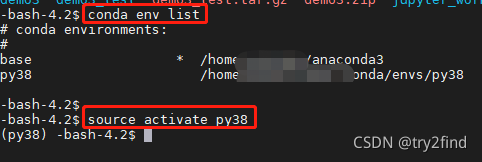
1、在linux上激活虚拟环境
-bash-4.2$ source activate py38
2、使用ipykernel为不同的虚拟环境配置不同名字
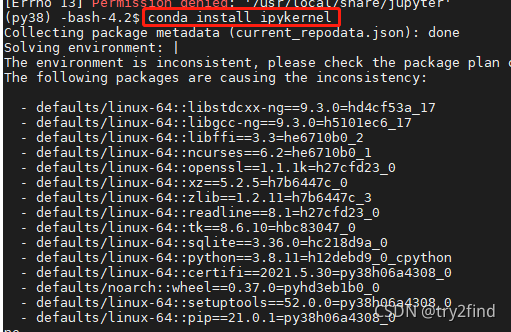
(1) 安装ipykernel
(py38) -bash-4.2$ conda install ipykernel
?(2) 配置虚拟环境的内核名称
python?-m?ipykernel?install?--user?--name=你的环境名称?--display-name?"Python?(环境名称)"??
(py38) -bash-4.2$ python -m ipykernel install --user --name=py38 --display-name "Python py38"
![]()
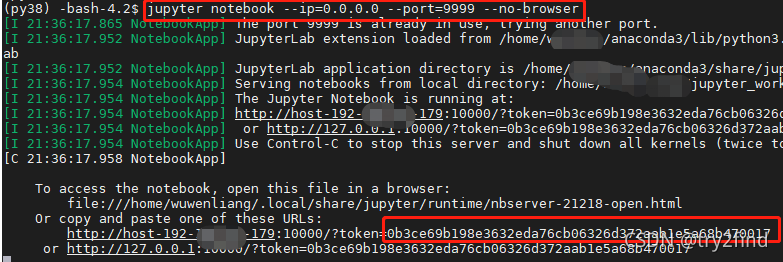
3 linux上启动jupyter
(py38) -bash-4.2$ jupyter notebook --ip=0.0.0.0 --port=9999 --no-browser
4 在windows访问linux上的jupyter
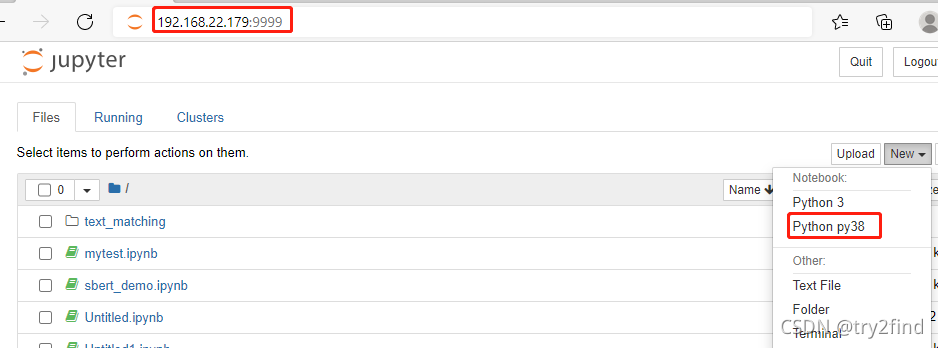
? 此时在?new?中可以看到我们命名的环境名称:Python 38
? 在代码中查看当前的环境:
import os
import sys
# sys.path.append(os.getcwd())
print(os.path)
print(os.getcwd())
val = os.system('ls -l')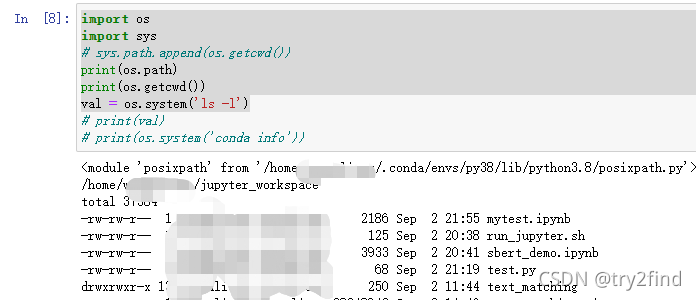
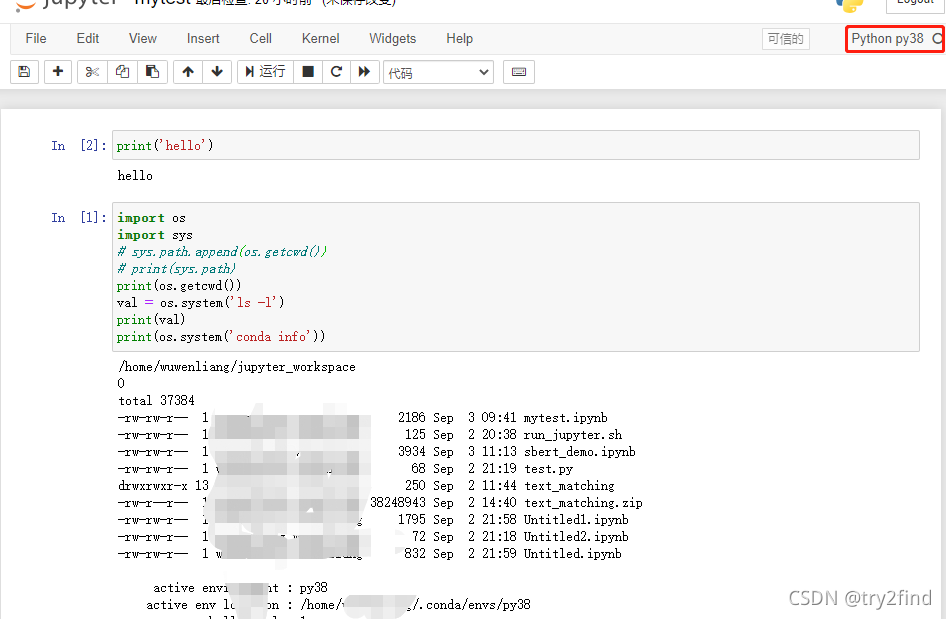
?5 对同一份代码切换不同的运行环境
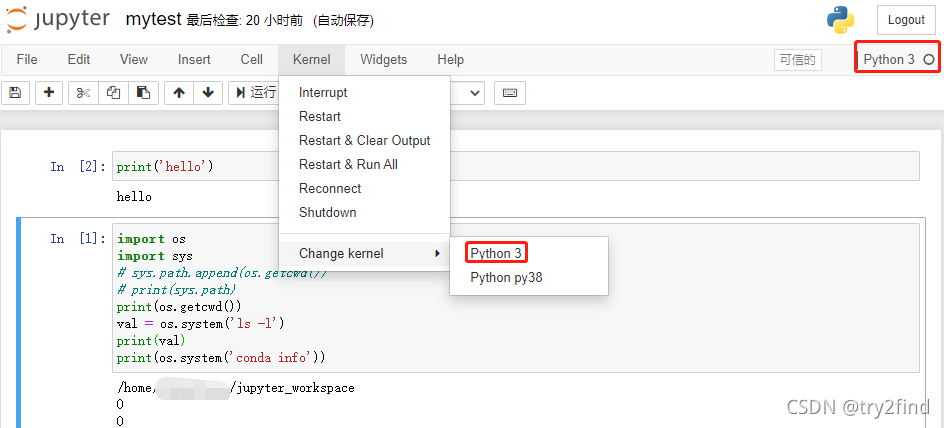
切换到 Python py38虚拟环境
参考文章:
(1)?https://www.qedev.com/python/331225.html
(2)?https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42167712/article/details/100057079