编程练习上的一些个人拙见,仅供参考,个人习惯注释写的较全,可以查看。另外代码有比较多的空行,没清掉,代码排版是vscode自动格式化的,没清空行功能。
(其实和自己交上去的作业是一模一样的,我抄我自己)
1.手机类
(1)定义一个手机类,定义若干属性,方法和构造方法;
(2)定义测试类,其中定义多个手机类对象,并设置不同的初始值;
(3)调用手机类的相关方法,测试该类的功能。
public class T1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
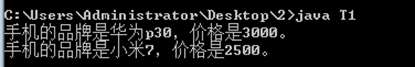
Phone hw = new Phone("华为p30", 3000);
Phone mi = new Phone("小米7", 2500); // 定义测试类
hw.printPhone(); // 调用手机类方法
mi.printPhone();
}
}
class Phone // 手机类
{
String brand;
int price;
public Phone(String brand, int price) {
this.brand = brand;
this.price = price;
}
public void printPhone() {
System.out.println("手机的品牌是" + brand + ",价格是" + price + "。");
}
}
测试结果
2.电视机类
定义一个电视机类,实现电视机的基本功能(换台,调整音量,开关),并测试其功能。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class T2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int opt, temp;
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
Tv a = new Tv(true, 50, 10);
System.out.println("电视开机了,关闭后将退出程序");
while (a.Run) {
System.out.println("功能测试:1 换台 2 调音量 3 关机");
opt = s.nextInt();
switch (opt) {
case 2:
temp = s.nextInt();
a.setVoice(temp);
break;
case 1:
temp = s.nextInt();
a.setPindao(temp);
break;
case 3:
a.setRun();
break;
default:
System.out.println("指令错误重新输入!");
}
}
}
}
class Tv // 电视类
{
boolean Run;
int Voice;
int Pindao;
public Tv(boolean Run, int Voice, int Pindao) { // 构造函数
this.Run = Run;
this.Voice = Voice;
this.Pindao = Pindao;
}
public void setVoice(int newVoice) { // 以下分别是 设定音量 设定频道 开关机
System.out.println("原本的音量是" + Voice);
this.Voice = newVoice;
System.out.println("音量已修改为" + Voice);
}
public void setPindao(int newPindao) {
System.out.println("现在是" + Pindao + "台");
this.Pindao = newPindao;
System.out.println("电视频道已调整为" + Pindao);
}
public void setRun() {
if (this.Run) {
this.Run = false;
System.out.println("关闭中......电视已关机!");
} else {
this.Run = true;
System.out.println("开启中......电视已开机!");
}
}
}
测试结果

3.分数类
(1)设计一个分数类,分数的分子和分母用两个整型数表示,类中定义方法对分数进行加、减、乘、除运算;
(2)在测试类中定义分数类对象,运算并输出运算结果。
public class T3 {
public static int gcdfunc(int m, int n) {
if (m < n) {
int k = m;
m = n;
n = k;
}
if (m % n != 0) {
int temp = m % n;
return gcdfunc(n, temp);
} else
return n;
}
public static class Fen // 分数类
{
int Fenmom;
int Fenson;
public Fen(int Fenson, int Fenmom) { // 构造函数
this.Fenmom = Fenmom;
this.Fenson = Fenson;
}
/*
* public int Getgcd(int x, int y){ // 运用辗转相除法求两个数的最大公约数 if(y == 0) return x;
* else return Getgcd(y,x%y); }
*/
public void jia(Fen a, Fen b) { // 以下分别是 + - * /
int result_son = a.Fenson * b.Fenmom + b.Fenson * a.Fenmom;
int result_mom = a.Fenmom * b.Fenmom;
int result_gcd = gcdfunc(result_son, result_mom);
System.out.println("a加b的结果是" + result_son / result_gcd + '/' + result_mom / result_gcd);
}
public void jian(Fen a, Fen b) {
int result_son = a.Fenson * b.Fenmom - b.Fenson * a.Fenmom;
int result_mom = a.Fenmom * b.Fenmom;
if (result_son < 0) {
result_son = -result_son;
int result_gcd = gcdfunc(result_son, result_mom);
System.out.println("a减b的结果是-" + result_son / result_gcd + '/' + result_mom / result_gcd);
} else {
int result_gcd = gcdfunc(result_son, result_mom);
System.out.println("a减b的结果是" + result_son / result_gcd + '/' + result_mom / result_gcd);
}
}
public void cheng(Fen a, Fen b) {
int result_son = a.Fenson * b.Fenson;
int result_mom = a.Fenmom * b.Fenmom;
int result_gcd = gcdfunc(result_son, result_mom);
System.out.println("a乘b的结果是" + result_son / result_gcd + '/' + result_mom / result_gcd);
}
public void chu(Fen a, Fen b) {
int result_son = a.Fenson * b.Fenmom;
int result_mom = a.Fenmom * b.Fenson;
int result_gcd = gcdfunc(result_son, result_mom);
System.out.println("a除以b的结果是" + result_son / result_gcd + '/' + result_mom / result_gcd);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Fen m = new Fen(1, 5);
Fen n = new Fen(2, 3);
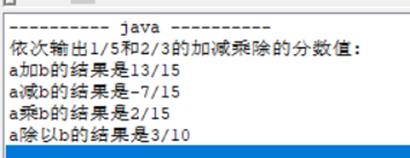
System.out.println("依次输出1/5和2/3的加减乘除的分数值:");
m.jia(m, n);
m.jian(m, n);
m.cheng(m, n);
m.chu(m, n);
}
}
测试结果
4.最大值类
定义一个类,其中定义三个方法,分别求两个整数最大值、三个整数最大值和三个小数最大值,并测试其效果。
public class T4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Max a = new Max();
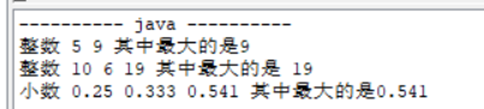
System.out.print("整数 5 9 其中最大的是");
System.out.println(a.getMax(5, 9));
System.out.print("整数 10 6 19 其中最大的是 ");
System.out.println(a.getMax(10, 6, 19));
System.out.print("小数 0.25 0.333 0.541 其中最大的是");
System.out.println(a.getMax(0.25, 0.333, 0.541));
}
public static class Max { // 使用重载,多个相同名字的方法参数不同,调用的结果不同
int getMax(int a, int b) {
if (a > b)
return a;
else
return b;
}
int getMax(int a, int b, int c) {
if (a > b)
if (a > c)
return a;
else
return c;
else if (b > c)
return b;
else
return c;
}
double getMax(double a, double b, double c) {
if (a > b)
if (a > c)
return a;
else
return c;
else if (b > c)
return b;
else
return c;
}
}
}
测试结果
5.基本类型和引用类型传参(加法类)
(1)定义一个类,包含x、y两个属性,一个add方法实现对两个属性的加法运算,即x、y分别加上10和20,并定义该类的构造方法;
(2)通过定义add方法的重载,联系两种形参的传递方式(基本类型和引用类型);
(3)定义测试类,测试该类的重载方法的效果,总结两种参数传递的区别。
public class T5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Mathxy a = new Mathxy(1, 1);
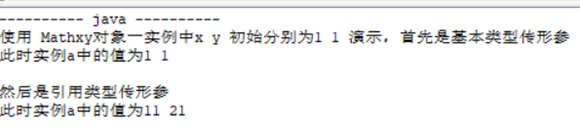
System.out.println("使用 Mathxy对象一实例中x y 初始分别为1 1 演示,首先是基本类型传形参 ");
a.add(a.x, a.y);
System.out.println("此时实例a中的值为" + a.x + ' ' + a.y);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("然后是引用类型传形参 ");
a.add(a);
System.out.println("此时实例a中的值为" + a.x + ' ' + a.y);
}
public static class Mathxy {
int x;
int y;
public Mathxy(int x, int y) { // 构造函数
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
// 使用重载,多个相同名字的方法参数不同,调用的结果不同
public void add(int x, int y) { // 基本类型传形参
x += 10;
y += 20;
}
public void add(Mathxy ce) { // 引用类型(对象)传形参
ce.x += 10;
ce.y += 20;
}
}
}
测试结果
Java方法的形参如果是基本类型,是值传递,也就是说实参将数值传递给形参后,形参对值的操作跟实参变量毫无关系;而假如是引用类型作为形参,实际上指向的是内存中的地址,操纵时可以对实参变量进行修改。
6.学生类(类对象、类方法和实例对象、实例方法)
(1)设计一个学生类Student,包括构造方法(包含重载),至少两 个成员变量,和求得年龄的方法;
(2)定义测试类,实例化一个Student对象,然后调用该对象的相关方法和变量;
(3)分别为Student类定义一个类变量和类方法,然后用实例化后的对象调用他们,并分析与实例变量和方法的区别,总结静态变量调用的注意事项。
public class T6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student stu = new Student("张三", 2001);
System.out.println("调用实例化对象的结果(输出姓名出生日期 计算年龄):");
System.out.println("此学生的姓名是" + stu.name + ",出生日期是" + stu.birth + ",年龄是" + stu.getAge_ShiLi() + "岁");
System.out.println();
System.out.println("用实例化后的对象调用类变量和类方法:");
System.out.println("该学生的学校是" + stu.school + ",使用类方法求年龄的结果是" + Student.getAge_Lei(stu) + "岁");
}
public static class Student {
static String school = "henu"; // 类(静态)变量
String name;
int birth;
public Student(String name, int birth) { // 构造函数 有参数版
this.name = name;
this.birth = birth;
}
public Student() { // 无参数就创建但为空
}// 重载,多个相同名字的方法参数不同,调用的结果不同
public int getAge_ShiLi() { // 求这个学生实例的年龄 实例方法
return 2021 - this.birth;
}
static public int getAge_Lei(Student a) { // 求一个学生实例的年龄 类方法
return 2021 - a.birth;
}
}
}
测试结果

没有static修饰的,这些成员变量是对象中的成员,称为实例变量。有static修饰的,称为类变量。
类变量和实例变量的区别是:
存放位置:类变量随着类的加载而存在于方法区中;实例变量随着对象的建立而存在于堆内存中。生命周期:类变量生命周期最长,随着类的消失而消失;实例变量生命周期随着对象的消失而消失。
可以通过调用实例化对象中的变量名来直接访问实例变量,通过使用类名ClassName.VariableName调用来访问静态变量
而实例方法和类方法的定义与实例变量与类变量的相同,都是通过有无static关键字来进行区分,方法类型前有static的为类方法,反之则为实例方法。
实例方法与类方法对成员变量的操作。实例方法既可以操作类变量,也可以对实例变量进行操作。
此外,类方法可以通过类名调用,调用格式为类名+方法名,而实例方法不能通过类名调用,只能通过类创建对象,然后通过对象调用(类方法不能操作实例变量)。
注:无法在静态变量中引用非静态成员(非静态变量,非静态方法),因为非静态的变量是依赖于对象存在的,对象必须实例化之后,它的变量才会在内存中存在。
7.雇员类(签到方法,信息输出方法)
(1)设计一个雇员类,属性包括:编号、姓名、年龄、职务、部门、出勤人数;方法包括:构造方法、输出信息的方法、签到方法;
(2)创建雇员类对象,统计雇员的出勤人数。
注意考虑属性和方法的访问权限,方法的功能,及main方法中如何实现要求统计的信息。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class T7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Staff staff = new Staff();
System.out.println("签到程序已开始运行 []~( ̄▽ ̄)~*");
staff.SignIn();
System.out.println("签到程序结束完成 开始输出签到数据 ( ̄▽ ̄)~*");
staff.output();
}
public static class Staff { //员工类 因为是个签到程序,一个对象要存储多个数据,所以使用数组存储一组数据
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
public String[] num = new String[2333]; //编号、姓名、年龄、职务、部门、出勤人数 使用public使之公开访问
public String[] name = new String[2333];
public String[] age = new String[2333];
public String[] job = new String[2333];
public String[] department = new String[2333];
public int attendNum = 0;
public Staff() { //构造函数 不需提前数据,为空
}
public void SignIn () { //签到函数
boolean run=true;
int i=0;
String p;
//函数运行指示器
while (run) {
System.out.print("请输入你的编号:"); //依次输入
this.num[i] = input.nextLine();
System.out.print("请输入你的姓名:");
this.name[i] = input.nextLine();
System.out.print("请输入你的年龄:");
this.age[i] = input.nextLine();
System.out.print("请输入你的职务:");
this.job[i] = input.nextLine();
System.out.print("请输入你的部门:");
this.department[i] = input.nextLine();
this.attendNum++;
System.out.print("如果你是最后一个签到的请输入1,反之输入0:");
p=input.nextLine();
System.out.println();
i++;
if (p.equals("1")) {
run=false;
}
}
}
public void output() { //信息输出函数
System.out.println("出勤人数合计为"+this.attendNum);
for(int i = 0;i<this.attendNum;i++) {
System.out.println("编号:"+num[i]);
System.out.println("姓名:"+name[i]);
System.out.println("年龄:"+age[i]);
System.out.println("职务:"+job[i]);
System.out.println("部门:"+department[i]);
System.out.println("==================");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}
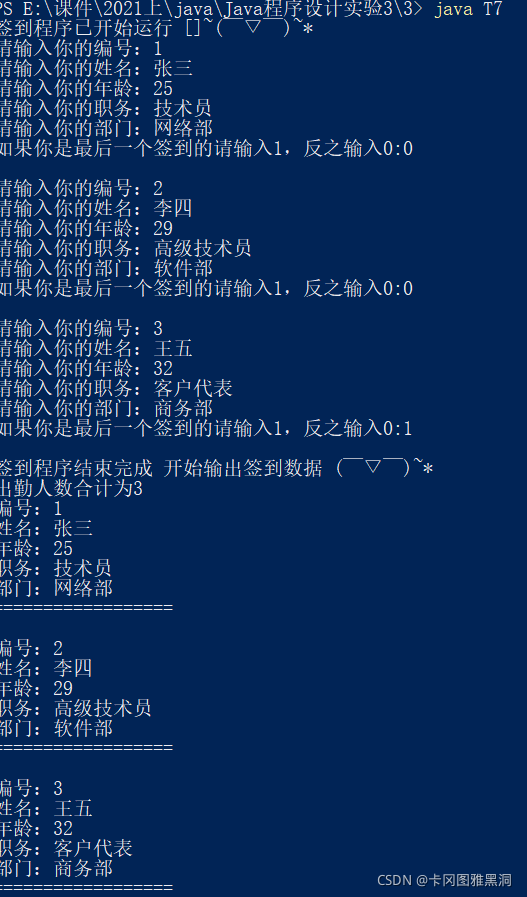
测试结果
8.学生借书程序(是选做,下次再写)
仿照超市购物的例子编写一个学生借书的程序。提示:
思考需要定义的类,例如:本程序需要用到学生、借书卡、书等对象,最后实现借书的过程,如果有指定的书,则输出“***借到了***书”,否则输出“没有借到书”。
还需要认真思考每个类中有哪些属性和方法,能够更好的完成这个程序。
空缺