test”设备节点。参数是“led_test”的设备节点路径 */
led_device_node = of_find_node_by_path("/led_test");
if(led_device_node == NULL)
{
printk(KERN_ALERT "\n get led_device_node failed ! \n");
return -1;
}
/* 根据 led_device_node 设备节点结构体输出节点的基本信息 */
/* 获取成功后得到的是一个device_node类型的结构体指针,然后我们就可以从这个结构体中获得我们想要的数据。获取完整的属性信息可能还需要使用其他of函数 */
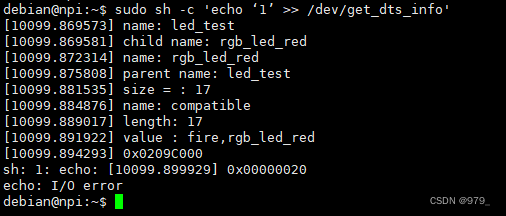
printk(KERN_ALERT "name: %s",led_device_node->name); //输出节点名
printk(KERN_ALERT "child name: %s",led_device_node->child->name); //输出子节点的节点名
/* 获取 rgb_led_red_device_node 的子节点 */
/* 可以使用“of_get_next_child”函数获取它的子节点。当然我们也可以从“led”节点的“设备节点结构体”中直接读取得到它的第一个子节点 */
rgb_led_red_device_node = of_get_next_child(led_device_node,NULL);
if(rgb_led_red_device_node == NULL)
{
printk(KERN_ALERT "\n get rgb_led_red_device_node failed ! \n");
return -1;
}
printk(KERN_ALERT "name: %s", rgb_led_red_device_node->name); //输出节点名
printk(KERN_ALERT "parent name: %s", rgb_led_red_device_node->parent->name); //输出父节点的节点名
/* 获取 rgb_led_red_device_node 节点 的"compatible" 属性 */
/* 使用“of_find_property”函数获取“rgb_led_red”节点的“compatible”属性 */
rgb_led_red_property = of_find_property(rgb_led_red_device_node,"compatible",&size);
if(rgb_led_red_property == NULL)
{
printk(KERN_ALERT "\n get rgb_led_red_property failed ! \n");
return -1;
}
printk(KERN_ALERT "size = : %d",size); //实际读取得到的长度
printk(KERN_ALERT "name: %s",rgb_led_red_property->name); //输出属性名
printk(KERN_ALERT "length: %d",rgb_led_red_property->length); //输出属性长度
printk(KERN_ALERT "value : %s",(char*)rgb_led_red_property->value); //属性值
/* 获取 reg 地址属性 */
/* 使用“of_property_read_u32_array”函数获取reg属性 */
error_status = of_property_read_u32_array(rgb_led_red_device_node, "reg", out_values, 2);
if(error_status != 0)
{
printk(KERN_ALERT "\n get out_values failed ! \n");
return -1;
}
printk(KERN_ALERT"0x%08X ", out_values[0]);
printk(KERN_ALERT"0x%08X ", out_values[1]);
return 0;
}
编译成功后将驱动.ko拷贝到开发板,使用insmod安装驱动模块然后可以在/dev/目录下找到get_dts_info。
向驱动模块随便输入一个字符
?