关于classloader的两个resource方法的资源路径问题
- 首先要明确的是
resource类路径具体所指,即Source Root和Resource Root的路径所在位置,在idea中它们两个分别所指src和resource这两个包,需要注意的是它们两个并不是自己创建,而是Mark Diectory as的具体所选择的资源包- idea中相对应的在硬盘中的位置就是
out目录下的class类文件所在的文件夹,而这个就是上文所说的Source Root和Reource Root的存放位置
参考贴吧老哥所说的一句话
You need to make sure that Student.xml is located in a folder that is marked as a
resources rootin the IntelliJ IDEA project structure. Then it will be copied to the output directory together with the .class files, and you’ll be able to access it using getResourceAsStream().
reousrces root 资源根目录即问题的所在
参考地址
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/49470053/intellij-idea-return-null-with-classloader-getsystemresourceasstreammyfile-xml#
关于getSystemResourceAsStream()和getResourceAsStream()
- 在一般的情况下,方法一会将这个加载资源的过程下放给类加载器来实现,除非这个类加载器为
null
ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader0();
if (cl==null) {
// A system class.
return ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream(name);
}
return cl.getResourceAsStream(name);
他们两个
通过debug可以得知,clasloader.getSystemResourceAsStream,调用了getSystemResource,获取到系统类加载器 调用getResource,和双亲委派机制类似先访问上层类加载器
// 第一种方法先会获取类加载器, 根据类加载器来选择具体的资源获取路径
public static URL getSystemResource(String name) {
ClassLoader system = getSystemClassLoader();
if (system == null) {
return getBootstrapResource(name);
}
return system.getResource(name);
}
// 第二种方法是直接去getResoruce()获取路径
public InputStream getResourceAsStream(String name) {
URL url = getResource(name);
try {
return url != null ? url.openStream() : null;
} catch (IOException e) {
return null;
}
}
public URL getResource(String name) {
URL url;
// 访问上层, url获取结果为null
if (parent != null) {
url = parent.getResource(name);
} else {
url = getBootstrapResource(name);
}
if (url == null) {
// 进去真正的资源文件获取路径
url = findResource(name);
}
return url;
}
// 在这里返回的就是class文件存放目录的绝对路径
public URL findResource(final String name) {
/*
* The same restriction to finding classes applies to resources
*/
URL url = AccessController.doPrivileged(
new PrivilegedAction<URL>() {
public URL run() {
return ucp.findResource(name, true);
}
}, acc);
return url != null ? ucp.checkURL(url) : null;
}
从这里可以得知
- getSystemResourceAsStream 会先获取系统类加载器,如果系统类加载器为null,会从启动类加载器中获取资源路径再将其返回
- getResourceAsStream 直接就去获取资源的访问路径了
如果第一种方法使用的是系统类加载器,那么最后返回的资源路径和第二种一样,都是class文件所在的绝对路径
只是了解到这两种方法在类加载器的使用上的不同,针对简单项目他们应该都是使用了appClassLoader,但是在web项目下,会出现不是同一类加载器的情况
注:
需要明确的是,class调用的getResourceStream的对象指代是当前的class类,这个在源码中有具体的体现
在测试中使用的是绝对路径,而不是"/"相对路径
public InputStream getResourceAsStream(String name) {
// name = "/domain/pro.properties"
// 在此会截取"/", 从而去掉
name = resolveName(name);
// 获取类加载器, 后续和getSystemResource一致
ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader0();
if (cl==null) {
// A system class.
return ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream(name);
}
return cl.getResourceAsStream(name);
}
/**
* Add a package name prefix if the name is not absolute Remove leading "/"
* if name is absolute
* 很明显, 如果是相对路径就会将"/"截取掉
* 如果不是以/开头的, 会帮你把当前类的路径进行拼接转换, 注意是根据项目路径下的src路径进行拼接的
*/
private String resolveName(String name) {
if (name == null) {
return name;
}
if (!name.startsWith("/")) {
Class<?> c = this;
while (c.isArray()) {
c = c.getComponentType();
}
String baseName = c.getName();
int index = baseName.lastIndexOf('.');
if (index != -1) {
name = baseName.substring(0, index).replace('.', '/')
+"/"+name;
}
} else {
name = name.substring(1);
}
// name = cn/heartbaner/reflect/prop.properties
return name;
}
使用clas.getResourceStream
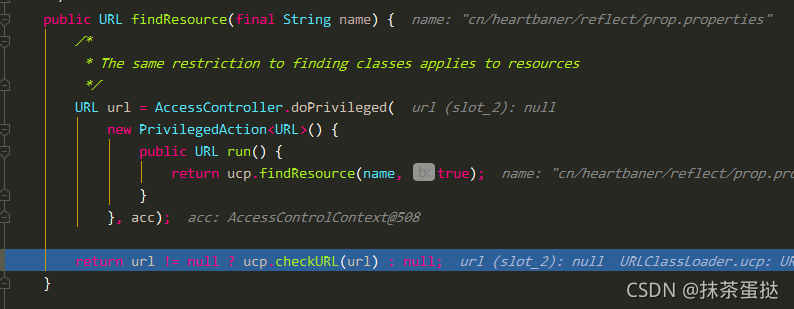
这次测试中,class.getResourceStream方法的参数不是相对路径,所以在resolveName方法中获取的拼接之后的name在此方法中获取不到真实的url路径,显示文件的资源路径为null,所以class.getResourceAsStream在使用的时候请使用"/"相对路径,只有使用相对路径它才会帮我们拼接成当前class文件所在目录的绝对路径
使用classloader.getResourceSystem
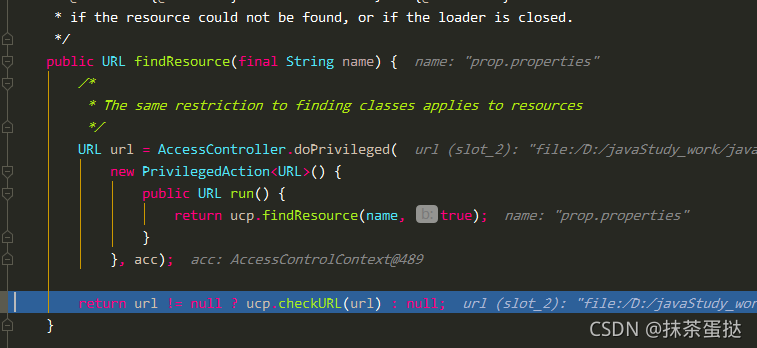
此方法的参数直接就是resource Root资源根目录下的文件,所以拼接之后获取到了真正的url路径
// 上面的两个方法都会调用classloader的getResourceAsStream方法
public InputStream getResourceAsStream(String name) {
// 根据路径名获取inputStream
URL url = getResource(name);
try {
if (url == null) {
return null;
}
URLConnection urlc = url.openConnection();
InputStream is = urlc.getInputStream();
if (urlc instanceof JarURLConnection) {
JarURLConnection juc = (JarURLConnection)urlc;
JarFile jar = juc.getJarFile();
synchronized (closeables) {
if (!closeables.containsKey(jar)) {
closeables.put(jar, null);
}
}
} else if (urlc instanceof sun.net.www.protocol.file.FileURLConnection) {
synchronized (closeables) {
closeables.put(is, null);
}
}
return is;
} catch (IOException e) {
return null;
}
}
// 而最关键的核心就是这个方法
public URL findResource(final String name) {
/*
* The same restriction to finding classes applies to resources
*/
URL url = AccessController.doPrivileged(
new PrivilegedAction<URL>() {
public URL run() {
// 在此方法中获取拼接完成的url路径
return ucp.findResource(name, true);
}
}, acc);
return url != null ? ucp.checkURL(url) : null;
}