1、统一 properties 编码
首先在IDEA中统一设置properties的编码为UTF-8
编写国际化配置文件,抽取页面需要显示的国际化页面消息。我们可以去登录页面查看一下,哪些内容我们需要编写国际化的配置!
2、编写 i18n 国际化资源文件
- 在resources目录下新建一个 i18n 包,其中放置国际化相关的配置
- 什么是i18n?

- 类似的还有K8S
其中新建三个配置文件,用来配置语言:
- login.properties:无语言配置时候生效
- login_en_US.properties:英文生效
- login_zh_CN.properties:中文生效
命名方式是下划线的组合:文件名_语言_国家.properties;
以此方式命名,IDEA会帮我们识别这是个国际化配置包,自动绑定在一起转换成如下的模式:
此时我们发现 IDEA自动识别了我们要做国际化操作;文件夹变了!

绑定在一起后,我们想要添加更过语言配置,只需要在大的资源包右键添加到该绑定配置文件即可

此时只需要输入区域名即可创建成功,比如输入en_US,就会自动识别
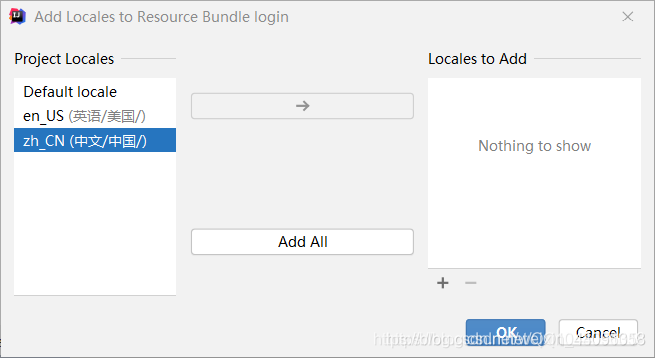
然后打开英文或者中文语言的配置文件,点击Resource Bundle进入可视化编辑页面

进入到可视化编辑页面后,点击加号,添加属性,首先新建一个login.tip代表首页中的提示

然后对该提示分别做三种情况的语言配置,在三个对应的输入框输入即可(注意:IDEA2020.1可能无法保存,建议直接在配置文件中编写)
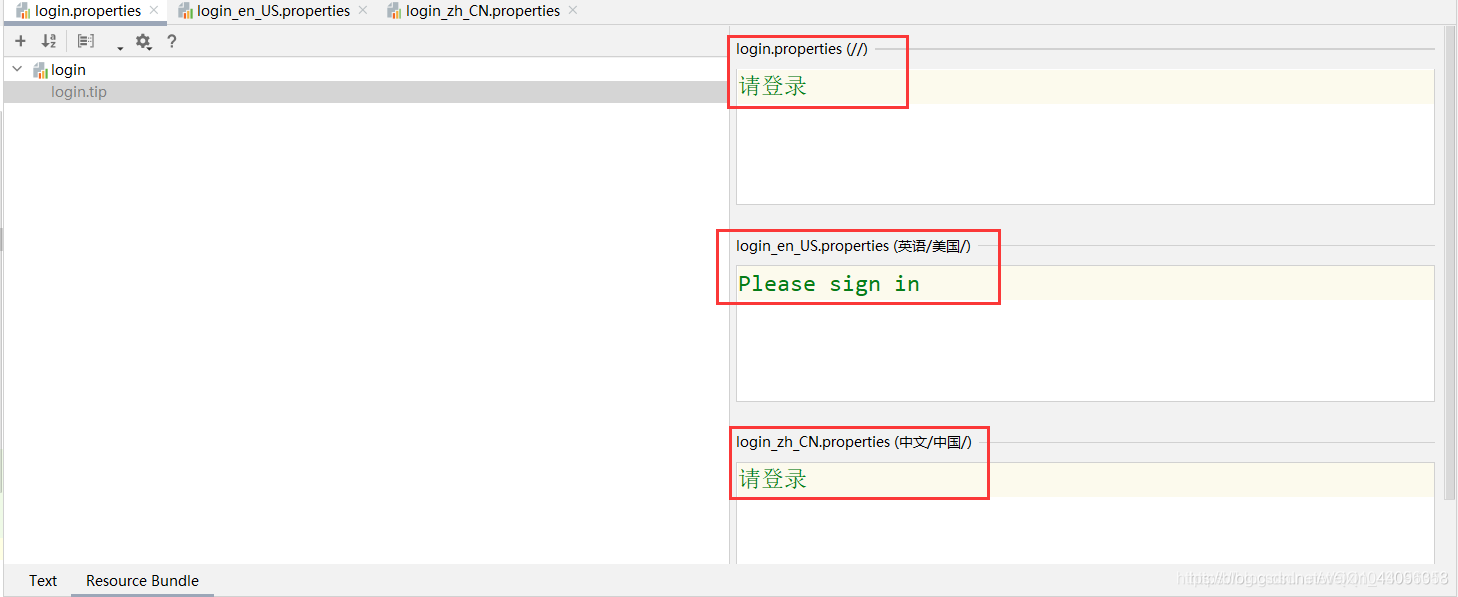
双击点来login.tip 我们可以发现 我们可视化的方便,一次性就可以配置3种
接下来再配置所有要转换语言的变量(注意:IDEA2020.1可能无法保存,建议直接在配置文件中编写)

然后打开三个配置文件的检查 查看其中的文本内容,可以看到已经做好了全部的配置
login.properties
login.btn=登录
login.password=密码
login.remember=记住我
login.tip=请登录
login.username=用户名
login_en_US.properties
login.btn=Sign in
login.password=Password
login.remember=Remember me
login.tip=Please sign in
login.username=username
login_zh_CN.properties
login.btn=登录
login.password=密码
login.remember=记住我
login.tip=请登录
login.username=用户名
3、配置国际化资源文件名称
在Spring程序中,国际化主要是通过 ResourceBundleMessageSource 这个类来实现的
Spring Boot通过== MessageSourceAutoConfiguration ==为我们自动配置好了管理国际化资源文件的组件
我们在IDEA中查看以下MessageSourceAutoConfiguration类
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = AbstractApplicationContext.MESSAGE_SOURCE_BEAN_NAME, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE)
@Conditional(ResourceBundleCondition.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties
public class MessageSourceAutoConfiguration {
private static final Resource[] NO_RESOURCES = {};
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.messages")
public MessageSourceProperties messageSourceProperties() {
return new MessageSourceProperties();
}
@Bean
public MessageSource messageSource(MessageSourceProperties properties) {
ResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource = new ResourceBundleMessageSource();
if (StringUtils.hasText(properties.getBasename())) {
//他可以设置我们Basenames 基本的名字
messageSource.setBasenames(StringUtils
//然后他会从properties.getBasename(),我们的配置文件去找
.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(StringUtils.trimAllWhitespace(properties.getBasename())));
}
if (properties.getEncoding() != null) {
messageSource.setDefaultEncoding(properties.getEncoding().name());
}
messageSource.setFallbackToSystemLocale(properties.isFallbackToSystemLocale());
Duration cacheDuration = properties.getCacheDuration();
if (cacheDuration != null) {
messageSource.setCacheMillis(cacheDuration.toMillis());
}
messageSource.setAlwaysUseMessageFormat(properties.isAlwaysUseMessageFormat());
messageSource.setUseCodeAsDefaultMessage(properties.isUseCodeAsDefaultMessage());
return messageSource;
}
//......
}
主要了解messageSource()这个方法:
public MessageSource messageSource(MessageSourceProperties properties);
可以看到,它的参数为MessageSourceProperties对象,我们看看这个类
public class MessageSourceProperties {
/**
* Comma-separated list of basenames (essentially a fully-qualified classpath
* location), each following the ResourceBundle convention with relaxed support for
* slash based locations. If it doesn't contain a package qualifier (such as
* "org.mypackage"), it will be resolved from the classpath root.
*/
private String basename = "messages";
/**
* Message bundles encoding.
*/
private Charset encoding = StandardCharsets.UTF_8;
类中首先声明了一个属性basename,默认值为messages;
我们翻译其注释:
/**
* Comma-separated list of basenames (essentially a fully-qualified classpath
* location), each following the ResourceBundle convention with relaxed support for
* slash based locations. If it doesn't contain a package qualifier (such as
* "org.mypackage"), it will be resolved from the classpath root.
*/
- 逗号分隔的基名列表(本质上是完全限定的类路径位置)
- 每个都遵循ResourceBundle约定,并轻松支持于斜杠的位置
- 如果不包含包限定符(例如"org.mypackage"),它将从类路径根目录中解析
意思是:
- 如果你不在springboot配置文件中指定以.分隔开的国际化资源文件名称的话
- 它默认会去类路径下找messages.properties作为国际化资源文件
这里我们自定义了国际化资源文件,因此我们需要在SpringBoot配置文件application.yml中加入以下配置指定我们配置文件的名称
# 我们的配置文件的真实位置
spring.messages.basename=i18n.login
4、首页获取显示国际化值
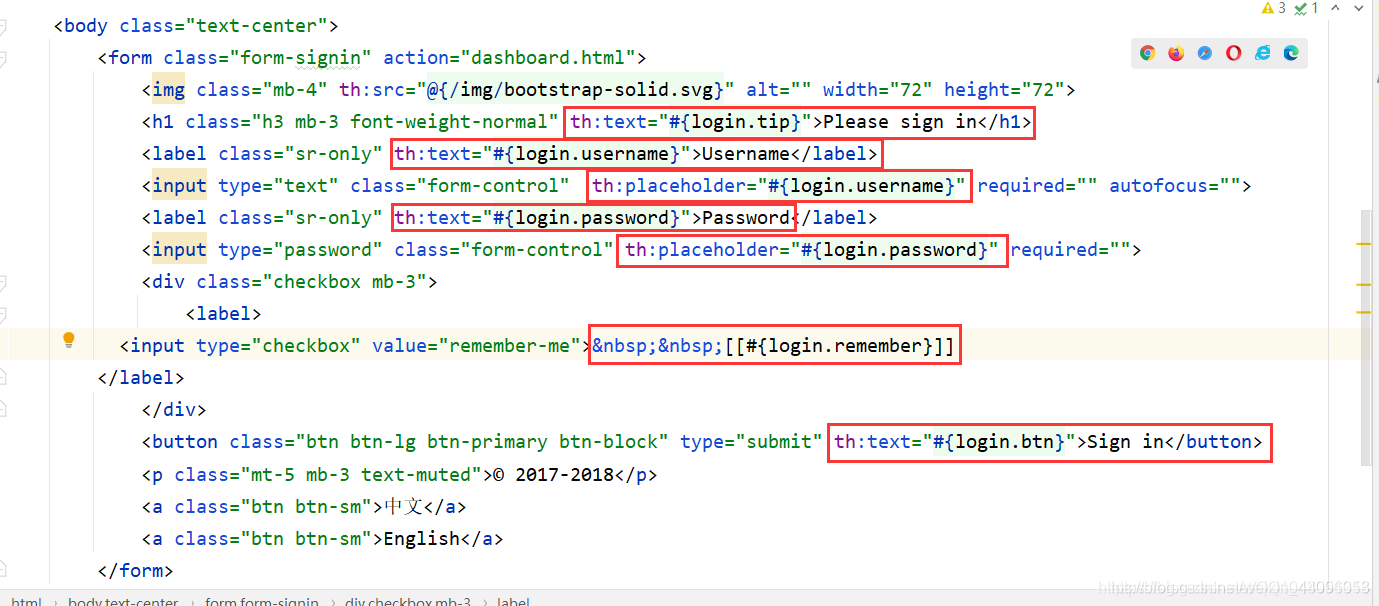
去页面获取国际化的值,查看Thymeleaf的文档,找到message取值操作为:#{…}。
IDEA还有提示,非常智能的!
利用#{…} 消息表达式,去首页index.html获取国际化的值,没在<>内的,使用#[[#{ }]]
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, shrink-to-fit=no">
<meta name="description" content="">
<meta name="author" content="">
<title>Signin Template for Bootstrap</title>
<!-- Bootstrap core CSS -->
<link th:href="@{/css/bootstrap.min.css}" rel="stylesheet">
<!-- Custom styles for this template -->
<link th:href="@{/css/signin.css}" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body class="text-center">
<form class="form-signin" action="dashboard.html">
<img class="mb-4" th:src="@{/img/bootstrap-solid.svg}" alt="" width="72" height="72">
<h1 class="h3 mb-3 font-weight-normal" th:text="#{login.tip}">Please sign in</h1>
<input type="text" class="form-control" th:placeholder="#{login.username}" required="" autofocus="">
<input type="password" class="form-control" th:placeholder="#{login.password}" required="">
<div class="checkbox mb-3">
<label>
<input type="checkbox" value="remember-me" > [[#{login.remember}]]
</label>
</div>
<button class="btn btn-lg btn-primary btn-block" type="submit">[[#{login.bgn}]]</button>
<p class="mt-5 mb-3 text-muted">? 2017-2018</p>
<!--这里传入参数不需要使用?使用key=value-->
<a class="btn btn-sm" th:href="@{/index.html(l='zh_CN')}">中文</a>
<a class="btn btn-sm" th:href="@{/index.html(l='en_US')}">English</a>
</form>
</body>
</html>
5、其他

MyLocaleResolver:
public class MyLocaleResolver implements LocaleResolver {
//解析请求
@Override
public Locale resolveLocale(HttpServletRequest request) {
//获取请求中的语言参数
String language = request.getParameter("l");
Locale locale = Locale.getDefault();//如果没有就使用默认的
//如果请求的连接携带了国际化的参数
if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(language)){
//zh_CN
String[] split = language.split("_");
locale = new Locale(split[0],split[1]);
}
return locale;
}
@Override
public void setLocale(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Locale locale) {
}
}
MyMvcConfig:
@Configuration
public class MyMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("index");
registry.addViewController("/index.html").setViewName("index");
}
//自定义的国际化组件就生效了
@Bean
public LocaleResolver localeResolver(){
return new MyLocaleResolver();
}
}